|
1
|
Li C, Xia G, Jianqing Z, Mei Y, Ge B and
Li Z: Serum differential protein identification of Xinjiang Kazakh
esophageal cancer patients based on the two-dimensional
liquid-phase chromatography and LTQ MS. Mol Biol Rep. 41:2893–2905.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang J, Jia Y, Wang N, Zhang X, Tan B,
Zhang G and Cheng Y: The clinical significance of
tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and neutrophil-to-CD8+ lymphocyte
ratio in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Transl Med. 12:72014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X,
Wang N, Zhang L, Tang J, Chen J, Wei K, et al: Cancer survival in
China, 2003–2005: A population-based study. Int J Cancer.
136:1921–1930. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y: Distribution of Esophageal Cancer
in Xinjiang. J Xinjiang Med Univ. 11:139–145. 1988.(In
Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Wang XM, Jie ES and Yan-Qing MA:
Case-control study on risk factors of esophageal cancer in Xinjiang
Kazakh nationality. Chinese J Public Health. 23:737–738. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
7
|
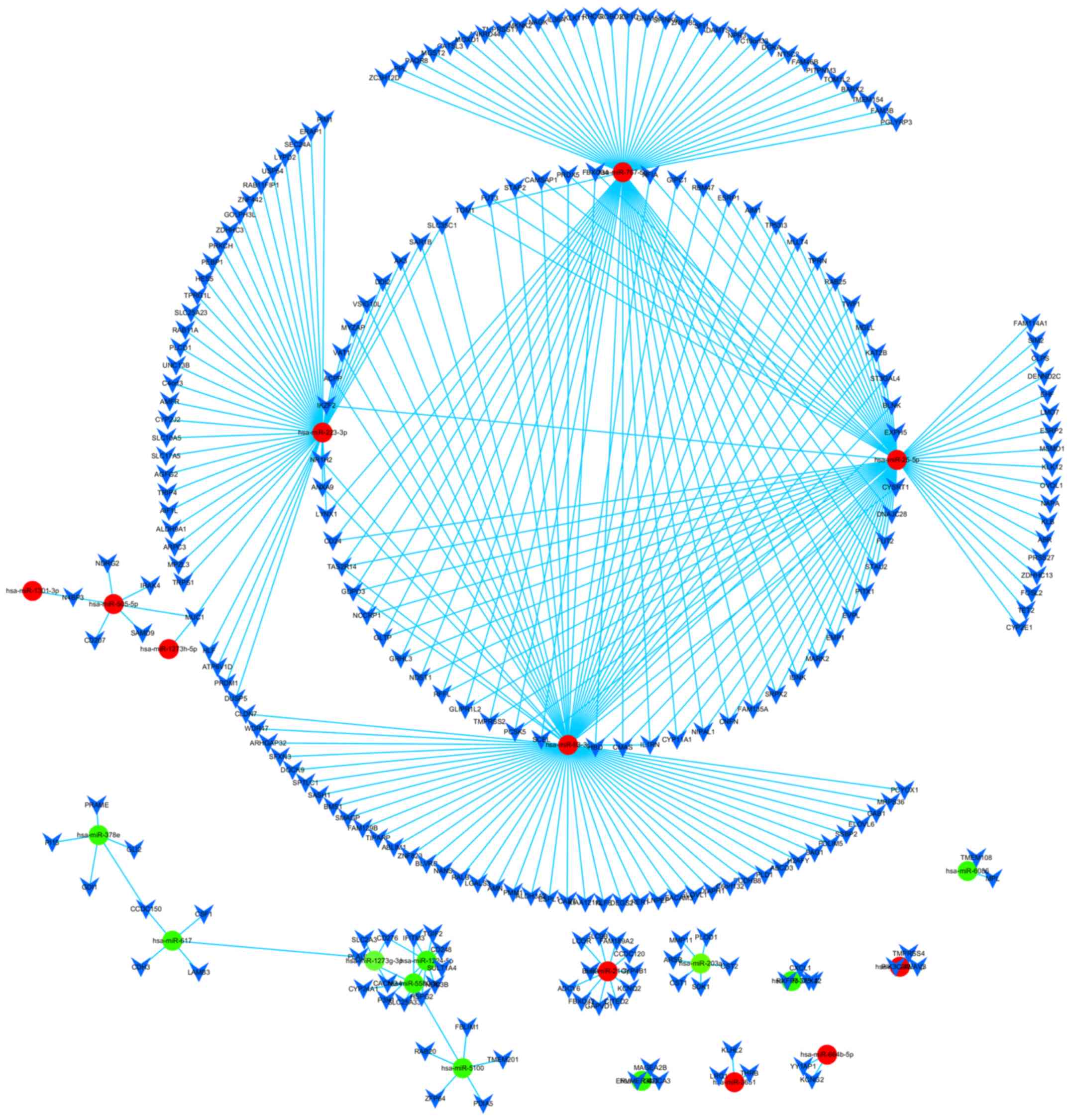
Kozomara A and Griffithsjones S: miRBase:
Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D68–D73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi
SP and Bartel DP: The impact of microRNAs on protein output.
Nature. 455:64–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harada K, Baba Y, Ishimoto T, Shigaki H,
Kosumi K, Yoshida N, Watanabe M and Baba H: The role of microRNA in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 51:520–530.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laganà A, Russo F, Sismeiro C, Giugno R,
Pulvirenti A and Ferro A: Variability in the incidence of miRNAs
and genes in fragile sites and the role of repeats and CpG islands
in the distribution of genetic material. PLoS One. 5:e111662010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Friedman JM and Jones PA: MicroRNAs:
Critical mediators of differentiation, development and disease.
Swiss Med Wkly. 139:466–472. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao W, Shen H, Liu L, Xu J, Xu J and Shu
Y: MiR-21 overexpression in human primary squamous cell lung
carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 137:557–566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu JM, Chang AM, Chen YZ, Yuan XL and Li
F: Regulatory Role of miR-203 in occurrence and progression of
kazakh esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 6:237802016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song X, You W, Zhu J, Cui X, Hu J, Chen Y,
Liu W, Wang L, Li S, Wei Y, et al: A genetic variant in miRNA-219-1
is associated with risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in
chinese kazakhs. Dis Markers. 2015:5415312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Miyazaki Y,
Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori M and Doki
Y: Evaluation of the nodal status in the 7th edition of the
UICC-TNM classification for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:
Proposed modifications for improved survival stratification: Impact
of lymph node metastases on overall survival after esophagectomy.
Ann Surg Oncol. 21:2850–2856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao T and Liu H: ‘Sparse Additive
Machine’, International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Statistics. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Domper Arnal MJ, Ferrandez Arenas A and
Lanas Arbeloa A: Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, screening and
endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7933–7943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo Y, Chen Z, Zhang L, Zhou F, Shi S,
Feng X, Li B, Meng X, Ma X, Luo M, et al: Distinctive microRNA
profiles relating to patient survival in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:26–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang L, Ji Y, Chen L, Li M, Wu F, Hu J,
Jiang J, Cui X, Chen Y, Pang L, et al: Genetic variability in LMP2
and LMP7 is associated with the risk of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma in the Kazakh population but is not associated with HPV
infection. PLoS One. 12:e01863192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou YX, Zhou KM, Liu Q, Wang H, Wang W,
Shi Y and Ma YQ: The effect of Glut1 and c-myc on prognosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma of Kazakh and Han patients.
Future Oncol. 14:1801–1815. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
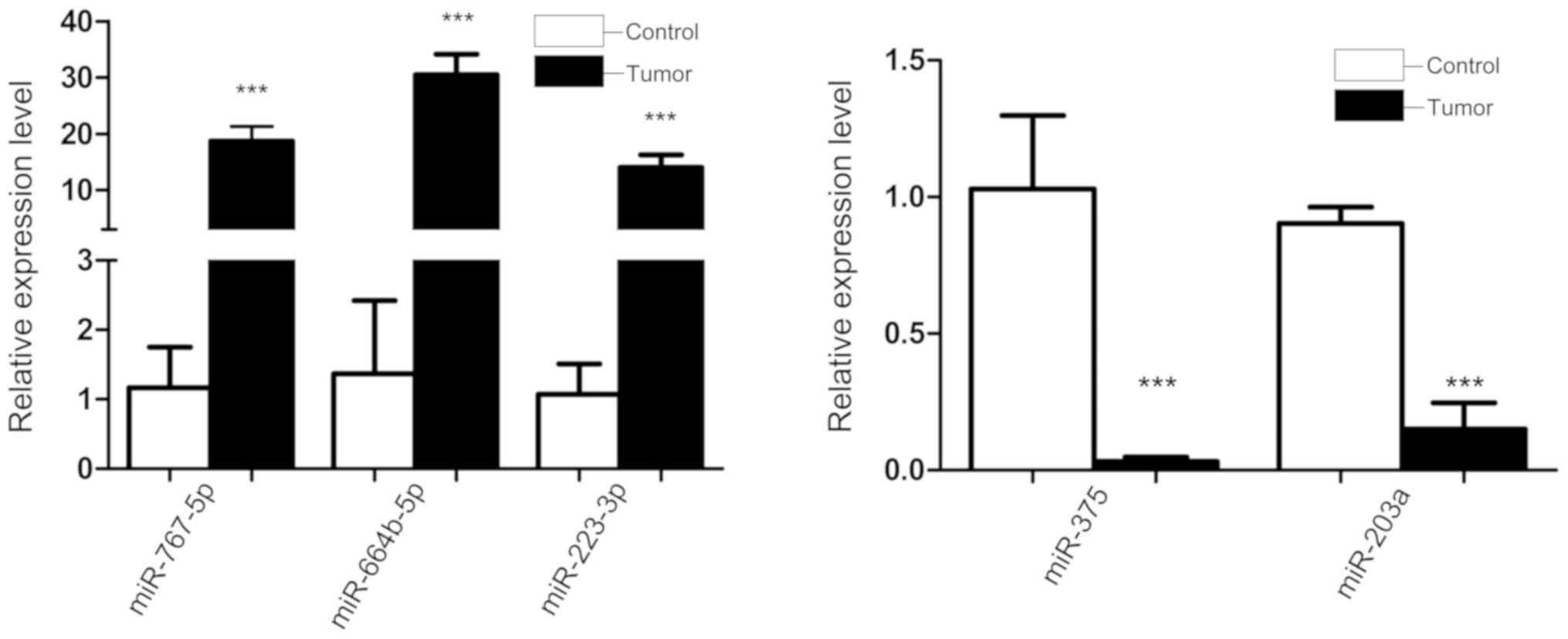
Li J, Li X, Li Y, Yang H, Wang L, Qin Y,
Liu H, Fu L and Guan XY: Cell-specific detection of mir-375
downregulation for predicting the prognosis of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma by miRNA in situ hybridization. PLoS One.
8:e535822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang G: Erratum: Differential expression
of miR-21 and miR-75 in esophageal carcinoma patients and its
clinical implication. Am J Transl Res. 9:19612017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang C, Guan S, Chen X, Liu B, Liu F, Han
L, Un Nesa E, Song Q, Bao C, Wang X and Cheng Y: Clinical potential
of miR-3651 as a novel prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous
cell cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 465:30–34. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tian L, Li M, Ge J, Guo Y, Sun Y, Liu M
and Xiao H: MiR-203 is downregulated in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma and can suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis of
tumours. Tumour Biol. 35:5953–5963. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Ren F, Rong M, Luo Y, Dang Y and
Chen G: Association between underexpression of microrna-203 and
clinicopathological significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
tissues. Cancer Cell Int. 15:622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
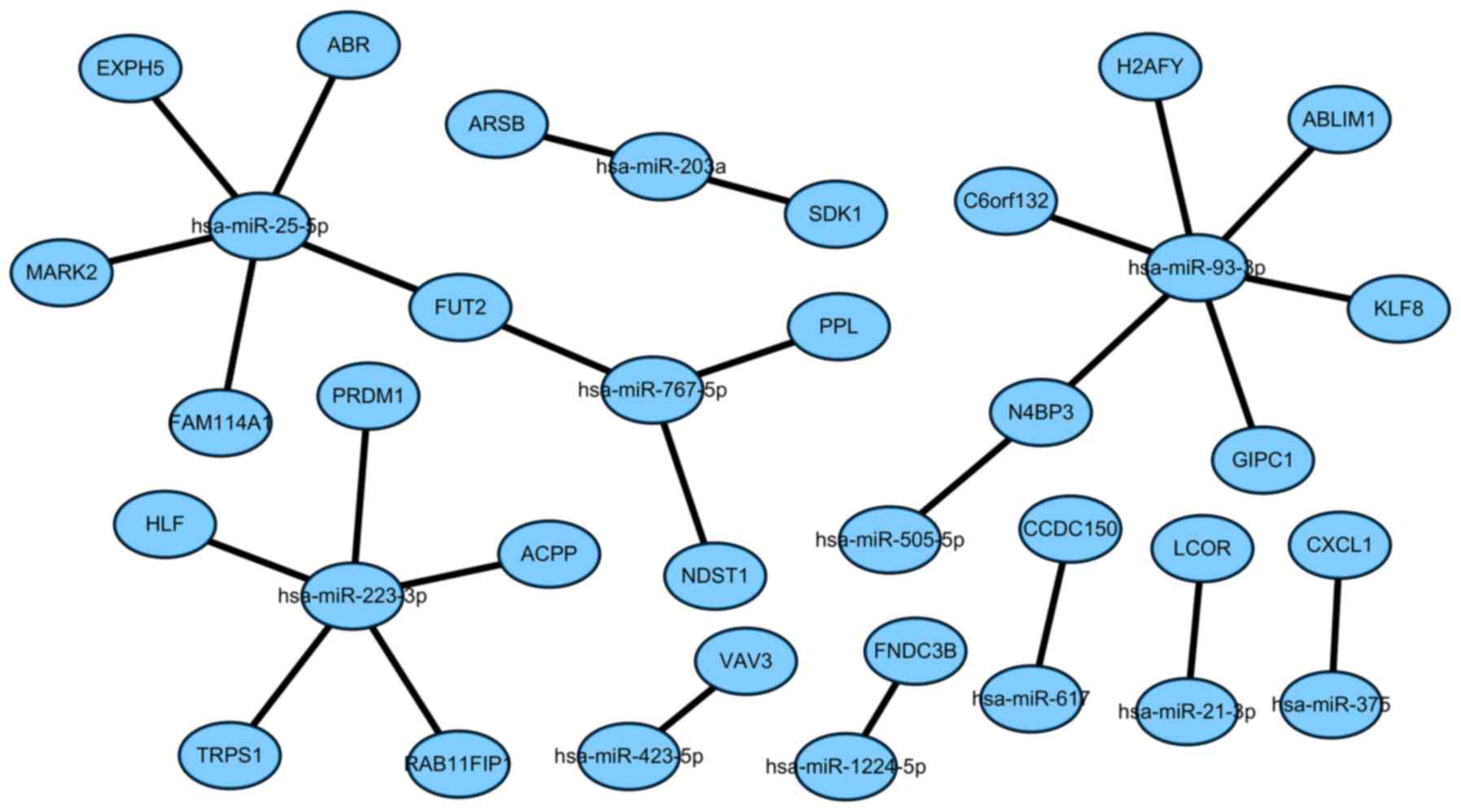
Mao L, Zhang Y, Mo W, Yu Y and Lu H: BANF1
is downregulated by IRF1-regulated microRNA-203 in cervical cancer.
PLoS One. 10:e01170352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang N, Liang H, Zhou Y, Wang C, Zhang S,
Pan Y, Wang Y, Yan X, Zhang J, Zhang CY, et al: miR-203 suppresses
the proliferation and migration and promotes the apoptosis of lung
cancer cells by targeting SRC. PLoS One. 9:e1055702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Tan W, Neo TW, Aung MO, Wasser S,
Lim SG and Tan TM: Role of the miR-106b-25microRNA cluster in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:1234–1242. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang M, Liu R, Sheng J, Liao J, Wang Y,
Pan E, Guo W, Pu Y and Yin L: Differential expression profiles of
microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:169–176. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu T, Liu Q, Zheng S, Gao X, Lu M, Yang
C, Dai F, Sheyhidin I and Lu X: MicroRNA-21 promotes cell growth
and migration by targeting programmed cell death 4 gene in Kazakh's
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2014:2328372014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Savita U and Karunagaran D:
MicroRNA-106b-25 cluster targets β-TRCP2, increases the expression
of Snail and enhances cell migration and invasion in H1299 (non
small cell lung cancer) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
434:841–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li BS, Zuo QF, Zhao YL, Xiao B, Zhuang Y,
Mao XH, Wu C, Yang SM, Zeng H, Zou QM and Guo G: MicroRNA-25
promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by
directly targeting transducer of ERBB2, 1 and correlates with poor
survival. Oncogene. 34:2556–2565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao Z, Liu J, Wang C, Wang Y, Jiang Y and
Guo M: MicroRNA-25 regulates small cell lung cancer cell
development and cell cycle through cyclin E2. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:7726–7234. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qu J, Li M, Zhong W and Hu C: Prognostic
role of microRNA-25 in cancers: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:12921–12927. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu X, Chen Z, Zhao X, Wang J, Ding D, Wang
Z, Tan F, Tan X, Zhou F, Sun J, et al: MicroRNA-25 promotes cell
migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:640–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qian J, Li R, Wang YY, Shi Y, Luan WK, Tao
T, Zhang JX, Xu YC and You YP: MiR-1224-5p acts as a tumor
suppressor by targeting CREB1 in malignant gliomas. Mol Cell
Biochem. 403:33–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang H, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Chen T, Yang L,
He H, Lin Z, Liu T, Yang T, Kamp DW, Wu B and Liu G: miR-5100
promotes tumor growth in lung cancer by targeting Rab6. Cancer
Lett. 362:15–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Matamala N, Vargas MT, Gonzalez-Campora R,
Miñambres R, Arias JI, Menéndez P, Andrés-León E, Gómez-López G,
Yanowsky K, Calvete-Candenas J, et al: Tumor MicroRNA expression
profiling identifies circulating MicroRNAs for early breast cancer
detection. Clin Chem. 61:1098–1106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Song W, Tang L, Xu Y, Xu J, Zhang W, Xie
H, Wang S and Guan X: Corrigendum: PARP inhibitor increases
chemosensitivity by upregulating miR-664b-5p in BRCA1-mutated
triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Rep. 7:443462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zha R, Guo W, Zhang Z, Qiu Z, Wang Q, Ding
J, Huang S, Chen T, Gu J, Yao M and He X: Genome-wide screening
identified that miR-134 acts as a metastasis suppressor by
targeting integrin β1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e876652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zang W, Wang Y, Du Y, Xuan X, Wang T, Li
M, Ma Y, Li P, Chen X, Dong Z and Zhao G: Differential expression
profiling of microRNAs and their potential involvement in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 35:3295–3304.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hakomori S: Aberrant glycosylation in
cancer cell membranes as focused on glycolipids: Overview and
perspectives. Cancer Res. 45:2405–2414. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Alikhani N, Ferguson RD, Novosyadlyy R,
Gallagher EJ, Scheinman EJ, Yakar S and LeRoith D: Mammary tumor
growth and pulmonary metastasis are enhanced in a hyperlipidemic
mouse model. Oncogene. 32:961–967. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Berridge MJ, Lipp P and Bootman MD: The
versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 1:11–21. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao P, Xiao L, Peng J, Qian YQ and and
Huang CC: Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
improve osteoporosis through promoting osteoblast proliferation via
MAPK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:3962–3970.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weyant MJ, Carothers AM, Bertagnolli ME
and Bertagnolli MM: Colon cancer chemopreventive drugs modulate
integrin-mediated signaling pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 6:949–956.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
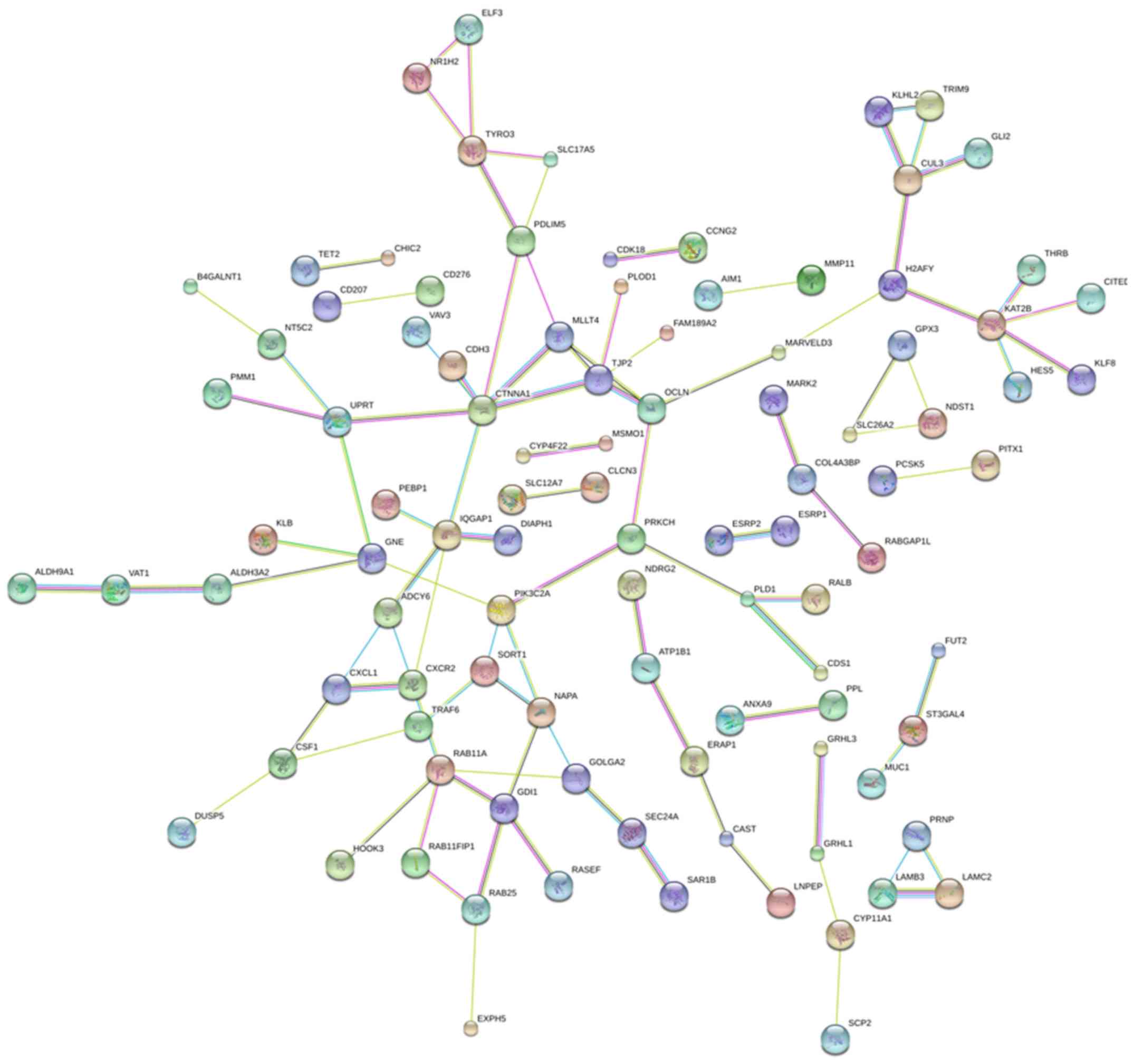
Choi S and Anderson RA: IQGAP1 is a
phosphoinositide effector and kinase scaffold. Adv Biol Regul.
60:29–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang XX, Wang K, Li XZ, Zhai LQ, Qu CX,
Zhao Y, Liu ZR, Wang HZ, An QJ, Jing LW and Wang XH: Targeted
knockdown of IQGAP1 inhibits the progression of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 9:e965012014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu CQ, Zhu ST, Wang M, Guo SL, Sun XJ,
Cheng R, Xing J, Wang WH, Shao LL and Zhang ST: Pathway analysis of
differentially expressed genes in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:1652–1661. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Vij M, Shanmugam NP, Reddy MS,
Sankaranarayanan S and Rela M: Paediatric hepatocellular carcinoma
in tight junction protein 2 (TJP2) deficiency. Virchows Arch.
471:679–683. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ganguly P and Ganguly N: Transcriptomic
analyses of genes differentially expressed by high-risk and
low-risk human papilloma virus E6 oncoproteins. Virusdisease.
26:105–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang G, Zhang W, Li B, Stringer-Reasor E,
Chu C, Sun L, Bae S, Chen D, Wei S, Jiao K, et al: MicroRNA-200c
and microRNA- 141 are regulated by a FOXP3-KAT2B axis and
associated with tumor metastasis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res. 19:732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|