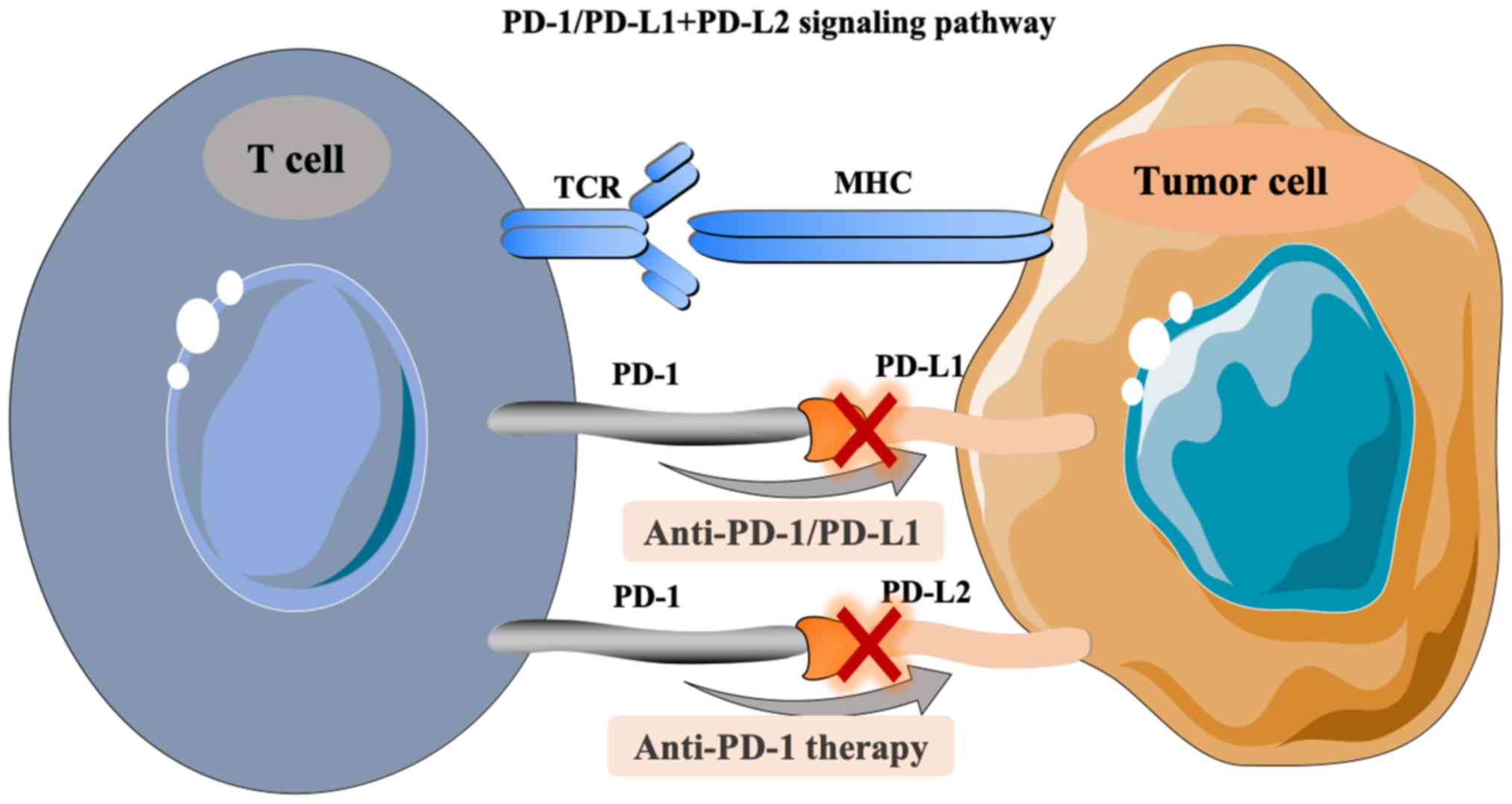
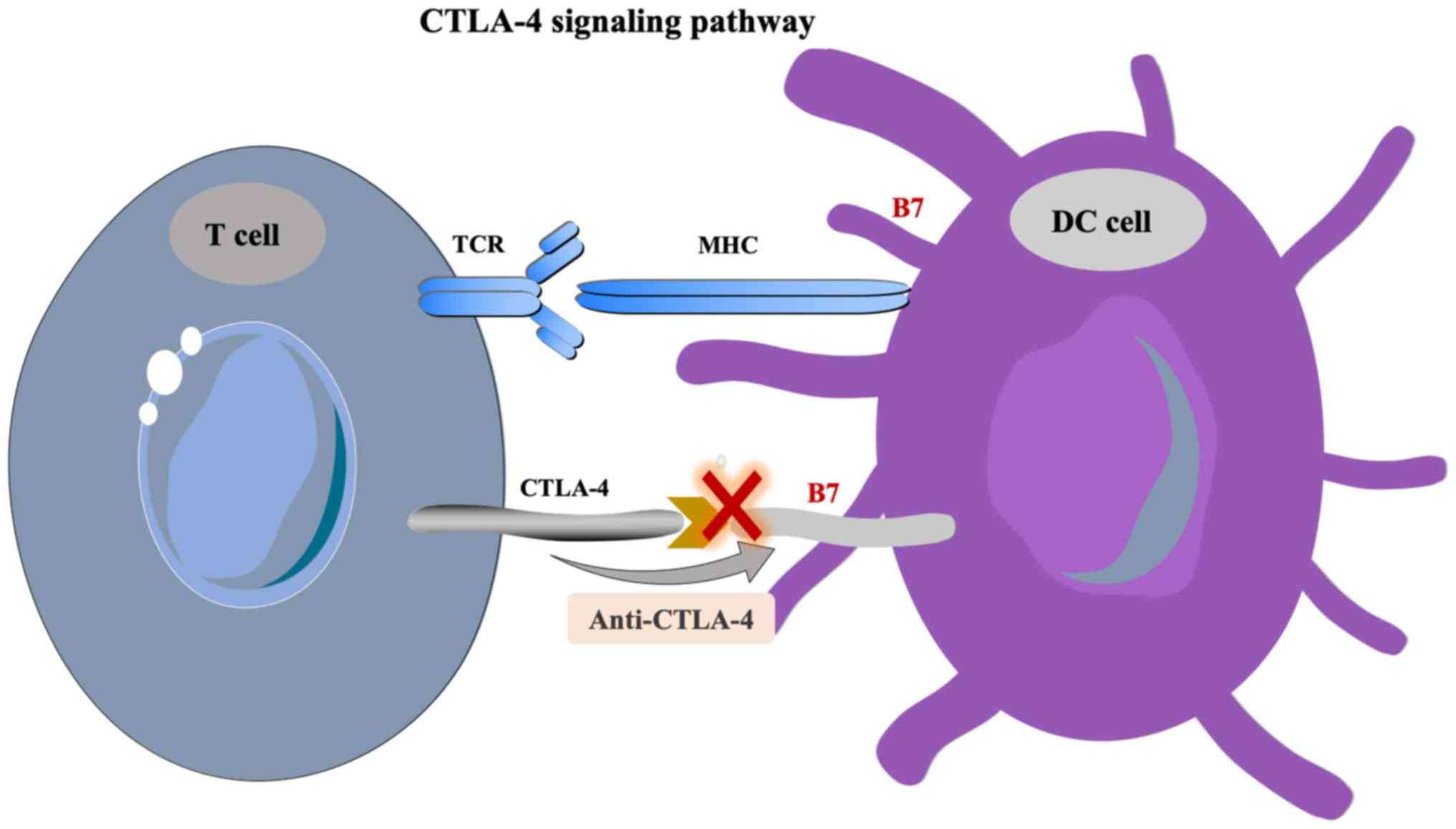
|
1
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and London WT:
Global Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An emphasis on
demographic and regional variability. Clin Liver Dis. 19:223–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB,
Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL and Siegel
RL: Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J
Clin. 69:363–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Ji JS,
Zou X, Xia C, Sun K, Yang Z, Li H, et al: Changing cancer survival
in China during 2003–15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based
cancer registries. Lancet Glob Health. 6:e555–e567. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kanwal F, Kramer J, Asch SM, Chayanupatkul
M, Cao Y and El-Serag HB: Risk of hepatocellular cancer in HCV
patients treated with direct-acting antiviral agents.
Gastroenterology. 153:996–1005.e1. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan AT, Yang N, Lee Krishnamoorthy T, Oei
V, Chua A, Zhao X, Tan HS, Chia A, Le Bert N, Low D, et al: Use of
expression profiles of HBV-DNA integrated into genomes of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to select T cells for immunotherapy.
Gastroenterology. 156:1862–1876.e9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vogel A, Cervantes A, Chau I, Daniele B,
Llovet JM, Meyer T, Nault JC, Neumann U, Ricke J, Sangro B, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 30:871–873. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Benson AB III, D'Angelica MI, Abbott DE,
Abrams TA, Alberts SR, Saenz DA, Are C, Brown DB, Chang DT, Covey
AM, et al: NCCN guidelines insights: Hepatobiliary cancers, version
1.2017. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 15:563–573. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bruix J, Reig M and Sherman M:
Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 150:835–853. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kudo M, Ueshima K, Ikeda M, Torimura T,
Tanabe N, Aikata H, Izumi N, Yamasaki T, Nojiri S, Hino K, et al:
Randomised, multicentre prospective trial of transarterial
chemoembolisation (TACE) plus sorafenib as compared with TACE alone
in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: TACTICS trial. Gut.
69:1492–1501. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cui J, Wang N, Zhao H, Jin H, Wang G, Niu
C, Terunuma H, He H and Li W: Combination of radiofrequency
ablation and sequential cellular immunotherapy improves
progression-free survival for patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 134:342–351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lencioni R, Llovet JM, Han G, Tak WY, Yang
J, Guglielmi A, Paik SW, Reig M, Kim DY, Chau GY, et al: Sorafenib
or placebo plus TACE with doxorubicin-eluting beads for
intermediate stage HCC: The SPACE trial. J Hepatol. 64:1090–1098.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Meyer T, Cheng AL,
El-Khoueiry AB, Rimassa L, Ryoo BY, Cicin I, Merle P, Chen Y, Park
JW, et al: Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 379:54–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang
YH, Bodoky G, Pracht M, Yokosuka O, Rosmorduc O, Breder V, et al:
Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who
progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 389:56–66.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Greten TF, Lai CW, Li G and
Staveley-O'Carroll KF: Targeted and immune-based therapies for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 156:510–524. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Maur M, Tomasello C, Frassoldati A, Dieci
MV, Barbieri E and Conte P: Posterior reversible encephalopathy
syndrome during ipilimumab therapy for malignant melanoma. J Clin
Oncol. 30:e76–e78. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Buchbinder EI and Desai A: CTLA-4 and PD-1
Pathways: Similarities, differences, and implications of their
inhibition. Am J Clin Oncol. 39:98–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sprinzl MF and Galle PR: Current progress
in immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
66:482–484. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Prieto J, Melero I and Sangro B:
Immunological landscape and immunotherapy of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:681–700. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L and Wang FS: Clinical immunology
and immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current progress
and challenges. Hepatol Int. 13:521–533. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kudo M: Immuno-oncology in hepatocellular
carcinoma: 2017 Update. Oncology. 93 (Suppl 1):S147–S159. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Waidmann O: Recent developments with
immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
18:905–910. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Johnston MP and Khakoo SI: Immunotherapy
for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current and future. World J
Gastroenterol. 25:2977–2989. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tian M, Shi Y, Liu W and Fan J:
Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: Strategies for
combinatorial intervention. Sci China Life Sci. 62:1138–1143. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Finn RS, Ryoo BY, Merle P, Kudo M,
Bouattour M, Lim HY, Breder VV, Edeline J, Chao Y, Ogasawara S, et
al: Results of KEYNOTE-240: Phase 3 study of pembrolizumab (Pembro)
vs best supportive care (BSC) for second line therapy in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Clin Oncol. 37 (15
Suppl):S40042019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Eggert T and Greten TF: Tumor regulation
of the tissue environment in the liver. Pharmacol Ther. 173:47–57.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishida N and Kudo M: Immunological
microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical
implication. Oncology. 92 (Suppl 1):S40–S49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tiegs G and Lohse AW: Immune tolerance:
What is unique about the liver. J Autoimmun. 34:1–6. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huz JI, Melis M and Sarpel U: Spontaneous
regression of hepatocellular carcinoma is most often associated
with tumour hypoxia or a systemic inflammatory response. HPB
(Oxford). 14:500–505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Crispe IN: Liver antigen-presenting cells.
J Hepatol. 54:357–365. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang Y, Han QJ and Zhang J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms of progression and
immunotherapy. World J Gastroenterol. 25:3151–3167. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF and Rudensky AY:
Regulatory T cells: Mechanisms of differentiation and function.
Annu Rev Immunol. 30:531–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gong J, Chehrazi-Raffle A, Reddi S and
Salgia R: Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of
cancer immunotherapy: A comprehensive review of registration trials
and future considerations. J Immunother Cancer. 6:82018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zou W, Wolchok JD and Chen L: PD-L1
(B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms,
response biomarkers, and combinations. Sci Transl Med.
8:328rv42016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Calderaro J, Rousseau B, Amaddeo G, Mercey
M, Charpy C, Costentin C, Luciani A, Zafrani ES, Laurent A, Azoulay
D, et al: Programmed death ligand 1 expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Relationship with clinical and pathological features.
Hepatology. 64:2038–2046. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei F, Zhong S, Ma Z, Kong H, Medvec A,
Ahmed R, Freeman GJ, Krogsgaard M and Riley JL: Strength of PD-1
signaling differentially affects T-cell effector functions. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E2480–E2489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
El Dika I, Khalil DN and Abou-Alfa GK:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer.
125:3312–3319. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Noonan A and Pawlik TM: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: An update on investigational drugs in phase I and II
clinical trials. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 28:941–949. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mizukoshi E and Kaneko S: Immune cell
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 12:522019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liang SC, Latchman YE, Buhlmann JE,
Tomczak MF, Horwitz BH, Freeman GJ and Sharpe AH: Regulation of
PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 expression during normal and autoimmune
responses. Eur J Immunol. 33:2706–2716. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang S, Bajorath J, Flies DB, Dong H,
Honjo T and Chen L: Molecular modeling and functional mapping of
B7-H1 and B7-DC uncouple costimulatory function from PD-1
interaction. J Exp Med. 197:1083–1091. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Elhag OA, Hu XJ, Wen-Ying Z, Li X, Yuan
YZ, Deng LF, Liu DL, Liu YL and Hui G: Reconstructed
adeno-associated virus with the extracellular domain of murine PD-1
induces antitumor immunity. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4031–4036.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Intlekofer AM and Thompson CB: At the
bench: Preclinical rationale for CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade as cancer
immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol. 94:25–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Taube JM, Klein A, Brahmer JR, Xu H, Pan
X, Kim JH, Chen L, Pardoll DM, Topalian SL and Anders RA:
Association of PD-1, PD-1 ligands, and other features of the tumor
immune microenvironment with response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:5064–5074. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Benson AB 3rd, D'Angelica MI, Abbott DE,
et al: NCCN Guidelines Insights: Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version
1.2017. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 15:563–573. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi
TS, Kudo M, Hsu C, Kim TY, Choo SP, Trojan J, Welling TH Rd, et al:
Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
(CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose
escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 389:2492–2502. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yau T, Hsu C, Kim TY, Choo SP, Kang YK,
Hou MM, Numata K, Yeo W, Chopra A, Ikeda M, et al: Nivolumab in
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Sorafenib-experienced Asian
cohort analysis. J Hepatol. 71:543–552. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sangro B, Park JW, Cruz CMD, Anderson J,
Lang L, Neely J, Shaw JW and Cheng AL: A randomized, multicenter,
phase 3 study of nivolumab vs sorafenib as first-line treatment in
patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC):
CheckMate-459. J Clin Oncol. 34 (15 Suppl):TPS41472016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Exposito MJ, Akce M, Alvarez J, Assenat E,
Balart L, Baron A, Decaens T, Heurgue-Berlot A, Martin A, Paik S,
et al: Abstract No. 526 CheckMate-9DX: Phase 3, randomized,
double-blind study of adjuvant nivolumab vs placebo for patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc) at high risk of recurrence
after curative resection or ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiology.
30:S227–S228. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S,
Ogasawara S, Palmer D, Verslype C, Zagonel V, Fartoux L, Vogel A,
et al: Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A
non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:940–952.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Finn RS, Chan SL, Zhu AX, Knox JJ, Cheng
AL, Siegel AB, Bautista O and Kudo M: Phase 3, randomized study of
pembrolizumab (pembro) vs best supportive care (BSC) for
second-line advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): KEYNOTE-240. J
Clin Oncol. 35 (15 Suppl):TPS41432017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Qin SK, Ren ZG, Meng ZQ, Chen ZD, Chai XL,
Xiong JP, Bai YX, Yang L, Zhu H, Fang WJ, et al: LBA27A randomized
multicentered phase II study to evaluate SHR-1210 (PD-1 antibody)
in subjects with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who failed
or intolerable to prior systemic treatment. Ann Oncol. 29 (Suppl
8):mdy424.029. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Qin SK, Ren Z, Meng Z, Chen Z, Chai X,
Xiong J, Bai Y, Yang L, Zhu H, Fang W, et al: Camrelizumab in
patients with previously treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma:
A multicentre, open-label, parallel-group, randomised, phase 2
trial. Lancet Oncol. 21:571–580. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu JM, Zhang Y, Jia R, Wang Y, Liu R,
Zhang G, Zhao C, Zhang Y, Zou J and Wang Q: Anti-programmed death-1
antibody SHR-1210 (S) combined with apatinib (A) for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), gastric cancer (GC) or
esophagogastric junction (EGJ) cancer refractory to standard
therapy: A phase 1 trial. J Clin Oncol. 36 (15 Suppl):S40752018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Qin S, Chen Z, Liu Y, Xiong J, Ren Z, Meng
Z, Gu S, Wang L, Zou J; Jinling Hospital, ; et al: A phase II study
of anti-PD-1 antibody camrelizumab plus FOLFOX4 or GEMOX systemic
chemotherapy as first-line therapy for advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma or biliary tract cancer. J Clin Oncol. 37 (15
Suppl):S40742019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Pishvaian MJ, Lee M, Ryoo BY, Stein S, Lee
KH, Stein W, Spahn J, Shao H, Liu B and Iizuka K: LBA26Updated
safety and clinical activity results from a phase Ib study of
atezolizumab + bevacizumab in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann
Oncol. 29 (Suppl 8):viii718–viii719. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cheng AL, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle P, Ducreux
M, Zhu A, Kim TY, Merle P, Kaseb A, Li D, et al: IMbrave150:
Efficacy and safety results from a ph III study evaluating
atezolizumab (atezo)+ bevacizumab (bev) vs sorafenib (Sor) as first
treatment (tx) for patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC). Ann Oncol. 30:ix186–ix187. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Qin SK, Ren ZG, Feng Y, et al: Efficacy
and safety of atezolizumab + bevacizumab vs sorafenib in Chinese
patients with unresectable HCC in the phase III IMbrave150 study.
EASL Liver Cancer Summit 2020. OP02-03. Ann Oncol. 30:v8752020.
|
|
59
|
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K,
Piscaglia F, Baron A, Park JW, Han G, Jassem J, et al: Lenvatinib
versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3
non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 391:1163–1173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ikeda M, Sung MW, Kudo M, Kobayashi M,
Baron AD, Finn RS, Kaneko S, Kraljevic S, Ishikawa K, Siegel AB, et
al: A phase 1b trial of lenvatinib (LEN) plus pembrolizumab (PEM)
in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
(uHCC). J Clin Oncol. 36 (15 Suppl):S40762018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Jeon MY, Lee HW, Kim BK, Park JY, Kim DY,
Ahn SH, Han KH, Baek SE, Kim HS, Kim SU and Park MS:
Reproducibility of European Association for the Study of the liver
criteria and modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors
in patients treated with sorafenib. Liver Int. 38:1655–1663. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Llovet J, Shepard KV, Finn RS, Ikeda M,
Sung M, Baron DA, Kudo M, Okusaka T, Kobayashi M, Kumada H, et al:
A phase Ib trial of lenvatinib (LEN) plus pembrolizumab (PEMBRO) in
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): Updated results. Ann
Oncol. 30:v286–v287. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kudo M, Ikeda M, Motomura K, Okusaka T,
Kato N, Dutcus CE, Hisai T, Suzuki M, Ikezawa H, Iwata T, et al: A
phase 1b study of lenvatinib plus nivolumab in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (Study 117). J Clin Oncol. 38
(4 Suppl):S5132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Agdashian D, ElGindi M, Xie C, Sandhu M,
Pratt D, Kleiner DE, Figg WD, Rytlewski JA, Sanders C, Yusko EC, et
al: The effect of anti-CTLA4 treatment on peripheral and
intra-tumoral T cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 68:599–608. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sangro B, Gomez-Martin C, de la Mata M,
Iñarrairaegui M, Garralda E, Barrera P, Riezu-Boj JI, Larrea E,
Alfaro C, Sarobe P, et al: A clinical trial of CTLA-4 blockade with
tremelimumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic
hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 59:81–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yau T, Kang YK, Kim TY, El-Khoueiry AB,
Santoro A, Sangro B, Melero I, Kudo M, Hou MM, Matilla A, et al:
Nivolumab (NIVO) + ipilimumab (IPI) combination therapy in patients
(pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC): Results from
CheckMate 040. J Clin Oncol. 37 (15 Suppl):S40122019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Finkelmeier F, Waidmann O and Trojan J:
Nivolumab for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 18:1169–1175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Opdivo Prescribing Information. Opdivo
U.S. Product Information. Last updated. March. 2020, Princeton, NJ:
Bristol Myers Squibb Company;
|
|
69
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Chan SL, Furuse J, Galle PR,
Kelley RK, Qin S, Armstrong J, Darilay A, Vlahovic G, Negro A and
Sangro B: A randomized, multicenter phase 3 study of durvalumab (D)
and tremelimumab (T) as first-line treatment in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): HIMALAYA study. J Clin
Oncol. 36 (15 Suppl):TPS41442018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kelley RK, Abou-Alfa GK, Bendell JC, Kim
TY, Borad MJ, Yong WP, Morse M, Kang YK, Rebelatto M, Makowsky M,
et al: Phase I/II study of durvalumab and tremelimumab in patients
with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Phase I safety
and efficacy analyses. J Clin Oncol. 35 (15 Suppl):S40732017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Choi C, Yoo GS, Cho WK and Park HC:
Optimizing radiotherapy with immune checkpoint blockade in
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 25:2416–2429.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hilmi M, Neuzillet C, Calderaro J, Lafdil
F, Pawlotsky JM and Rousseau B: Angiogenesis and immune checkpoint
inhibitors as therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: current
knowledge and future research directions. J Immunother Cancer.
7:3332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xu W, Liu K, Chen M, Sun JY, McCaughan GW,
Lu XJ and Ji J: Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Recent
advances and future perspectives. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
11:17588359198626922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Loosen SH, Schulze-Hagen M, Bruners P,
Tacke F, Trautwein C, Kuhl C, Luedde T and Roderburg C: Sarcopenia
is a negative prognostic factor in patients undergoing
transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for hepatic malignancies.
Cancers (Basel). 11:15032019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Harding JJ, Erinjeri JP, Tan BR, Reiss KA,
Mody K, Khalil D, Yarmohammadi H, Nadolski G, Giardina JD, Capanu
M, et al: A multicenter pilot study of nivolumab (NIVO) with drug
eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (deb-TACE) in patients
(pts) with liver limited hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Clin
Oncol. 36 (15 Suppl):TPS41462018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Chen CL, Pan QZ, Zhao JJ, Wang Y, Li YQ,
Wang QJ, Pan K, Weng DS, Jiang SS, Tang Y, et al: PD-L1 expression
as a predictive biomarker for cytokine-induced killer cell
immunotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncoimmunology. 5:e11766532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhu AX, Kang YK, Yen CJ, Finn RS, Galle
PR, Llovet JM, Assenat E, Brandi G, Pracht M, Lim HY, et al:
Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations
(REACH-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:282–296. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhu AX, Park JO, Ryoo BY, Yen CJ, Poon R,
Pastorelli D, Blanc JF, Chung HC, Baron AD, Pfiffer TE, et al:
Ramucirumab versus placebo as second-line treatment in patients
with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma following first-line therapy
with sorafenib (REACH): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 16:859–870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Sideras K, Biermann K, Verheij J,
Takkenberg BR, Mancham S, Hansen BE, Schutz HM, de Man RA,
Sprengers D, Buschow SI, et al: PD-L1, Galectin-9 and CD8+
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 6:e12733092017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Li H, Wu K, Tao K, Chen L, Zheng Q, Lu X,
Liu J, Shi L, Liu C, Wang G and Zou W: Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling
pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in
patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 56:1342–1351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Eso Y, Shimizu T, Takeda H, Takai A and
Marusawa H: Microsatellite instability and immune checkpoint
inhibitors: Toward precision medicine against gastrointestinal and
hepatobiliary cancers. J Gastroenterol. 55:15–26. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Latham A, Srinivasan P, Kemel Y, Shia J,
Bandlamudi C, Mandelker D, Middha S, Hechtman J, Zehir A,
Dubard-Gault M, et al: Microsatellite instability is associated
with the presence of lynch syndrome pan-cancer. J Clin Oncol.
37:286–295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H,
Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK, Lu S, Kemberling H, Wilt C, Luber BS, et
al: Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to
PD-1 blockade. Science. 357:409–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kawaoka T, Ando Y, Yamauchi M, Suehiro Y,
Yamaoka K, Kosaka Y, Fuji Y, Uchikawa S, Morio K, Fujino H, et al:
Incidence of microsatellite instability-high hepatocellular
carcinoma among Japanese patients and response to pembrolizumab.
Hepatol Res. 50:885–888. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Goumard C, Desbois-Mouthon C, Wendum D,
Calmel C, Merabtene F, Scatton O and Praz F: Low levels of
microsatellite instability at simple repeated sequences commonly
occur in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Genomics
Proteomics. 14:329–339. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ando Y, Yamauchi M, Suehiro Y, Yamaoka K,
Kosaka Y, Fuji Y, Uchikawa S, Kodama K, Morio K, Fujino H, et al:
Complete response to pembrolizumab in advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma with microsatellite instability. Clin J Gastroenterol.
Feb 4–2020.(Online ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Scheiner B, Kirstein MM, Hucke F,
Finkelmeier F, Schulze K, von Felden J, Koch S, Schwabl P, Hinrichs
JB, Waneck F, et al: Programmed cell death protein-1
(PD-1)-targeted immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma:
Efficacy and safety data from an international multicentre
real-world cohort. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 49:1323–1333. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Boni C, Barili V, Acerbi G, Rossi M,
Vecchi A, Laccabue D, Penna A, Missale G, Ferrari C and Fisicaro P:
HBV immune-therapy: from molecular mechanisms to clinical
applications. Int J Mol Sci. 20:27542019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Gao L, Yang X, Yi C and Zhu H: Adverse
events of concurrent immune checkpoint inhibitors and
antiangiogenic agents: A systematic review. Front Pharmacol.
10:11732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|