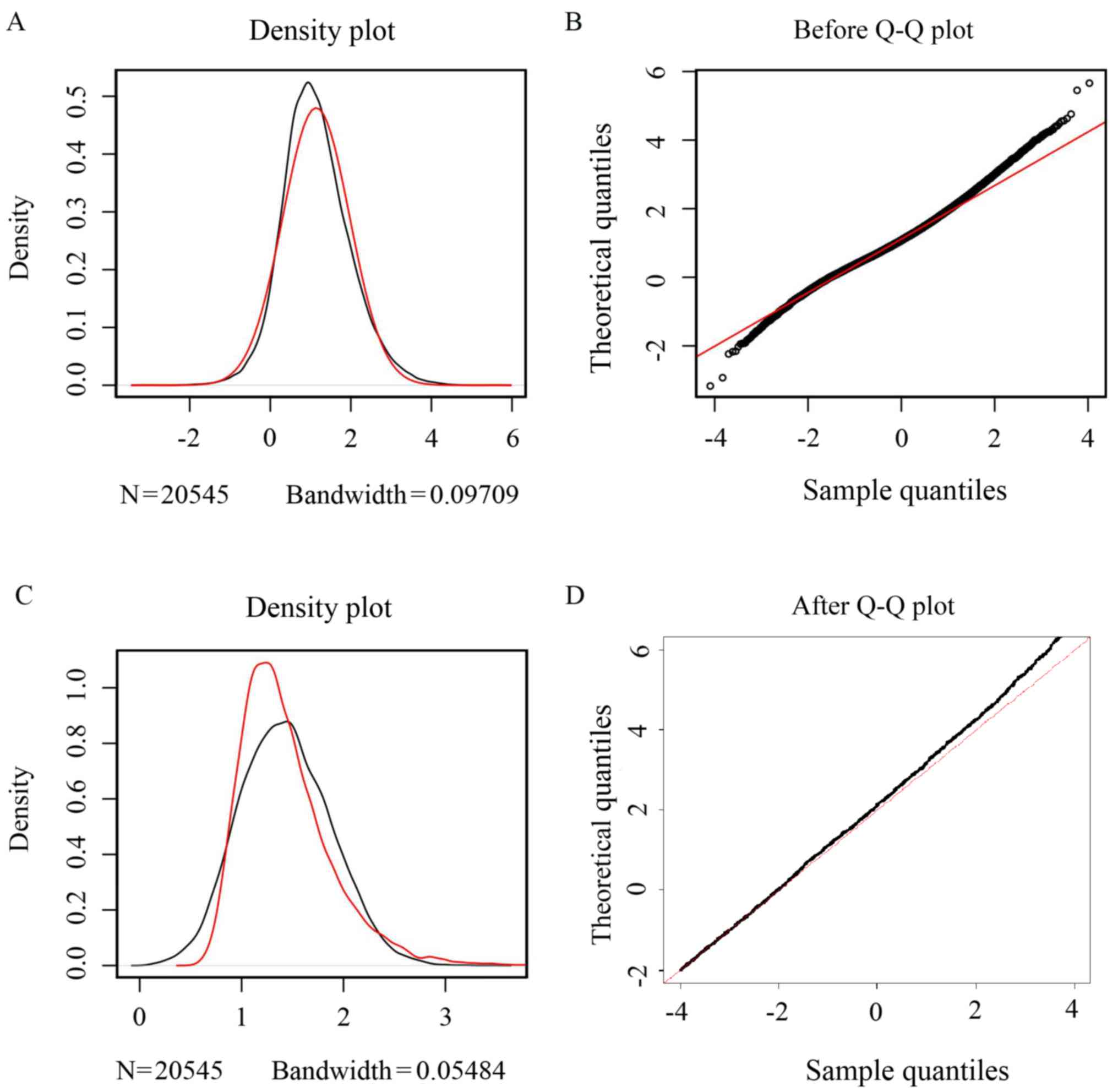
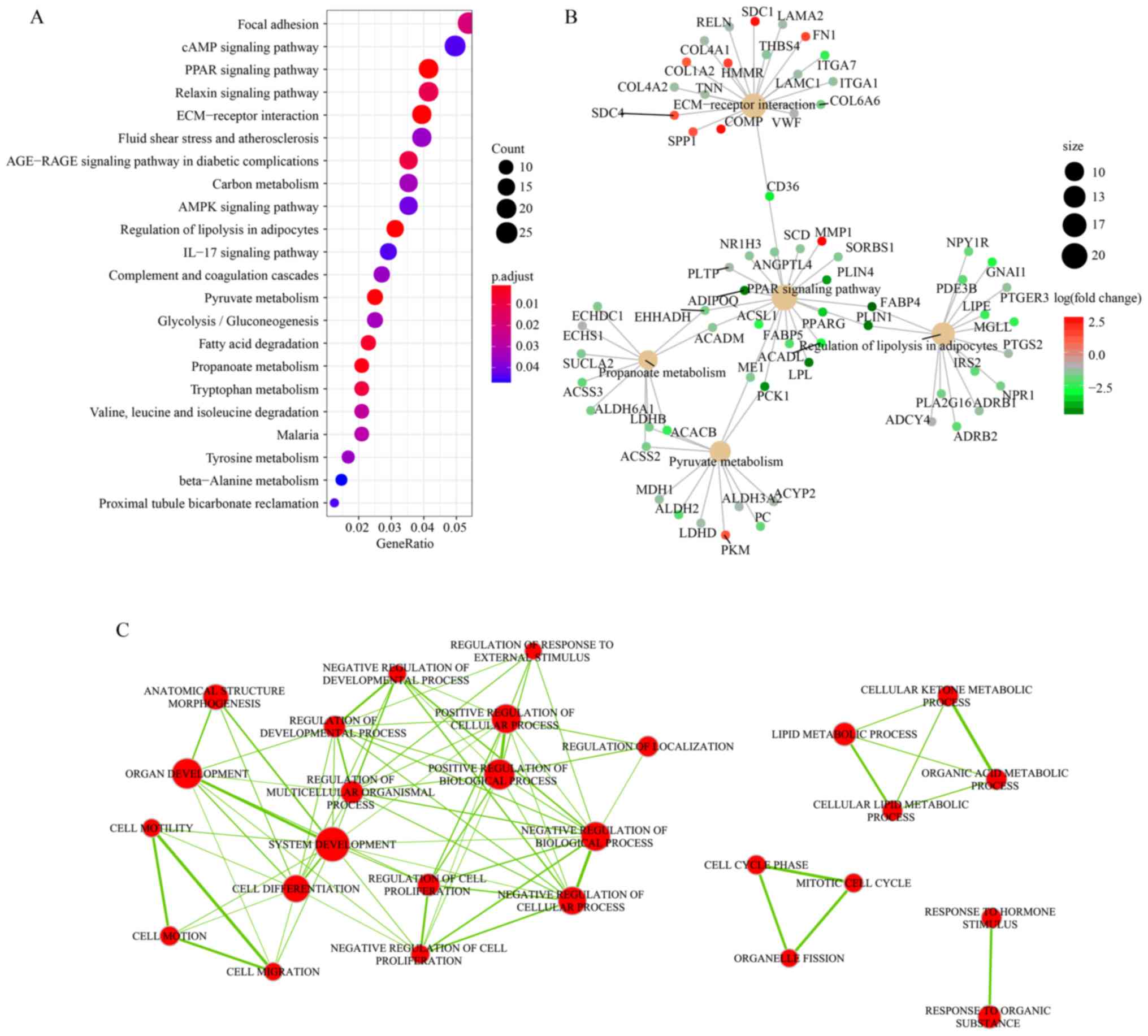
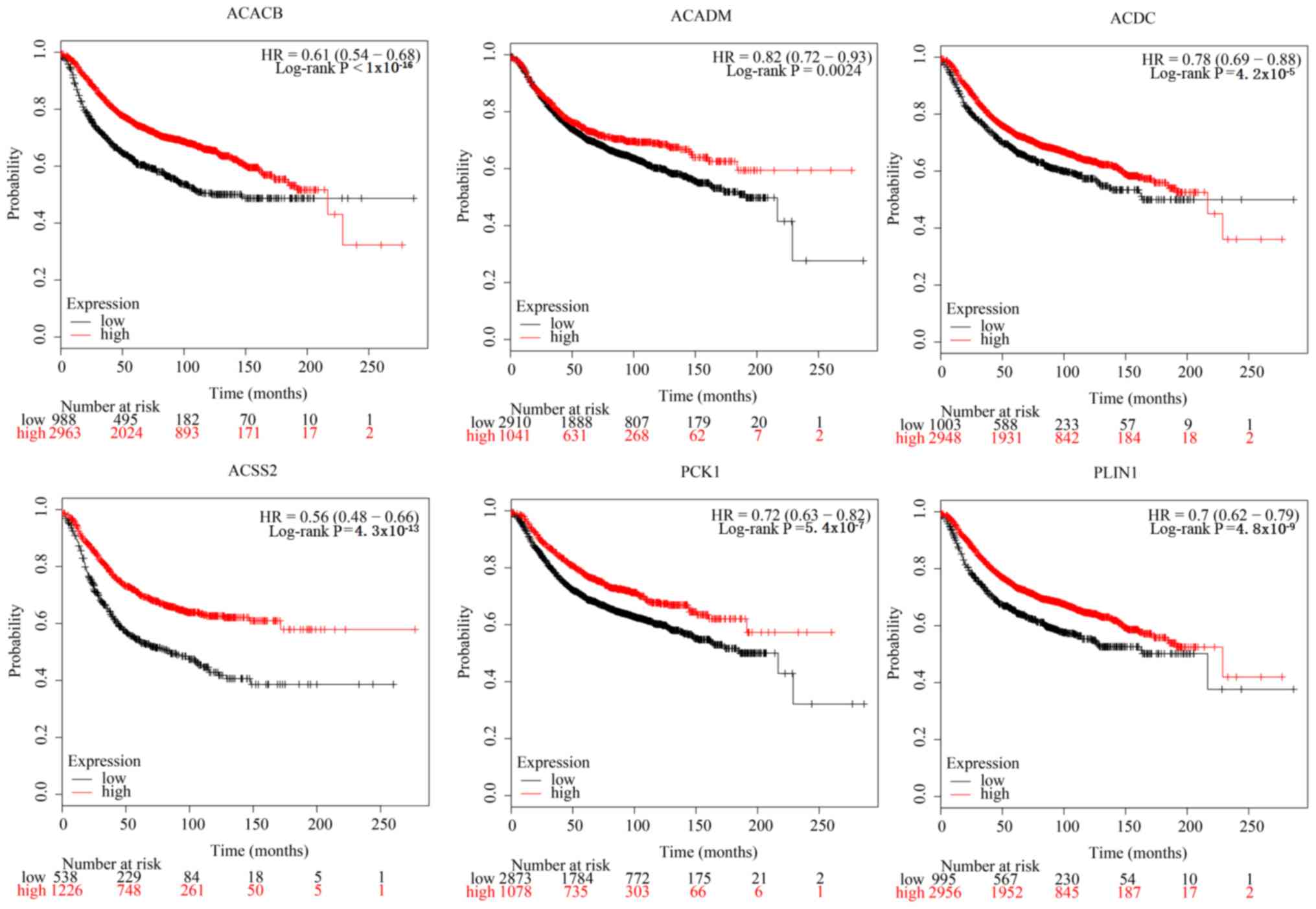
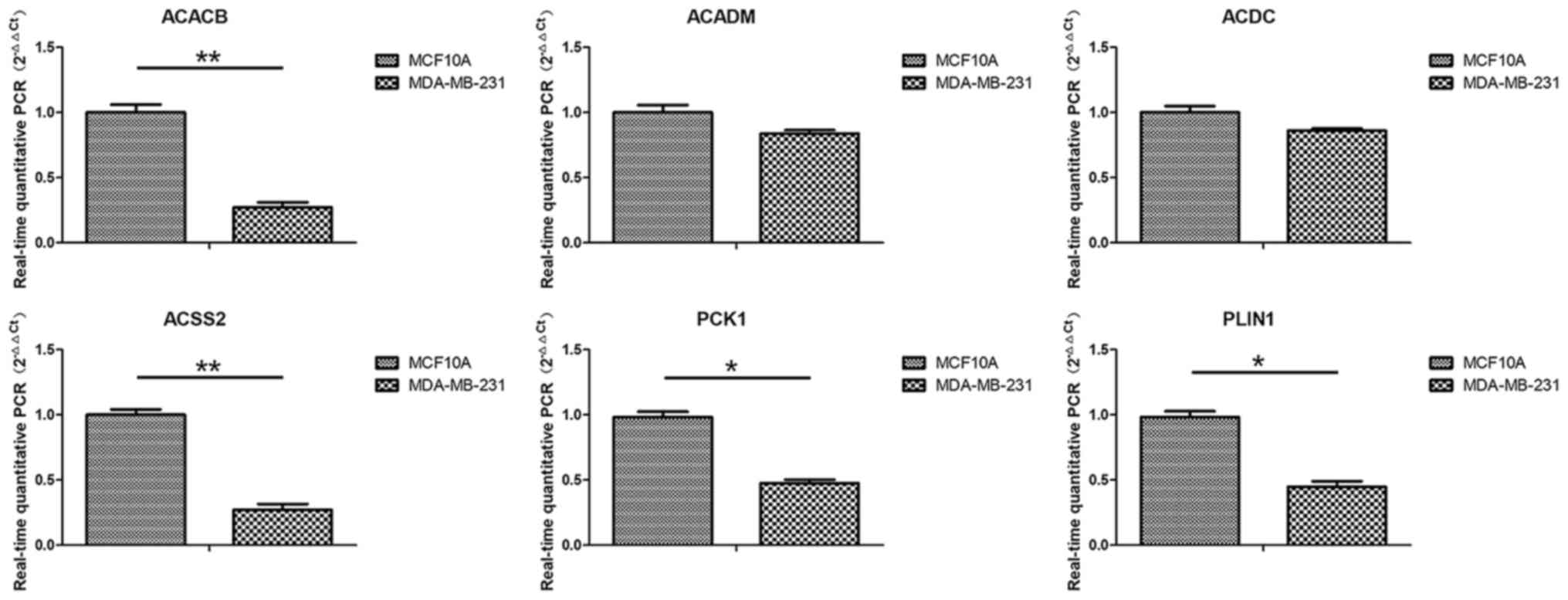
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss PE: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al-Mubarak M, Sacher AG, Ocana A,
Vera-Badillo F, Seruga B and Amir E: Fulvestrant for advanced
breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev. 39:753–758. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qiu AF, Miao ZL, Ge GK, Wang CB, Bian J,
Ma HY and Xu Q: Response and prognosis of neoadjuvant dose-dense or
standard schedule chemotherapy with anthracyclines and taxanes for
Luminal B breast cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 97:3466–3470.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumors. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie
T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, et
al: Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent
gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8418–8423.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu Z, Fan C, Oh DS, Marron JS, He X,
Qaqish BF, Livasy C, Carey LA, Reynolds E, Dressler L, et al: The
molecular portraits of breast tumors are conserved across
microarray platforms. BMC Genomics. 7:962006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kumar M, Sahu RK, Goyal A, Sharma S, Kaur
N, Mehrotra R, Singh UR and Hedau S: BRCA1 promoter methylation and
expression-associations with ER+, PR+ and HER2+ subtypes of breast
carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:3293–3299. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meisel J, Zhang C, Neely C, Mendoza P, You
S, Han T, Liu Y, Sahin AA, O'Regan R and Li X: Evaluation of
prognosis in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative and lymph
node-negative breast cancer with low oncotype DX recurrence score.
Clin Breast Cancer. 18:347–352. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nik-Zainal S, Davies H, Staaf J,
Ramakrishna M, Glodzik D, Zou X, Martincorena I, Alexandrov LB,
Martin S, Wedge DC, et al: Landscape of somatic mutations in 560
breast cancer whole-genome sequences. Nature. 534:47–54. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moldovan L, Mitroi A, Petrescu C and
Aschie M: Classification of breast carcinomas according to gene
expression profiles. J Med Life. 6:14–17. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shaposhnikov SA, Akopov SB, Chernov IP,
Thomsen PD, Joergensen C, Collins AR, Frengen E and Nikolaev LG: A
map of nuclear matrix attachment regions within the breast cancer
loss of heterozygosity region on human chromosome16q22.1. Genomics.
89:354–361. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tryndyak V, Kovalchuk O and Pogribny IP:
Identification of differentially methylated sites within
unmethylated DNA domains in normal and cancer cells. Anal Biochem.
356:202–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hakim AA, Barry CP, Barnes HJ, Anderson
KE, Petitte J, Whitaker R, Lancaster JM, Wenham RM, Carver DK,
Turbov J, et al: Ovarian Adenocarcinomas in the Laying Hen and
Women Share Similar Alterations in p53, ras and HER-2/neu. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 2:114–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mcglynn LM, Kirkegaard T, Edwards J, Tovey
S, Cameron D, Twelves C, Bartlett JM and Cooke TG: Ras/Raf-1/MAPK
pathway mediates response to tamoxifen but not chemotherapy in
breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1487–1495. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Boras-Granic K and Wysolmerski JJ: Wnt
signaling in breast organogenesis. Organogenesis. 4:116–122. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shao H, Ma J, Guo T and Hu R: Triptolide
induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells via a mechanism associated
with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 8:505–508.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klintman M, Buus R, Cheang MC, Sheri A,
Smith IE and Dowsett M: Changes in expression of genes representing
key biologic processes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast
cancer, and prognostic implications in residual disease. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:2405–2416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu F, Wu Y, Mi Y, Gu L, Sang M and Geng
C: Identification of core genes and potential molecular mechanisms
in breast cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Pathol Res Pract.
215:1524362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cuadros M, Cano C, López FJ, Talavera P,
García-Peréz I, Blanco A and Concha Á: HER2 status in breast
cancer: Experience of a Spanish national reference Centre. Clin
Transl Oncol. 13:335–340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Clarke C, Madden SF, Doolan P, Aherne ST,
Joyce H, O'Driscoll L, Gallagher WM, Hennessy BT, Moriarty M, Crown
J, et al: Correlating transcriptional networks to breast cancer
survival: A large-scale coexpression analysis. Carcinogenesis.
34:2300–2381. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grinchuk OV, Motakis E, Yenamandra SP, Ow
GS, Jenjaroenpun P, Tang Z, Yarmishyn AA, Ivshina AV and Kuznetsov
VA: Sense-antisense gene-pairs in breast cancer and associated
pathological pathways. Oncotarget. 6:42197–42221. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aswad L, Yenamandra SP, Ow GS, Grinchuk O,
Ivshina AV and Kuznetsov VA: Genome and transcriptome delineation
of two major oncogenic pathways governing invasive ductal breast
cancer development. Oncotarget. 6:36652–36674. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Linton KM, Hey Y, Saunders E, Jeziorska M,
Denton J, Wilson CL, Swindell R, Dibben S, Miller CJ, Pepper SD, et
al: Acquisition of biologically relevant gene expression data by
Affymetrix microarray analysis of archival formalin-fixed
paraffin-embedded tumours. Br J Cancer. 98:1403–1414. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leek JT and Storey JD: Capturing
heterogeneity in gene expression studies by surrogate variable
analysis. PLoS Genet. 3:1724–1735. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang M, Huang J, Liu Y, Ma L, Potash JB
and Han S: COMBAT: A combined association test for genes using
summary statistics. Genetics. 207:883–891. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray data. Bioinf Computat Biol Solutions Using R
Bioconductor. 397–420. 2011.
|
|
30
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Belldegrun A, Tsui KH, deKernion JB and
Smith RB: Efficacy of nephron-sparing surgery for renal cell
carcinoma: Analysis based on the new 1997 tumor-node-metastasis
staging system. J Clin Oncol. 17:2868–2875. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wright KL, Adams JR, Liu JC, Loch AJ, Wong
RG, Jo CE, Beck LA, Santhanam DR, Weiss L, Mei X, et al: Ras
signaling is a key determinant for metastatic dissemination and
poor survival of luminal breast cancer patients. Cancer Res.
75:4960–4972. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paliouras M, Borgono C and Diamandis EP:
Human tissue kallikreins: The cancer biomarker family. Cancer Lett.
249:61–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin Q, Hemminki K, Enquist K, Lenner P,
Grzybowska E, Klaes R, Henriksson R, Chen B, Pamula J, Pekala W, et
al: Vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphisms in relation to
breast cancer development and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res.
11:3647–3653. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gatza ML, Lucas JE, Barry WT, Kim JW, Wang
Q, Crawford MD, Datto MB, Kelley M, Mathey-Prevot B, Potti A and
Nevins JR: A pathway-based classification of human breast cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:6994–6999. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wiechmann L, Sampson M, Stempel M, Jacks
LM, Patil SM, King T and Morrow M: Presenting features of breast
cancer differ by molecular subtype. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:2705–2710.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Savage K, Leung S, Todd SK, Brown LA,
Jones RL, Robertson D, James M, Parry S, Rodrigues Pinilla SM,
Huntsman D and Reis-Filho JS: Distribution and significance of
caveolin 2 expression in normal breast and invasive breast cancer:
An immunofluorescence and immunohistochemical analysis. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 110:245–256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J,
Cronin M, Baehner FL, Walker MG, Watson D, Park T, et al: A
multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated,
node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 351:2817–2826. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hartmann S, Gerber B, Elling D, Heintze K
and Reimer T: The 70-Gene signature as prognostic factor for
elderly women with hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative breast
cancer. Breast Care (Basel). 7:19–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Klijn JG, Zhang Y, Sieuwerts AM,
Look MP, Yang F, Talantov D, Timmermans M, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Yu
J, et al: Gene-expression profiles to predict distant metastasis of
lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer. Lancet. 365:671–679.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chan KT, Cortesio CL and Huttenlocher A:
FAK alters invadopodia and focal adhesion composition and dynamics
to regulate breast cancer invasion. J Cell Biol. 185:357–370. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hiscox S, Barnfather P, Hayes E, Bramble
P, Christensen J, Nicholson RI and Barrett-Lee P: Inhibition of
focal adhesion kinase suppresses the adverse phenotype of
endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells and improves endocrine
response in endocrine-sensitive cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
125:659–669. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen CS, Alonso JL, Ostuni E, Whitesides
GM and Ingber DE: Cell shape provides global control of focal
adhesion assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 307:355–361. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tamura M, Gu J, Takino T and Yamada KM:
Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibition of cell invasion, migration, and
growth: Differential involvement of focal adhesion kinase and
p130Cas. Cancer Res. 59:442–449. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hihi AK, Michalik L and Wahli W: PPARs:
Transcriptional effectors of fatty acids and their derivatives.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:790–798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen YZ, Xue JY, Chen CM, Yang BL, Xu QH,
Wu F, Liu F, Ye X, Meng X, Liu GY, et al: PPAR signaling pathway
may be an important predictor of breast cancer response to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 70:637–644.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Balaban S, Shearer RF, Lee LS, van
Geldermalsen M, Schreuder M, Shtein HC, Cairns R, Thomas KC,
Fazakerley DJ, Grewal T, et al: Adipocyte lipolysis links obesity
to breast cancer growth: Adipocyte-derived fatty acids drive breast
cancer cell proliferation and migration. Cancer Metab. 5:12017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ligibel JA and Strickler HD: Obesity and
its impact on breast cancer: Tumor incidence, recurrence, survival,
and possible interventions. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 52–59.
2013.doi: 10.1200/EdBook_AM.2013.33.52. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dirat B, Bochet L, Dabek M, Daviaud D,
Dauvillier S, Majed B, Wang YY, Meulle A, Salles B, Le Gonidec S,
et al: Cancer-associated adipocytes exhibit an activated phenotype
and contribute to breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 71:2455–2465.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Carter JC and Church FC: Mature breast
adipocytes promote breast cancer cell motility. Exp Mol Pathol.
92:312–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang C, Gao C, Meng K, Qiao H and Wang Y:
Human adipocytes stimulate invasion of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by
secreting IGFBP-2. PLoS One. 10:e01193482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Delort L, Lequeux C, Dubois V, Dubouloz A,
Billard H, Mojallal A, Damour O, Vasson MP and Caldefie-Chézet F:
Reciprocal interactions between breast tumor and its adipose
microenvironment based on a 3D adipose equivalent model. PLoS One.
8:e662842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Riancho JA, Vázquez L, García-Pérez MA,
Sainz J, Olmos JM, Hernández JL, Pérez-López J, Amado JA,
Zarrabeitia MT, Cano A and Rodríguez-Rey JC: Association of ACACB
polymorphisms with obesity and diabetes. Mol Genet Metab.
104:670–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ma L, Mondal AK, Murea M, Sharma NK,
Tönjes A, Langberg KA, Das SK, Franks PW, Kovacs P, Antinozzi PA,
et al: The effect of ACACB cis-variants on gene expression and
metabolic traits. PLoS One. 6:e238602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Klintman M, Buus R, Cheang MC, Sheri A,
Smith IE and Dowsett M: Changes in expression of genes representing
key biologic processes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast
cancer, and prognostic implications in residual disease. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:2405–2416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jones JE, Esler WP, Patel R, Lanba A, Vera
NB, Pfefferkorn JA and Vernochet C: Inhibition of Acetyl-CoA
carboxylase 1 (ACC1) and 2 (ACC2) reduces proliferation and de novo
lipogenesis of EGFRviii human glioblastoma cells. PLoS One.
12:e01695662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Svensson RU, Parker SJ, Eichner LJ, Kolar
MJ, Wallace M, Brun SN, Lombardo PS, Van Nostrand JL, Hutchins A,
Vera L, et al: Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses
fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer
in preclinical models. Nat Med. 22:1108–1119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Luo J, Hong Y, Lu Y, Qiu S, Chaganty BK,
Zhang L, Wang X, Li Q and Fan Z: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase rewires
cancer metabolism to allow cancer cells to survive inhibition of
the Warburg effect by Cetuximab. Cancer Lett. 384:39–49. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bifulco M: Role of the isoprenoid pathway
in ras transforming activity, cytoskeleton organization, cell
proliferation and apoptosis. Life Sci. 77:1740–1749. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kreeger PK, Mandhana R, Alford SK, Haigis
KM and Lauffenburger DA: RAS mutations affect tumor necrosis
factor-induced apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells via
ERK-modulatory negative and positive feedback circuits along with
Non-ERK pathway effects. Cancer Res. 69:8191–8199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bazan V, Migliavacca M, Zanna I, Tubiolo
C, Grassi N, Latteri MA, La Farina M, Albanese I, Dardanoni G,
Salerno S, et al: Specific codon 13 K-ras mutations are predictive
of clinical outcome in colorectal cancer patients, whereas codon 12
K-ras mutations are associated with mucinous histotype. Ann Oncol.
13:1438–1446. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sun T, Aceto N, Meerbrey KL, Kessler JD,
Zhou C, Migliaccio I, Nguyen DX, Pavlova NN, Botero M, Huang J, et
al: Activation of multiple proto-oncogenic tyrosine kinases in
breast cancer via loss of the PTPN12 phosphatase. Cell.
144:703–718. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li T and Sparano JA: Inhibiting Ras
signaling in the therapy of breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer.
3:405–420. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Del Grosso C, Antoniol G, Merlo E, et al:
The impact of Ras/MAPK/S6K signaling pathway on prediction of
clinical outcome in metastatic Her-2 positive breast cancer
patients treated with trastuzumab. Cancer Res. 74 (19
Suppl):Abstract nr LB-181. 2014.
|
|
67
|
Giltnane JM and Balko JM: Rationale for
targeting the Ras/MAPK pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.
Discov Med. 17:275–283. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|