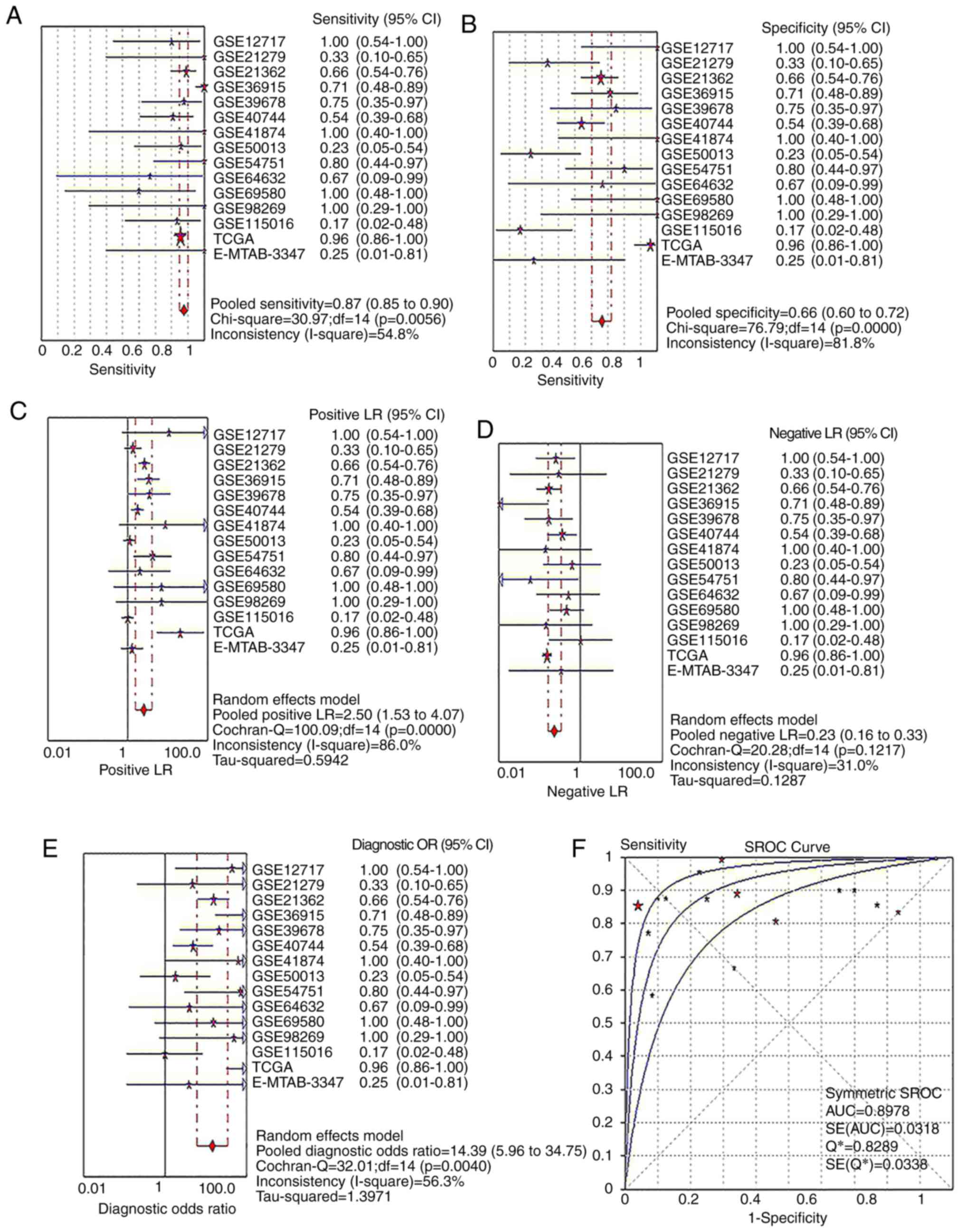
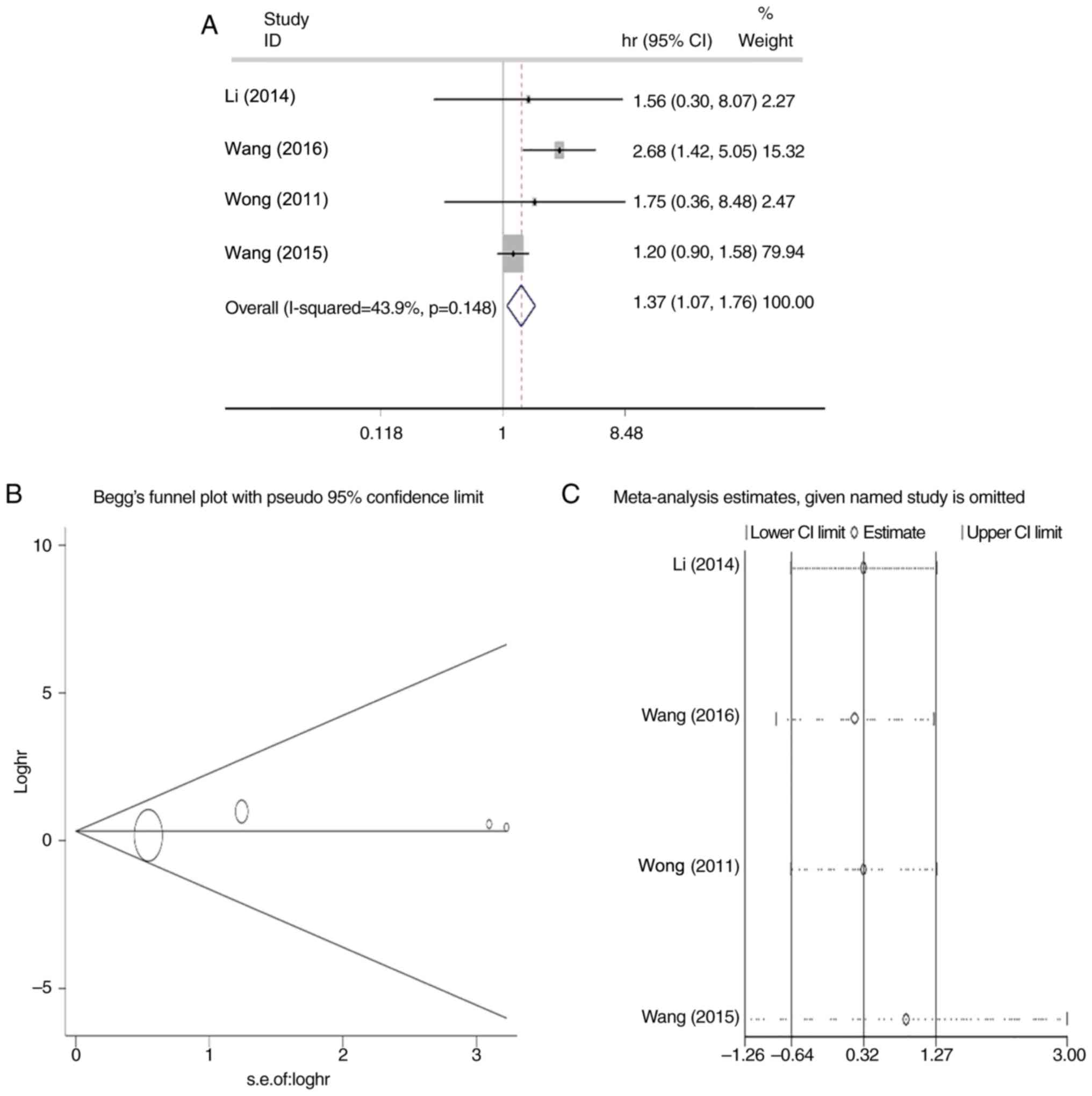
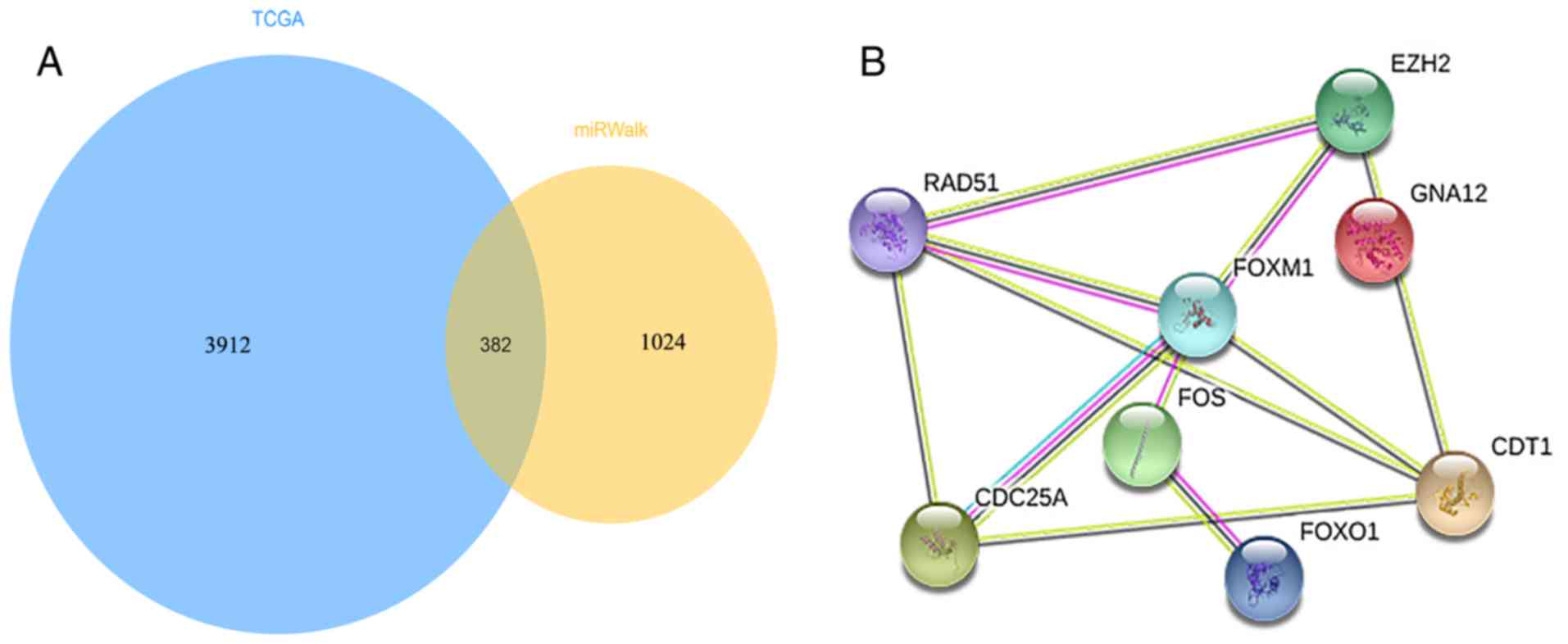
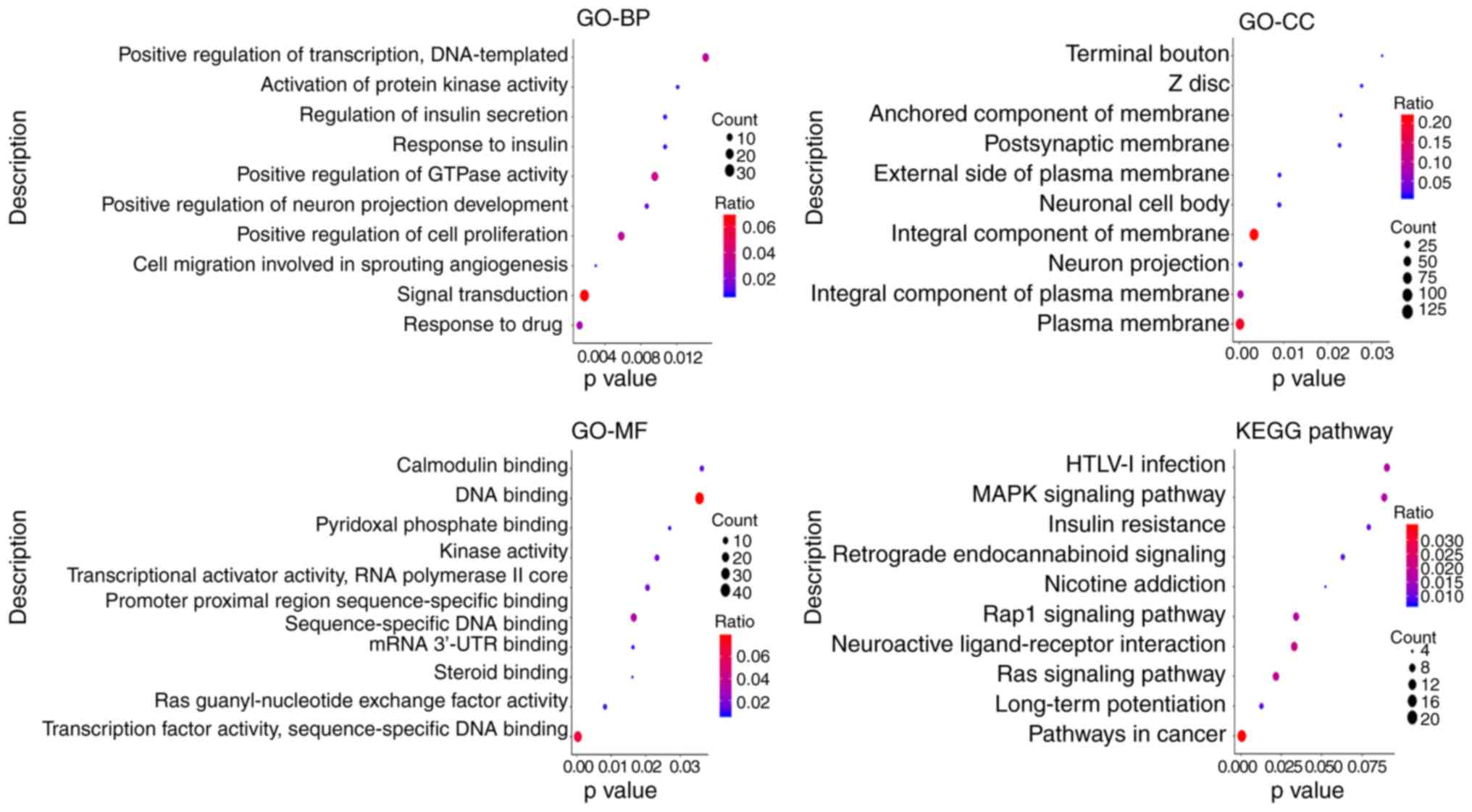
|
1
|
Bray F and Soerjomataram I: The changing
global burden of cancer: Transitions in human development and
implications for cancer prevention and control. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yeh SH and Chen PJ: Gender disparity of
hepatocellular carcinoma: The roles of sex hormones. Oncology. (78
Suppl 1):S172–S179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Aghemo A: Update on HCC management and
review of the new EASL guidelines. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY).
14:384–386. 2018.
|
|
6
|
Singal AG and El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular
carcinoma from epidemiology to prevention: Translating knowledge
into practice. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:2140–2151. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Otedo A, Simbiri KO, Were V, Ongati O and
Estambale BA: Risk factors for liver Cancer in HIV endemic areas of
Western Kenya. Infect Agent Cancer. 13:412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oweira H, Petrausch U, Helbling D, Schmidt
J, Mehrabi A, Schöb O, Giryes A and Abdel-Rahman O: Prognostic
value of site-specific extra-hepatic disease in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A SEER database analysis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 11:695–701. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Intaraprasong P, Siramolpiwat S and
Vilaichone RK: Advances in management of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:3697–3703. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Valinezhad Orang A, Safaralizadeh R and
Kazemzadeh-Bavili M: Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated gene regulation
from common downregulation to mRNA-specific upregulation. Int J
Genomics. 2014:9706072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fanini F and Fabbri M: MicroRNAs and
cancer resistance: A new molecular plot. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
99:485–493. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Manikandan J, Aarthi JJ, Kumar SD and
Pushparaj PN: Oncomirs: The potential role of non-coding microRNAs
in understanding cancer. Bioinformation. 2:330–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yates LA, Norbury CJ and Gilbert RJ: The
long and short of microRNA. Cell. 153:516–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beca F and Schmitt F: MicroRNA signatures
in cytopathology: Are they ready for prime time? Cancer Cytopathol.
124:613–615. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Chen J and Sen S: MicroRNA as
biomarkers and diagnostics. J Cell Physiol. 231:25–30. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Keller A, Rounge T, Backes C, Ludwig N,
Gislefoss R, Leidinger P, Langseth H and Meese E: Sources to
variability in circulating human miRNA signatures. RNA Biol.
14:1791–1798. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Z, Yu T, Cabay RJ, Jin Y, Mahjabeen
I, Luan X, Huang L, Dai Y and Zhou X: miR-486-3p, miR-139-5p, and
miR-21 as biomarkers for the detection of oral tongue squamous cell
carcinoma. Biomark Cancer. 9:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zou F, Mao R, Yang L, Lin S, Lei K, Zheng
Y, Ding Y, Zhang P, Cai G, Liang X and Liu J: Targeted deletion of
miR-139-5p activates MAPK, NF-κB and STAT3 signaling and promotes
intestinal inflammation and colorectal cancer. FEBS J.
283:1438–1452. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu H, Yin Y, Hu Y, Feng Y, Bian Z, Yao S,
Li M, You Q and Huang Z: miR-139-5p sensitizes colorectal cancer
cells to 5-fluorouracil by targeting NOTCH-1. Pathol Res Pract.
212:643–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu Y, Deng C, Zhang H, Zhang J, Peng B and
Hu C: Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes cell growth and metastasis
through regulating miR-139-5p mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 8:94554–94568. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, Li C, Jiang Y, Wan Y, Zhou S and
Cheng W: Tumor-suppressor role of miR-139-5p in endometrial cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 18:512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hua S, Lei L, Deng L, Weng X, Liu C, Qi X,
Wang S, Zhang D, Zou X, Cao C, et al: miR-139-5p inhibits aerobic
glycolysis, cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in
hepatocellular carcinoma via a reciprocal regulatory interaction
with ETS1. Oncogene. 37:1624–1636. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Ding Q, Li Y, Liu Q, Wu W, Wu L
and Yu H: Reanalysis of microRNA expression profiles identifies
novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Tumour
Biol. 37:14779–14787. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ni H, Dai X, Leng X, Deng M, Qin Y, Ji Q,
Xu C, Li J and Liu Y: Higher variety and quantity of
microRNA-139-5p isoforms confer suppressive role in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 119:6806–6813. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang YH, Ji J, Weng H, Wang BC and Wang
FB: MiR-139 in digestive system tumor diagnosis and detection:
Bioinformatics and meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 485:33–41. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang L, Liu M, Zhu H, Rong W, Wu F, An S,
Liu F, Feng L, Wu J and Xu N: Identification of recurrence-related
serum microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma following hepatectomy.
Cancer Biol Ther. 16:1445–1452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wong CC, Wong CM, Tung EK, Au SL, Lee JM,
Poon RT, Man K and Ng IO: The microRNA miR-139 suppresses
metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by
down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology. 140:322–331. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Clough E and Barrett T: The gene
expression omnibus database. Methods Mol Biol. 1418:93–110. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P and Wiznerowicz M:
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of
knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19:A68–A77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Parkinson H, Sarkans U, Kolesnikov N,
Abeygunawardena N, Burdett T, Dylag M, Emam I, Farne A, Hastings E,
Holloway E, et al: ArrayExpress update-an archive of microarray and
high-throughput sequencing-based functional genomics experiments.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D1002–D1004. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett
S and Sydes MR: Practical methods for incorporating summary
time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 8:162007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vamvakas EC: Meta-analyses of studies of
the diagnostic accuracy of laboratory tests: A review of the
concepts and methods. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 122:675–686.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A and
Gretz N: miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA
binding sites. PLoS One. 13:e02062392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW,
Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH, et al: miRTarBase
update 2018: A resource for experimentally validated
microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D296–D302.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vergoulis T, Vlachos IS, Alexiou P,
Georgakilas G, Maragkakis M, Reczko M, Gerangelos S, Koziris N,
Dalamagas T and Hatzigeorgiou AG: TarBase 6.0: Capturing the
exponential growth of miRNA targets with experimental support.
Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D222–D229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bandyopadhyay S and Mitra R: TargetMiner:
MicroRNA target prediction with systematic identification of
tissue-specific negative examples. Bioinformatics. 25:2625–2631.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhattacharya A, Ziebarth JD and Cui Y:
PolymiRTS Database 3.0: Linking polymorphisms in microRNAs and
their target sites with human diseases and biological pathways.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D86–D91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Loher P and Rigoutsos I: Interactive
exploration of RNA22 microRNA target predictions. Bioinformatics.
28:3322–3323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hsu SD, Chu CH, Tsou AP, Chen SJ, Chen HC,
Hsu PW, Wong YH, Chen YH, Chen GH and Huang HD: miRNAMap 2.0:
Genomic maps of microRNAs in metazoan genomes. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:D165–D169. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu W and Wang X: Prediction of functional
microRNA targets by integrative modeling of microRNA binding and
target expression data. Genome Biol. 20:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pontén F, Schwenk JM, Asplund A and
Edqvist PH: The human protein atlas as a proteomic resource for
biomarker discovery. J Intern Med. 270:428–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li T, Yin J, Yuan L, Wang S, Yang L, Du X
and Lu J: Downregulation of microRNA-139 is associated with
hepatocellular carcinoma risk and short-term survival. Oncol Rep.
31:1699–1706. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jiao W, Zhang J, Wei Y, Feng J, Ma M, Zhao
H, Wang L and Jiao W: MiR-139-5p regulates VEGFR and downstream
signaling pathways to inhibit the development of esophageal cancer.
Dig Liver Dis. 51:149–156. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Qin L, Deng HY, Chen SJ, Wei W and Zhang
YT: miR-139 acts as a tumor suppressor in T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia by targeting CX chemokine receptor 4. Am J
Transl Res. 9:4059–4070. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen J, Yu Y, Chen X, He Y, Hu Q, Li H,
Han Q, Ren F, Li J, Li C, et al: MiR-139-5p is associated with poor
prognosis and regulates glycolysis by repressing PKM2 in
gallbladder carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 51:e125102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang HD, Sun DW, Mao L, Zhang J, Jiang
LH, Li J, Wu Y, Ji H, Chen W, Wang J, et al: MiR-139-5p inhibits
the biological function of breast cancer cells by targeting Notch1
and mediates chemosensitivity to docetaxel. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 465:702–713. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ren Y, Zhu H, Chi C, Yang F and Xu X:
MiRNA-139 regulates oral cancer Tca8113 cells apoptosis through Akt
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4588–4594.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Au SL, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Tsang FH,
Ng IO and Wong CM: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically
silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver
cancer metastasis. Hepatology. 56:622–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Xu K, Shen K, Liang X, Li Y, Nagao N, Li
J, Liu J and Yin P: MiR-139-5p reverses CD44+/CD133+-associated
multidrug resistance by downregulating NOTCH1 in colorectal
carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 7:75118–75129. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yoon EL, Yeon JE, Ko E, Lee HJ, Je JH, Yoo
YJ, Kang SH, Suh SJ, Kim JH, Seo YS, et al: An explorative analysis
for the role of serum miR-10b-3p levels in predicting response to
sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Korean Med Sci. 32:212–220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Huang LL, Huang LW, Wang L, Tong BD, Wei Q
and Ding XS: Potential role of miR-139-5p in cancer diagnosis,
prognosis and therapy. Oncol Lett. 14:1215–1222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cox AD and Der CJ: The dark side of Ras:
Regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene. 22:8999–9006. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bos JL: Ras oncogenes in human cancer: A
review. Cancer Res. 49:4682–4689. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bos JL: The ras gene family and human
carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 195:255–271. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Prior IA, Lewis PD and Mattos C: A
comprehensive survey of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res.
72:2457–2467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Schwarz R, Ramer R and Hinz B: Targeting
the endocannabinoid system as a potential anticancer approach. Drug
Metab Rev. 50:26–53. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lu Y and Anderson HD: Cannabinoid
signaling in health and disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
95:311–327. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Vago R, Bettiga A, Salonia A, Ciuffreda P
and Ottria R: Development of new inhibitors for
N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase as promising tool
against bladder cancer. Bioorg Med Chem. 25:1242–1249. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Martínez-Martínez E, Martín-Ruiz A, Martín
P, Calvo V, Provencio M and García JM: CB2 cannabinoid receptor
activation promotes colon cancer progression via AKT/GSK3β
signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:68781–68791. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liontos M, Koutsami M, Sideridou M,
Evangelou K, Kletsas D, Levy B, Kotsinas A, Nahum O, Zoumpourlis V,
Kouloukoussa M, et al: Deregulated overexpression of hCdt1 and
hCdc6 promotes malignant behavior. Cancer Res. 67:10899–10909.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bravou V, Nishitani H, Song SY, Taraviras
S and Varakis J: Expression of the licensing factors, Cdt1 and
Geminin, in human colon cancer. Int J Oncol. 27:1511–1518.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Arentson E, Faloon P, Seo J, Moon E,
Studts JM, Fremont DH and Choi K: Oncogenic potential of the DNA
replication licensing protein CDT1. Oncogene. 21:1150–1158. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Karavias D, Maroulis I, Papadaki H, Gogos
C, Kakkos S, Karavias D and Bravou V: Overexpression of CDT1 is a
predictor of poor survival in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 20:568–579. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yu Z, Wang R, Chen F, Wang J and Huang X:
Five novel oncogenic signatures could be utilized as AFP-related
diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma based on
next-generation sequencing. Dig Dis Sci. 63:945–957. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhong Q, Chen CF, Li S, Chen Y, Wang CC,
Xiao J, Chen PL, Sharp ZD and Lee WH: Association of BRCA1 with the
hRad50-hMre11-p95 complex and the DNA damage response. Science.
285:747–750. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Chen CC, Chen CY, Ueng SH, Hsueh C, Yeh
CT, Ho JY, Chou LF and Wang TH: Corylin increases the sensitivity
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to chemotherapy through long
noncoding RNA RAD51-AS1-mediated inhibition of DNA repair. Cell
Death Dis. 9:5432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen CC, Chen CY, Wang SH, Yeh CT, Su SC,
Ueng SH, Chuang WY, Hsueh C and Wang TH: Melatonin sensitizes
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to chemotherapy through long
non-coding RNA RAD51-AS1-mediated suppression of DNA repair.
Cancers (Basel). 10:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Shao J, Xu Z, Peng X, Chen M, Zhu Y, Xu L,
Zhu H, Yang B, Luo P and He Q: Gefitinib synergizes with irinotecan
to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma via antagonizing
Rad51-mediated DNA-repair. PLoS One. 11:e01469682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Luo J, Si ZZ, Li T, Li JQ, Zhang ZQ, Chen
GS, Qi HZ and Yao HL: MicroRNA-146a-5p enhances radiosensitivity in
hepatocellular carcinoma through replication protein A3-induced
activation of the DNA repair pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
316:C299–C311. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chand V, Pandey A, Kopanja D, Guzman G and
Raychaudhuri P: Opposing roles of the forkhead box factors FoxM1
and FoxA2 in liver cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 17:1063–1074. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liang C, Zhao J, Ge H, Li G and Wu J:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of FoxM1 in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A meta-analysis. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:3561–3571. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tian C, Wu H, Li C, Tian X, Sun Y, Liu E,
Liao X and Song W: Downreguation of FoxM1 by miR-214 inhibits
proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene Ther.
25:312–319. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Song BN and Chu IS: A gene expression
signature of FOXM1 predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Exp Mol Med. 50:e4182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lin P, He RQ, Dang YW, Wen DY, Ma J, He Y,
Chen G and Yang H: An autophagy-related gene expression signature
for survival prediction in multiple cohorts of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 9:17368–17395. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Chang Y, Zhou C, Fan L, Qiu G, Wang G, Wei
G, Chang X and Li X: Upregulation of microRNA-300 induces the
proliferation of liver cancer by downregulating transcription
factor FOXO1. Oncol Rep. 40:3561–3572. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Xu H, Li G, Yue Z and Li C: HCV core
protein-induced upregulation of microRNA-196a promotes aberrant
proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FOXO1. Mol
Med Rep. 13:5223–5229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yang XW, Shen GZ, Cao LQ, Jiang XF, Peng
HP, Shen G, Chen D and Xue P: MicroRNA-1269 promotes proliferation
in human hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulation of FOXO1. BMC
Cancer. 14:9092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Xu X, Yamamoto H, Sakon M, Yasui M, Ngan
CY, Fukunaga H, Morita T, Ogawa M, Nagano H, Nakamori S, et al:
Overexpression of CDC25A phosphatase is associated with hypergrowth
activity and poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinomas.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:1764–1772. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Xu X, Yamamoto H, Liu G, Ito Y, Ngan CY,
Kondo M, Nagano H, Dono K, Sekimoto M and Monden M: CDC25A
inhibition suppresses the growth and invasion of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 21:145–152.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Kelly P, Moeller BJ, Juneja J, Booden MA,
Der CJ, Daaka Y, Dewhirst MW, Fields TA and Casey PJ: The G12
family of heterotrimeric G proteins promotes breast cancer invasion
and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:8173–8178. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kelly P, Stemmle LN, Madden JF, Fields TA,
Daaka Y and Casey PJ: A role for the G12 family of heterotrimeric G
proteins in prostate cancer invasion. J Biol Chem. 281:26483–26490.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chia CY, Kumari U and Casey PJ: Breast
cancer cell invasion mediated by Gα12 signaling involves expression
of interleukins-6 and −8, and matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Mol
Signal. 9:62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Udayappan UK and Casey PJ: c-Jun
contributes to transcriptional control of GNA12 expression in
prostate cancer cells. Molecules. 22:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Bakiri L, Hamacher R, Graña O,
Guío-Carrión A, Campos-Olivas R, Martinez L, Dienes HP, Thomsen MK,
Hasenfuss SC and Wagner EF: Liver carcinogenesis by FOS-dependent
inflammation and cholesterol dysregulation. J Exp Med.
214:1387–1409. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Watanabe T, Hiasa Y, Tokumoto Y, Hirooka
M, Abe M, Ikeda Y, Matsuura B, Chung RT and Onji M: Protein kinase
R modulates c-Fos and c-Jun signaling to promote proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatitis C virus infection. PLoS
One. 8:e677502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Fan Q, He M, Deng X, Wu WK, Zhao L, Tang
J, Wen G, Sun X and Liu Y: Derepression of c-Fos caused by
microRNA-139 down-regulation contributes to the metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem Funct. 31:319–324. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|