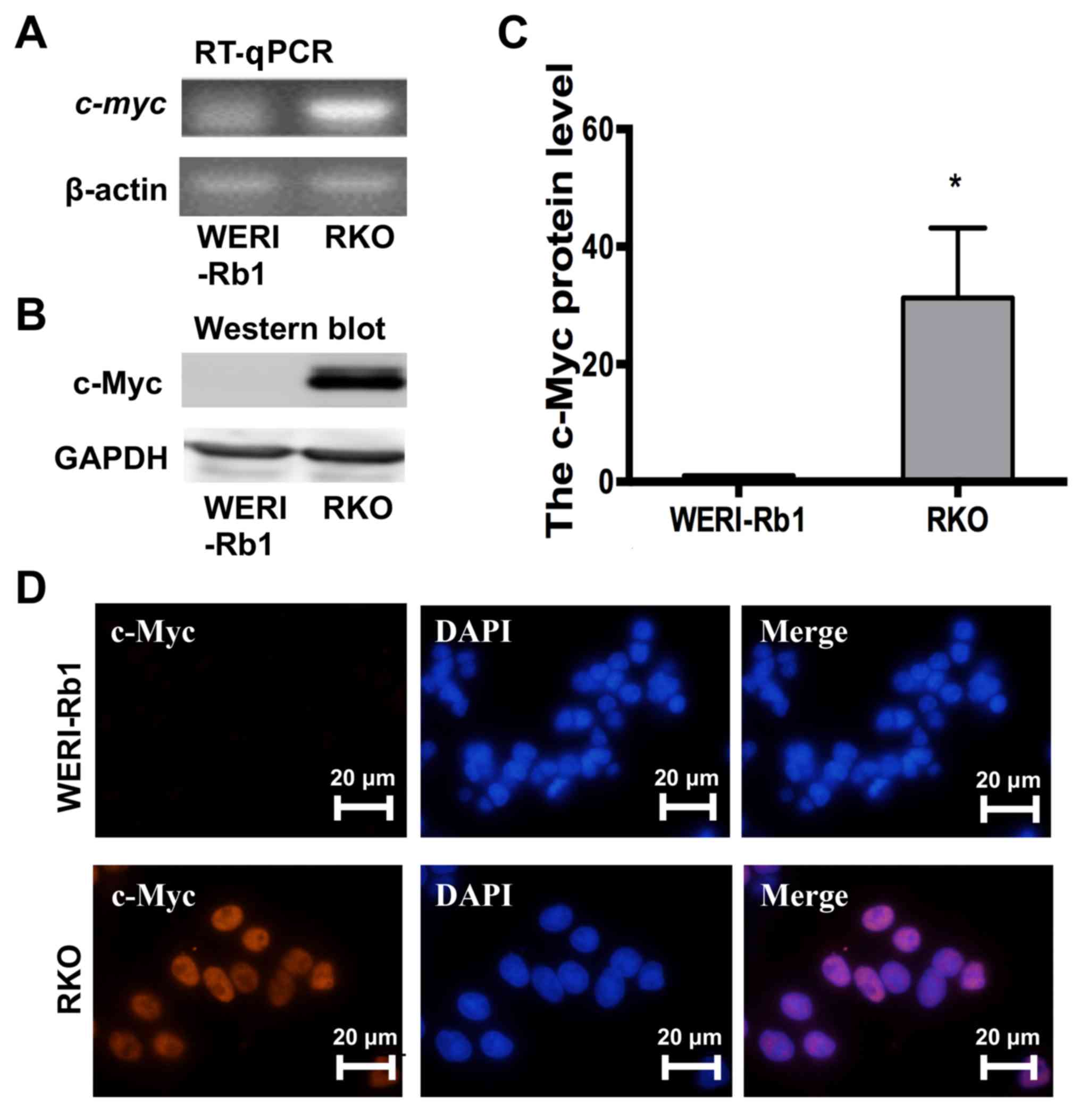
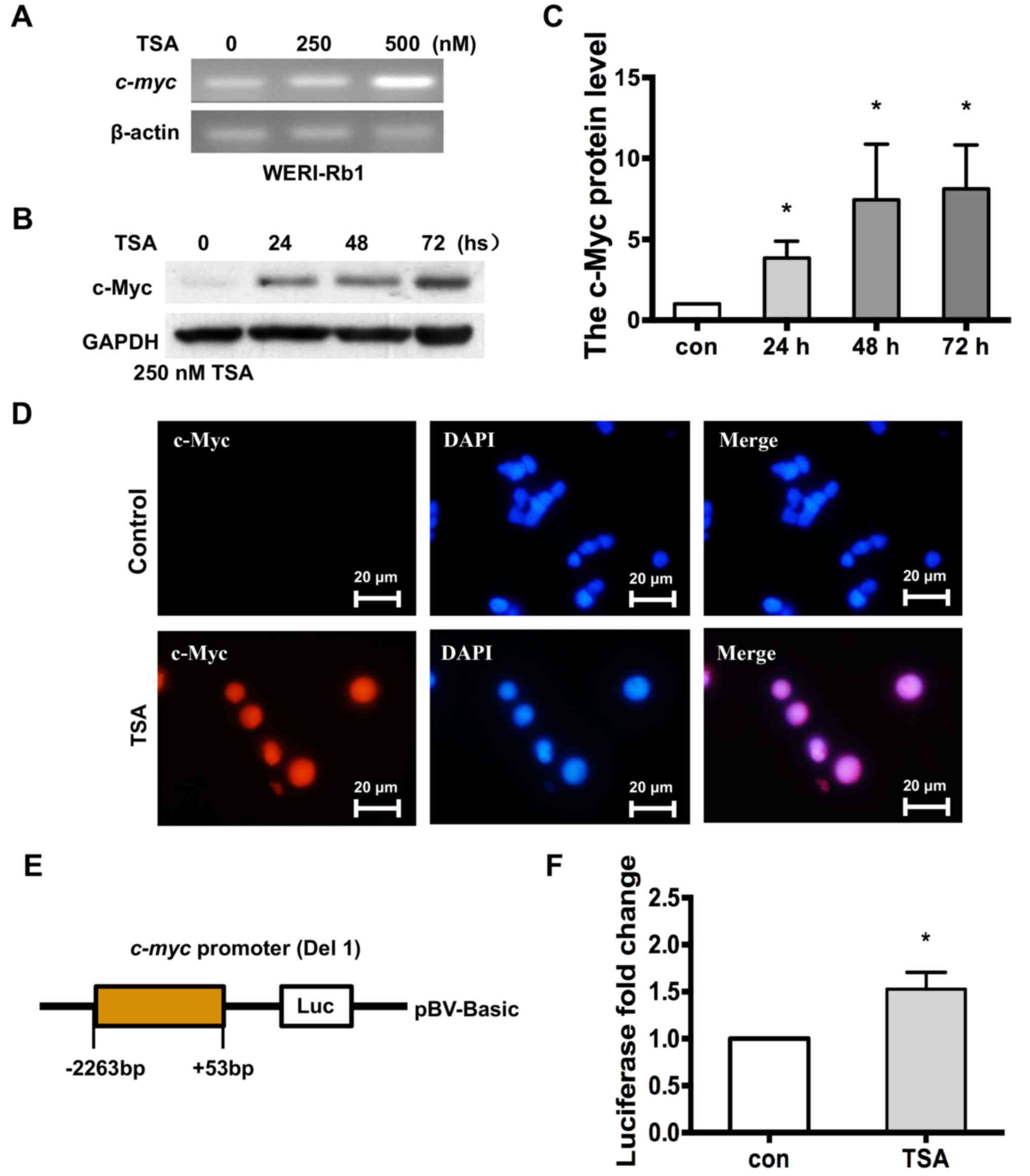
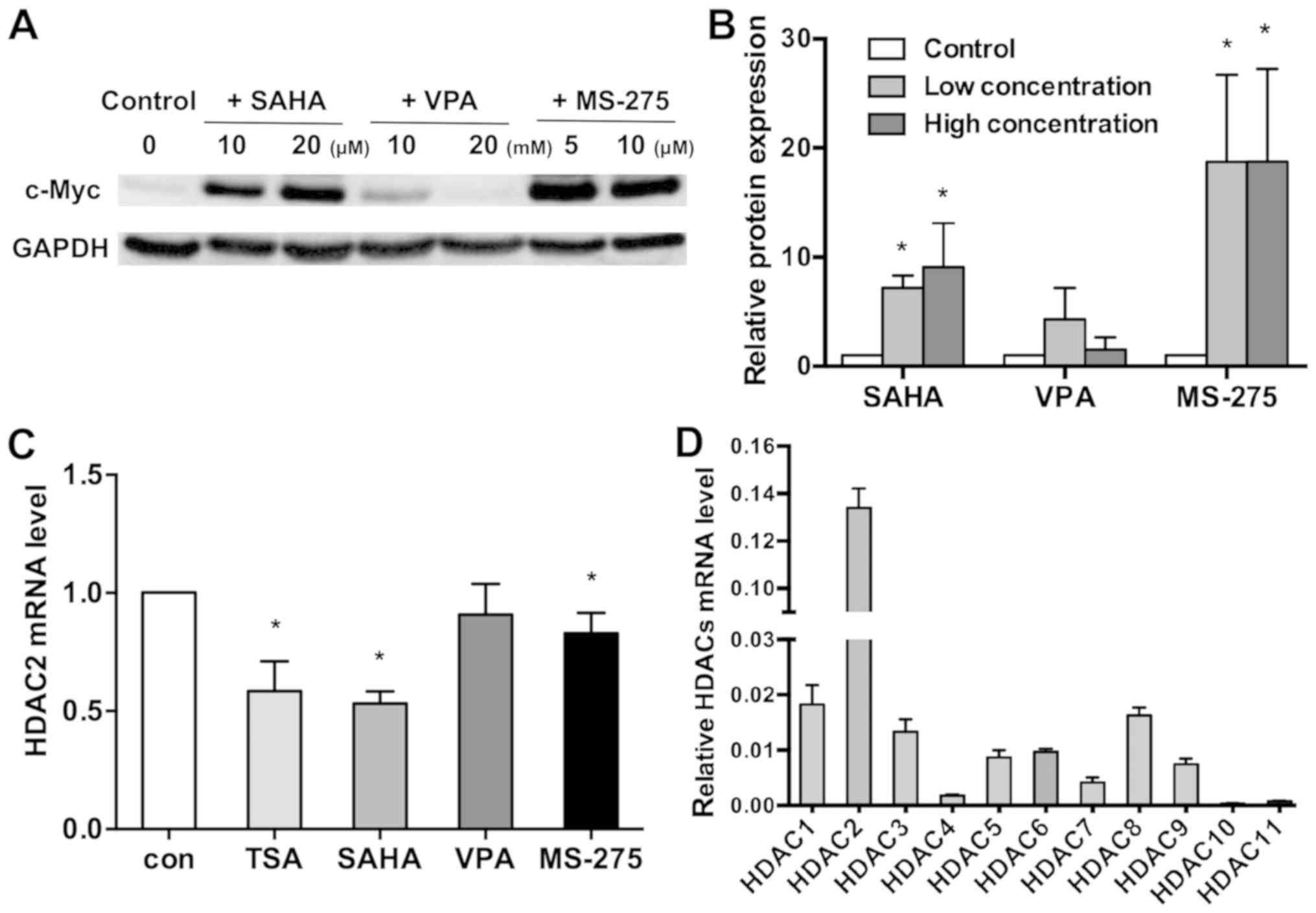
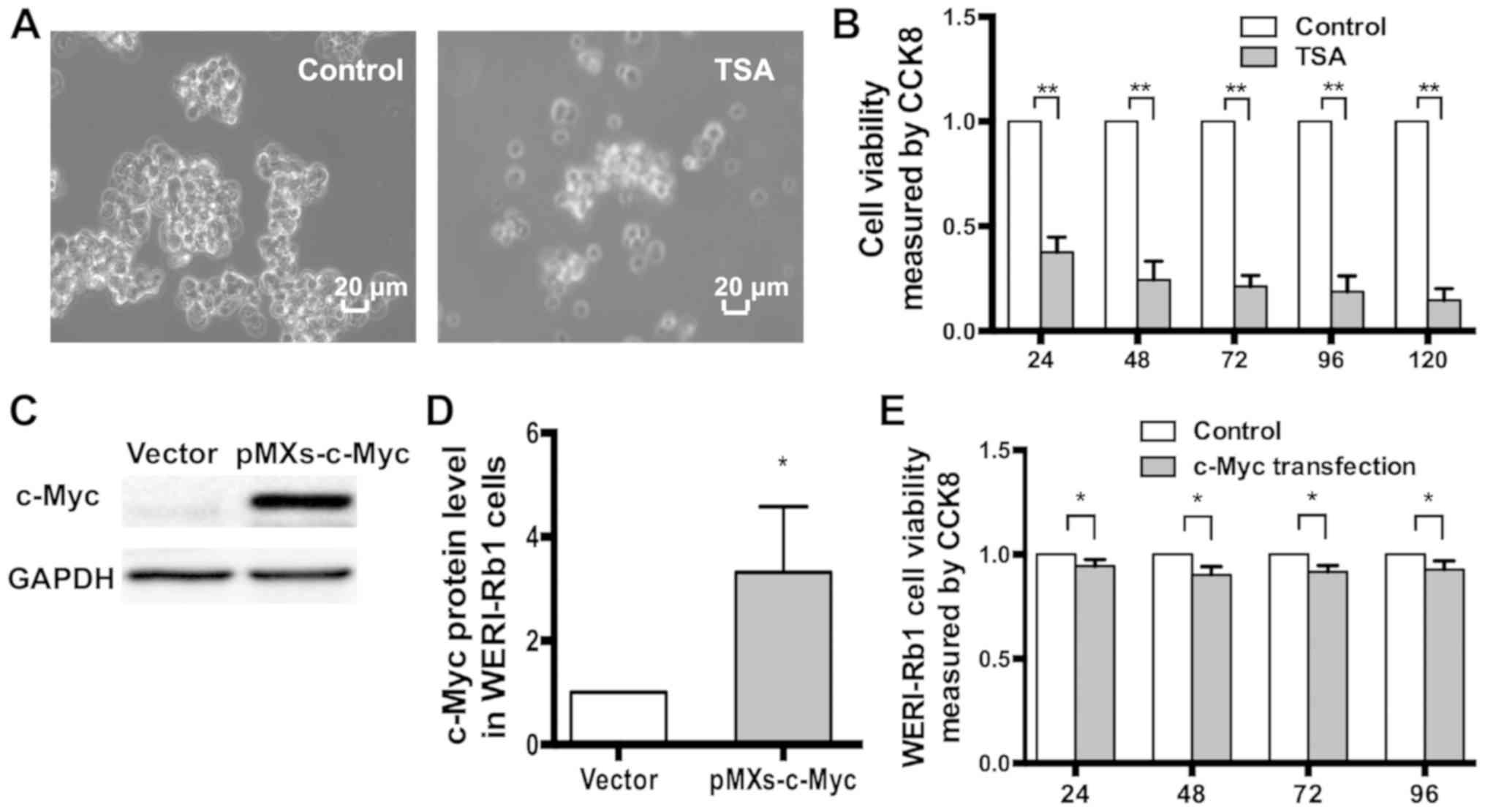
|
1
|
Dimaras H, Kimani K, Dimba EA, Gronsdahl
P, White A, Chan HS and Gallie BL: Retinoblastoma. Lancet.
379:1436–1446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fabian ID, Onadim Z, Karaa E, Duncan C,
Chowdhury T, Scheimberg I, Ohnuma SI, Reddy MA and Sagoo MS: The
management of retinoblastoma. Oncogene. 37:1551–1560. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kivela T: The epidemiological challenge of
the most frequent eye cancer: Retinoblastoma, an issue of birth and
death. Br J Ophthalmol. 93:1129–1131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Knudson AG Jr: Mutation and cancer:
Statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
68:820–823. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zimmerman K and Alt FW: Expression and
function of myc family genes. Crit Rev Oncog. 2:75–95.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nesbit CE, Tersak JM and Prochownik EV:
MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene. 18:3004–3016.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brodeur GM: Neuroblastoma: Biological
insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:203–216. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bociek RG: Adult Burkitt's lymphoma. Clin
Lymphoma. 6:11–20. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Horiuchi D, Anderton B and Goga A: Taking
on challenging targets: Making MYC druggable. Am Soc Clin Oncol
Educ Book. e497–e502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Conacci-Sorrell M, McFerrin L and Eisenman
RN: An overview of MYC and its interactome. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Med. 4:a0143572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chung HJ and Levens D: c-myc expression:
Keep the noise down! Mol Cells. 20:157–166. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kitagawa Y, Kyo S, Takakura M, Kanaya T,
Koshida K, Namiki M and Inoue M: Demethylating reagent
5-azacytidine inhibits telomerase activity in human prostate cancer
cells through transcriptional repression of hTERT. Clin Cancer Res.
6:2868–2875. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grandjenette C, Schnekenburger M, Karius
T, Ghelfi J, Gaigneaux A, Henry E, Dicato M and Diederich M:
5-aza-2′- deoxycytidine-mediated c-myc Down-regulation triggers
telomere-dependent senescence by regulating human telomerase
reverse transcriptase in chronic myeloid leukemia. Neoplasia.
16:511–528. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Long Y, Tsai WB, Chang JT, Estecio M,
Wangpaichitr M, Savaraj N, Feun LG, Chen HH and Kuo MT:
Cisplatin-induced synthetic lethality to arginine-starvation
therapy by transcriptional suppression of ASS1 is regulated by
DEC1, HIF-1α, and c-Myc transcription network and is independent of
ASS1 promoter DNA methylation. Oncotarget. 7:82658–82670. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H and Wu X: Histone deacetylase
inhibitor, Trichostatin A, activates p21WAF1/CIP1 expression
through downregulation of c-myc and release of the repression of
c-myc from the promoter in human cervical cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 324:860–867. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dang CV, Resar LM, Emison E, Kim S, Li Q,
Prescott JE, Wonsey D and Zeller K: Function of the c-Myc oncogenic
transcription factor. Exp Cell Res. 253:63–77. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo P, Nie Q, Lan J, Ge J, Qiu Y and Mao
Q: C-Myc negatively controls the tumor suppressor PTEN by
upregulating miR-26a in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 441:186–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Karn J, Watson JV, Lowe AD, Green SM and
Vedeckis W: Regulation of cell cycle duration by c-myc levels.
Oncogene. 4:773–787. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jain M, Arvanitis C, Chu K, Dewey W,
Leonhardt E, Trinh M, Sundberg CD, Bishop JM and Felsher DW:
Sustained loss of a neoplastic phenotype by brief inactivation of
MYC. Science. 297:102–104. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang C, Tai Y, Lisanti MP and Liao DJ:
c-Myc induction of programmed cell death may contribute to
carcinogenesis: A perspective inspired by several concepts of
chemical carcinogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:615–626. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okuyama H, Endo H, Akashika T, Kato K and
Inoue M: Downregulation of c-MYC protein levels contributes to
cancer cell survival under dual deficiency of oxygen and glucose.
Cancer Res. 70:10213–10223. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liva KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Futamura M, Monden Y, Okabe T,
Fujita-Yoshigaki J, Yokoyama S and Nishimura S: Trichostatin A
inhibits both ras-induced neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells and
morphological transformation of NIH3T3 cells. Oncogene.
10:1119–1123. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kretzner L, Scuto A, Dino PM, Kowolik CM,
Wu J, Ventura P, Jove R, Forman SJ, Yen Y and Kirschbaum MH:
Combining histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat with aurora
kinase inhibitors enhances lymphoma cell killing with repression of
c-Myc, hTERT, and microRNA levels. Cancer Res. 71:3912–3920. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nebbioso A, Carafa V, Conte M, Tambaro FP,
Abbondanza C, Martens J, Nees M, Benedetti R, Pallavicini I,
Minucci S, et al: c-Myc modulation & acetylation is a key HDAC
inhibitor target in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:2542–2555. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Napoli S, Pastori C, Magistri M, Carbone
GM and Catapano CV: Promoter-specific transcriptional interference
and c-myc gene silencing by siRNAs in human cells. EMBO J.
28:1708–1719. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Conte M, Dell'Aversana C, Sgueglia G,
Carissimo A and Altucci L: HDAC2-dependent miRNA signature in acute
myeloid leukemia. FEBS Lett. 593:2574–2584. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shan W, Jiang Y, Yu H, Huang Q, Liu L, Guo
X, Li L, Mi Q, Zhang K and Yang Z: HDAC2 overexpression correlates
with aggressive clinicopathological features and DNA-damage
response pathway of breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1213–1226.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Weichert W, Roske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T,
Stephan C, Jung K, Fritzsche FR, Niesporek S, Denkert C, Dietel M
and Kristiansen G: Histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly
expressed in prostate cancer and HDAC2 expression is associated
with shorter PSA relapse time after radical prostatectomy. Br J
Cancer. 98:604–610. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim JK, Noh JH, Eun JW, Jung KH, Bae HJ,
Shen Q, Kim MG, Chang YG, Kim SJ, Park WS, et al: Targeted
inactivation of HDAC2 restores p16INK4a activity and exerts
antitumor effects on human gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
11:62–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li S, Wang F, Qu Y, Chen X, Gao M, Yang J,
Zhang D, Zhang N, Li W and Liu H: HDAC2 regulates cell
proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell apoptosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma EC9706 cells. Oncol Lett.
13:403–409. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li L, Mei DT and Zeng Y: HDAC2 promotes
the migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells via
upregulation of fibronectin. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:284–290. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao H, Yu Z, Zhao L, He M, Ren J, Wu H,
Chen Q, Yao W and Wei M: HDAC2 overexpression is a poor prognostic
factor of breast cancer patients with increased multidrug
resistance-associated protein expression who received
anthracyclines therapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:893–902. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Krämer OH, Zhu P, Ostendorff HP,
Golebiewski M, Tiefenbach J, Peters MA, Brill B, Groner B, Bach I,
Heinzel T and Göttlicher M: The histone deacetylase inhibitor
valproic acid selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2.
EMBO J. 22:3411–3420. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwiecińska P, Wróbel A, Taubøll E and
Gregoraszczuk EŁ: Valproic acid, but not levetiracetam, selectively
decreases HDAC7 and HDAC2 expression in human ovarian cancer cells.
Toxicol Lett. 224:225–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jones J, Juengel E, Mickuckyte A, Hudak L,
Wedel S, Jonas D and Blaheta RA: The histone deacetylase inhibitor
valproic acid alters growth properties of renal cell carcinoma in
vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol Med. 13:2376–2385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Travaglini L, Vian L, Billi M, Grignani F
and Nervi C: Epigenetic reprogramming of breast cancer cells by
valproic acid occurs regardless of estrogen receptor status. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:225–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nebbioso A, Clarke N, Voltz E, Germain E,
Ambrosino C, Bontempo P, Alvarez R, Schiavone EM, Ferrara F,
Bresciani F, et al: Tumor-selective action of HDAC inhibitors
involves TRAIL induction in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Nat Med.
11:77–84. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Noh JH, Jung KH, Kim JK, Eun JW, Bae HJ,
Xie HJ, Chang YG, Kim MG, Park WS, Lee JY and Nam SW: Aberrant
regulation of HDAC2 mediates proliferation of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by deregulating expression of G1/S cell cycle
proteins. PLoS One. 6:e281032011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ecker J, Oehme I, Mazitschek R, Korshunov
A, Kool M, Hielscher T, Kiss J, Selt F, Konrad C, Lodrini M, et al:
Targeting class I histone deacetylase 2 in MYC amplified group 3
medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 3:222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Glaser KB, Staver MJ, Waring JF, Stender
J, Ulrich RG and Davidsen SK: Gene expression profiling of multiple
histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors: Defining a common gene set
produced by HDAC inhibition in T24 and MDA carcinoma cell lines.
Mol Cancer Ther. 2:151–163. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bookstein R, Lee EY, To H, Young LJ, Sery
TW, Hayes RC, Friedmann T and Lee WH: Human retinoblastoma
susceptibility gene: Genomic organization and analysis of
heterozygous intragenic deletion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
85:2210–2214. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Busch M, Philippeit C, Weise A and Dünker
N: Re-characterization of established human retinoblastoma cell
lines. Histochem Cell Biol. 143:325–338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ross DT, Scherf U, Eisen MB, Perou CM,
Rees C, Spellman P, Iyer V, Jeffrey SS, Van de Rijn M, Waltham M,
et al: Systematic variation in gene expression patterns in human
cancer cell lines. Nat Genet. 24:227–235. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Askew DS, Ashmun RA, Simmons BC and
Cleveland JL: Constitutive c-Myc expression in an IL-3 dependent
myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates
apoptosis. Oncogene. 6:1915–1922. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Evan GI, Wyllie AH, Gilbert CS, Littlewood
TD, Land H, Brooks M, Waters CM, Penn LZ and Hancock DC: Induction
of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-Myc protein. Cell. 69:119–128.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Harrington EA, Bennett MR, Fanidi A and
Evan GI: c-Myc-induced apoptosis in fibroblasts is inhibited by
specific cytokines. EMBO J. 13:3286–3295. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|