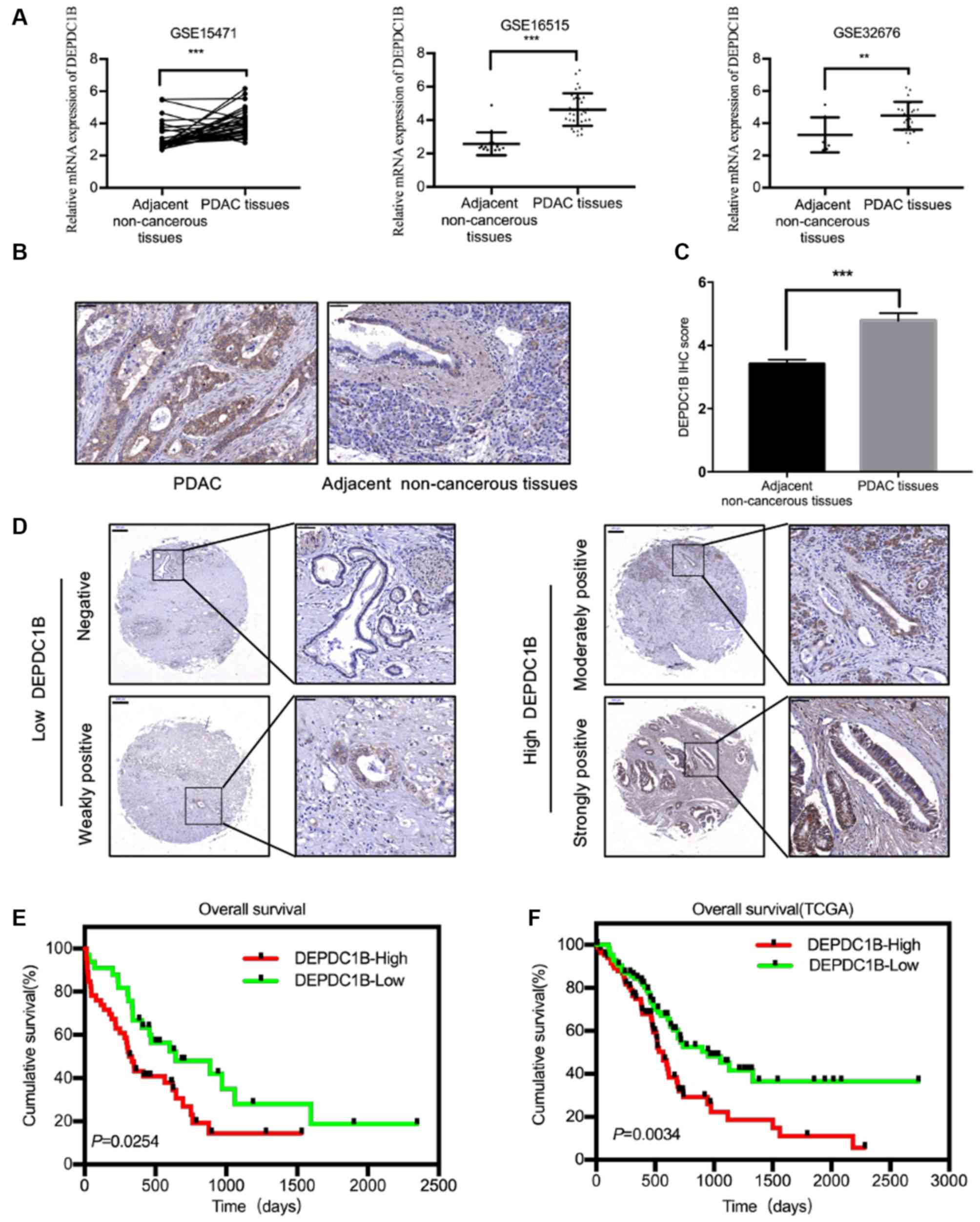
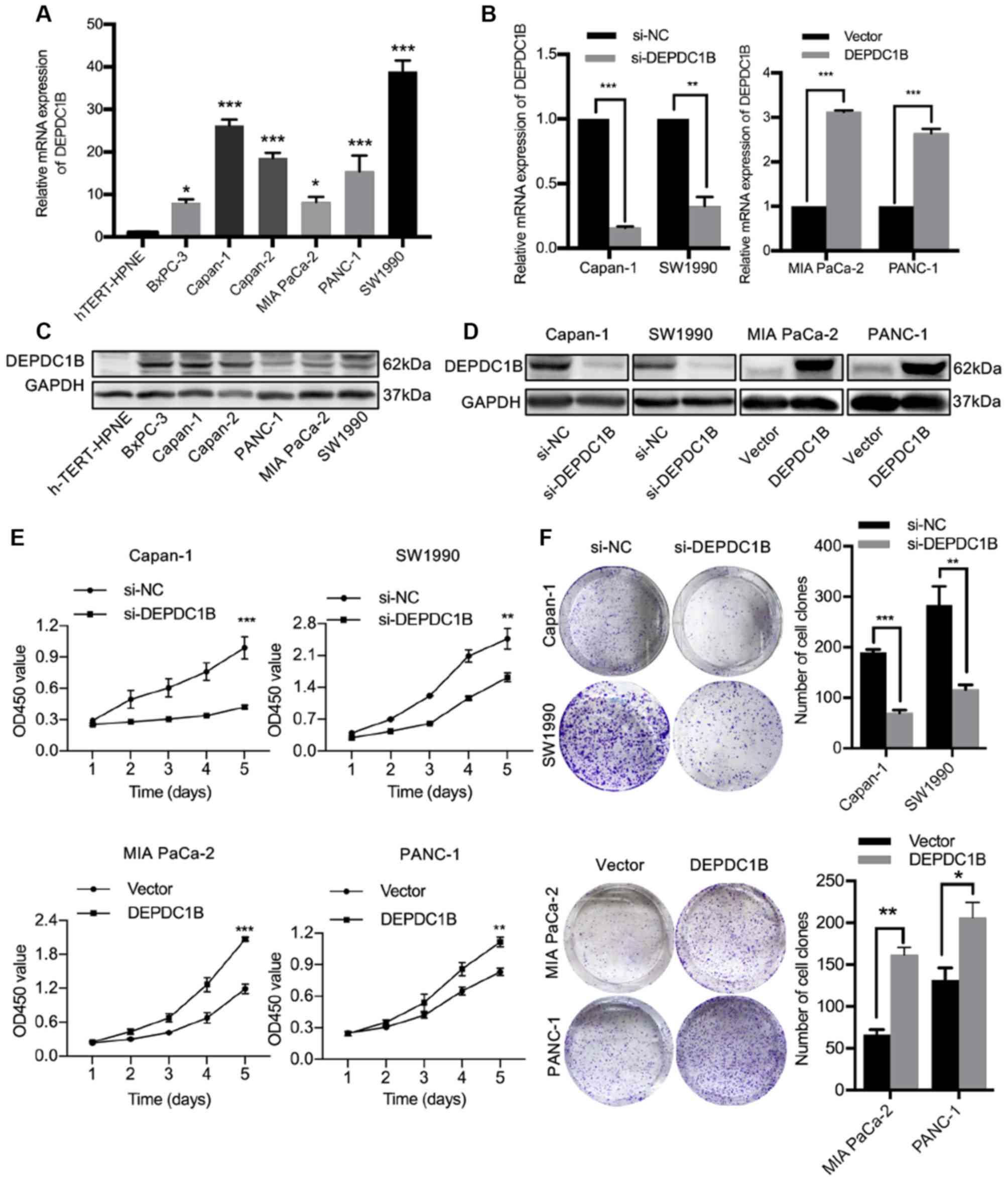
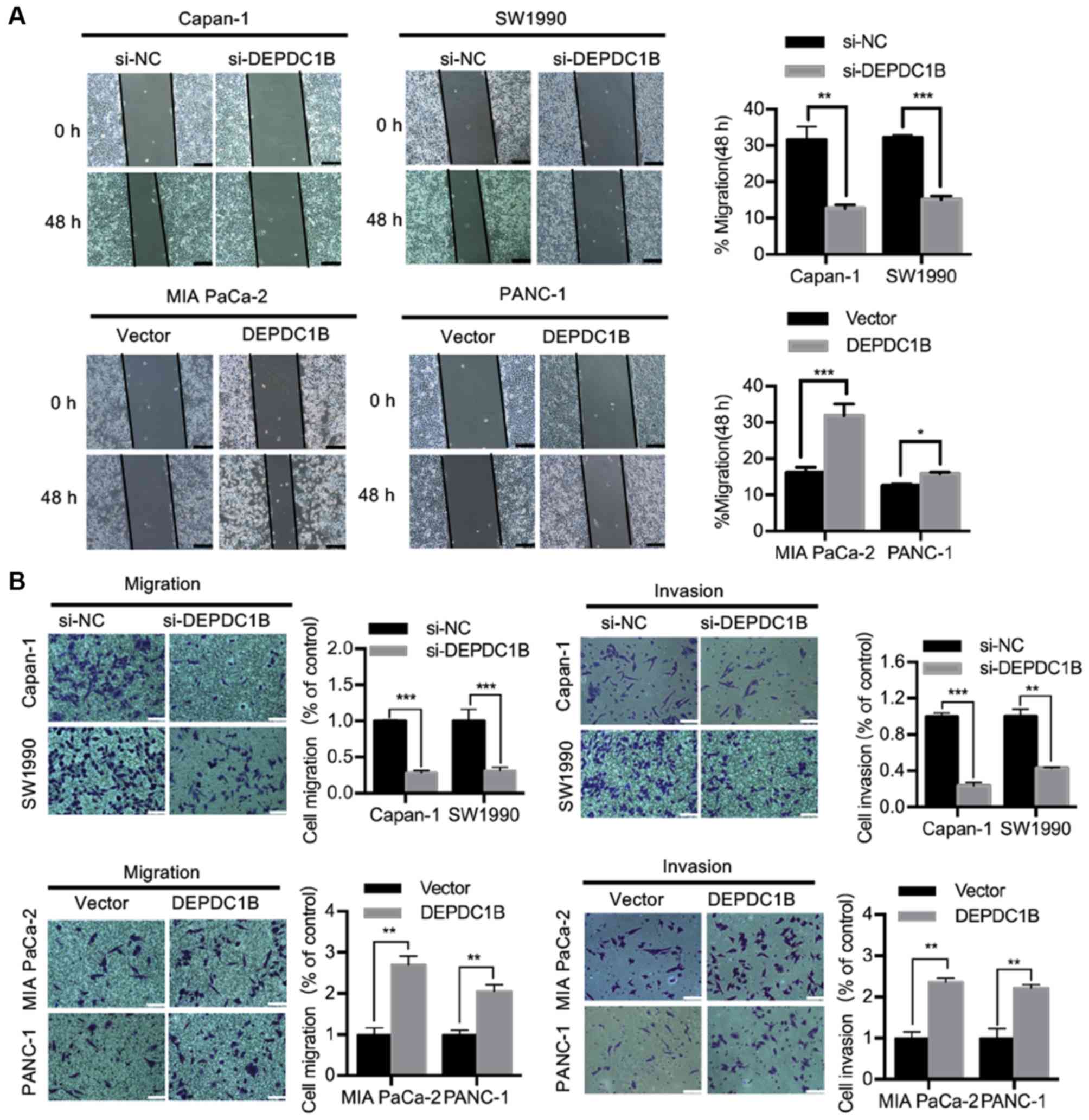
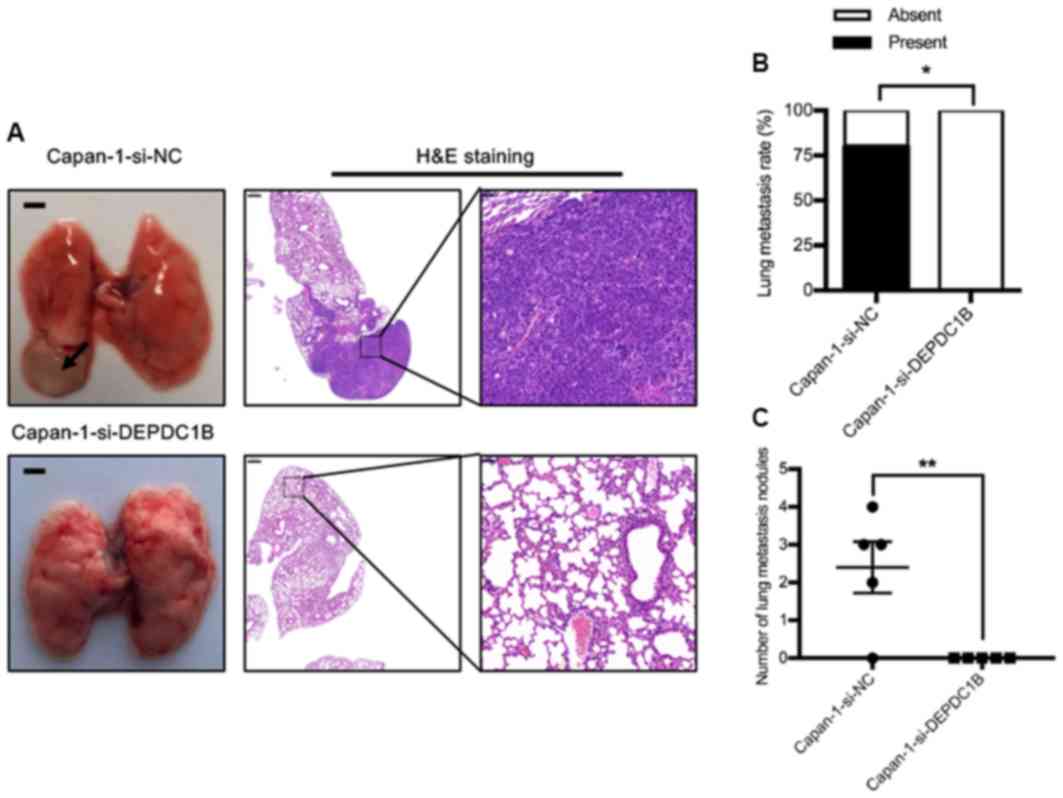
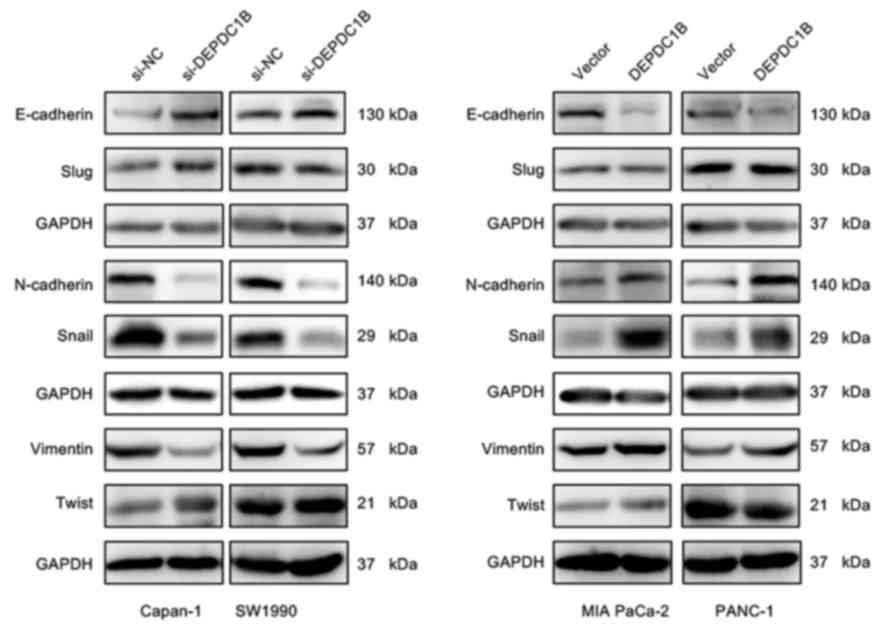
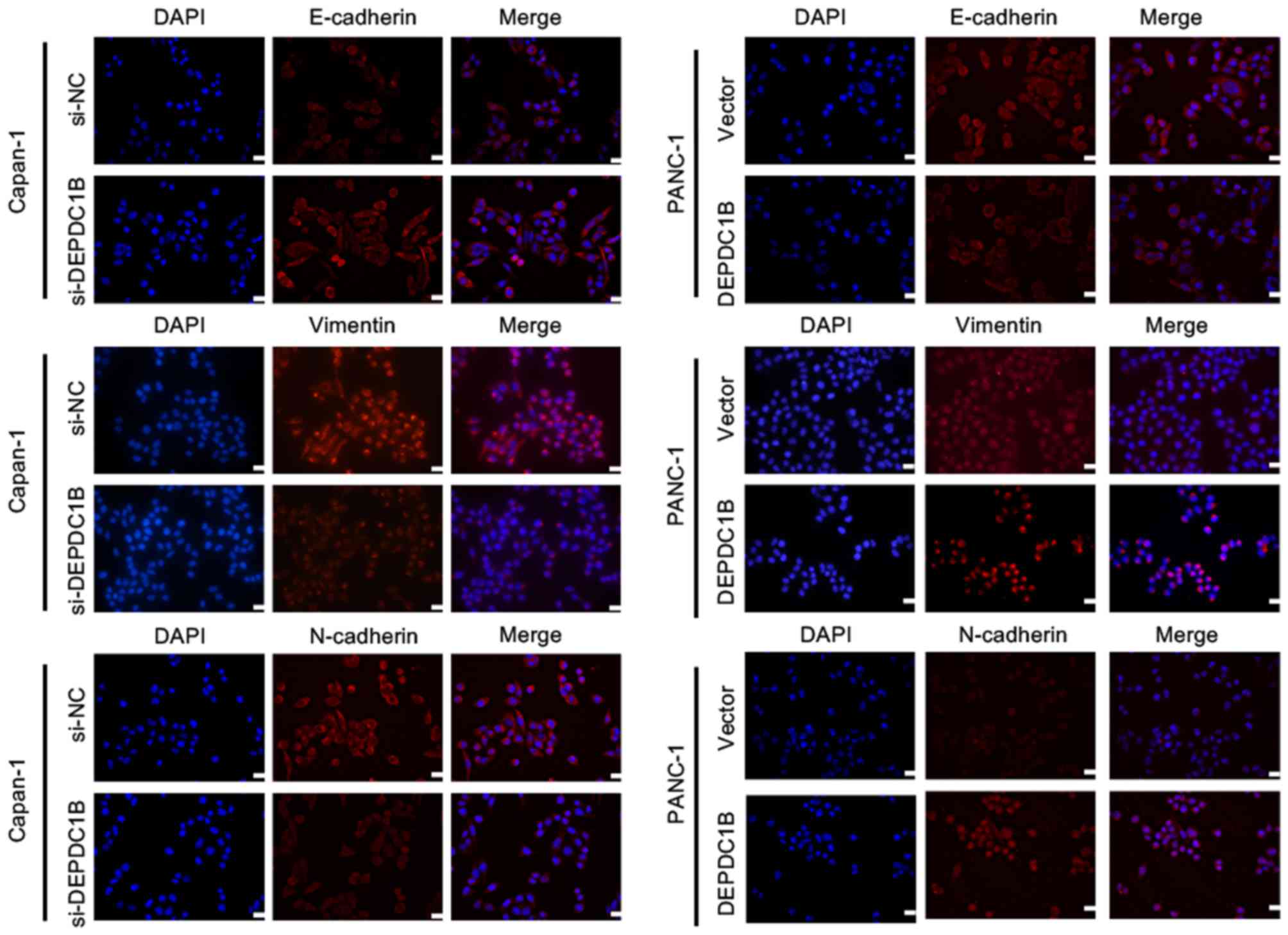
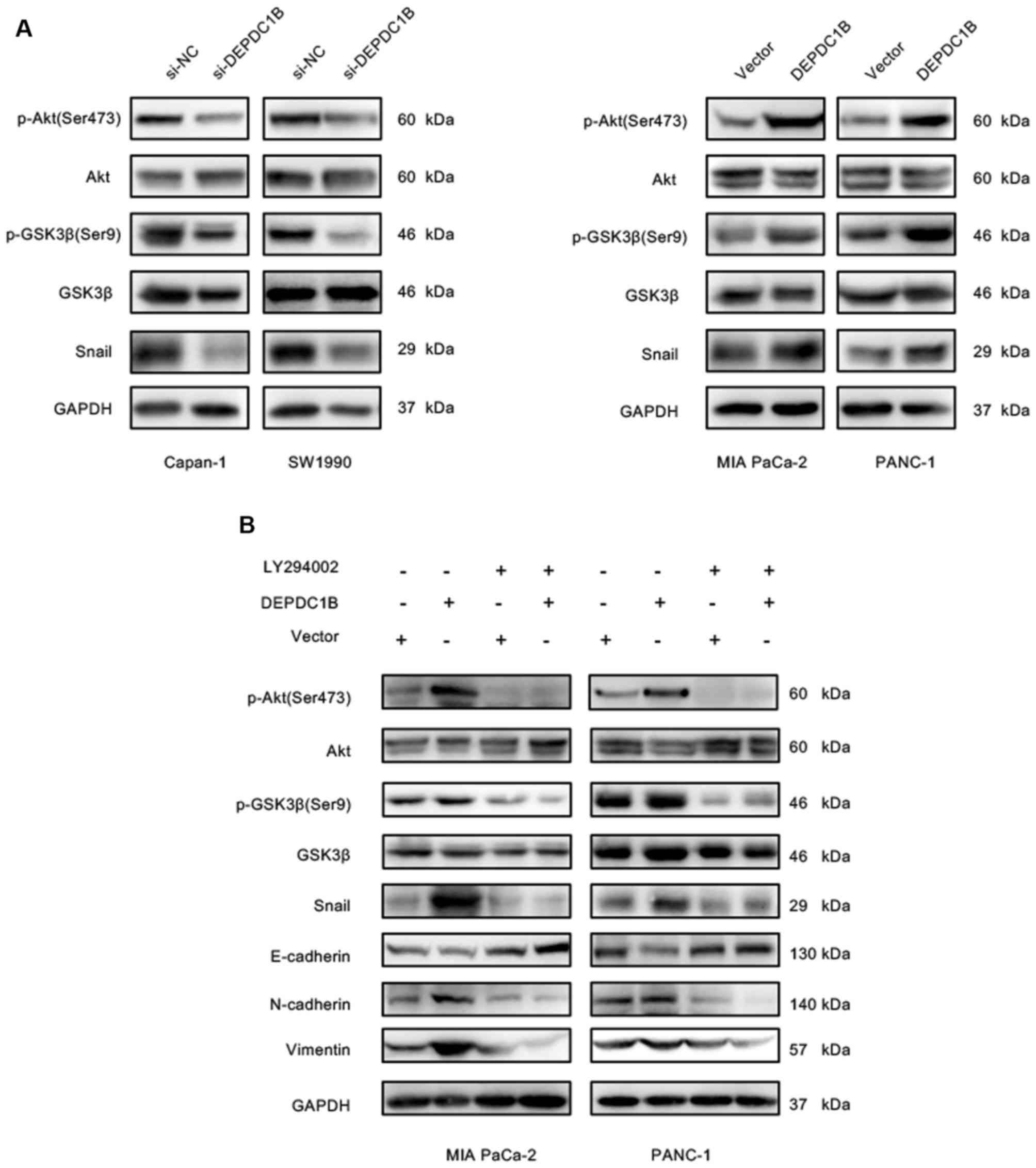
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamisawa T, Wood LD, Itoi T and Takaori K:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 388:73–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marchesi S, Montani F, Deflorian G,
D'Antuono R, Cuomo A, Bologna S, Mazzoccoli C, Bonaldi T, Di Fiore
PP and Nicassio F: DEPDC1B coordinates de-adhesion events and
cell-cycle progression at mitosis. Dev Cell. 31:420–433. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Garcia-Mata R: Arrested detachment: A
DEPDC1B-mediated de-adhesion mitotic checkpoint. Dev Cell.
31:387–389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ahuja P and Singh K: In silico approach
for SAR analysis of the predicted model of DEPDC1B: A novel target
for oral cancer. Adv Bioinformatics. 2016:31360242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boudreau HE, Broustas CG, Gokhale PC,
Kumar D, Mewani RR, Rone JD, Haddad BR and Kasid U: Expression of
BRCC3, a novel cell cycle regulated molecule, is associated with
increased phospho-ERK and cell proliferation. Int J Mol Med.
19:29–39. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Y, Liu L, Cai J, Wu J, Guan H, Zhu X,
Yuan J and Li M: DEPDC1B enhances migration and invasion of
non-small cell lung cancer cells via activating Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:899–905. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bai S, Chen T, Du T, Chen X, Lai Y, Ma X,
Wu W, Lin C, Liu L and Huang H: High levels of DEPDC1B predict
shorter biochemical recurrence-free survival of patients with
prostate cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:6801–6808. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Su YF, Liang CY, Huang CY, Peng CY, Chen
CC, Lin MC, Lin RK, Lin WW, Chou MY, Liao PH and Yang JJ: A
putative novel protein, DEPDC1B, is overexpressed in oral cancer
patients, and enhanced anchorage-independent growth in oral cancer
cells that is mediated by Rac1 and ERK. J Biomed Sci. 21:672014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu Y, Sun W, Zheng B, Liu X, Luo Z, Kong
Y, Xu M and Chen Y: DEPDC1B knockdown inhibits the development of
malignant melanoma through suppressing cell proliferation and
inducing cell apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 379:48–54. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg Robert A: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial- mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chaffer CL, San Juan BP, Lim E and
Weinberg RA: EMT, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 35:645–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: EMT: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rhim AD, Mirek ET, Aiello NM, Maitra A,
Bailey JM, McAllister F, Reichert M, Beatty GL, Rustgi AK,
Vonderheide RH, et al: EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic
tumor formation. Cell. 148:349–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen T, You Y, Jiang H and Wang ZZ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A biological process in
the development, stem cell differentiation, and tumorigenesis. J
Cell Physiol. 232:3261–3272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rhim AD, Mirek ET, Aiello NM, Maitra A,
Bailey JM, McAllister F, Reichert M, Beatty GL, Rustgi AK,
Vonderheide RH, et al: EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic
tumor formation. Cell. 148:349–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mihaljevic AL, Michalski CW, Friess H and
Kleeff J: Molecular mechanism of pancreatic cancer-understanding
proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Langenbecks Arch Surg.
395:295–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lan Y, Han J, Wang Y, Wang J, Yang G, Li
K, Song R, Zheng T, Liang Y, Pan S, et al: STK17B promotes
carcinogenesis and metastasis via AKT/GSK-3β/Snail signaling in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 9:2362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu L, Dai Y, Chen J, Zeng T, Li Y, Chen
L, Zhu YH, Li J, Li Y, Ma S, et al: Maelstrom promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by way of Akt/GSK-3β/Snail
signaling. Hepatology. 59:531–543. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang H, Zhou Z, Jin S, Xu K, Zhang H and
Xu J, Sun Q, Wang J and Xu J: PRMT9 promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma invasion and metastasis via activating
PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling. Cancer Sci. 109:1414–1427. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM,
Gunduz M and Hung MC: Dual regulation of Snail by
GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 6:931–940. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bachelder RE, Yoon SO, Franci C, de
Herreros AG and Mercurio AM: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an
endogenous inhibitor of Snail transcription: Implications for the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 168:29–33. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou BP and Hung MC: Wnt, hedgehog, and
snail: Sister pathways that control by GSK-3beta and beta-Trcp in
the regulation of metastasis. Cell Cycle. 4:772–776. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Badea L, Herlea V, Dima SO, Dumitrascu T
and Popescu I: Combined gene expression analysis of whole-tissue
and microdissected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma identifies
genes specifically overexpressed in tumor epithelia.
Hepatogastroenterology. 55:2016–2027. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pei H, Li L, Fridley BL, Jenkins GD,
Kalari KR, Lingle W, Petersen G, Lou Z and Wang L: FKBP51 affects
cancer cell response to chemotherapy by negatively regulating Akt.
Cancer Cell. 16:259–266. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Donahue TR, Tran LM, Hill R, Li Y,
Kovochich A, Calvopina JH, Patel SG, Wu N, Hindoyan A, Farrell JJ,
et al: Integrative survival-based molecular profiling of human
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1352–1363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen R, Wang Q, Cheng S, Liu T, Jiang H,
Zhu J, Wu Y and Wang L: The biological features of PanIN initiated
from oncogenic Kras mutation in genetically engineered mouse
models. Cancer Lett. 339:135–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu W, Yang Z and Lu N: A new role for the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Adh Migr. 9:317–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X and Zhou BP:
The role of snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 13:963–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nieto MA: The snail superfamily of
zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:155–166. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qiao M, Sheng S and Pardee AB: Metastasis
and AKT activation. Cell Cycle. 7:2991–2996. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ryan DP, Hong TS and Bardeesy N:
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 371:2140–2141. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Garrido-Laguna I and Hidalgo M: Pancreatic
cancer: From state-of-the-art treatments to promising novel
therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 12:319–334. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Infante JR, Somer BG, Park JO, Li CP,
Scheulen ME, Kasubhai SM, Oh DY, Liu Y, Redhu S, Steplewski K and
Le N: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
trametinib, an oral MEK inhibitor, in combination with gemcitabine
for patients with untreated metastatic adenocarcinoma of the
pancreas. Eur J Cancer. 50:2072–2081. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ballon DR, Flanary PL, Gladue DP, Konopka
JB, Dohlman HG and Thorner J: DEP-domain-mediated regulation of
GPCR signaling responses. Cell. 126:1079–1093. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Consonni SV, Maurice MM and Bos JL: DEP
domains: Structurally similar but functionally different. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 15:357–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Khalil BD, Hsueh C, Cao Y, Abi Saab WF,
Wang Y, Condeelis JS, Bresnick AR and Backer JM: GPCR signaling
mediates tumor metastasis via PI3Kβ. Cancer Res. 76:2944–2953.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Murga C, Fukuhara S and Gutkind JS: A
novel role for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase beta in signaling from
G protein-coupled receptors to Akt. J Biol Chem. 275:12069–12073.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dbouk HA, Vadas O, Shymanets A, Burke JE,
Salamon RS, Khalil BD, Barrett MO, Waldo GL, Surve C, Hsueh C, et
al: G protein-coupled receptor-mediated activation of p110beta by
Gbetagamma is required for cellular transformation and
invasiveness. Sci Signal. 5:ra892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Allen PJ, Kuk D, Castillo CF, Basturk O,
Wolfgang CL, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, Ferrone CR, Morales-Oyarvide
V, He J, et al: Multi-institutional validation study of the
American joint commission on cancer (8th Edition) changes for T and
N staging in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg.
265:185–191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|