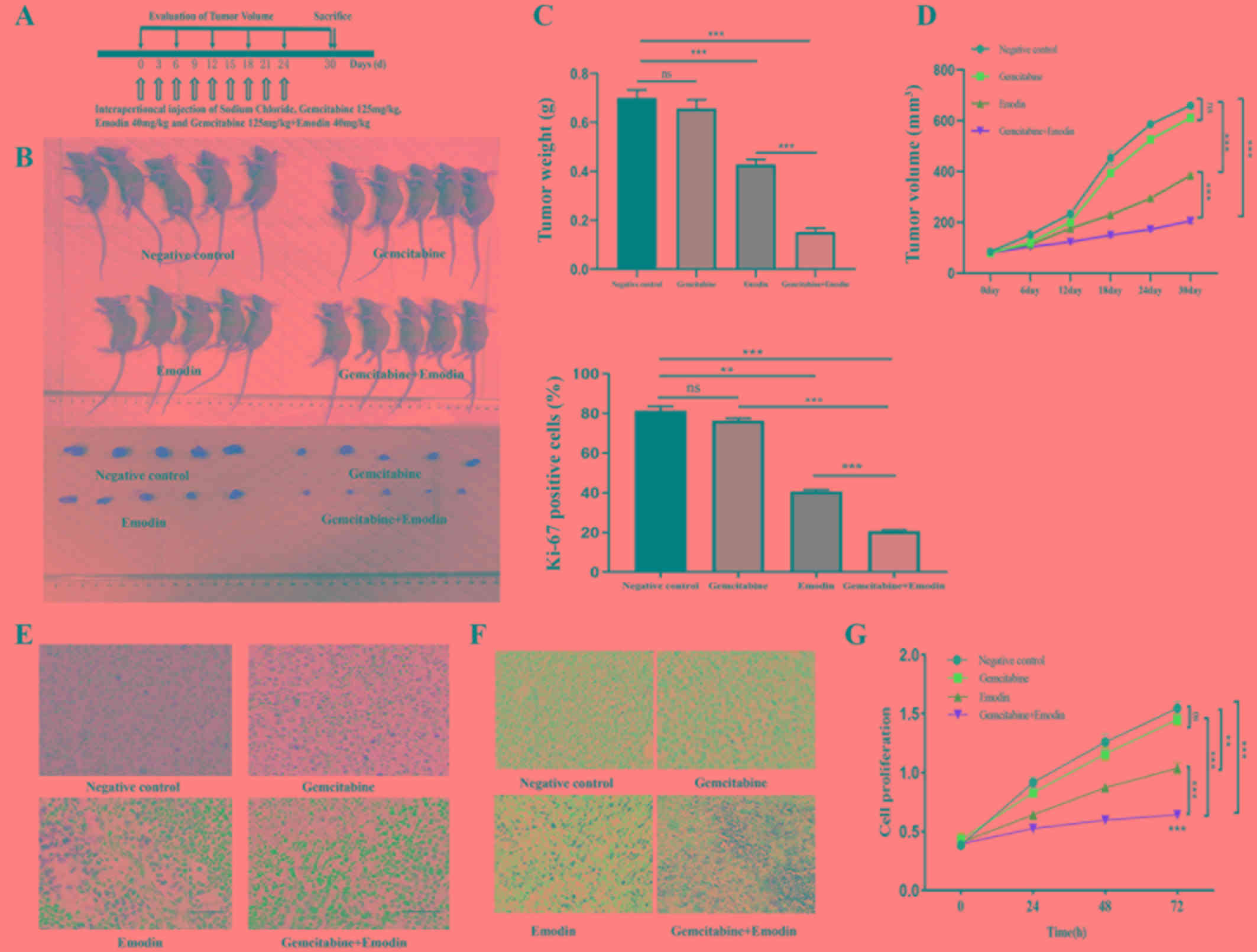
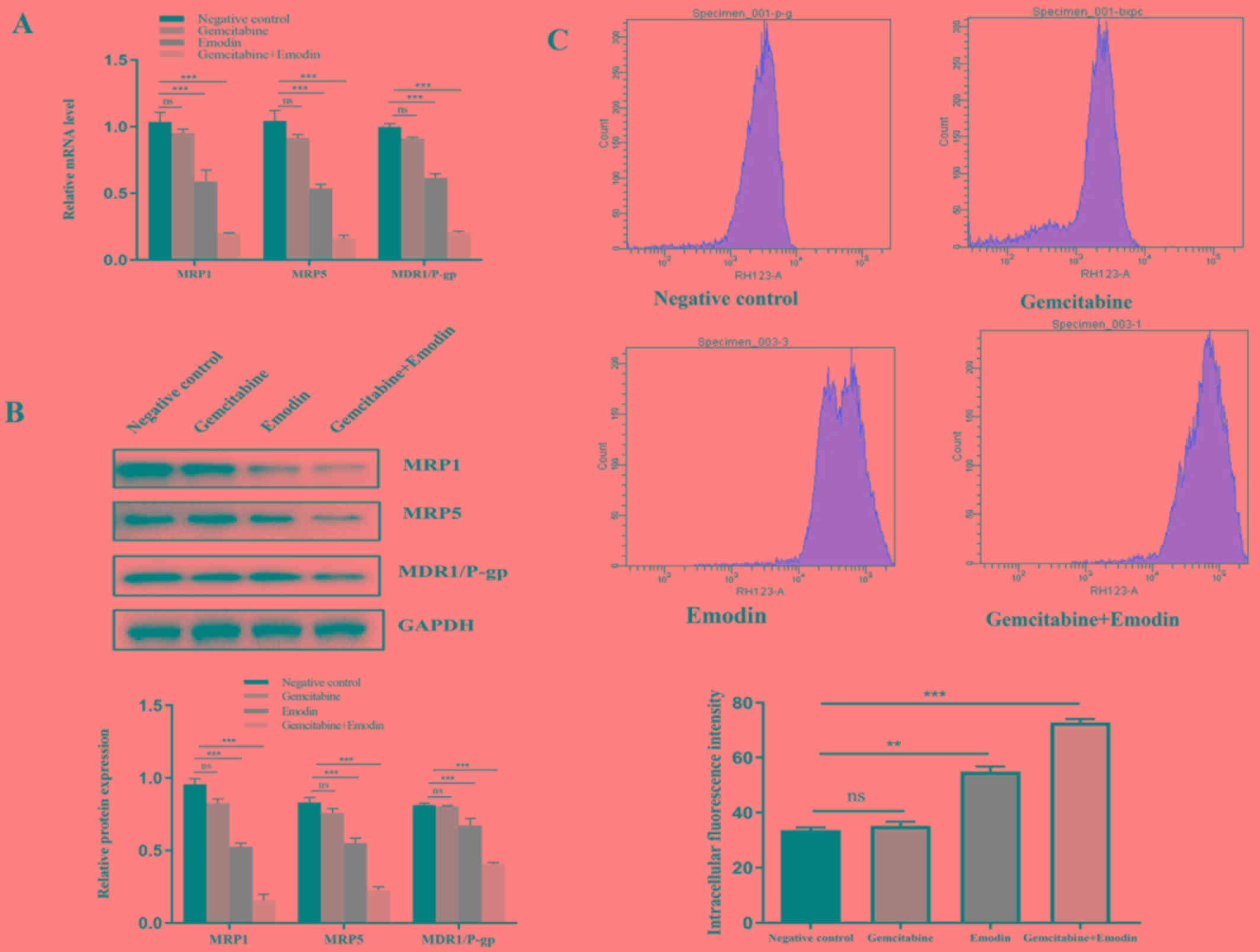
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reske SN: PET and PET-CT of malignant
tumors of the exocrine pancreas. Radiologe. 49:131–136. 2009.(In
German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stathis A and Moore MJ: Advanced
pancreatic carcinoma: Current treatment and future challenges. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 7:163–172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim MP and Gallick GE: Gemcitabine
resistance in pancreatic cancer: Picking the key players. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:1284–1285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Azmi
AS, Kong D and Sarkar FH: Pancreatic cancer: Understanding and
overcoming chemoresistance. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:27–33.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arends JJ, Sleeboom HP, Leys MB, Ten
Bokkel Huinink D, de Jong RS, Smit JM, Nortier JW and Tesselaar ME:
A phase II study of raltitrexed and gemcitabine in patients with
advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 92:445–448. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hagmann W, Jesnowski R and Löhr JM:
Interdependence of gemcitabine treatment, transporter expression,
and resistance in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Neoplasia.
12:740–747. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li HL, Chen HL, Li H, Zhang KL, Chen XY,
Wang XW, Kong QY and Liu J: Regulatory effects of emodin on
NF-kappaB activation and inflammatory cytokine expression in RAW
264.7 macrophages. Int J Mol Med. 16:41–47. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin SZ, Chen KJ, Tong HF, Jing H, Li H and
Zheng SS: Emodin attenuates acute rejection of liver allografts by
inhibiting hepatocellular apoptosis and modulating the Th1/Th2
balance in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:790–794.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li-Weber M: Targeting apoptosis pathways
in cancer by Chinese medicine. Cancer Lett. 332:304–312. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang Q, Lu G, Shen HM, Chung MC and Ong
CN: Anti-cancer properties of anthraquinones from rhubarb. Med Res
Rev. 27:609–630. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu A, Chen H, Wei W, Ye S, Liao W, Gong
J, Jiang Z, Wang L and Lin S: Antiproliferative and antimetastatic
effects of emodin on human pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep. 26:81–89.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu A, Chen H, Tong H, Ye S, Qiu M, Wang
Z, Tan W, Liu J and Lin S: Emodin potentiates the antitumor effects
of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells via inhibition of nuclear
factor-κB. Mol Med Rep. 4:221–227. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Liu P, Mao H, Wanga A and Zhang X:
Emodin sensitizes paclitaxel-resistant human ovarian cancer cells
to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in vitro. Oncol Rep.
21:1605–1610. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ko JC, Su YJ, Lin ST, Jhan JY, Ciou SC,
Cheng CM and Lin YW: Suppression of ERCC1 and Rad51 expression
through ERK1/2 inactivation is essential in emodin-mediated
cytotoxicity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:655–664. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chun-Guang W, Jun-Qing Y, Bei-Zhong L,
Dan-Ting J, Chong W, Liang Z, Dan Z and Yan W: Anti-tumor activity
of emodin against human chronic myelocytic leukemia K562 cell lines
in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 627:33–41. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang ZH, Chen H, Guo HC, Tong HF, Liu JX,
Wei WT, Tan W, Ni ZL, Liu HB and Lin SZ: Enhanced antitumor
efficacy by the combination of emodin and gemcitabine against human
pancreatic cancer cells via downregulation of the expression of
XIAP in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 39:1123–1131.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei WT, Chen H, Ni ZL, Liu HB, Tong HF,
Fan L, Liu A, Qiu MX, Liu DL, Guo HC, et al: Antitumor and
apoptosis-promoting properties of emodin, an anthraquinone
derivative from Rheum officinale Baill, against pancreatic cancer
in mice via inhibition of Akt activation. Int J Oncol.
39:1381–1390. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kusuhara H and Sugiyama Y: Role of
transporters in the tissue-selective distribution and elimination
of drugs: Transporters in the liver, small intestine, brain and
kidney. J Control Release. 78:43–54. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee CA, Cook JA, Reyner EL and Smith DA:
P-glycoprotein related drug interactions: Clinical importance and a
consideration of disease states. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol.
6:603–619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
O'Driscoll L, Walsh N, Larkin A, Ballot J,
Ooi WS, Gullo G, O'Connor R, Clynes M, Crown J and Kennedy S:
MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP-1 drug efflux pumps in pancreatic
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 27:2115–2120. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leonessa F and Clarke R: ATP binding
cassette transporters and drug resistance in breast cancer. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 10:43–73. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu Y, Ding F, Gao M, Jia YF and Ren L:
Establishment and characterization of the gemcitabine-resistant
human pancreatic cancer cell line SW1990/gemcitabine. Oncol Lett.
18:3065–3071. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lou C, Lu H, Ma Z, Liu C and Zhang Y:
Ginkgolide B enhances gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancer
cell lines via inhibiting PAFR/NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
109:563–572. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kong R, Sun B, Jiang H, Pan S, Chen H,
Wang S, Krissansen GW and Sun X: Downregulation of nuclear
factor-kappaB p65 subunit by small interfering RNA synergizes with
gemcitabine to inhibit the growth of pancreatic cancer. Cancer
Lett. 291:90–98. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shain KH and Dalton WS: Cell adhesion is a
key determinant in de novo multidrug resistance (MDR): New targets
for the prevention of acquired MDR. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:69–78.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schinkel AH and Jonker JW: Mammalian drug
efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: An
overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 55:3–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takakuwa O, Oguri T, Ozasa H, Uemura T,
Kasai D, Miyazaki M, Maeno K and Sato S: Over-expression of MDR1 in
amrubicinol-resistant lung cancer cells. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 68:669–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Konig J, Hartel M, Nies AT, Martignoni ME,
Guo J, Büchler MW, Friess H and Keppler D: Expression and
localization of human multidrug resistance protein (ABCC) family
members in pancreatic carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 115:359–367. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Noma B, Sasaki T, Fujimoto Y, Serikawa M,
Kobayashi K, Inoue M, Itsuki H, Kamigaki M, Minami T and Chayama K:
Expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 is involved
in chemotherapy resistance in human pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol.
33:1187–1194. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|