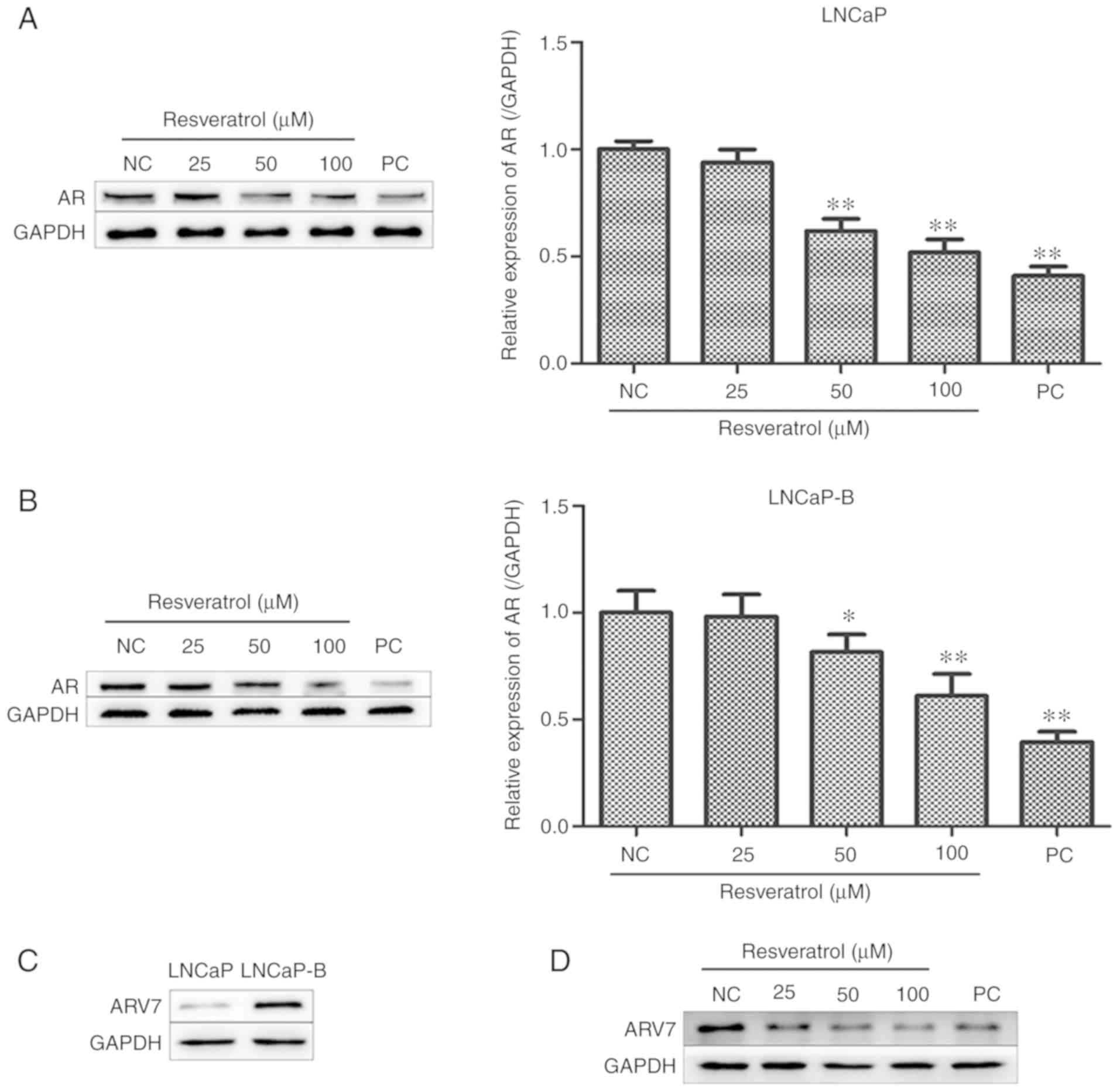
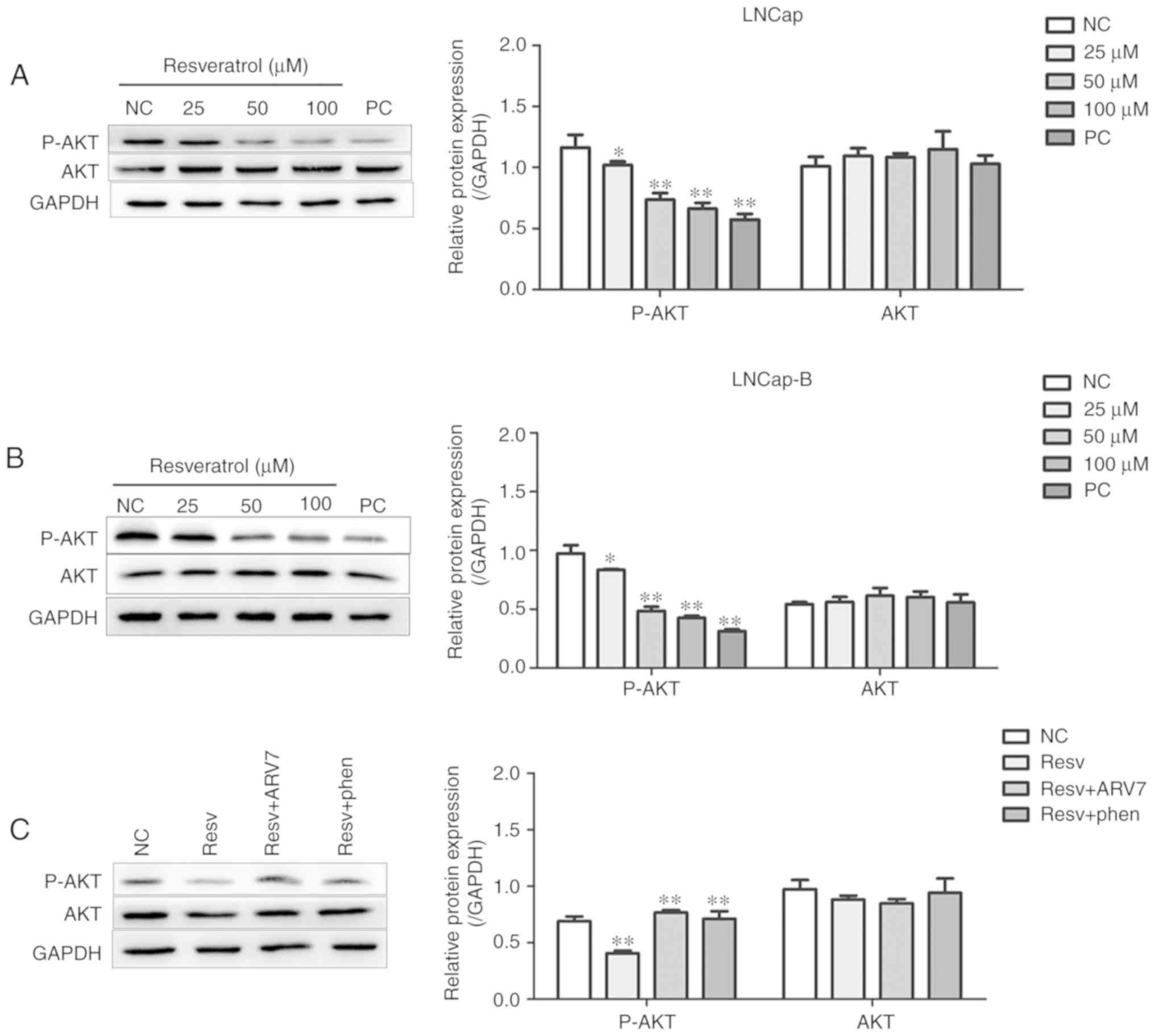
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Park JW, Jang WS, Koh DH, Ham WS, Rha KH,
Hong SJ and Choi YD: Impact of early salvage androgen deprivation
therapy in localized prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy: A
propensity score matched analysis. Yonsei Med J. 59:580–587. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharifi N, Gulley JL and Dahut WL:
Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. JAMA.
294:238–244. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scher HI, Beer TM, Higano CS, Anand A,
Taplin ME, Efstathiou E, Rathkopf D, Shelkey J, Yu EY, Alumkal J,
et al: Antitumour activity of MDV3100 in castration-resistant
prostate cancer: A phase 1–2 study. Lancet. 375:1437–1446. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taneja SS: Re: Abiraterone in metastatic
prostate cancer without previous chemotherapy. J Urol. 190:8802013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shafi AA, Yen AE and Weigel NL: Androgen
receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 140:223–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ryan CJ and Tindall DJ: Androgen receptor
rediscovered: The new biology and targeting the androgen receptor
therapeutically. J Clin Oncol. 29:3651–3658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tilley WD, Buchanan G, Hickey TE and
Bentel JM: Mutations in the androgen receptor gene are associated
with progression of human prostate cancer to androgen independence.
Clin Cancer Res. 2:277–285. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He B, Gampe RJ Jr, Kole AJ, Hnat AT,
Stanley TB, An G, Stewart EL, Kalman RI, Minges JT and Wilson EM:
Structural basis for androgen receptor interdomain and coactivator
interactions suggests a transition in nuclear receptor activation
function dominance. Mol Cell. 16:425–438. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shang Y, Myers M and Brown M: Formation of
the androgen receptor transcription complex. Mol Cell. 9:601–610.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Montgomery RB, Mostaghel EA, Vessella R,
Hess DL, Kalhorn TF, Higano CS, True LD and Nelson PS: Maintenance
of intratumoral androgens in metastatic prostate cancer: A
mechanism for castration- resistant tumor growth. Cancer Res.
68:4447–4454. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Waltering KK, Helenius MA, Sahu B, Manni
V, Linja MJ, Jänne OA and Visakorpi T: Increased expression of
androgen receptor sensitizes prostate cancer cells to low levels of
androgens. Cancer Res. 69:8141–8149. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen
R, Vessella R, Rosenfeld MG and Sawyers CL: Molecular determinants
of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med. 10:33–39. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moradi A, Srinivasan S, Clements J and
Batra J: Beyond the biomarker role: Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
in the prostate cancer microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
38:333–346. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reebye V, Querol Cano L, Lavery DN, Brooke
GN, Powell SM, Chotai D, Walker MM, Whitaker HC, Wait R, Hurst HC
and Bevan CL: Role of the HSP90-associated cochaperone p23 in
enhancing activity of the androgen receptor and significance for
prostate cancer. Mol Endocrinol. 26:1694–1706. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin CY, Jan YJ, Kuo LK, Wang BJ, Huo C,
Jiang SS, Chen SC, Kuo YY, Chang CR and Chuu CP: Elevation of
androgen receptor promotes prostate cancer metastasis by induction
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and reduction of KAT5. Cancer
Sci. 109:3564–3574. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu R, Dunn TA, Wei S, Isharwal S, Veltri
RW, Humphreys E, Han M, Partin AW, Vessella RL, Isaacs WB, et al:
Ligand-independent androgen receptor variants derived from splicing
of cryptic exons signify hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer
Res. 69:16–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hörnberg E, Ylitalo EB, Crnalic S, Antti
H, Stattin P, Widmark A, Bergh A and Wikström P: Expression of
androgen receptor splice variants in prostate cancer bone
metastases is associated with castration-resistance and short
survival. PLoS One. 6:e190592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stewart JR, Artime MC and O'Brian CA:
Resveratrol: A candidate nutritional substance for prostate cancer
prevention. J Nutr. 133 (7 Suppl):2440S–2443S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Patel KR, Brown VA, Jones DJ, Britton RG,
Hemingway D, Miller AS, West KP, Booth TD, Perloff M, Crowell JA,
et al: Clinical pharmacology of resveratrol and its metabolites in
colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Res. 70:7392–7399. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aggarwal BB, Bhardwaj A, Aggarwal RS,
Seeram NP, Shishodia S and Takada Y: Role of resveratrol in
prevention and therapy of cancer: Preclinical and clinical studies.
Anticancer Res. 24:2783–2840. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aluyen JK, Ton QN, Tran T, Yang AE,
Gottlieb HB and Bellanger RA: Resveratrol: Potential as anticancer
agent. J Diet. (Suppl 9):45–56. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Delmas D, Lancon A, Colin D, Jannin B and
Latruffe N: Resveratrol as a chemopreventive agent: A promising
molecule for fighting cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 7:423–442. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jang YG, Go RE, Hwang KA and Choi KC:
Resveratrol inhibits DHT-induced progression of prostate cancer
cell line through interfering with the AR and CXCR4 pathway. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 192:1054062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mitchell SH, Zhu W and Young CY:
Resveratrol inhibits the expression and function of the androgen
receptor in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 59:5892–5895.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo Z, Yang X, Sun F, Jiang R, Linn DE,
Chen H, Chen H, Kong X, Melamed J, Tepper CG, et al: A novel
androgen receptor splice variant is up-regulated during prostate
cancer progression and promotes androgen depletion-resistant
growth. Cancer Res. 69:2305–2313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sobhani N, Generali D, D'Angelo A, Aieta M
and Roviello G: Current status of androgen receptor-splice variant
7 inhibitor niclosamide in castrate-resistant prostate-cancer.
Invest New Drug. 36:1133–1137. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Deng Y, Bi R, Zhu Z, Li S, Xu B, Rather WA
and Wang C: A surveillance, epidemiology and end results database
analysis of the prognostic value of organ-specific metastases in
patients with advanced prostatic adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett.
18:1057–1070. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saad F, Chi KN, Finelli A, Hotte SJ, Izawa
J, Kapoor A, Kassouf W, Loblaw A, North S, Rendon R, et al: The
2015 CUA-CUOG Guidelines for the management of castration-resistant
prostate cancer (CRPC). Can Urol Assoc J. 9:90–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Penning TM: Mechanisms of drug resistance
that target the androgen axis in castration resistant prostate
cancer (CRPC). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 153:105–113. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thakur A, Vaishampayan U and Lum LG:
Immunotherapy and immune evasion in prostate cancer. Cancers.
5:569–590. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV,
Thomas CF, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Farnsworth NR, Kinghorn AD, Mehta
RG, et al: Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a
natural product derived from grapes. Science. 275:218–220. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kuwajerwala N, Cifuentes E, Gautam S,
Menon M, Barrack ER and Reddy GP: Resveratrol induces prostate
cancer cell entry into s phase and inhibits DNA synthesis. Cancer
Res. 62:2488–2492. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Isaacs JT and Isaacs WB: Androgen receptor
outwits prostate cancer drugs. Nat Med. 10:26–27. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Scher HI and Sawyers CL: Biology of
progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: Directed
therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin
Oncol. 23:8253–8261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thakur MK, Heilbrun LK, Sheng S, Stein M,
Liu G, Antonarakis ES, Vaishampayan U, Dzinic SH, Li X, Freeman S,
et al: A phase II trial of ganetespib, a heat shock protein 90
Hsp90) inhibitor, in patients with docetaxel-pretreated metastatic
castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC)-a prostate cancer
clinical trials consortium (PCCTC) study. Invest New Drugs.
34:112–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Vellky JE, Bauman TM, Ricke EA, Huang W
and Ricke WA: Incidence of androgen receptor and androgen receptor
variant 7 coexpression in prostate cancer. Prostate. 79:1811–1822.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hsu CL, Liu JS, Wu PL, Guan HH, Chen YL,
Lin AC, Ting HJ, Pang ST, Yeh SD, Ma WL, et al: Identification of a
new androgen receptor (AR) co-regulator BUD31 and related peptides
to suppress wild-type and mutated AR-mediated prostate cancer
growth via peptide screening and X-ray structure analysis. Mol
Oncol. 8:1575–1587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen H, Zhou L, Wu X, Li R, Wen J, Sha J
and Wen X: The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate
cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 21:1084–1091. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liao Y, Grobholz R, Abel U, Trojan L,
Michel MS, Angel P and Mayer D: Increase of AKT/PKB expression
correlates with gleason pattern in human prostate cancer. Int J
Cancer. 107:676–680. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pilling AB and Hwang C: Targeting
prosurvival BCL2 signaling through Akt blockade sensitizes
castration-resistant prostate cancer cells to enzalutamide.
Prostate. 79:1347–1359. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin HK, Hu YC, Yang L, Altuwaijri S, Chen
YT, Kang HY and Chang C: Suppression versus induction of androgen
receptor functions by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
in prostate cancer LNCaP cells with different passage numbers. J
Biol Chem. 278:50902–50907. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|