|
1
|
Harbeck N and Gnant M: Breast cancer.
Lancet. 389:1134–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Smith RA, Caleffi M, Albert US, Chen TH,
Duffy SW, Franceschi D and Nyström L; Global Summit Early Detection
and Access to Care Panel, . Breast cancer in limited-resource
countries: Early detection and access to care. Breast J. 12 (Suppl
1):S16–S26. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:409–418. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee MC and Jagsi R: Postmastectomy
radiation therapy: Indications and controversies. Surg Clin North
Am. 87511–526. (xi)2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group, .
Nielsen HM, Overgaard M, Grau C, Jensen AR and Overgaard J: Study
of failure pattern among high-risk breast cancer patients with or
without postmastectomy radiotherapy in addition to adjuvant
systemic therapy: Long-term results from the Danish breast cancer
cooperative group DBCG 82 b and c randomized studies. J Clin Oncol.
24:2268–2275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ragaz J, Olivotto IA, Spinelli JJ,
Phillips N, Jackson SM, Wilson KS, Knowling MA, Coppin CM, Weir L,
Gelmon K, et al: Locoregional radiation therapy in patients with
high-risk breast cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: 20-year
results of the British Columbia randomized trial. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 97:116–126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weigelt B, Peterse JL and van't Veer LJ:
Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:591–602. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bach DH, Lee SK and Sood AK: Circular RNAs
in cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 16:118–129. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gandellini P, Doldi V and Zaffaroni N:
microRNAs as players and signals in the metastatic cascade:
Implications for the development of novel anti-metastatic
therapies. Semin Cancer Biol. 44:132–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP and Lawler S:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol
Med. 20:460–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bertoli G, Cava C and Castiglioni I:
MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy
prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics.
5:1122–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Q, Peng F and Chen J: The role of
exosomal MicroRNAs in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 20:38842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Asiaf A, Ahmad ST, Arjumand W and Zargar
MA: MicroRNAs in breast cancer: Diagnostic and therapeutic
potential. Methods Mol Biol. 1699:23–43. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Troschel FM, Böhly N, Borrmann K, Braun T,
Schwickert A, Kiesel L, Eich HT, Götte M and Greve B: miR-142-3p
attenuates breast cancer stem cell characteristics and decreases
radioresistance in vitro. Tumour Biol. 40:10104283187918872018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Soheilyfar S, Velashjerdi Z, Sayed
Hajizadeh Y, Fathi Maroufi N, Amini Z, Khorrami A, Haj Azimian S,
Isazadeh A, Taefehshokr S and Taefehshokr N: In vivo and in vitro
impact of miR-31 and miR-143 on the suppression of metastasis and
invasion in breast cancer. J BUON. 23:1290–1296. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen C, Liu X, Chen C, Chen Q, Dong Y and
Hou B: Clinical significance of let-7a-5p and miR-21-5p in patients
with breast cancer. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 49:302–308. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li M, Zou X, Xia T, Wang T, Liu P, Zhou X,
Wang S and Zhu W: A five-miRNA panel in plasma was identified for
breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Med. 8:7006–7017. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang C, Pang L, Shi Q, Liu X and Liu Y:
The diagnostic value of serum miR-129 in breast cancer patients
with bone metastasis. Clin Lab. 66:1904382020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shao Y, Yao Y, Xiao P, Yang X and Zhang D:
Serum miR-22 could be a potential biomarker for the prognosis of
breast cancer. Clin Lab. 65:2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang HL, Wang XX and Zhang F:
Correlations of the MiR-330 expression with the pathogenesis and
prognosis of breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:1584–1590. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anwar SL, Sari DNI, Kartika AI, Fitria MS,
Tanjung DS, Rakhmina D, Wardana T, Astuti I, Haryana SM and
Aryandono T: Upregulation of circulating MiR-21 expression as a
potential biomarker for therapeutic monitoring and clinical outcome
in breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 20:1223–1228. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Song C, Tang H, Zhang C, Tang J,
Li X, Chen B and Xie X: miR-629-3p may serve as a novel biomarker
and potential therapeutic target for lung metastases of
triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 19:722017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He M, Zhan M, Chen W, Xu S, Long M, Shen
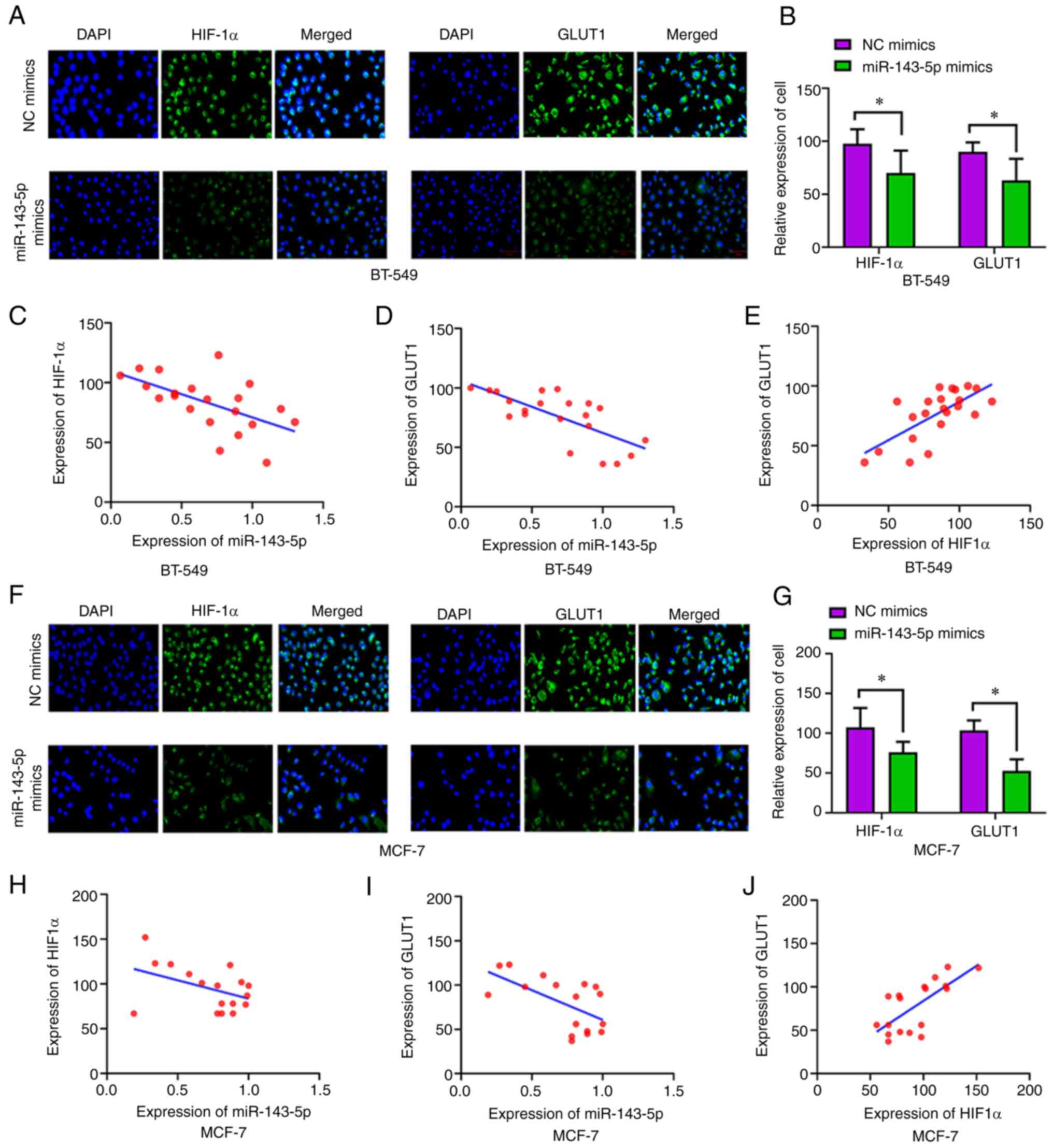
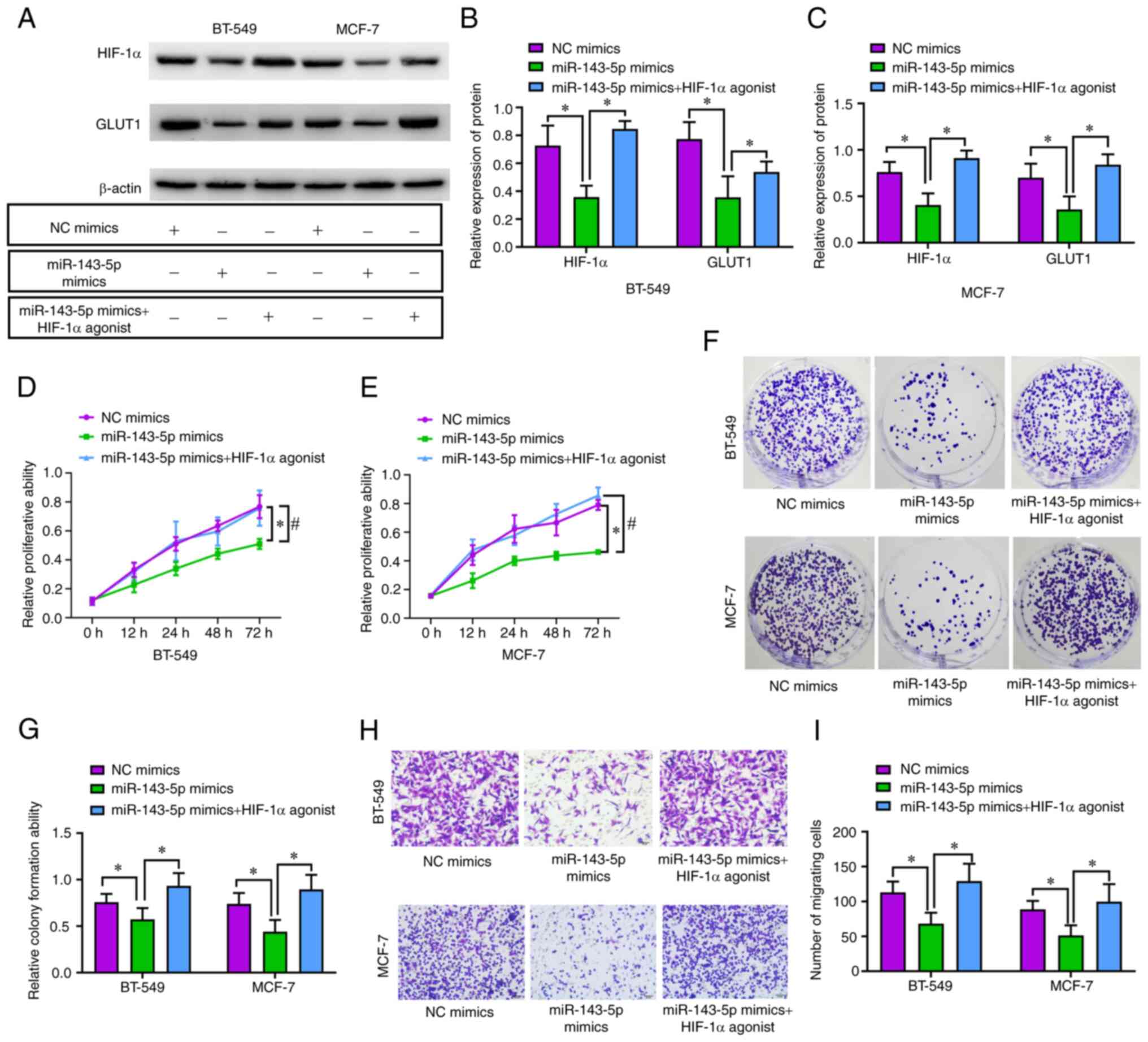
H, Shi Y, Liu Q, Mohan M and Wang J: MiR-143-5p deficiency triggers
EMT and metastasis by targeting HIF-1α in gallbladder cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 42:2078–2092. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sanada H, Seki N, Mizuno K, Misono S,
Uchida A, Yamada Y, Moriya S, Kikkawa N, Machida K, Kumamoto T, et
al: Involvement of dual strands of miR-143 (miR-143-5p and
miR-143-3p) and their target oncogenes in the molecular
pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 20:44822019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu C, Wang JO, Zhou WY, Chang XY, Zhang
MM, Zhang Y and Yang XH: Long non-coding RNA LINC01207 silencing
suppresses AGR2 expression to facilitate autophagy and apoptosis of
pancreatic cancer cells by sponging miR-143-5p. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 493:1104242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu F, Gao H, Liu K, Gao B, Ren H, Li Z and
Liu F: The lncRNA ZEB2-AS1 is upregulated in gastric cancer and
affects cell proliferation and invasion via miR-143-5p/HIF-1α axis.
Onco Targets Ther. 12:657–667. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu X, Hu L, Li S, Shen J, Wang D, Xu R and
Yang H: Long non-coding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 promotes
osteosarcoma cell metastasis by mediating HIF-1α via miR-143-5p.
Cell Death Dis. 10:2802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ferrer CM, Lynch TP, Sodi VL, Falcone JN,
Schwab LP, Peacock DL, Vocadlo DJ, Seagroves TN and Reginato MJ:
O-GlcNAcylation regulates cancer metabolism and survival stress
signaling via regulation of the HIF-1 pathway. Mol Cell.
54:820–831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chan M, Liaw CS, Ji SM, Tan HH, Wong CY,
Thike AA, Tan PH, Ho GH and Lee AS: Identification of circulating
microRNA signatures for breast cancer detection. Clin Cancer Res.
19:4477–4487. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang S, Wei L, Sun Y, Zhou F, Zhu S, Yang
R, Huang Y, Zhang H, Xu H and Yang J: CA153 in breast secretions as
a potential molecular marker for diagnosing breast cancer: A meta
analysis. PLoS One. 11:e01630302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li X, Zeng Z, Wang J, Wu Y, Chen W, Zheng
L, Xi T, Wang A and Lu Y: MicroRNA-9 and breast cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 122:1096872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao W, Geng D, Li S, Chen Z and Sun M:
LncRNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration, invasion, and
apoptosis via the miR-20a-5p/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer. Cancer
Med. 7:842–855. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao B, Song X and Guan H: CircACAP2
promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting
miR-29a/b-3p-COL5A1 axis. Life Sci. 244:1171792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ren S, Liu J, Feng Y, Li Z, He L, Li L,
Cao X, Wang Z and Zhang Y: Knockdown of circDENND4C inhibits
glycolysis, migration and invasion by up-regulating miR-200b/c in
breast cancer under hypoxia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3882019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ardila HJ, Sanabria-Salas MC, Meneses X,
Rios R, Huertas-Salgado A and Serrano ML: Circulating miR-141-3p,
miR-143-3p and miR-200c-3p are differentially expressed in
colorectal cancer and advanced adenomas. Mol Clin Oncol.
11:201–207. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Toda H, Seki N, Kurozumi S, Shinden Y,
Yamada Y, Nohata N, Moriya S, Idichi T, Maemura K, Fujii T, et al:
RNA-sequence-based microRNA expression signature in breast cancer:
Tumor-suppressive miR-101-5p regulates molecular pathogenesis. Mol
Oncol. 14:426–446. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
García-Vazquez R, Ruiz-García E, Meneses
García A, Astudillo-de la Vega H, Lara-Medina F, Alvarado-Miranda
A, Maldonado-Martínez H, González-Barrios JA, Campos-Parra AD,
Rodríguez Cuevas S, et al: A microRNA signature associated with
pathological complete response to novel neoadjuvant therapy regimen
in triple-negative breast cancer. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177028992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Caritg O, Navarro A, Moreno I,
Martínez-Rodenas F, Cordeiro A, Muñoz C, Ruiz-Martinez M,
Santasusagna S, Castellano JJ and Monzó M: Identifying high-risk
stage II colon cancer patients: A three-MicroRNA-based score as a
prognostic biomarker. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 15:e175–e182. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li RL, He LY, Zhang Q, Liu J, Lu F, Duan
HX, Fan LH, Peng W, Huang YL and Wu CJ: HIF-1α is a potential
molecular target for herbal medicine to treat diseases. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 14:4915–4949. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xia Y, Jiang L and Zhong T: The role of
HIF-1α in chemo-/radioresistant tumors. Onco Targets Ther.
11:3003–3011. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ioannou M, Paraskeva E, Baxevanidou K,
Simos G, Papamichali R, Papacharalambous C, Samara M and Koukoulis
G: HIF-1α in colorectal carcinoma: Review of the literature. J
BUON. 20:680–689. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brooks DL, Schwab LP, Krutilina R, Parke
DN, Sethuraman A, Hoogewijs D, Schörg A, Gotwald L, Fan M, Wenger
RH and Seagroves TN: ITGA6 is directly regulated by
hypoxia-inducible factors and enriches for cancer stem cell
activity and invasion in metastatic breast cancer models. Mol
Cancer. 15:262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Byun Y, Choi YC, Jeong Y, Lee G, Yoon S,
Jeong Y, Yoon J and Baek K: MiR-200c downregulates HIF-1α and
inhibits migration of lung cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
24:282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li H, Jia Y and Wang Y: Targeting HIF-1α
signaling pathway for gastric cancer treatment. Pharmazie. 74:3–7.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Amann T and Hellerbrand C: GLUT1 as a
therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 13:1411–1427. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Moreno-Sánchez R, Rodríguez-Enríquez S,
Marín-Hernández A and Saavedra E: Energy metabolism in tumor cells.
FEBS J. 274:1393–1418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gu NJ, Wu MZ, He L, Wang XB, Wang S, Qiu
XS, Wang EH and Wu GP: HPV 16 E6/E7 up-regulate the expression of
both HIF-1α and GLUT1 by inhibition of RRAD and activation of NF-κB
in lung cancer cells. J Cancer. 10:6903–6909. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Song K, Li M, Xu XJ, Xuan L, Huang GN,
Song XL and Liu QF: HIF-1α and GLUT1 gene expression is associated
with chemoresistance of acute myeloid leukemia. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:1823–1829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen C, Pore N, Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F
and Maity A: Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible
factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J Biol Chem.
276:9519–9525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Murakami T, Nishiyama T, Shirotani T,
Shinohara Y, Kan M, Ishii K, Kanai F, Nakazuru S and Ebina Y:
Identification of two enhancer elements in the gene encoding the
type 1 glucose transporter from the mouse which are responsive to
serum, growth factor, and oncogenes. J Biol Chem. 267:9300–9306.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ebert BL, Firth JD and Ratcliffe PJ:
Hypoxia and mitochondrial inhibitors regulate expression of glucose
transporter-1 via distinct Cis-acting sequences. J Biol Chem.
270:29083–29089. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang E, Zhang C, Polavaram N, Liu F, Wu G,
Schroeder MA, Lau JS, Mukhopadhyay D, Jiang SW, O'Neill BP, et al:
The role of factor inhibiting HIF (FIH-1) in inhibiting HIF-1
transcriptional activity in glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS One.
9:e861022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|