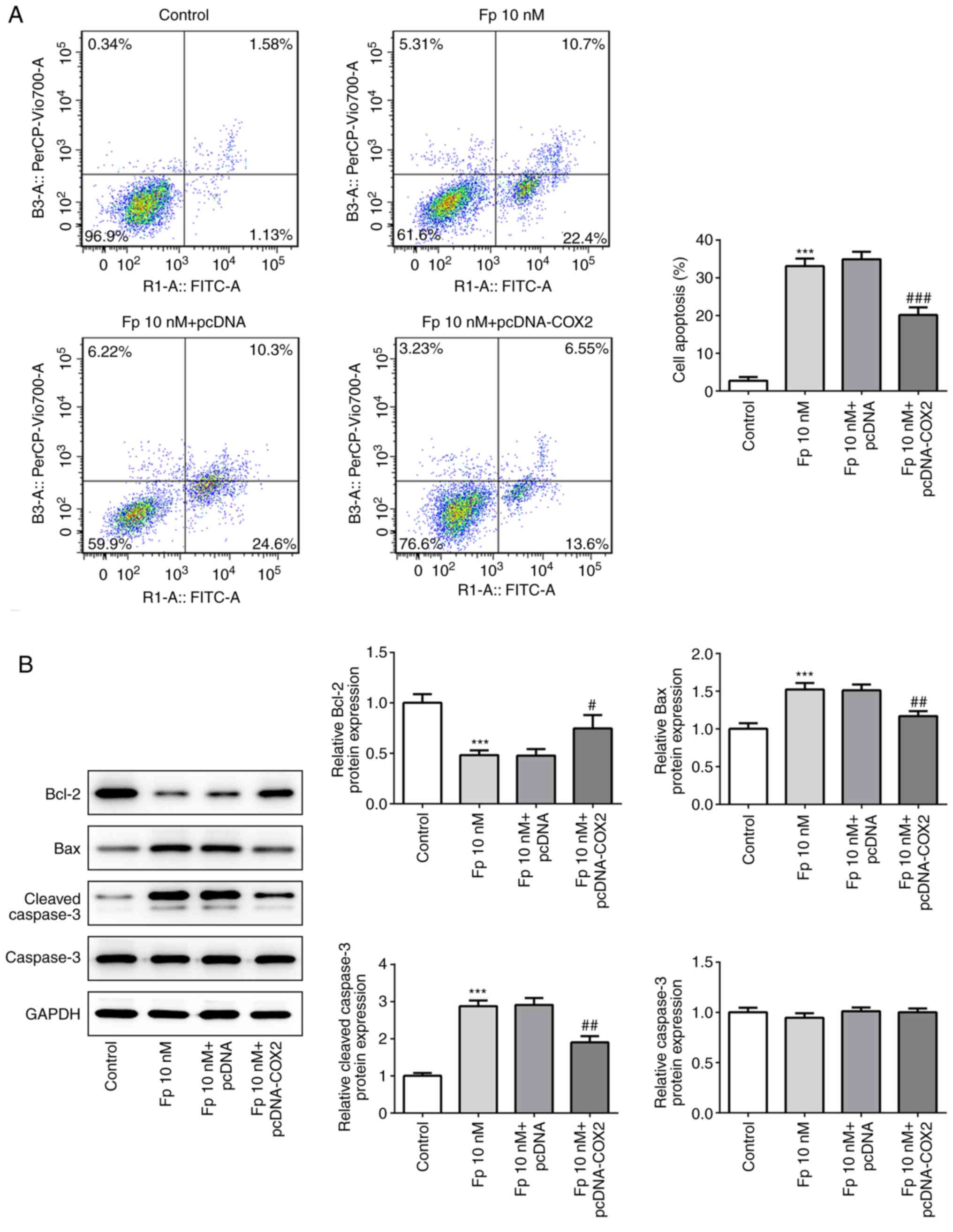
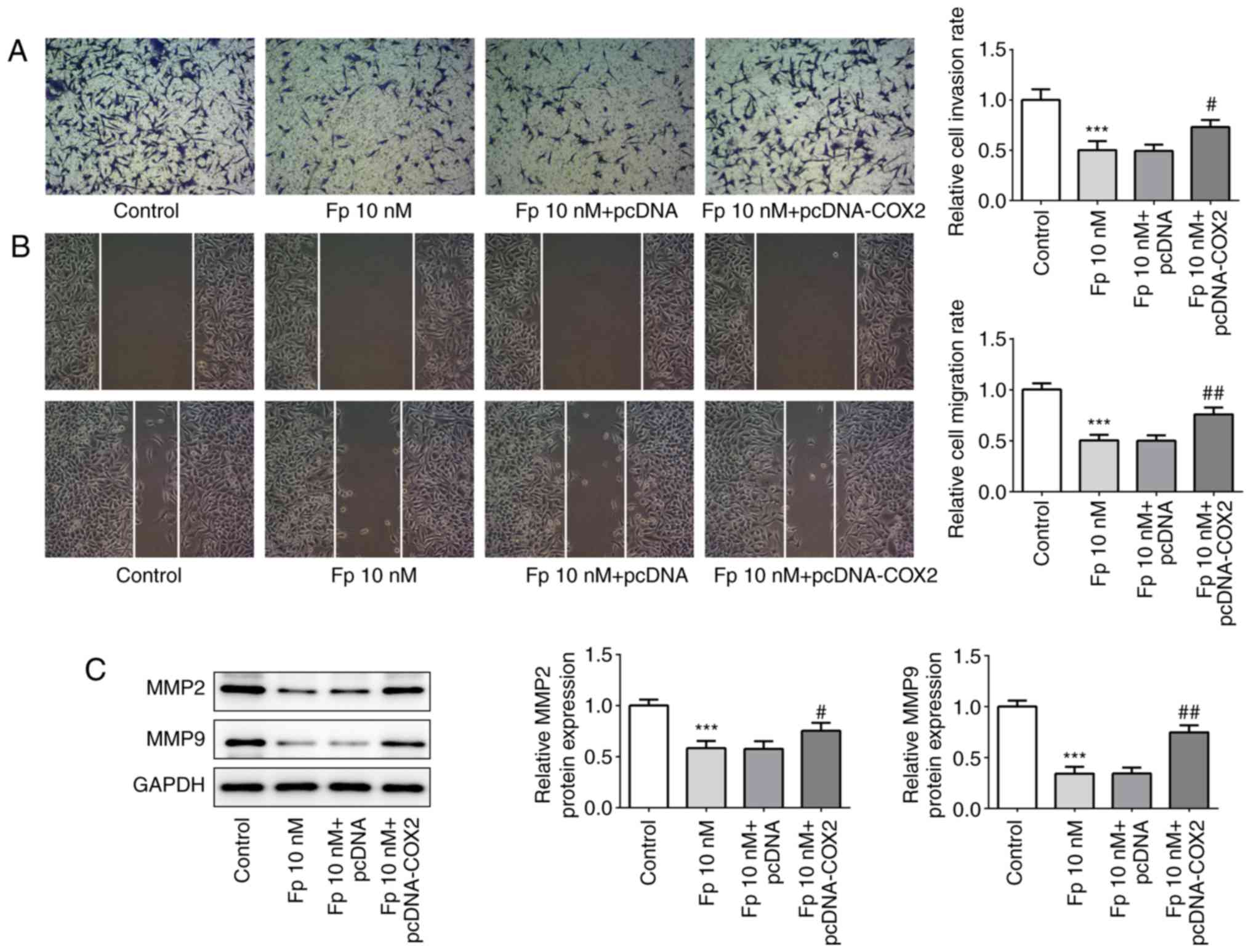
|
1
|
Cho YA, Lee J, Oh JH, Chang HJ, Sohn DK,
Shin A and Kim J: Inflammatory dietary pattern, IL-17F genetic
variant, and the risk of colorectal cancer. Nutrients. 10:7242018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Xue J, Ge X, Zhao W, Xue L, Dai C, Lin F
and Peng W: PIPKIγ regulates CCL2 expression in colorectal cancer
by activating AKT-STAT3 signaling. J Immunol Res. 2019:36905612019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu M, Chen X, Lin K, Zeng K, Liu X, Pan B,
Xu X, Xu T, Hu X, Sun L, et al: The long noncoding RNA SNHG1
regulates colorectal cancer cell growth through interactions with
EZH2 and miR-154-5p. Mol Cancer. 17:1412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lal N, White BS, Goussous G, Pickles OJ,
Mason M, Beggs AD, Taniere P, Willcox BE, Guinney J and Middleton
G: KRAS mutation and consensus molecular subtypes 2 and 3 are
independently associated with reduced immune infiltration and
reactivity in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:224–233. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liang Q, Ma D, Zhu X, Wang Z, Sun TT, Shen
C, Yan T, Tian X, Yu T, Guo F, et al: RING-finger protein 6
amplification activates JAK/STAT3 pathway by modifying SHP-1
ubiquitylation and associates with poor outcome in colorectal
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:1473–1485. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hannigan GD, Duhaime MB, Ruffin MT,
Koumpouras CC and Schloss PD: Diagnostic potential and interactive
dynamics of the colorectal cancer Virome. MBio. 9:e2248–e2218.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ricker CN, Hanna DL, Peng C, Nguyen NT,
Stern MC, Schmit SL, Idos GE, Patel R, Tsai S, Ramirez V, et al:
DNA mismatch repair deficiency and hereditary syndromes in latino
patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer. 123:3732–3743. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Riley JM, Cross AW, Paulos CM, Rubinstein
MP, Wrangle J and Camp ER: The clinical implications of
immunogenomics in colorectal cancer: A path for precision medicine.
Cancer. 124:1650–1659. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karuturi MS, Holmes HM, Lei X, Johnson M,
Barcenas CH, Cantor SB, Gallick GE, Bast RC and Giordano SH:
Potentially inappropriate medications defined by STOPP criteria in
older patients with breast and colorectal cancer. J Geriatr Oncol.
10:705–708. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Subramanian S, Hoover S, Tangka FKL,
DeGroff A, Soloe CS, Arena LC, Schlueter DF, Joseph DA and Wong FL:
A conceptual framework and metrics for evaluating multicomponent
interventions to increase colorectal cancer screening within an
organized screening program. Cancer. 124:4154–4162. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Shu R, Zhao Q, Li Y, Yu Y and
Wang G: Preoperative butorphanol and flurbiprofen axetil therapy
attenuates remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia after laparoscopic
gynaecological surgery: A randomized double-blind controlled trial.
Br J Anaesth. 117:504–511. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wobst I, Ebert L, Birod K, Wegner MS,
Hoffmann M, Thomas D, Angioni C, Parnham MJ, Steinhilber D, Tegeder
I, et al: R-flurbiprofen traps prostaglandins within cells by
inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated protein-4. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:682016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Zhang HB, Xia B, Wang GM and Zhang
MY: Preemptive analgesic effects of flurbiprofen axetil in patients
undergoing radical resection of esophageal carcinoma via the left
thoracic approach. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:579–582. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ashraf Z, Alamgeer, Kanwal M, Hassan M,
Abdullah S, Waheed M, Ahsan H and Kim SJ: Flurbiprofen-antioxidant
mutual prodrugs as safer nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
Synthesis, pharmacological investigation, and computational
molecular modeling. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:2401–2419. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou Y, Huang J, Bai Y, Li C and Lu X:
Effects of preemptive analgesia with flurbiprofen ester on
lymphocytes and natural killer cells in patients undergoing
esophagectomy: A randomized controlled pilot study. Thorac Cancer.
8:649–654. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang D, Yang XL, Chai XQ, Shu SH, Zhang
XL, Xie YH, Wei X, Wu YJ and Wei W: A short-term increase of the
postoperative naturally circulating dendritic cells subsets in
flurbiprofen-treated patients with esophageal carcinoma undergoing
thoracic surgery. Oncotarget. 7:18705–18712. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Otsuka N, Yataba I, Matsushita I,
Matsumoto H, Hoshino Y and Terada Y: A minimal impact of long-term
S-flurbiprofen plaster application on kidney function in
osteoarthritis patients. Clin Exp Nephrol. 21:1060–1067. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin Y, Yi Y, Yu J, Sun X, Liu C and Xu F:
Effects of flurbiprofen on serum level of interleukin-6,
prostacyclin and corticosteroid A2 in patients with bone metastases
of cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:1545–1548. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ooki A, Del Carmen Rodriguez Pena M,
Marchionni L, Dinalankara W, Begum A, Hahn NM, VandenBussche CJ,
Rasheed ZA, Mao S, Netto GJ, et al: YAP1 and COX2 coordinately
regulate urothelial cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 78:168–181.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aich A, Wang C, Chowdhury A, Ronsör C,
Pacheu-Grau D, Richter-Dennerlein R, Dennerlein S and Rehling P:
COX16 promotes COX2 metallation and assembly during respiratory
complex IV biogenesis. Elife. 7:e325722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Basudhar D, Glynn SA, Greer M,
Somasundaram V, No JH, Scheiblin DA, Garrido P, Heinz WF, Ryan AE,
Weiss JM, et al: Coexpression of NOS2 and COX2 accelerates tumor
growth and reduces survival in estrogen receptor-negative breast
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:13030–13035. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun Y, Dai H, Chen S, Zhang Y, Wu T, Cao
X, Zhao G, Xu A, Wang J and Wu L: Disruption of chromosomal
architecture of cox2 locus sensitizes lung cancer cells to
radiotherapy. Mol Ther. 26:2456–2465. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang WW, Wang QH, Peng P, Liao YJ, Duan
HX, Xu M, Li Y and Zhang PB: Effects of flurbiprofen axetil on
postoperative serum IL-2 and IL-6 levels in patients with
colorectal cancer. Genet Mol Res. 14:16469–16475. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wirrig EE, Gomez MV, Hinton RB and Yutzey
KE: COX2 inhibition reduces aortic valve calcification in vivo.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:938–947. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu J, Jiang L, Gao Y, Sun Q, Liu B, Hu Y
and Han X: Interaction between BMSCs and EPCs promotes IUA
angiogenesis via modulating PI3K/Akt/Cox2 axis. Am J Transl Res.
10:4280–4289. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee CW, Lin ZC, Hu SC, Chiang YC, Hsu LF,
Lin YC, Lee IT, Tsai MH and Fang JY: Urban particulate matter
down-regulates filaggrin via COX2 expression/PGE2 production
leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Sci Rep. 6:279952016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ooki A, Begum A, Marchionni L,
VandenBussche CJ, Mao S, Max K and Hoque MO: Arsenic promotes the
COX2/PGE2-SOX2 axis to increase the malignant stemness properties
of urothelial cells. Int J Cancer. 143:113–126. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Marutha Muthu AK, Cheah PL, Koh CC, Chew
MF, Toh YF and Looi LM: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) expression in
adenocarcinoma surpasses that of squamous cell carcinoma in the
uterine cervix. Malays J Pathol. 39:251–255. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim SR, Park JH, Lee ME, Park JS, Park SC
and Han JA: Selective COX-2 inhibitors modulate cellular senescence
in human dermal fibroblasts in a catalytic activity-independent
manner. Mech Ageing Dev. 129:706–713. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
MacDowell KS, Marsá MD, Buenache E,
Villatoro JML, Moreno B, Leza JC and Carrasco JL: Inflammatory and
antioxidant pathway dysfunction in borderline personality disorder.
Psychiatry Res. 284:1127822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiao J, Wang F, Lu H, Xu S, Zou L, Tian Q,
Fu Y, Lin X, Liu L, Yuan P, et al: Targeting the COX2/MET/TOPK
signaling axis induces apoptosis in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC
cells. Cell Death Dis. 10:7772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shan ZG, Sun ZW, Zhao LQ, Gou Q, Chen ZF,
Zhang JY, Chen W, Su CY, You N, Zhuang Y and Zhao YL: Up-regulation
of TINAGL1 promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis by
regulating multiple MMPs expression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. Jun
14–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1111/jgh.15150. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ji L, Chen S, Gu L and Zhang X:
Exploration of potential roles of m6A regulators in colorectal
cancer prognosis. Front Oncol. 10:7682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shu X, Xiang YB, Rothman N, Yu D, Li HL,
Yang G, Cai H, Ma X, Lan Q, Gao YT, et al: Prospective study of
blood metabolites associated with colorectal cancer risk. Int J
Cancer. 143:527–534. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mojica CM, Glenn BA, Chang C and Bastani
R: The relationship between neighborhood immigrant composition,
limited english proficiency, and late-stage colorectal cancer
diagnosis in california. Biomed Res Int. 2015:4601812015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Butt J, Blot WJ, Teras LR, Visvanathan K,
Le Marchand L, Haiman CA, Chen Y, Bao Y, Sesso HD,
Wassertheil-Smoller S, et al: Antibody responses to streptococcus
gallolyticus subspecies gallolyticus proteins in a large
prospective colorectal cancer cohort consortium. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 27:1186–1194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li H, Zhou J, Wei X, Chen R, Geng J, Zheng
R, Chai J, Li F and Jiang S: miR-144 and targets, c-fos and
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), modulate synthesis of PGE2 in the amnion
during pregnancy and labor. Sci Rep. 6:279142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shiow LR, Favrais G, Schirmer L, Schang
AL, Cipriani S, Andres C, Wright JN, Nobuta H, Fleiss B, Gressens P
and Rowitch DH: Reactive astrocyte COX2-PGE2 production inhibits
oligodendrocyte maturation in neonatal white matter injury. Glia.
65:2024–2037. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Amrite AC and Kompella UB: Celecoxib
inhibits proliferation of retinal pigment epithelial and
choroid-retinal endothelial cells by a cyclooxygenase-2-independent
mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 324:749–758. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duncan K, Uwimpuhwe H, Czibere A, Sarkar
D, Libermann TA, Fisher PB and Zerbini LF: NSAIDs induce apoptosis
in nonproliferating ovarian cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth
in vivo. IUBMB Life. 64:636–643. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu JC, Chai XQ, Wang D, Shu SH, Magnussen
CG, Xie LX and Hu SS: Intraoperative flurbiprofen treatment alters
immune checkpoint expression in patients undergoing elective
thoracoscopic resection of lung cancer. Med Princ Pract.
29:150–159. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|