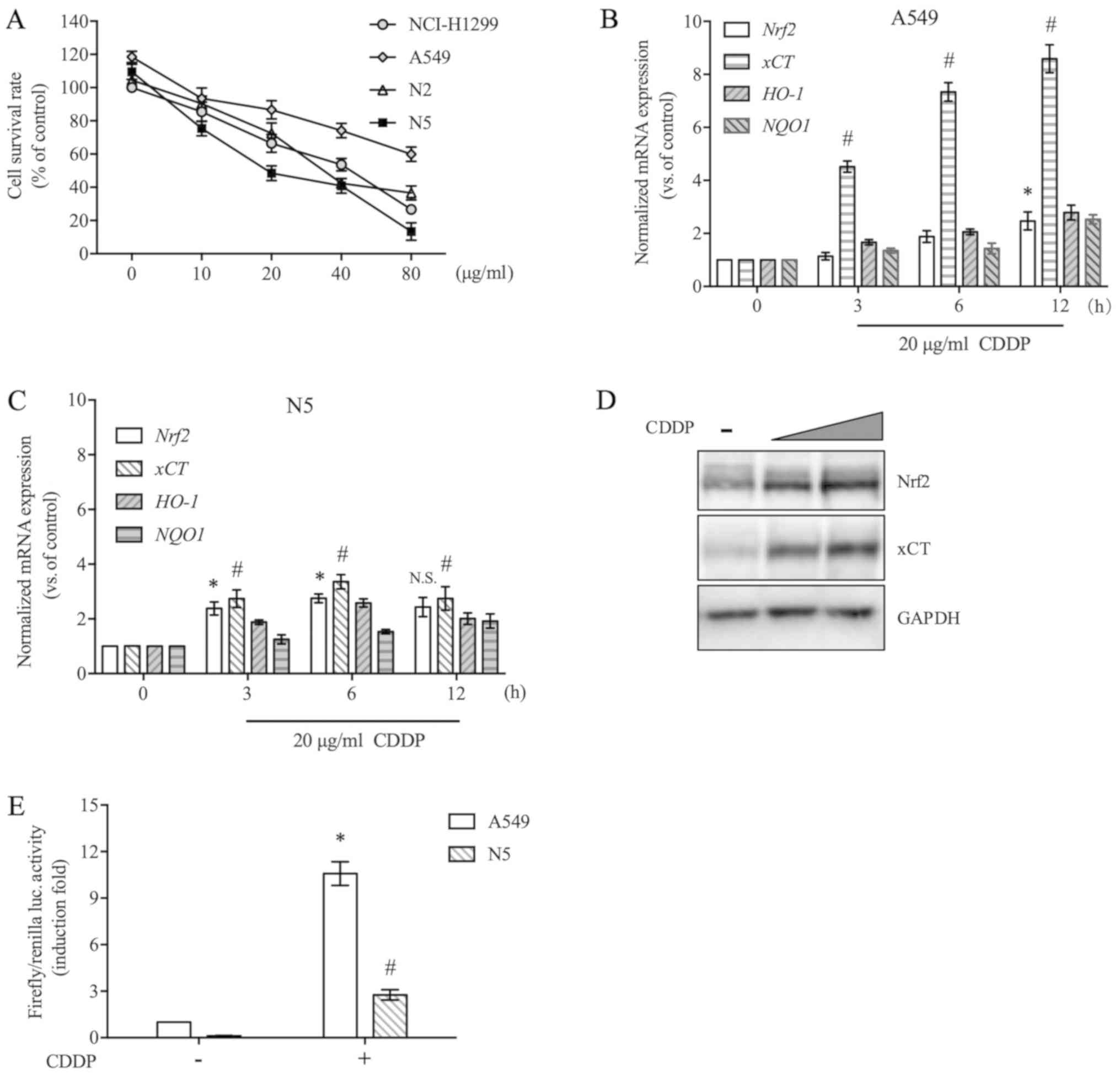
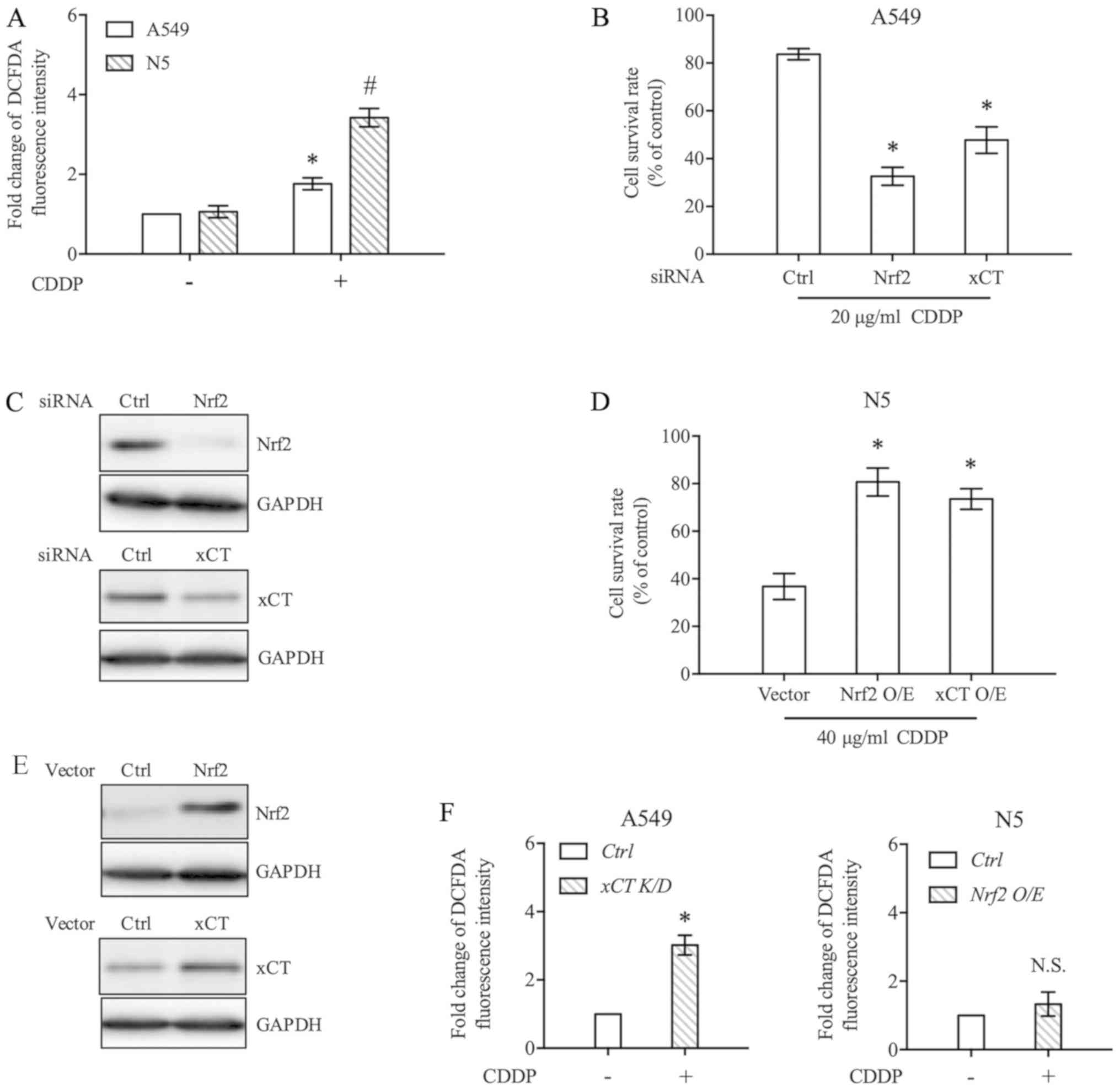
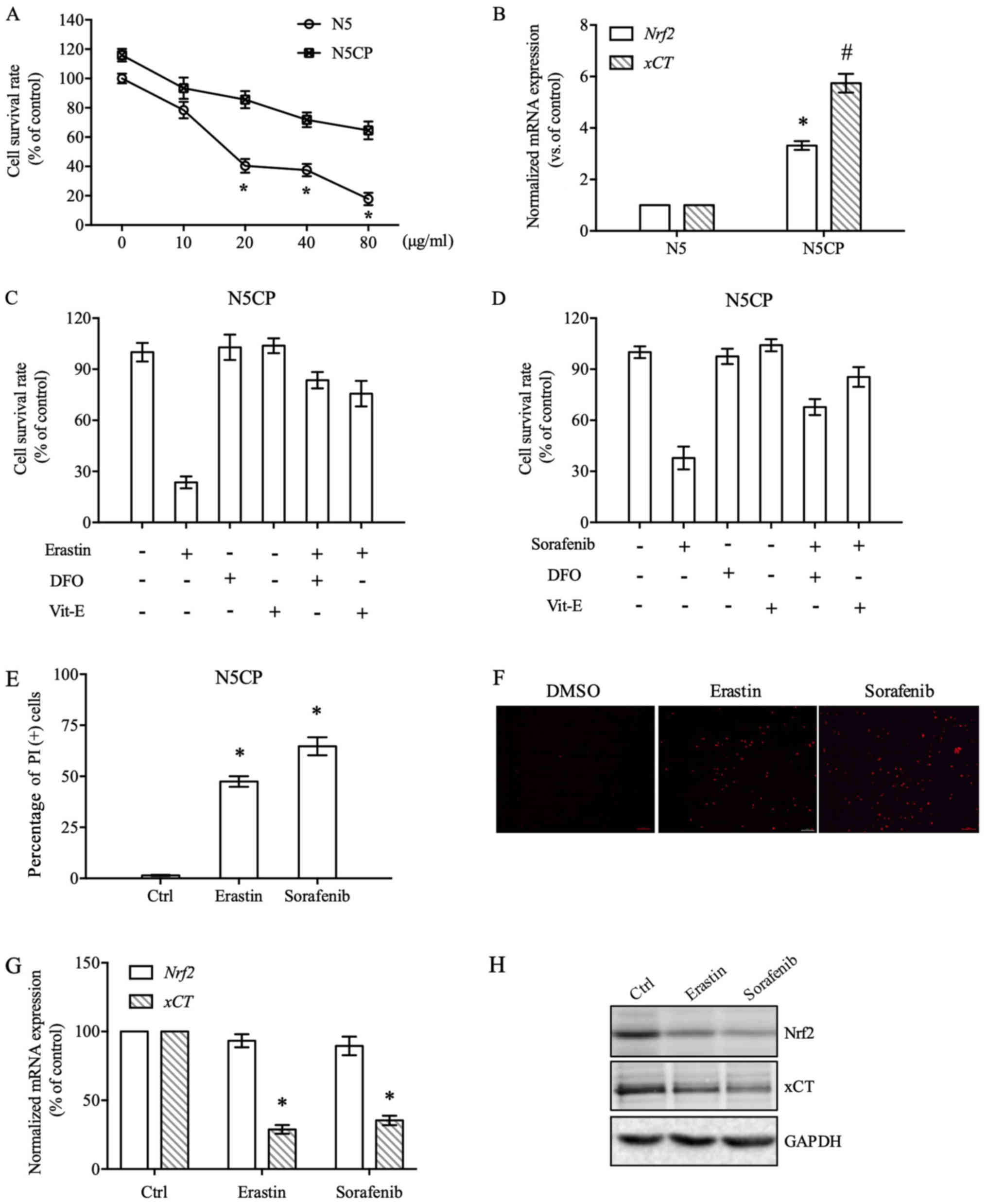
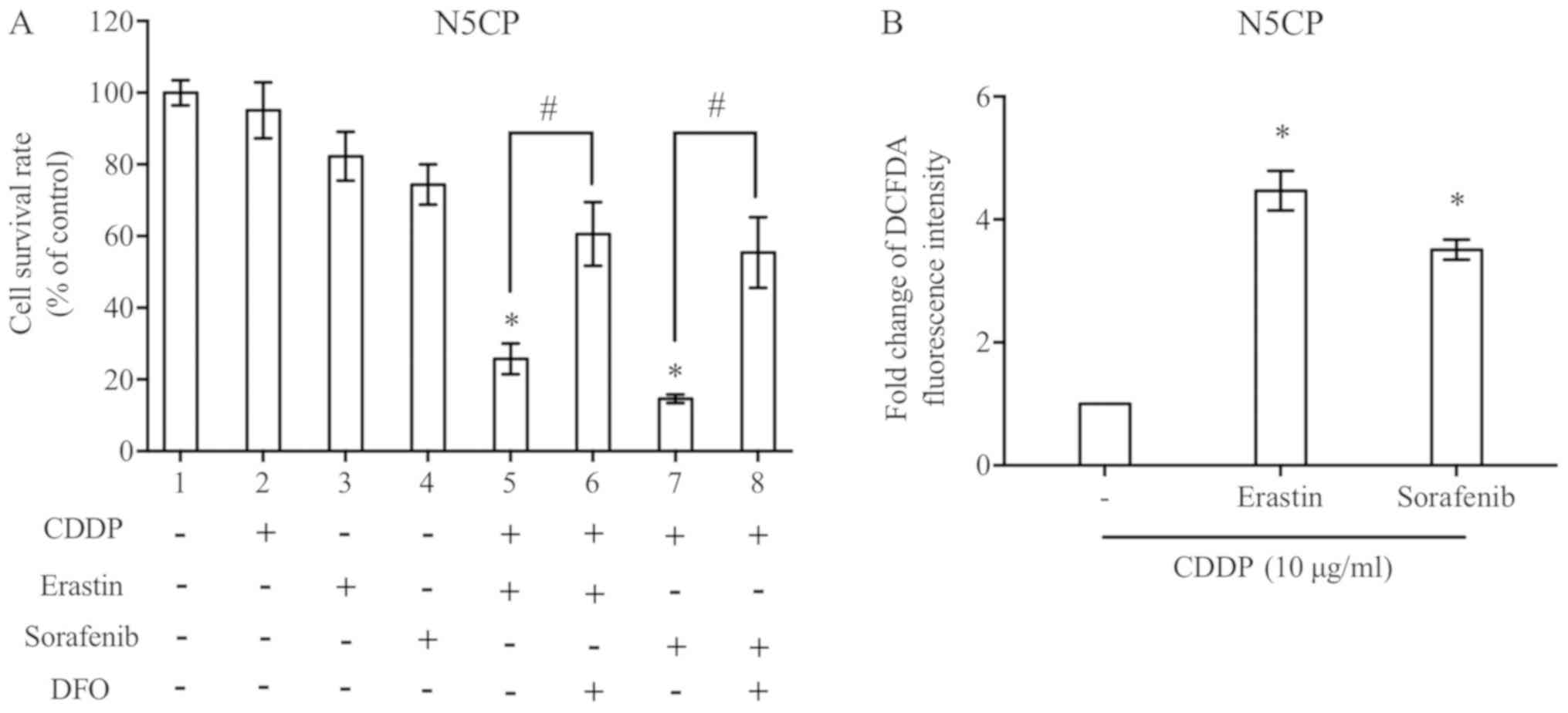
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Casiraghi M, Maisonneuve P, Piperno G,
Bellini R, Brambilla D, Petrella F, Marinis F and Spaggiari L:
Salvage surgery after definitive chemoradiotherapy for non-small
cell lung cancer. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 29:233–241. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D and
Bray F: Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe:
Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 49:1374–1403.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tiseo M, Franciosi V, Grossi F and
Ardizzoni A: Adjuvant chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer:
Ready for clinical practice? Eur J Cancer. 42:8–16. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roh JL, Kim EH, Jang HJ, Park JY and Shin
D: Induction of ferroptotic cell death for overcoming cisplatin
resistance of head and neck cancer. Cancer Lett. 381:96–103. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaminskyy VO, Piskunova T, Zborovskaya IB,
Tchevkina EM and Zhivotovsky B: Suppression of basal autophagy
reduces lung cancer cell proliferation and enhances
caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis by stimulating ROS
formation. Autophagy. 8:1032–1044. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian Y, Wu K, Liu Q, Han N, Zhang L, Chu Q
and Chen Y: Modification of platinum sensitivity by KEAP1/NRF2
signals in non-small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 9:832016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hou X, Bai X, Gou X, Zeng H, Xia C, Zhuang
W, Chen X, Zhao Z, Huang M and Jin J:
3′,4′,5′,5,7-pentamethoxyflavone sensitizes Cisplatin-resistant
A549 cells to Cisplatin by inhibition of Nrf2 pathway. Mol Cells.
38:396–401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ansari MA: Sinapic acid modulates
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in
rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 93:646–653. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang P, Wang W, Wei Z, Xu LI, Yang X and
Du Y: xCT expression modulates cisplatin resistance in Tca8113
tongue carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 12:307–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ye P, Mimura J, Okada T, Sato H, Liu T,
Maruyama A, Ohyama C and Itoh K: Nrf2- and ATF4-dependent
upregulation of xCT modulates the sensitivity of T24 bladder
carcinoma cells to proteasome inhibition. Mol Cell Biol.
34:3421–3434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lachaier E, Louandre C, Godin C, Saidak Z,
Baert M, Diouf M, Chauffert B and Galmiche A: Sorafenib induces
ferroptosis in human cancer cell lines originating from different
solid tumors. Anticancer Res. 34:6417–6422. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pillai MM, Elakkiya V, Gopinathan J,
Sabarinath C, Shanthakumari S, Sahanand KS, Dinakar Rai BK,
Bhattacharyya A and Selvakumar R: A combination of biomolecules
enhances expression of E-cadherin and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gene leading to increased cell
proliferation in primary human meniscal cells: An in vitro study.
Cytotechnology. 68:1747–1761. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Homma S, Ishii Y, Morishima Y, Yamadori T,
Matsuno Y, Haraguchi N, Kikuchi N, Satoh H, Sakamoto T, Hizawa N,
et al: Nrf2 enhances cell proliferation and resistance to
anticancer drugs in human lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:3423–3432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Namani A, Cui QQ, Wu Y, Wang H, Wang XJ
and Tang X: NRF2-regulated metabolic gene signature as a prognostic
biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 8:69847–69862.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen D, Fan Z, Rauh M, Buchfelder M,
Eyupoglu IY and Savaskan N: ATF4 promotes angiogenesis and neuronal
cell death and confers ferroptosis in a xCT-dependent manner.
Oncogene. 36:5593–5608. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao M, Monian P, Pan Q, Zhang W, Xiang J
and Jiang X: Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell
Res. 26:1021–1032. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R
and Tang D: Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects
against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology.
63:173–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R and
Jiang X: Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 59:298–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kelland L: The resurgence of
platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:573–584.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hamilton G and Rath B: A short update on
cancer chemoresistance. Wien Med Wochenschr. 164:456–460. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Friedman R: Drug resistance in cancer:
Molecular evolution and compensatory proliferation. Oncotarget.
7:11746–11755. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Batra A, Thakar A and Bakhshi S:
Ototoxicity in retinoblastoma survivors treated with carboplatin
based chemotherapy: A cross-sectional study of 116 patients.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 62:20602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nishio M, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K,
Solomon BJ, Shaw AT, Hashigaki S, Ohki E, Usari T, Paolini J, et
al: Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in asian patients with
ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat.
50:691–700. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG,
Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe
S, et al: Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 375:1823–1833. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth
B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, Herbach N, Aichler M, Walch
A, Eggenhofer E, et al: Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator
Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol.
16:1180–1191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Latunde-Dada GO: Ferroptosis: Role of
lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta
Gen Subj. 1861:1893–1900. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Macrez R, Stys PK, Vivien D, Lipton SA and
Docagne F: Mechanisms of glutamate toxicity in multiple sclerosis:
Biomarker and therapeutic opportunities. Lancet Neurol.
15:1089–1102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zenlea T and Peppercorn MA:
Immunosuppressive therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:3146–3152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma MZ, Chen G, Wang P, Lu WH, Zhu CF, Song
M, Yang J, Wen S, Xu RH, Hu Y and Huang P: Xc- inhibitor
sulfasalazine sensitizes colorectal cancer to cisplatin by a
GSH-dependent mechanism. Cancer Lett. 368:88–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shitara K, Doi T, Nagano O, Fukutani M,
Hasegawa H, Nomura S, Sato A, Kuwata T, Asai K, Einaga Y, et al:
Phase 1 study of sulfasalazine and cisplatin for patients with
CD44v-positive gastric cancer refractory to cisplatin (EPOC1407).
Gastric Cancer. 20:1004–1009. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, Villanueva
A, Llovet JM and Lynch M: Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a
multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3129–3140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rushmore TH, Morton MR and Pickett CB: The
antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and
identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for
functional activity. J Biol Chem. 266:11632–11639. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hayes JD and McMahon M: Molecular basis
for the contribution of the antioxidant responsive element to
cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Lett. 174:103–113. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chang LC, Chiang SK, Chen SE, Yu YL, Chou
RH and Chang WC: Heme oxygenase-1 mediates BAY 11–7085 induced
ferroptosis. Cancer Lett. 416:124–137. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Houessinon A, Francois C, Sauzay C,
Louandre C, Mongelard G, Godin C, Bodeau S, Takahashi S, Saidak Z,
Gutierrez L, et al: Metallothionein-1 as a biomarker of altered
redox metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells exposed to
sorafenib. Mol Cancer. 15:382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sun H, Zhu J, Lin H, Gu K and Feng F:
Recent progress in the development of small molecule Nrf2
modulators: A patent review (2012–2016). Expert Opin Ther Pat.
27:763–785. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|