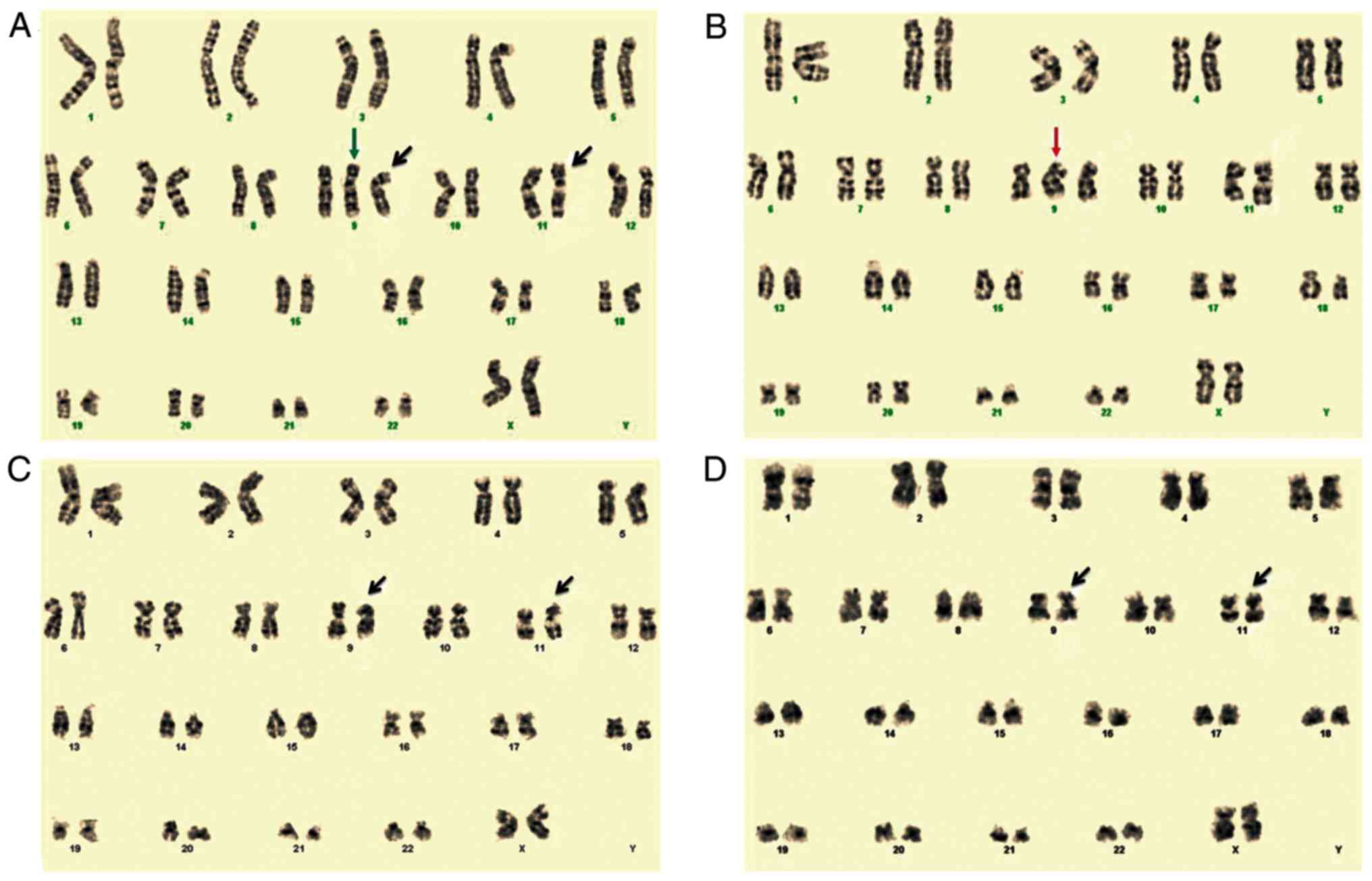
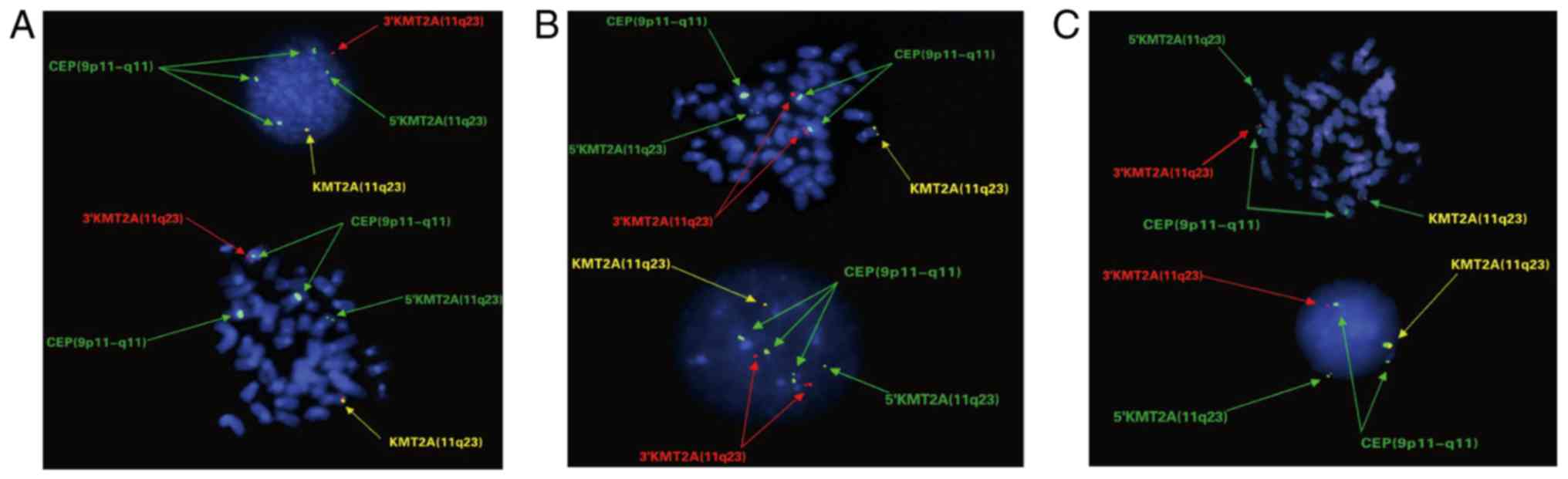
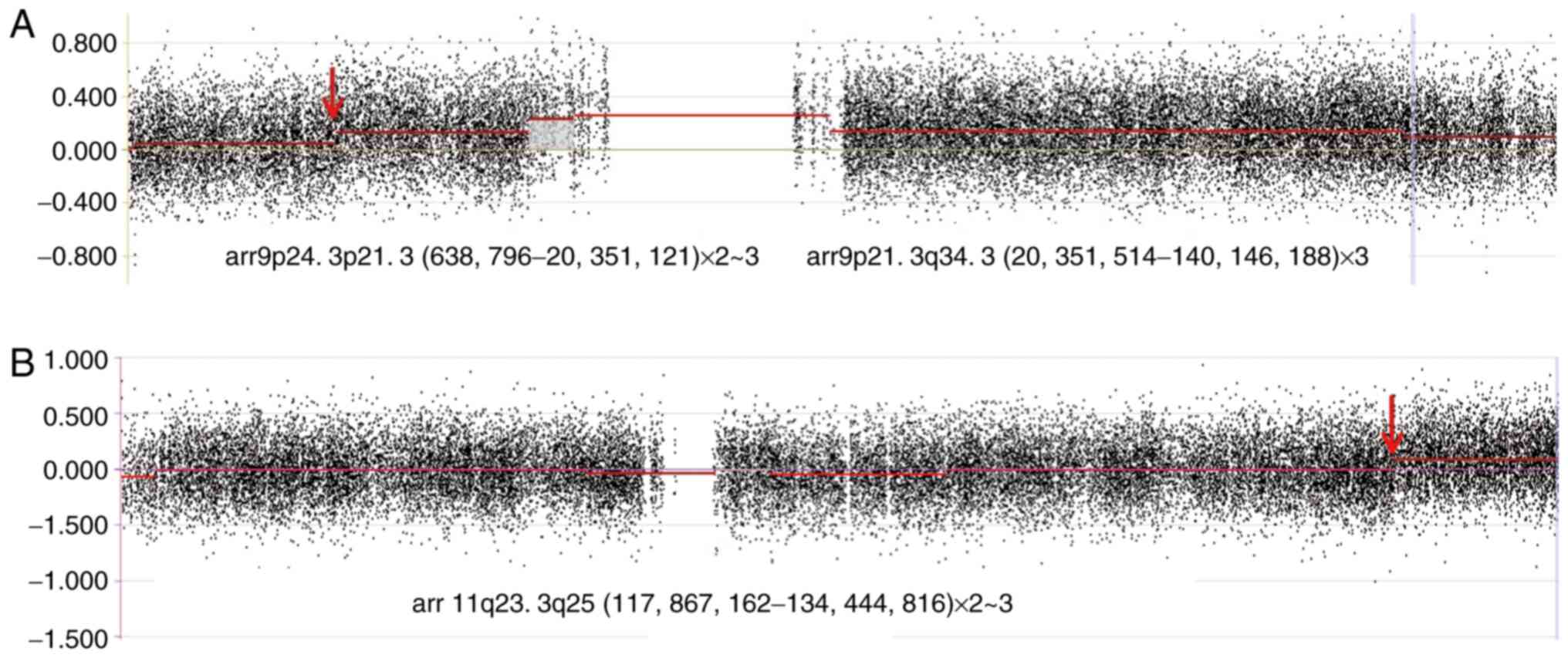
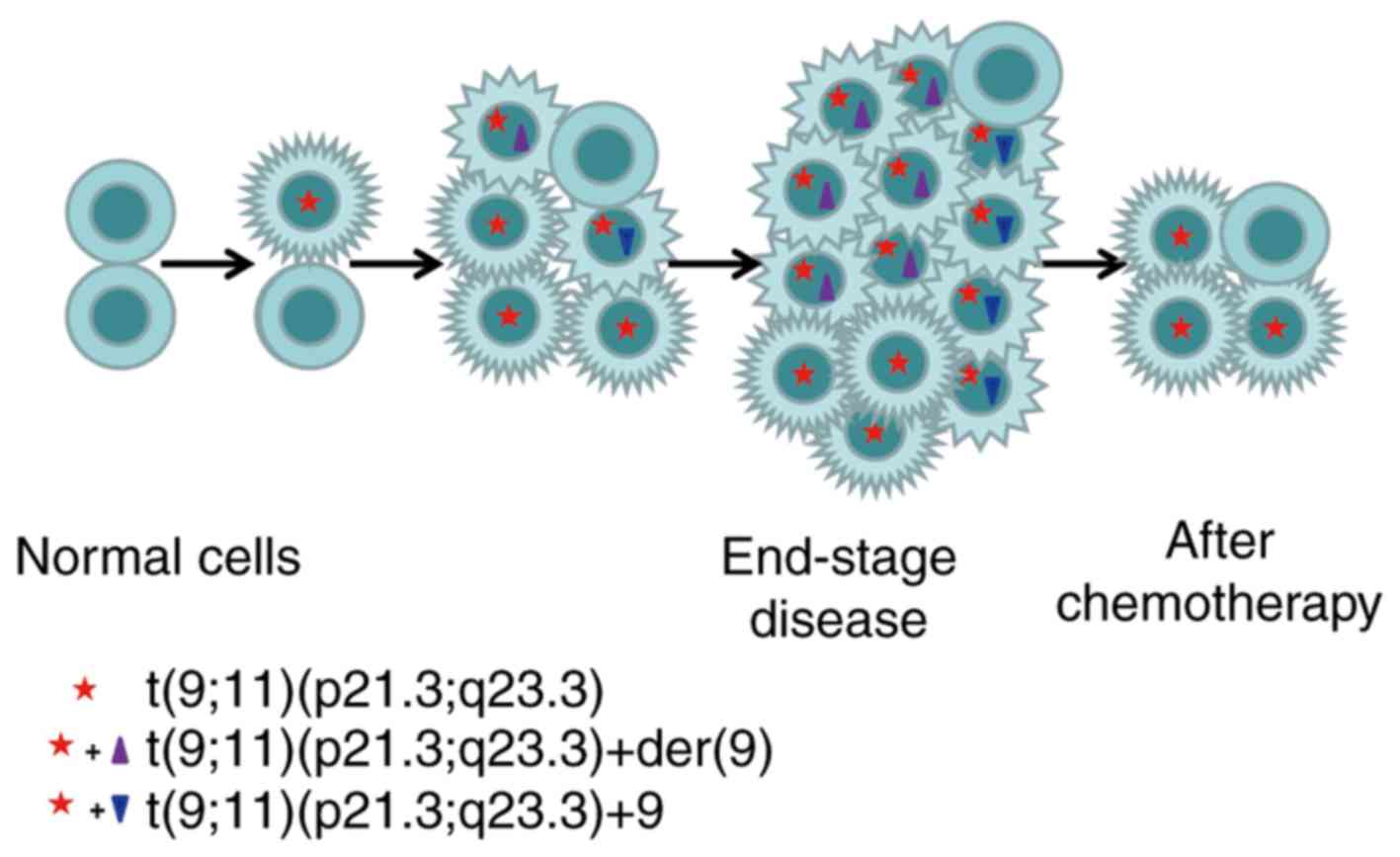
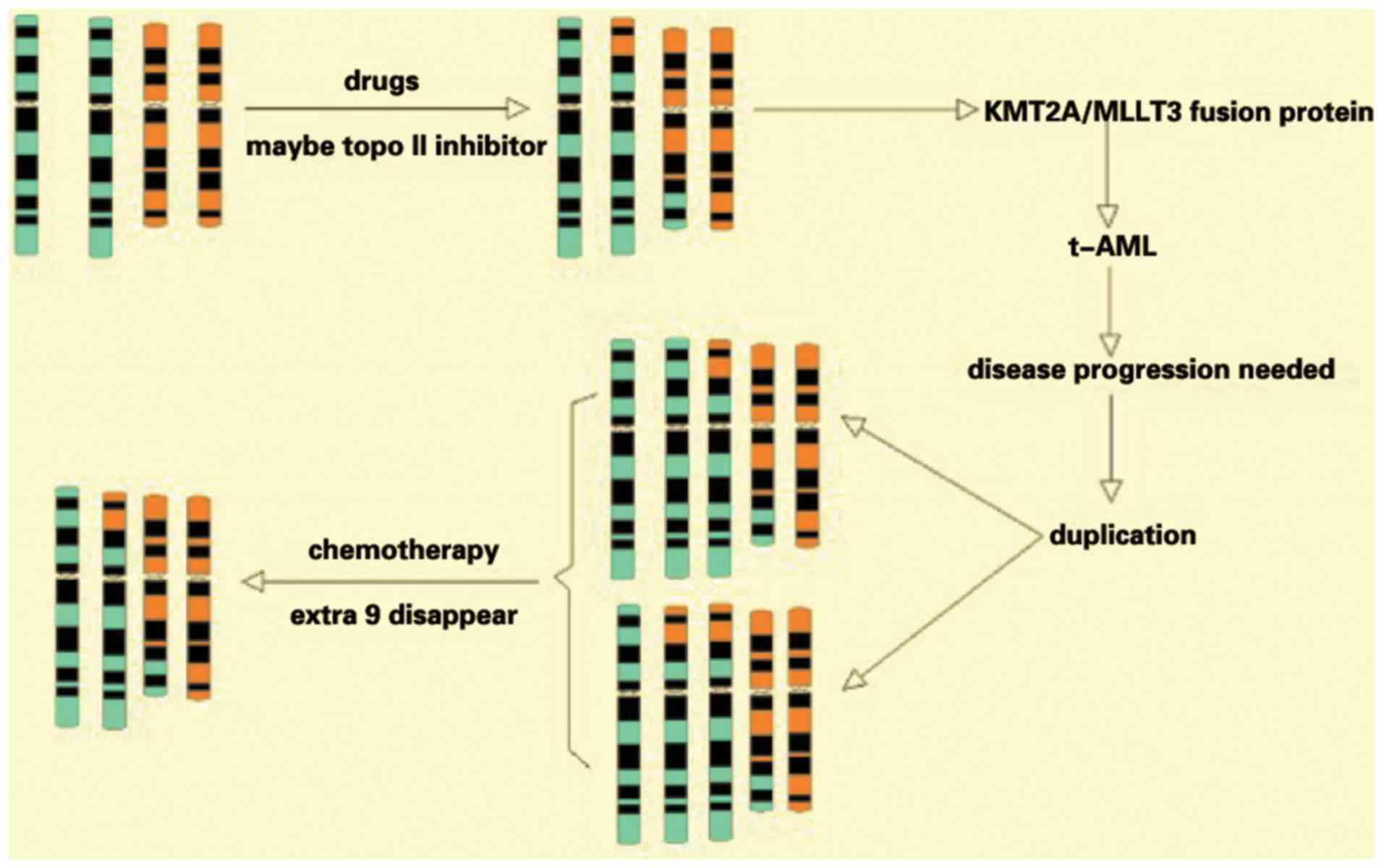
|
1
|
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J,
Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, Bloomfield CD, Cazzola M and vardiman JW:
The 2016 revision to world health organization classification of
myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 127:2391–2405. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meyer C, Schneider B, Reichel M,
Angermuneller S, Strehl S, Schnittger S, Schoch C, Jansen MW, van
Dongen JJ, Pieters R, et al: Diagnostic tool for the identification
of MLL rearrangements including unknown partner genes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:449–454. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meyer C, Kowarz E, Hofmann J, Rennevilla
A, Zuna J, Trka J, Ben Abdelali R, Macintyre E, De Braekeleer E, De
Braekeleer M, et al: New insights to the MLL recombinome of acute
leukemias. Leukemia. 23:1490–1499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meyer C, Hofmann J, Burmeister T, Gröger
D, Park TS, Emerenciano M, Pombo de Oliveira M, Renneville A,
Villarese P, Macintyre E, et al: The MLL recombinome of acute
leukemias in 2013. Leukemia. 27:2165–2176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meyer C, Burmeister T, Gröger D, Tsaur G,
Fechina L, Renneville A, Sutton R, Venn NC, Emerenciano M,
Pombo-de-Oliveira MS, et al: The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias
in 2017. Leukemia. 32:273–284. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Asou N: Myeloid neoplasms in the world
health organization 2016 classification. Rinsho Ketsueki.
58:2178–2187. 2017.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Biondi A, Cimino G, Pieters R and Pui CH:
Biological and therapeutic aspects of infant leukemia. Blood.
96:24–33. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Corral J, Lavenir I, Impey H, Warren AJ,
Forster A, Larson TA, Bell S, McKenzie AN, King G and Rabbitts TH:
An MLL-AF9 fusion gene made by homologous recombination causes
acute leukemia in chimeric mice: A method to create fusion
oncogenes. Cell. 85:853–861. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dobson CL, Warren AJ, Pannel R, Forster A,
Lavenir I, Corral J, Smith AJ and Rabbitts TH: The MLL-AF9 gene
fusion in mice controls myeloproliferation and specifies acute
myeloid leukaemogenesis. EMBO J. 18:3564–3574. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Somervaille TC and Cleary ML:
Identification and characterization of leukemia stem cells in
murine MLL-AF9 acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 10:257–268.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anguita E, Barrio CG, González FA, Ferro
MT, del Potro E, Ropero P and Villegas A: Association of
t(9;11)-MLL AF9 and trisomy 8 in an AML-M5 preceded by
pancytopenia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 120:144–147. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McGowan-Jordan J, Simons A and Schmid M:
ISCN 2016: An International System for Human Cytogenomic
NomenclatureReprint of Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 149. 1st.
Karger Publishers; Basel, Switzerland: 2016
|
|
13
|
Krivtsov AV, Twomey D, Feng Z, Stubbs MC,
Wang Y, Faber J, Levine JE, Wang J, Hahn WC, Gilliland DG, et al:
Transformation from committed progenitor to leukemia stem cell
initiated by MLL-AF9. Nature. 442:818–822. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schneidawind C, Jeong J, Schneidawind D,
Kim IS, Duque-Afonso J, Wong SHK, Iwasaki M, Breese EH, Zehnder JL,
Porteus M and Cleary ML: MLL leukemia induction by t(9;11)
chromosomal translocation in human hematopoietic stem cells using
genome editing. Blood Adv. 2:832–845. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bredeson CN, Barnett MJ, Horsman DE, Dalal
BI, Ragaz J and Phillips GL: Therapy-related acute myologenous
leukemia associated with 11q23 chromosomal abnormalities and
topoisomerase II inhibitors: Report of four additional cases and
brief commentary. Leuk Lymphoma. 11:141–145. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Langer T, Metzler M, Reinhardt D, Viehmann
S, Borkhardt A, Reichel M, Stanulla M, Schrappe M, Creutzig U,
Ritter J, et al: Analysis of t(9;11) chromosomal breakpoint
sequences in childhood acute leukemia: Almost identical MLL
breakpoints in therapy-related AML after treatment without
etoposides. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 36:393–401. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chandra P, Luthra R, Zuo Z, Yao H, Ravandi
F, Reddy N, Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian H and Jones D: Acute
myeloid leukemia with t(9;11)(p21-22;q23): Common properties of
dysregulated ras pathway signaling and genomic progression
characterize de novo and therapy-related cases. Am J Clin Pathol.
133:686–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Strick R, Strissel PL, Borgers S, Smith SL
and Rowley JD: Dietary bioflavonoids induce cleavage in the MLL
gene and may contribute to infant leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:4790–4795. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bariar B, Vestal CG, Deem B, Goodenow D,
Ughetta M, Engledove RW, Sahyouni M and Richardson C: Bioflavonoids
promote stable translocation between MLL-AF9 breakpoint cluster
regions independent of normal chromosomal context: Model system to
screen environmental risks. Environ Mol Mutagen. 60:154–167. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Strissel PL, Strick R, Tomek RJ, Roe BA,
Rowley JD and Zeleznik-Le NJ: DNA structural properties of AF9 are
similar to MLL and could act as recombination hot spots resulting
in MLL/AF9 translocations and leukemogenesis. Hum Mol Genet.
9:1671–1679. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Johansson B, Moorman AV and Secker-Walker
LM: Derivative chromosomes of 11q23-translocations in hematologic
malignancies. European 11q23 Workshop participants. Leukemia.
12:828–833. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Krauter J, Peter W, Pascheberg U, Heinze
B, Bergmann L, Hoelzer D, Lübbert M, Schlimok G, Arnold R, Kirchner
H, et al: Detection of karyotypic aberrations in acute myeloblastic
leukaemia: A prospective comparison between PCR/FISH and standard
cytogenetics in 140 patients with de novo AML. Br J Haematol.
103:72–78. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mrózek K, Heinonen K, Lawrence D, Carroll
AJ, Koduru PR, Rao KW, Strout MP, Hutchison RE, Moore JO, Mayer RJ,
et al: Adult patient with de novo acute myeloid leukemia and
t(9;11)(p22;q23) have a superior outcome to patient with other
translocation involving band 11q23: A cancer and leukemia group B
study. Blood. 90:4532–4538. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rubnitz JE, Raimondi SC, Tong X,
Srivastava DK, Razzouk BI, Shurtleff SA, Downing JR, Pui CH,
Ribeiro RC and Behm FG: Favorable impact of the t(9;11) in
childhood acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 20:2302–2309. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Balgobind BV, Raimondi SC, Harbott J,
Zimmermann M, Alonzo TA, Auvrignon A, Beverloo HB, Chang M,
Creutzig U, Dworzak MN, et al: Novel prognostic subgroups in
childhood 11q23/MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia: Results of
an international retrospective study. Blood. 114:2489–2496. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stӧlzel F, Mohr B, Kramer M, Oelschlӓgel
U, Bochtler T, Berdel WE, Kaufmann M, Baldus CD, Schӓfer-Eckart K,
Stuhlmann R, et al: Karyotype complexity and prognosis in acute
myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 6:e3862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pession A, Martino V, Tonelli R,
Beltramini C, Locatelli F, Biserni G, Franzoni M, Freccero F,
Montemrro L, Pattacini L and Paolucci G: MLL-AF9 oncogene
expression affects cell growth but not terminal differentiation and
is downregulated during monocyte-macrophage maturation in AML-M5
THP-1 cells. Oncogene. 22:8671–8676. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sambani C, La Starza R, Roumier C,
Crescenzi B, Stavropoulou C, Katsarou O Karafoulidou A, Dhalle JH,
Lai JL, Preudhomme C, et al: Partial duplication of the MLL
oncogene in patients with aggressive acute myeloid leukemia.
Haematologica. 89:403–407. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Andreeva SV, Drozdova VD and Kavardakova
NV: Phenomenon of the evolution of clonal chromosomal abnormalities
in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Tsitol Genet. 44:41–52.
2010.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li M, Wen L, Cen J, Feng Y and Chen S:
JAK2V617F allele burden in patients with myeloproliferative
neoplasms carrying trisomy 9 and its relationship with clinical
phenotypes. Int J Hematol. 103:599–601. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|