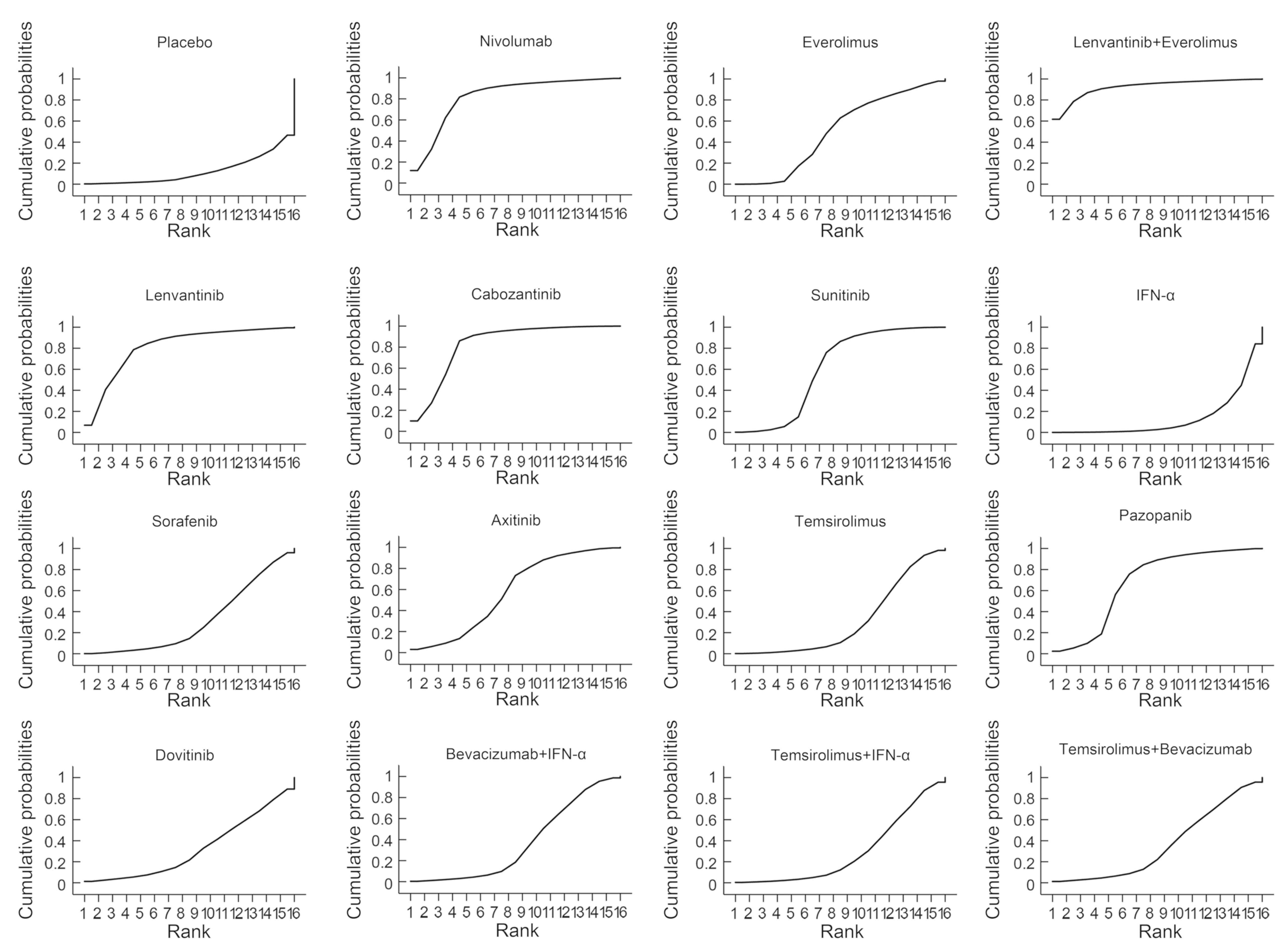
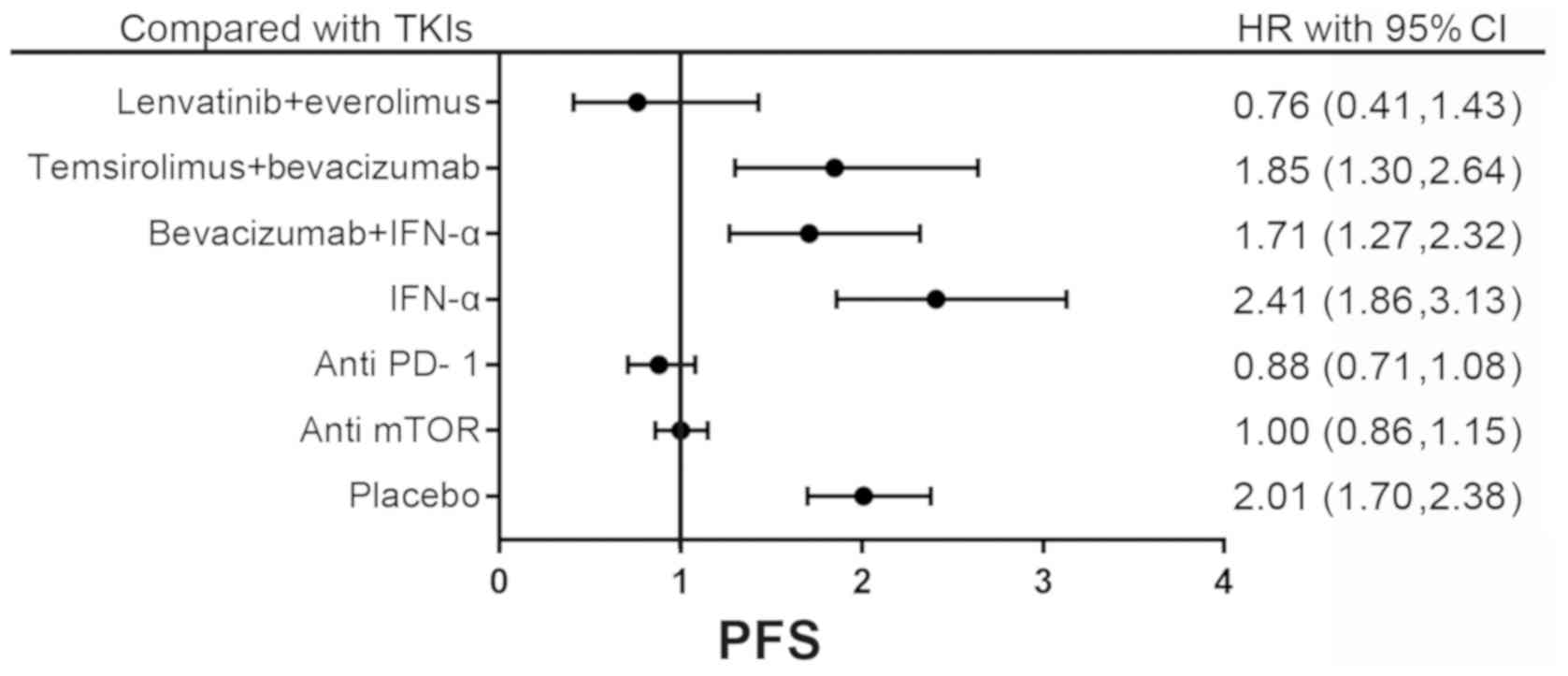
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brookman-May SD, May M, Shariat SF, Novara
G, Zigeuner R, Cindolo L, De Cobelli O, De Nunzio C, Pahernik S,
Wirth MP, et al: Time to recurrence is a significant predictor of
cancer-specific survival after recurrence in patients with
recurrent renal cell carcinoma-results from a comprehensive
multi-centre database (CORONA/SATURN-Project). BJU Int.
112:909–916. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tosco L, Van Poppel H, Frea B, Gregoraci G
and Joniau S: Survival and impact of clinical prognostic factors in
surgically treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol.
63:646–652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garcia JA and Rini BI: Recent progress in
the management of advanced renal cell carcinoma. CA Cancer J Clin.
57:112–125. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hartmann JT and Bokemeyer C: Chemotherapy
for renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 19:1541–1543.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Motzer RJ and Russo P: Systemic therapy
for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 163:408–417. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gore ME and Larkin JM: Challenges and
opportunities for converting renal cell carcinoma into a chronic
disease with targeted therapies. Br J Cancer. 104:399–406. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Murphy BA, Russo P and
Mazumdar M: Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical
trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J
Clin Oncol. 20:289–296. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harding MW: Immunophilins, mTOR and
Pharmacodynamic Strategies for a targeted cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:2882–2886. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG,
Christensen JG, Li G, Schreck RE, Abrams TJ, Ngai TJ, Lee LB, et
al: In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase
inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and
platelet-derived growth factor receptors: Determination of a
pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res.
9:327–337. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gnarra JR, Tory K, Weng Y, Schmidt L, Wei
MH, Li H, Latif F, Liu S, Chen F, Duh FM, et al: Mutations of the
VHL tumour suppressor gene in renal carcinoma. Nat Genet. 7:85–90.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Na XI, Wu G, Ryan CK, Schoen SR,
di'Santagnese PA and Messing EM: Overproduction of vascular
endothelial growth factor related to von Hippel-Lindau tumor
suppressor gene mutations and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha
expression in renal cell carcinomas. J Urol. 170:588–592. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM, Hwu P,
Schwartzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, Steinberg SM, Chen HX and
Rosenberg SA: A Randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular
endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N
Engl J Med. 349:427–434. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Motzer RJ, Ravaud A, Patard JJ, Pandha HS,
George DJ, Patel A, Chang YH, Escudier B, Donskov F, Magheli A, et
al: Adjuvant Sunitinib for High-risk renal cell carcinoma after
nephrectomy: Subgroup analyses and updated overall survival
results. Eur Urol. 73:62–68. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tomita Y, Fukasawa S, Shinohara N,
Kitamura H, Oya M, Eto M, Tanabe K, Kimura G, Yonese J, Yao M, et
al: Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma:
Japanese subgroup analysis from the CheckMate 025 study. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 47:639–646. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hutson TE, Al-Shukri S, Stus VP, Lipatov
ON, Shparyk Y, Bair AH, Rosbrook B, Andrews GI and Vogelzang NJ:
Axitinib Versus Sorafenib in First-line metastatic renal cell
carcinoma: Overall survival from a randomized phase III trial. Clin
Genitourin Cancer. 15:72–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choueiri TK, Halabi S, Sanford BL, Hahn O,
Michaelson MD, Walsh MK, Feldman DR, Olencki T, Picus J, Small EJ,
et al: Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial targeted therapy
for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of poor or
intermediate risk: The alliance A031203 CABOSUN trial. J Clin
Oncol. 35:591–597. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, George DJ,
Pantuck AJ, Patel A, Chang YH, Escudier B, Donskov F, Magheli A, et
al: Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after
nephrectomy. N Engl J Med. 375:2246–2254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Ren M, Dutcus C and
Larkin J: Independent assessment of lenvatinib plus everolimus in
patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol.
17:e4–e5. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Haas NB, Manola J, Uzzo RG, Flaherty KT,
Wood CG, Kane C, Jewett M, Dutcher JP, Atkins MB, Pins M, et al:
Adjuvant sunitinib or sorafenib for high-risk, non-metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma (ECOG-ACRIN E2805): A double-blind,
placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet.
387:2008–2016. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choueiri TK, Escudier B, Powles T, Tannir
NM, Mainwaring PN, Rini BI, Hammers HJ, Donskov F, Roth BJ, Peltola
K, et al: Cabozantinib versus everolimus in advanced renal cell
carcinoma (METEOR): Final results from a randomised, open-label,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 17:917–927. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beaumont JL, Salsman JM, Diaz J, Deen KC,
McCann L, Powles T, Hackshaw MD, Motzer RJ and Cella D:
Quality-adjusted time without symptoms or toxicity analysis of
pazopanib versus sunitinib in patients with renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer. 122:1108–1115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qin S, Bi F, Jin J, Cheng Y, Guo J, Ren X,
Huang Y, Tarazi J, Tang J, Chen C, et al: Axitinib versus sorafenib
as a second-line therapy in Asian patients with metastatic renal
cell carcinoma: Results from a randomized registrational study.
Onco Targets Ther. 8:1363–1373. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Glen H, Michaelson
MD, Molina A, Eisen T, Jassem J, Zolnierek J, Maroto JP, Mellado B,
et al: Lenvatinib, everolimus and the combination in patients with
metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A randomised, phase 2, open-label,
multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 16:1473–1482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF,
George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, Sosman JA, Procopio G,
Plimack ER, et al: Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 373:1803–1813. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choueiri TK, Escudier B, Powles T,
Mainwaring PN, Rini BI, Donskov F, Hammers H, Hutson TE, Lee JL,
Peltola K, et al: Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in advanced
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 373:1814–1823. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rini BI, Bellmunt J, Clancy J, Wang K,
Niethammer AG, Hariharan S and Escudier B: Randomized phase III
trial of temsirolimus and bevacizumab versus interferon alfa and
bevacizumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: INTORACT trial. J
Clin Oncol. 32:752–759. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Motzer RJ, Porta C, Vogelzang NJ,
Sternberg CN, Szczylik C, Zolnierek J, Kollmannsberger C, Rha SY,
Bjarnason GA, Melichar B, et al: Dovitinib versus sorafenib for
third-line targeted treatment of patients with metastatic renal
cell carcinoma: An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 15:286–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hutson TE, Escudier B, Esteban E,
Bjarnason GA, Lim HY, Pittman KB, Senico P, Niethammer A, Lu DR,
Hariharan S and Motzer RJ: Randomized phase III trial of
temsirolimus versus sorafenib as second-line therapy after
sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 32:760–767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ueda T, Uemura H, Tomita Y, Tsukamoto T,
Kanayama H, Shinohara N, Tarazi J, Chen C, Kim S, Ozono S, et al:
Efficacy and safety of axitinib versus sorafenib in metastatic
renal cell carcinoma: Subgroup analysis of Japanese patients from
the global randomized Phase 3 AXIS trial. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
43:616–628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sternberg CN, Hawkins RE, Wagstaff J,
Salman P, Mardiak J, Barrios CH, Zarba JJ, Gladkov OA, Lee E,
Szczylik C, et al: A randomised, double-blind phase III study of
pazopanib in patients with advanced and/or metastatic renal cell
carcinoma: Final overall survival results and safety update. Eur J
Cancer. 49:1287–1296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J,
Hawkins R, Guo J, Nathan P, Staehler M, de Souza P, Merchan JR, et
al: Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma.
N Engl J Med. 369:722–731. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Hutson
TE, Michaelson MD, Negrier S, Oudard S, Gore ME, Tarazi J,
Hariharan S, et al: Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line
treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Overall survival
analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 14:552–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hutson TE, Lesovoy V, Al-Shukri S, Stus
VP, Lipatov ON, Bair AH, Rosbrook B, Chen C, Kim S and Vogelzang
NJ: Axitinib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients
with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: A randomised open-label phase
3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:1287–1294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Kaprin A,
Szczylik C, Hutson TE, Michaelson MD, Gorbunova VA, Gore ME,
Rusakov IG, et al: Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus
sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): A randomised
phase 3 trial. Lancet. 378:1931–1939. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J,
Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, Barrios CH, Salman P, Gladkov OA,
Kavina A, et al: Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal
cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin
Oncol. 28:1061–1068. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, Stadler
WM, Vaena DA, Archer L, Atkins JN, Picus J, Czaykowski P, Dutcher J
and Small EJ: Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa
versus interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic
renal cell carcinoma: Final results of CALGB 90206. J Clin Oncol.
28:2137–2143. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson
TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA,
Hollaender N, et al: Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic
renal cell carcinoma: Final results and analysis of prognostic
factors. Cancer. 116:4256–4265. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Pili
R, Bjarnason GA, et al: Overall survival and updated results for
sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic
renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 27:3584–3590. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dutcher JP, de Souza P, McDermott D,
Figlin RA, Berkenblit A, Thiele A, Krygowski M, Strahs A, Feingold
J and Hudes G: Effect of temsirolimus versus interferon-alpha on
outcome of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma of different
tumor histologies. Med Oncol. 26:202–209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, Stadler
WM, Vaena DA, Ou SS, Archer L, Atkins JN, Picus J, Czaykowski P, et
al: Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa
monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB
90206. J Clin Oncol. 26:5422–5428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson
TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA,
Hollaender N, et al: Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell
carcinoma: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III
trial. Lancet. 372:449–456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik
C, Kim ST, et al: Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J,
Figlin R, Kapoor A, Staroslawska E, Sosman J, McDermott D, Bodrogi
I, et al: Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:2271–2281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee SH, Lopes de Menezes D, Vora J, Harris
A, Ye H, Nordahl L, Garrett E, Samara E, Aukerman SL, Gelb AB and
Heise C: In vivo target modulation and biological activity of
CHIR-258, a multitargeted growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor,
in colon cancer models. Clin Cancer Res. 11:3633–3641. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tonin FS, Rotta I, Mendes AM and Pontarolo
R: Network meta-analysis: A technique to gather evidence from
direct and indirect comparisons. Pharm Pract (Granada). 15:9432017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Salanti G, Ades AE and Ioannidis JP:
Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results
from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: An overview and tutorial. J
Clin Epidemiol. 64:163–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani
A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, Ioannidis JP, Straus S, Thorlund K, Jansen
JP, et al: The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of
systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health
care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med.
162:777–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wei W, Peng R, Zeng L, Xu C, Cao Y, Chen W
and Xia S: Comparative efficacy and safety of targeted therapy in
the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: A Bayesian network analysis.
Value Health. 21 (Suppl 2):S1132018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Higgins JPT and Green S: Cochrane handbook
for systematic reviews of interventions 4.2.6The Cochrane Library.
4:157–161. 2006.
|
|
52
|
Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB,
Holland L and Bekhuis T: De-duplication of database search results
for systematic reviews in EndNote. J Med Libr Assoc. 104:240–243.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group, : Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int J Surg.
8:336–341. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chaimani A, Higgins JP, Mavridis D,
Spyridonos P and Salanti G: Graphical tools for network
meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS One. 8:e766542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA,
Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van
Oosterom AT, Christian MC and Gwyther SG: New guidelines to
evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European
Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer
Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of
Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:205–216. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, Rusch V,
Jaques D, Budach V, Langer C, Murphy B, Cumberlin R, Coleman CN and
Rubin P: CTCAE v3.0: Development of a comprehensive grading system
for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol.
13:176–181. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lunn DJ, Thomas A, Best N and
Spiegelhalter D: WinBUGS-A Bayesian modelling framework: Concepts,
structure and extensibility. Stat Computing. 10:325–337. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Woods BS, Hawkins N and Scott DA: Network
meta-analysis on the log-hazard scale, combining count and hazard
ratio statistics accounting for multi-arm trials: A tutorial. BMC
Med Res Methodol. 10:542010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Spiegelhalter DJ, Best NG, Carlin BP and
Van Der Linde A: Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J
Royal Stat Soc Series B (Statistical Methodology). 64:583–639.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Saber H, Tang S,
Williams G, Jee JM, Liang C, Booth B, Chidambaram N, Morse D, et
al: Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:7271–7278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wiecek W and Karcher H: Nivolumab versus
cabozantinib: Comparing overall survival in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01553892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Song F, Xiong T, Parekh-Bhurke S, Loke YK,
Sutton AJ, Eastwood AJ, Holland R, Chen YF, Glenny AM, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Inconsistency between direct and indirect comparisons of
competing interventions: Meta-epidemiological study. BMJ.
343:d49092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
He HL and Yao WX: A network meta-analysis
of short-term efficacy of different single-drug targeted therapies
in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Biosci Rep. 37(pii):
BSR201708272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rousseau B, Kempf E, Desamericq G,
Boissier E, Chaubet-Houdu M, Joly C, Saldana C, Boussion H,
Neuzillet C, Macquin-Mavier I, et al: First-line antiangiogenics
for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and
network meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 107:44–53. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|