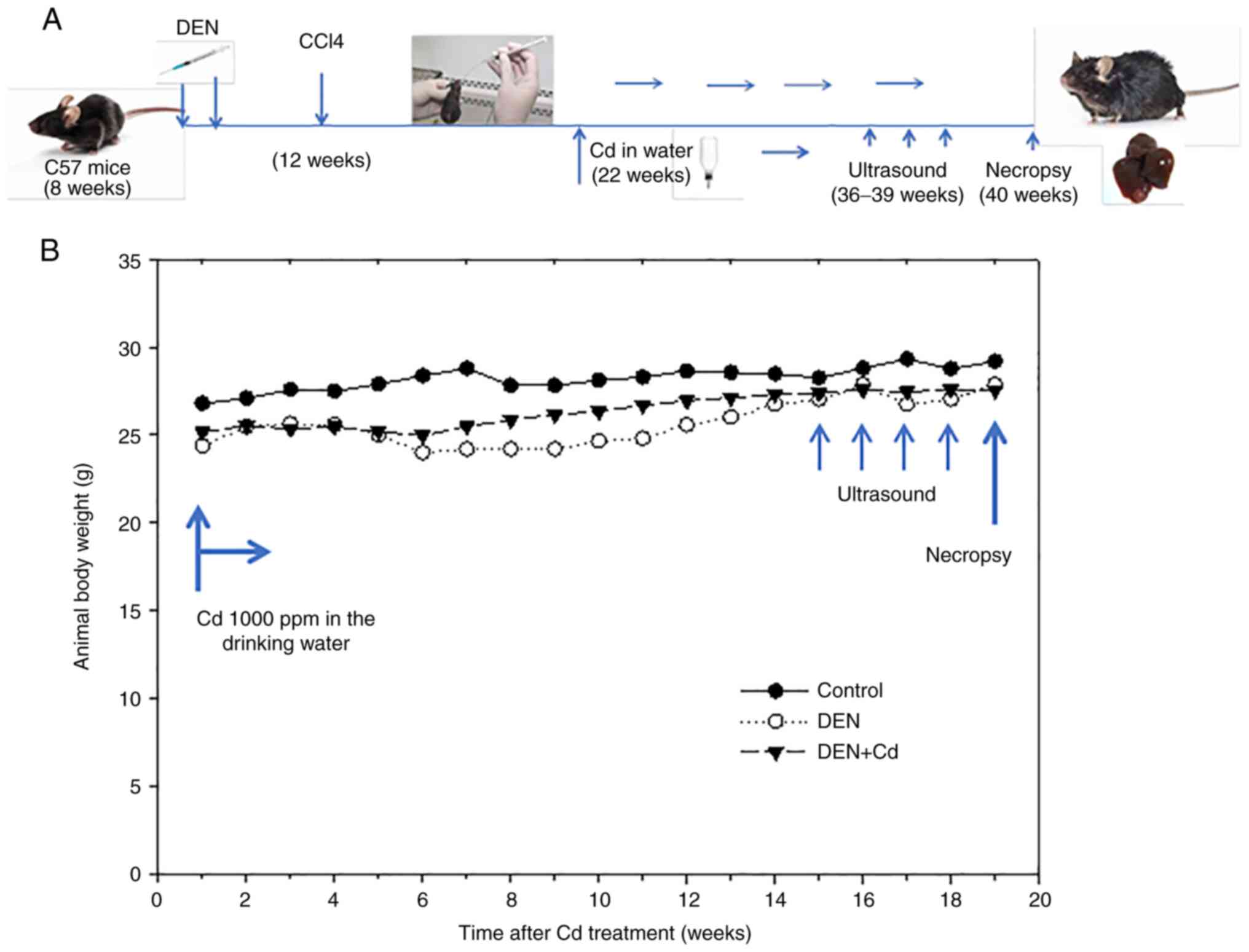
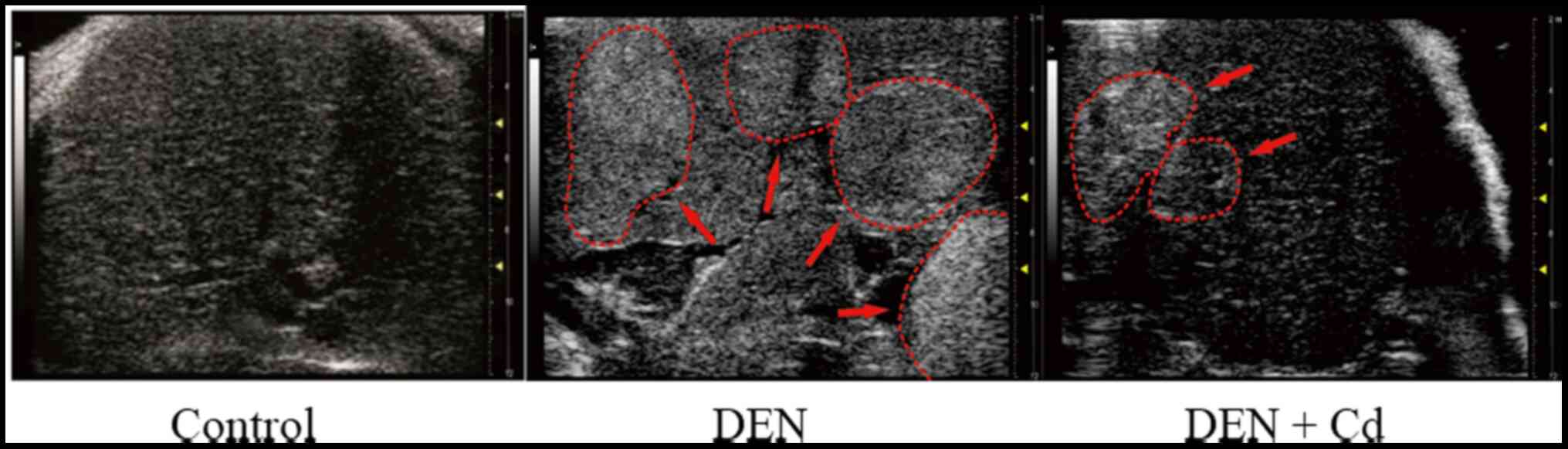
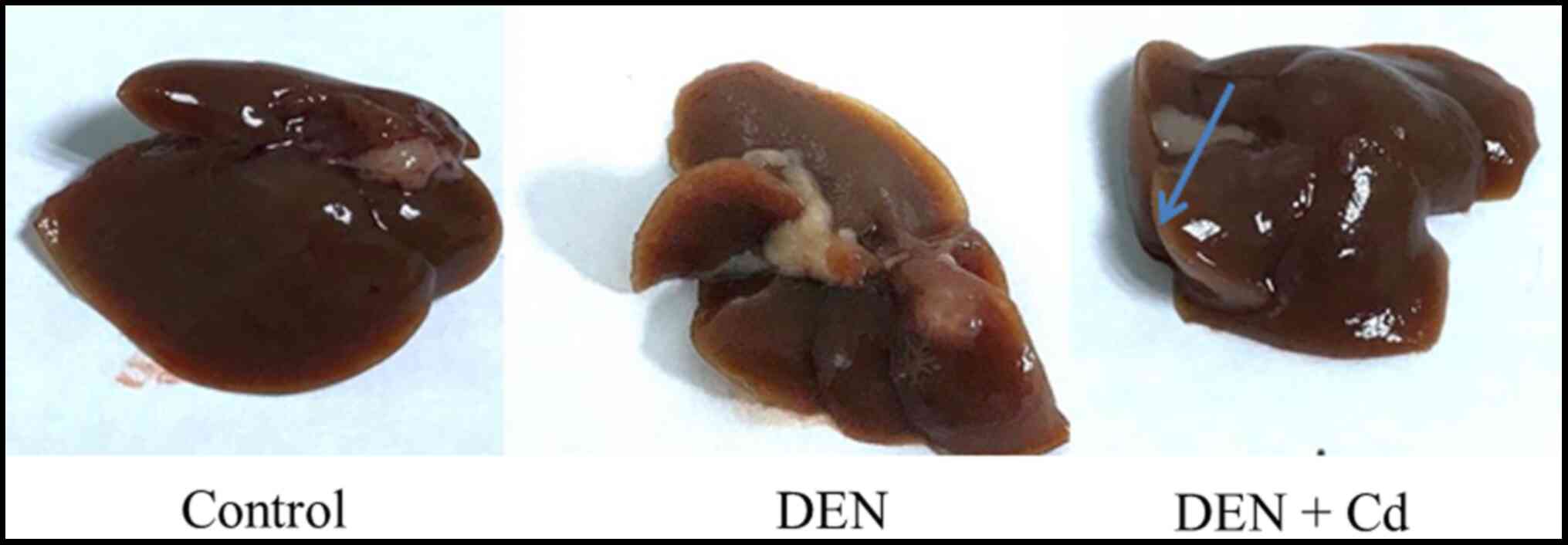
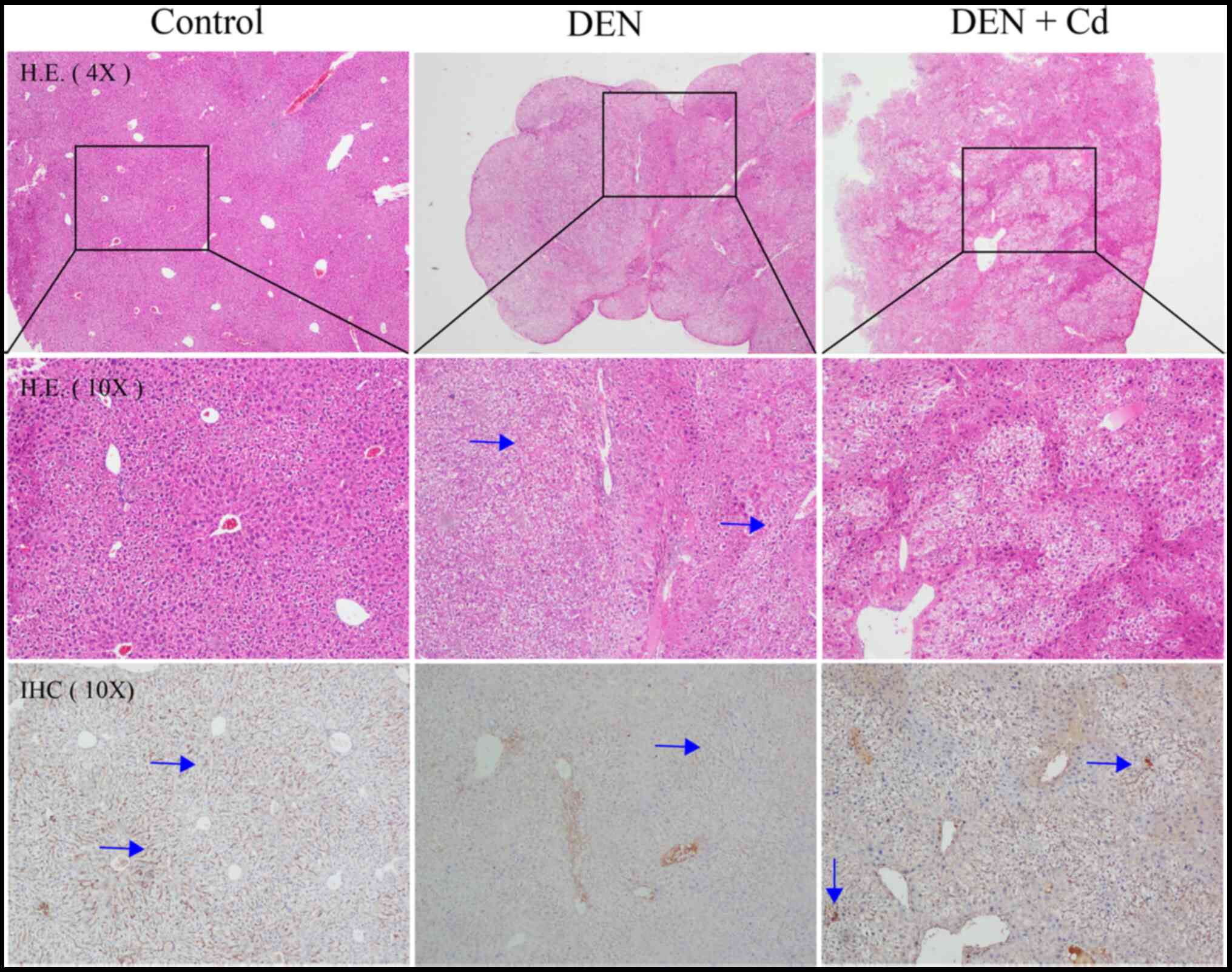
|
1
|
Wörns MA and Galle PR: Future perspectives
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 42 (Suppl 3):S302–S309.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Javan H, Dayyani F and Abi-Jaoudeh N:
Therapy in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin Intervent
Radiol. 37:466–474. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kaluderović GN and Paschke R: Anticancer
metallotherapeutics in preclinical development. Curr Med Chem.
18:4738–4752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Waalkes MP: Cadmium carcinogenesis. Mutat
Res. 533:107–120. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Satarug S: Long-term exposure to cadmium
in food and cigarette smoke, liver effects and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Curr Drug Metab. 13:257–271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Waalkes MP, Diwan BA, Rehm S, Ward JM,
Moussa M, Cherian MG and Goyer RA: Down-regulation of
metallothionein expression in human and murine hepatocellular
tumors: Association with the tumor-necrotizing and antineoplastic
effects of cadmium in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 277:1026–1033.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Waalkes MP, Diwan BA, Weghorst CM, Bare
RM, Ward JM and Rice JM: Anticarcinogenic effects of cadmium in
B6C3F1 mouse liver and lung. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 110:327–335.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Waalkes MP, Diwan BA, Weghorst CM, Ward
JM, Rice JM, Cherian MG and Goyer RA: Further evidence of the
tumor-suppressive effects of cadmium in the B6C3F1 mouse liver and
lung: Late stage vulnerability of tumors to cadmium and the role of
metallothionein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 266:1656–1663.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du H, Liu X, Liu Y, Jin M, Huang W and Sun
Z: Inhibition effect of cadmium chloride on human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells SMMC7721. Chin J Publ Health. 22:194–195. 2006.
|
|
10
|
Du HJM, Liu Y, Liu X, Wang W and Sun Z:
Study on the anti-tumor effect of calcium chloride in vivo. Mod
Prev Med. 35:3763–3765. 2008.
|
|
11
|
Chen X, Wu J, Yang Q, Zhang X, Zhang P,
Liao S, He Z, Wang X, Zhao C and Liu J: Cadmium pyrithione
suppresses tumor growth in vitro and in vivo through inhibition of
proteasomal deubiquitinase. Biometals. 31:29–43. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu N, Piao M, Arkin K, Ren L, Zhang J, Hao
J, Zheng Y and Shang Q: Imaging of water soluble CdTe/CdS
core-shell quantum dots in inhibiting multidrug resistance of
cancer cells. Talanta. 201:309–316. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang G, Shi L, Selke M and Wang X: CdTe
quantum dots with daunorubicin induce apoptosis of
multidrug-resistant human hepatoma HepG2/ADM cells: In vitro and in
vivo evaluation. Nanoscale Res Lett. 6:4182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou X, Koizumi Y, Zhang M, Natsui M,
Koyota S, Yamada M, Kondo Y, Hamada F and Sugiyama T:
Cadmium-coordinated supramolecule suppresses tumor growth of T-cell
leukemia in mice. Cancer Sci. 106:635–641. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pérez JM, Cerrillo V, Matesanz AI, Millán
JM, Navarro P, Alonso C and Souza P: DNA interstrand cross-linking
efficiency and cytotoxic activity of novel
cadmium(II)-thiocarbodiazone complexes. ChemBioChem. 2:119–123.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo C, Li Y, Zhang H, Wang Z, Jin M, Zhang
L, An L, Hu G, Liu X, Liu Y, et al: Enhancement of
antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of cadmium chloride
combined with hSmac in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Chemotherapy. 57:27–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bjelogrlić S, Todorović TR, Cvijetić I,
Rodić MV, Vujčić M, Marković S, Araškov J, Janović B, Emhemmed F,
Muller CD, et al: A novel binuclear hydrazone-based Cd(II) complex
is a strong pro-apoptotic inducer with significant activity against
2D and 3D pancreatic cancer stem cells. J Inorg Biochem. 190:45–66.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jacob ST, Majumder S and Ghoshal K:
Suppression of metallothionein-I/II expression and its probable
molecular mechanisms. Environ Health Perspect. 110 (Suppl
5):827–830. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, Nishikawa Y,
Sugimoto H, Kanazumi N, Takeda S and Nakao A: Detection of
metallothionein 1G as a methylated tumor suppressor gene in human
hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel method of double combination
array analysis. Int J Oncol. 35:477–483. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tao X, Zheng JM, Xu AM, Chen XF and Zhang
SH: Downregulated expression of metallothionein and its
clinicopathological significance in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatol Res. 37:820–827. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Klaassen CD, Liu J and Choudhuri S:
Metallothionein: An intracellular protein to protect against
cadmium toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 39:267–294. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yi X, Long L, Yang C, Lu Y and Cheng M:
Maotai ameliorates diethylnitrosamine-initiated hepatocellular
carcinoma formation in mice. PLoS One. 9:e935992014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang B, Hu P, Hu A, Li Y, Shi W, Huang J,
Jiang Q, Xu S, Li L and Wu Q: Naringenin attenuates carotid
restenosis in rats after balloon injury through its
anti-inflammation and anti-oxidative effects via the RIP1-RIP3-MLKL
signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 855:167–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu A, Huang J, Li S, Gao Y, Wu L, Deng J,
Liu J, Gong Q, Li L and Xu S: Involvement of stromal cell-derived
factor-1α (SDF-1α), stem cell factor (SCF), fractalkine (FKN) and
VEGF in TSG protection against intimal hyperplasia in rat balloon
injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 110:887–894. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li H, Lu YF, Chen H and Liu J:
Dysregulation of metallothionein and circadian genes in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Chronobiol Int. 34:192–202. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fei W, Li C, Tao J, Cai X, Yao W, Ye Y,
Zhang Y, Yao Y, Song Q, Li F, et al: Construction of arsenic-metal
complexes loaded nanodrugs for solid tumor therapy: A mini review.
Int J Pharm. 583:1193852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iftode A, Drăghici GA, Macașoi I,
Marcovici I, Coricovac DE, Dragoi R, Tischer A, Kovatsi L,
Tsatsakis AM, Cretu O, et al: Exposure to cadmium and copper
triggers cytotoxic effects and epigenetic changes in human
colorectal carcinoma HT-29 cells. Exp Ther Med. 21:1002021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Anton N, Parlog A, Bou About G, Attia MF,
Wattenhofer-Donzé M, Jacobs H, Goncalves I, Robinet E, Sorg T and
Vandamme TF: Non-invasive quantitative imaging of hepatocellular
carcinoma growth in mice by micro-CT using liver-targeted iodinated
nano-emulsions. Sci Rep. 7:139352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Klaassen CD, Liu J and Diwan BA:
Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 238:215–220. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghufran H, Azam M, Mehmood A, Butt H and
Riazuddin S: Standardization of diethylnitrosamine-induced
hepatocellular carcinoma rat model with time based molecular
assessment. Exp Mol Pathol. 123:1047152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kayama F, Yoshida T, Elwell MR and Luster
MI: Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cadmium-induced
hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 131:224–234. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|