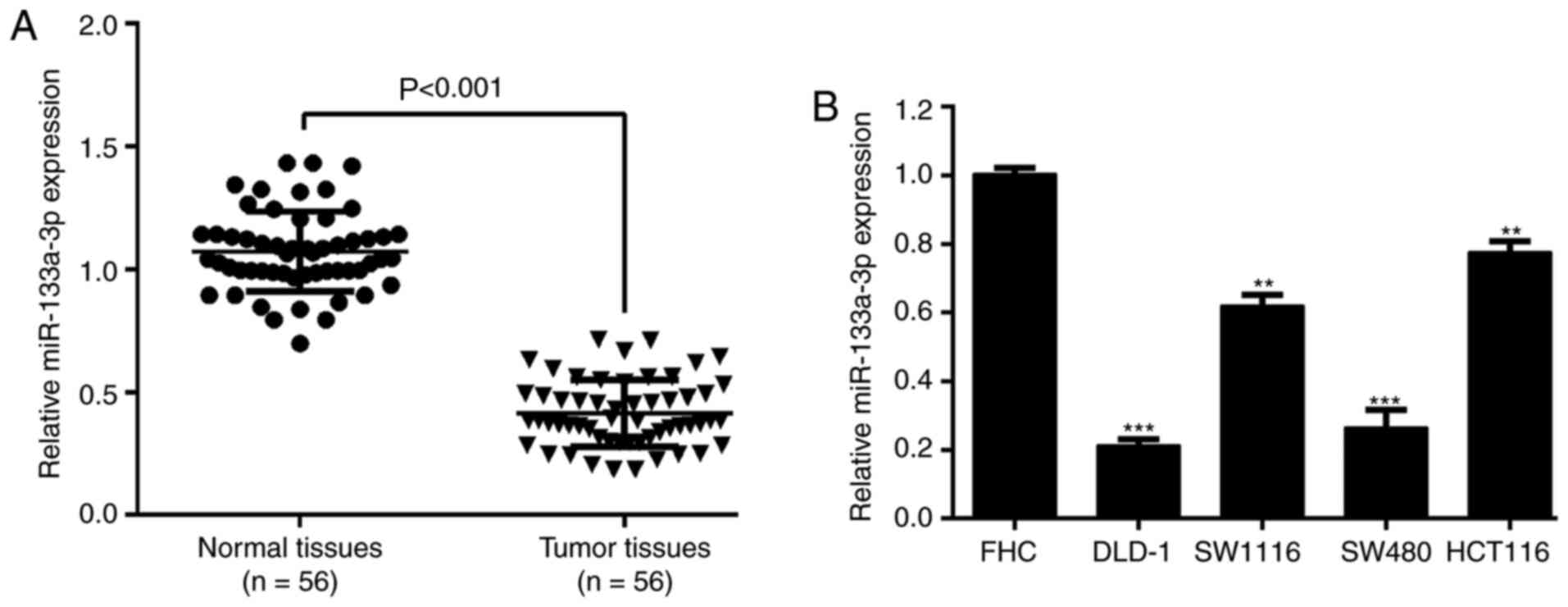
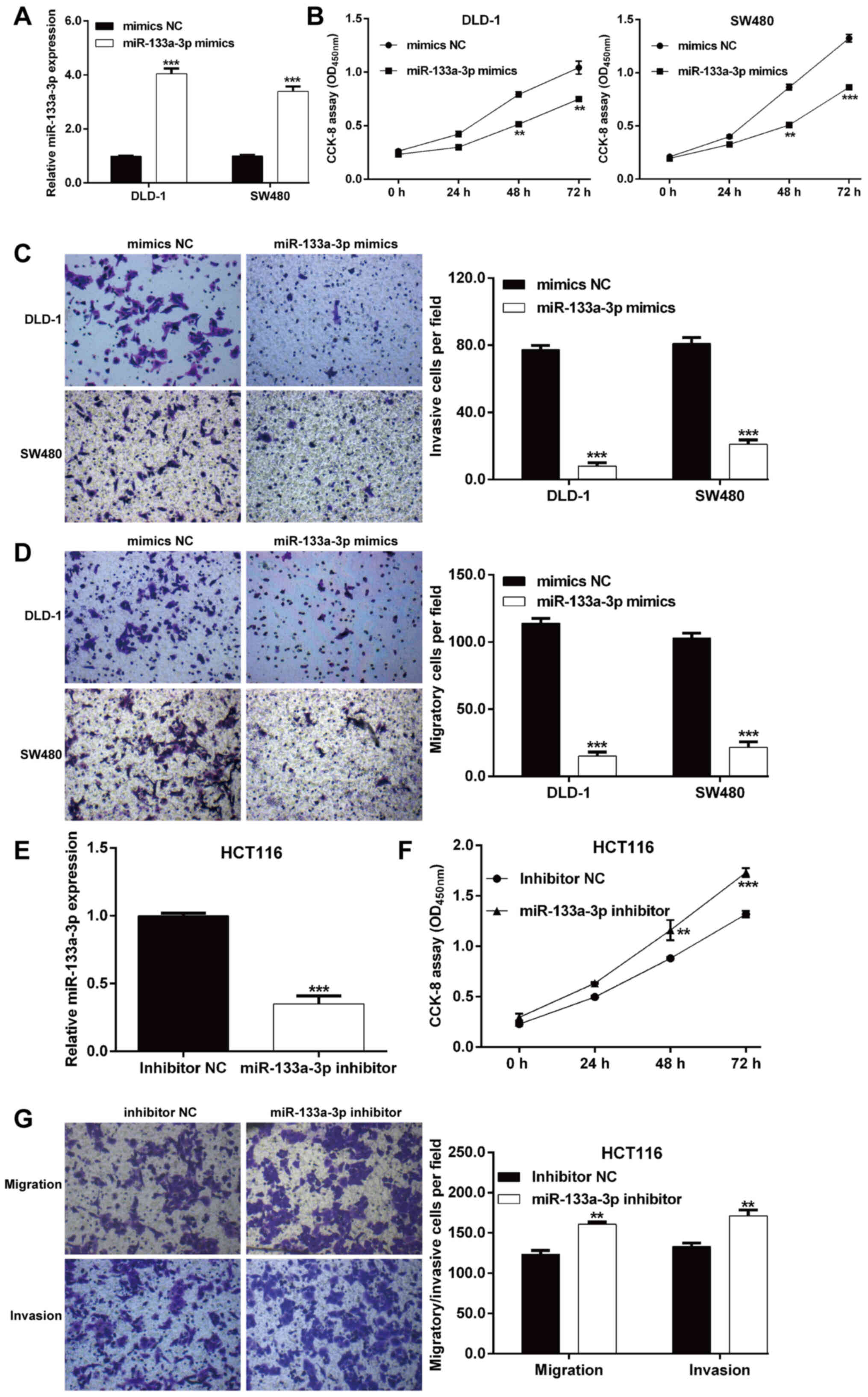
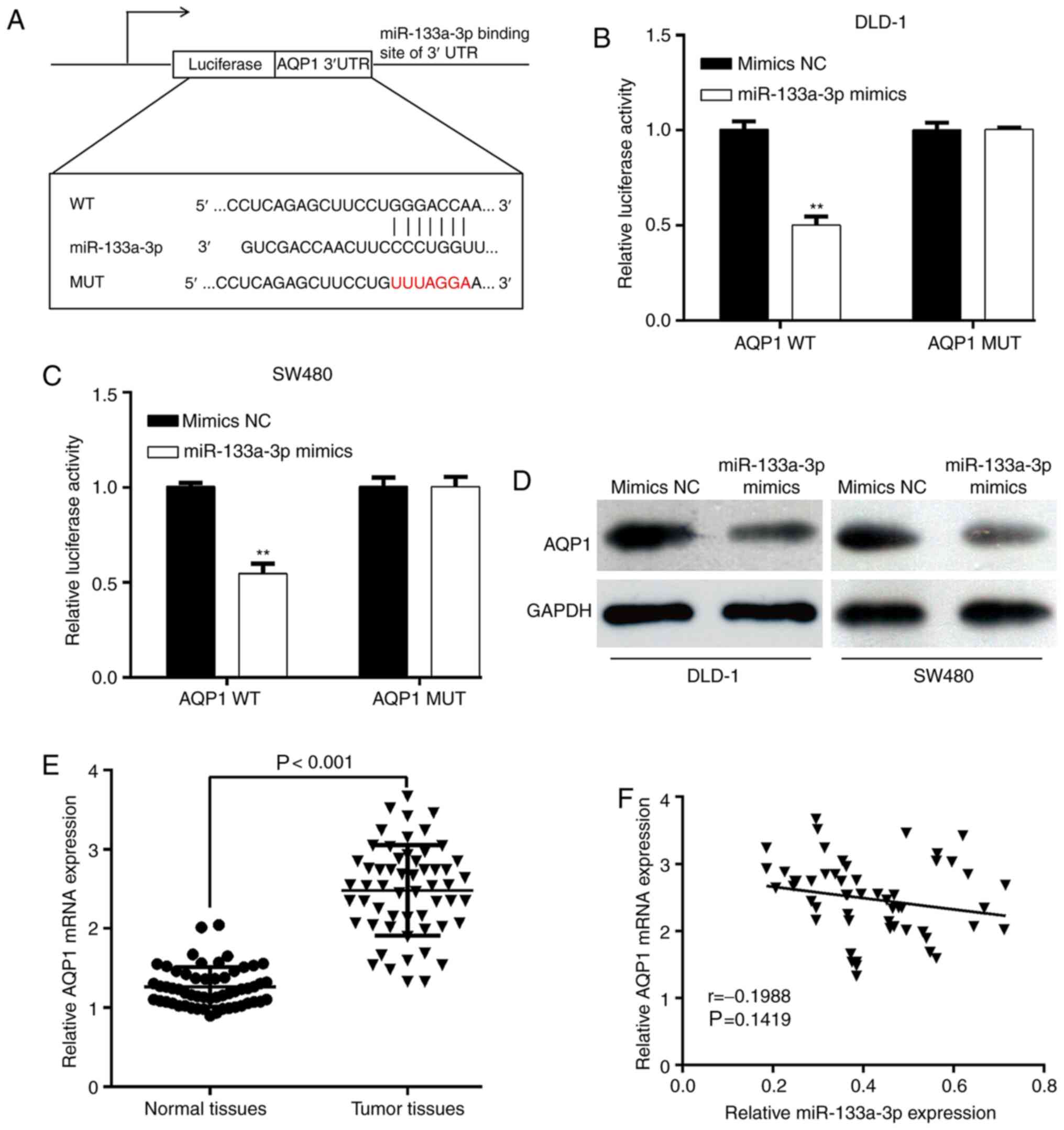
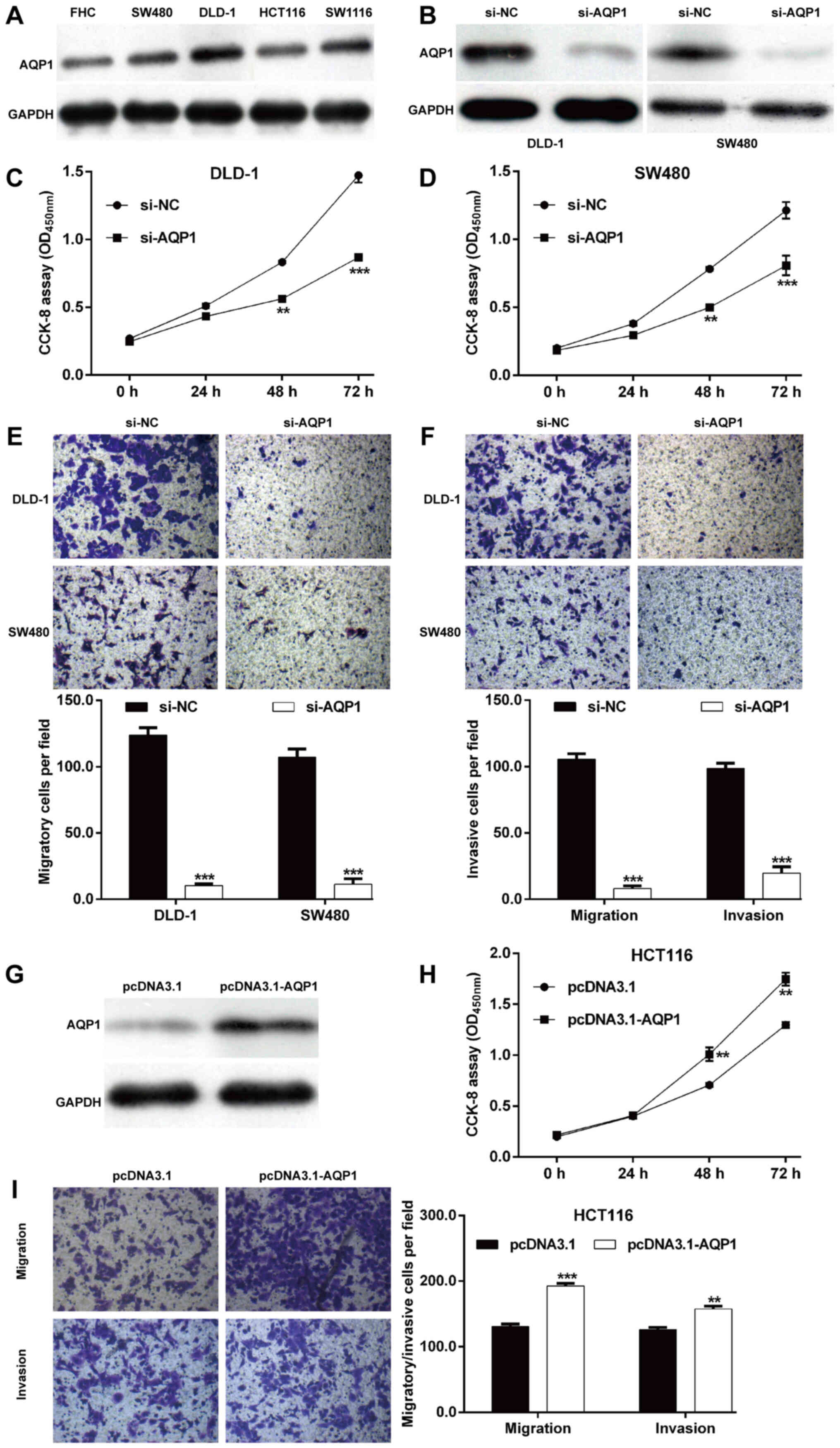
|
1
|
Cai Z and Liu Q: Understanding the Global
Cancer Statistics 2018: Implications for cancer control. Sci China
Life Sci. 64:1017–1020. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Andrews L: Dietary flavonoids for the
prevention of colorectal cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 17:671–672.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Altobelli E, Lattanzi A, Paduano R,
Varassi G and di Orio F: Colorectal cancer prevention in Europe:
Burden of disease and status of screening programs. Prev Med.
62:132–141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sugarbaker PH: Colorectal cancer:
Prevention and management of metastatic disease. BioMed Res Int.
2014:7828902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goldstein DA, Zeichner SB, Bartnik CM,
Neustadter E and Flowers CR: Metastatic colorectal cancer: A
systematic review of the value of current therapies. Clin
Colorectal Cancer. 15:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Shannessy DJ, Somers EB, Chandrasekaran
LK, Nicolaides NC, Bordeaux J and Gustavson MD: Influence of tumor
microenvironment on prognosis in colorectal cancer: Tissue
architecture-dependent signature of endosialin (TEM-1) and
associated proteins. Oncotarget. 5:3983–3995. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rawla P, Sunkara T and Barsouk A:
Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival,
and risk factors. Prz Gastroenterol. 14:89–103. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo L, Fu J, Sun S, Zhu M, Zhang L, Niu H,
Chen Z, Zhang Y, Guo L and Wang S: MicroRNA-143-3p inhibits
colorectal cancer metastases by targeting ITGA6 and ASAP3. Cancer
Sci. 110:805–816. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wu H, Li Y, Zhang Y, Liu
M, Li X and Tang H: miR-10a suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis
by modulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and anoikis.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e27392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo F, Zhou J, Wang S, Sun Z, Han Q and
Bai C: microRNA-222 promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and
invasion by targeting MST3. FEBS Open Bio. 9:901–913. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang Y, Wu Y, Dong J, Han D, Yang S and
Jiang L: MicroRNA-133a-3p exerts inhibitory effects on gallbladder
carcinoma via targeting RBPJ. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2448–2462.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yin Y, Du L, Li X, Zhang X and Gao Y:
miR-133a-3p suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion
and promotes apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J
Cell Physiol. 234:12757–12770. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Liu X, Wang W and Li C: miR-133a-3p
promotes apoptosis and induces cell cycle arrest by targeting CREB1
in retinoblastoma. Arch Med Sci. 16:941–956. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Li Z, Xuan Z, Xu P, Wang W, Chen
Z, Wang S, Sun G, Xu J and Xu Z: Novel role of miR-133a-3p in
repressing gastric cancer growth and metastasis via blocking
autophagy-mediated glutaminolysis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:3202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang Y, Pan J, Huang S, Peng X, Zou X, Luo
Y, Ren D, Zhang X, Li R, He P, et al: Downregulation of miR-133a-3p
promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT
signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou GQ, Han F, Shi ZL, Yu L, Li XF, Yu C,
Shen CL, Wan DW, Zhu XG, Li R, et al: miR-133a-3p targets
SUMO-specific protease 1 to inhibit cell proliferation and cell
cycle progress in colorectal cancer. Oncol Res. 26:795–800. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weber D, Amar L, Gödde D and Prinz C:
Extensive screening of microRNA populations identifies hsa-miR-375
and hsa-miR-133a-3p as selective markers for human rectal and colon
cancer. Oncotarget. 9:27256–27267. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verkman AS: More than just water channels:
Unexpected cellular roles of aquaporins. J Cell Sci. 118:3225–3232.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang WY, Tan ZF, Dong DW, Ding Y, Meng H,
Zhao Y, Xin XF and Bi W: Association of aquaporin 1 with tumor
migration, invasion and vasculogenic mimicry in glioblastoma
multiforme. Mol Med Rep. 17:3206–3211. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Fan Y, Zheng C and Zhang X:
Knockdown of AQP1 inhibits growth and invasion of human ovarian
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 16:5499–5504. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu Z, Li S, Liu J, Shi Y, Wang J, Chen D,
Luo L, Qian Y, Huang X and Wang H: RNAi-mediated silencing of AQP1
expression inhibited the proliferation, invasion and tumorigenesis
of osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 16:1332–1340. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamazato Y, Shiozaki A, Ichikawa D, Kosuga
T, Shoda K, Arita T, Konishi H, Komatsu S, Kubota T, Fujiwara H, et
al: Aquaporin 1 suppresses apoptosis and affects prognosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 9:29957–29974.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yoshida T, Hojo S, Sekine S, Sawada S,
Okumura T, Nagata T, Shimada Y and Tsukada K: Expression of
aquaporin-1 is a poor prognostic factor for stage II and III colon
cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:953–958. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Imaizumi H, Ishibashi K, Takenoshita S and
Ishida H: Aquaporin 1 expression is associated with response to
adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II and III colorectal cancer. Oncol
Lett. 15:6450–6456. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang Y, Ma R, Zhao Y, Li GJ, Wang AK, Lin
WL, Lan XM, Zhong SY and Cai JH: MEF2C/miR-133a-3p.1
circuit-stabilized AQP1 expression maintains endothelial water
homeostasis. FEBS Lett. 593:2566–2573. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang ZQ, Wu CA and Cheng YX: Prognostic
value of microRNA-133a expression and its clinicopathologic
significance in non-small cell lung cancer: A comprehensive study
based on meta-analysis and the TCGA database. Oncol Res Treat.
41:762–768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liang HW, Yang X, Wen DY, Gao L, Zhang XY,
Ye ZH, Luo J, Li ZY, He Y, Pang YY, et al: Utility of miR 133a 3p
as a diagnostic indicator for hepatocellular carcinoma: An
investigation combined with GEO, TCGA, meta analysis and
bioinformatics. Mol Med Rep. 17:1469–1484. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
House R, Majumder M, Janakiraman H,
Ogretmen B, Kato M, Erkul E, Hill E, Atkinson C, Barth J, Day TA,
et al: Smoking-induced control of miR-133a-3p alters the expression
of EGFR and HuR in HPV-infected oropharyngeal cancer. PLoS One.
13:e02050772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao L, Li SH, Tian YX, Zhu QQ, Chen G,
Pang YY and Hu XH: Role of downregulated miR-133a-3p expression in
bladder cancer: A bioinformatics study. OncoTargets Ther.
10:3667–3683. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi W, Tang T, Li X, Deng S, Li R, Wang Y,
Wang Y, Xia T, Zhang Y, Zen K, et al: Methylation-mediated
silencing of miR-133a-3p promotes breast cancer cell migration and
stemness via miR-133a-3p/MAML1/DNMT3A positive feedback loop. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 38:4292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He B, Lin X, Tian F, Yu W and Qiao B:
MiR-133a-3p inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
proliferation and invasion by suppressing COL1A1. J Cell Biochem.
119:338–346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu X, Wang D, Wang X, Sun S, Zhang Y, Wang
S, Miao R, Xu X and Qu X: CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes inflammation-driven
colorectal cancer progression through activation of RhoA signaling
by sponging miR-133a-3p. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:322019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pei HP, Liu Z, Huang LS and Zhu H:
Significance of aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-3 expression in
colorectal carcinoma. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 14:275–278.
2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kang BW, Kim JG, Lee SJ, Chae YS, Jeong
JY, Yoon GS, Park SY, Kim HJ, Park JS, Choi GS, et al: Expression
of aquaporin-1, aquaporin-3, and aquaporin-5 correlates with nodal
metastasis in colon cancer. Oncology. 88:369–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dorward HS, Du A, Bruhn MA, Wrin J, Pei
JV, Evdokiou A, Price TJ, Yool AJ and Hardingham JE:
Pharmacological blockade of aquaporin-1 water channel by AqB013
restricts migration and invasiveness of colon cancer cells and
prevents endothelial tube formation in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 35:362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Esteva-Font C, Jin BJ and Verkman AS:
Aquaporin-1 gene deletion reduces breast tumor growth and lung
metastasis in tumor-producing MMTV-PyVT mice. FASEB J.
28:1446–1453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Simone L, Gargano CD, Pisani F, Cibelli A,
Mola MG, Frigeri A, Svelto M and Nicchia GP: Aquaporin-1 inhibition
reduces metastatic formation in a mouse model of melanoma. J Cell
Mol Med. 22:904–912. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|