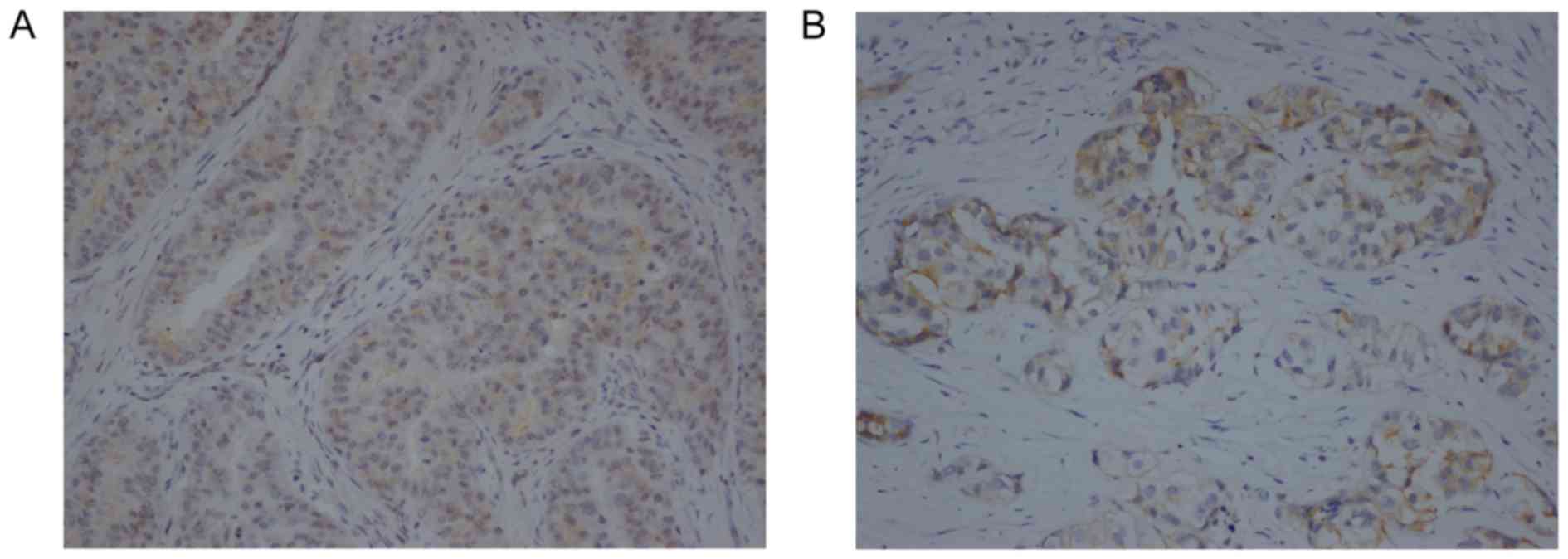
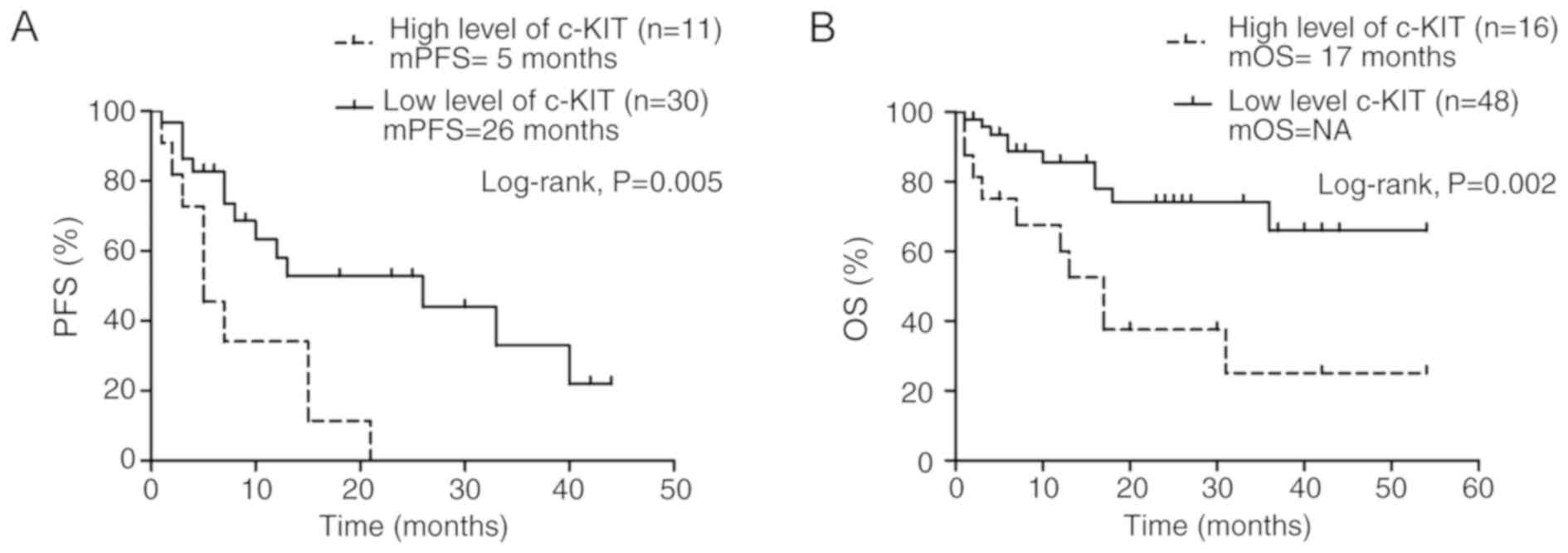
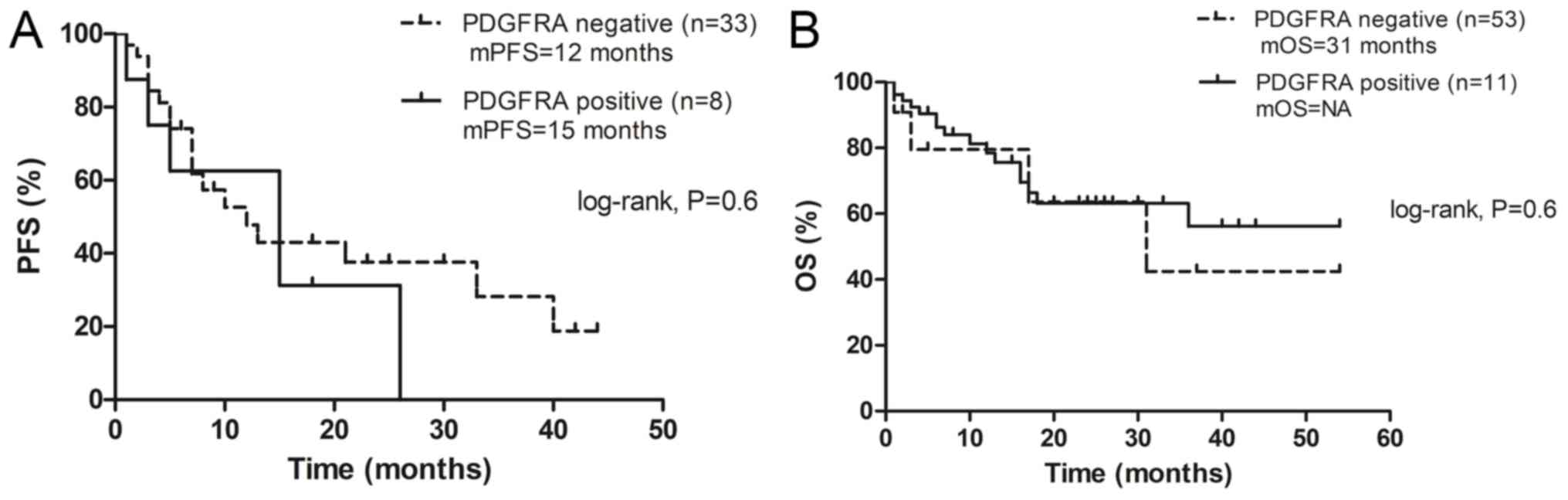
|
1
|
Zhou JX, Yang H, Deng Q, Gu X, He P, Lin
Y, Zhao M, Jiang J, Chen H, Lin Y, et al: Oncogenic driver
mutations in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer at various
clinical stages. Ann Oncol. 24:1319–1325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Auliac JB, Monnet I, Dubos-Arvis C,
Chiappa AM, Baize N, Bota S, Vergnenegre A, Doubre H, Locher C,
Bizieux A, et al: Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring ALK
translocations: Clinical characteristics and management in a
real-life setting: A French retrospective analysis (GFPC 02–14
study). Target Oncol. 12:833–838. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Katayama R, Shaw AT, Khan TM,
Mino-Kenudson M, Solomon BJ, Halmos B, Jessop NA, Wain JC, Yeo AT,
Benes C, et al: Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in
ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Sci Transl Med. 4:120ra172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ramos AH, Dutt A, Mermel C, Perner S, Cho
J, Lafargue CJ, Johnson LA, Stiedl AC, Tanaka KE, Bass AJ, et al:
Amplification of chromosomal segment 4q12 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:2042–2050. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kassis ES, Vaporciyan AA, Swisher SG,
Correa AM, Bekele BN, Erasmus JJ, Hofstetter WL, Komaki R, Mehran
RJ, Moran CA, et al: Application of the revised lung cancer staging
system (IASLC Staging Project) to a cancer center population. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 38:412–418.e1-e2. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwarts LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang H, Wang W, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Lin E,
Gao J and He J: The role of NF-E2-related factor 2 in predicting
chemoresistance and prognosis in advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 12:166–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Jiang T, Li X, Wang Y, Zhao C,
Zhao S, Xi L, Zhang S, Liu X, Jia Y, et al: Clinical features of
Bim deletion polymorphism and its relation with crizotinib primary
resistance in Chinese patients with ALK/ROS1 fusion-positive
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 123:2927–2935. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Woo CG, Seo S, Kim SW, Jang SJ, Park KS,
Song JY, Lee B, Richards MW, Bayliss R, Lee DH and Choi J:
Differential protein stability and clinical responses of EML4-ALK
fusion variants to various ALK inhibitors in advanced
ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 28:791–797.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Herpel E, Jensen K, Muley T, Warth A,
Schnabel PA, Meister M, Herth FJ, Dienemann H, Thomas M and
Gottschling S: The cancer stem cell antigens CD133, BCRP1/ABCG2 and
CD117/c-KIT are not associated with prognosis in resected
early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res.
31:4491–4500. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marech I, Gadaleta CD and Ranieri G:
Possible prognostic and therapeutic significance of c-Kit
expression, mast cell count and microvessel density in renal cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 15:13060–13076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Holtkamp N, Ziegenhagen N, Malzer E,
Hartmann C, Giese A and von Deimling A: Characterization of the
amplicon on chromosomal segment 4q12 in glioblastoma multiforme.
Neuro Oncol. 9:291–297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai W, Lin D, Wu C, Li X, Zhao C, Zheng L,
Chuai S, Fei K, Zhou C and Hirsch FR: Intratumoral heterogeneity of
ALK-rearranged and ALK/EGFR coaltered lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 33:3701–3709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qin A and Gadgeel S: The current landscape
of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer:
Emerging3 treatment paradigms and future directions. Target Oncol.
12:709–718. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa
K, Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T, et al:
First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 371:2167–2177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Solomon BJ, Cappuzzo F, Felip E, Blackhall
FH, Costa DB, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Wu YL, Mekhail T, Paolini J, et
al: Intracranial efficacy of crizotinib versus chemotherapy in
patients with advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer:
Results from PROFILE 1014. J Clin Oncol. 34:2858–2865. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liang J, Wu YL, Chen BJ, Zhang W, Tanaka Y
and Sugiyama H: The C-kit receptor-mediated signal transduction and
tumor-related diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 9:435–443. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li AS, Sun LN and Zhan ZL: Expression and
mutational analysis of c-kit gene in small cell lung cancer. Chin J
Cancer Prev Treat. 14:917–919. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Yokouchi H, Nishihara H, Harada T, Ishida
T, Yamazaki S, Kikuchi H, Oizumi S, Uramoto H, Tanaka F, Harada M,
et al: Immunohistochemical profiling of receptor tyrosine kinases,
MED12, and TGF-βRII of surgically resected small cell lung cancer,
and the potential of c-kit as a prognostic marker. Oncotarget.
8:39711–39726. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Terada T: An immunohistochemical and
molecular genetic analysis of KIT and PDGFRA in small cell lung
carcinoma in Japanese. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 5:331–338.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiao H, Wang J, Liu Y and Li L: Relative
influence of c-Kit expression and epidermal growth factor receptor
gene amplification on survival in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncol Lett. 8:582–588. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|