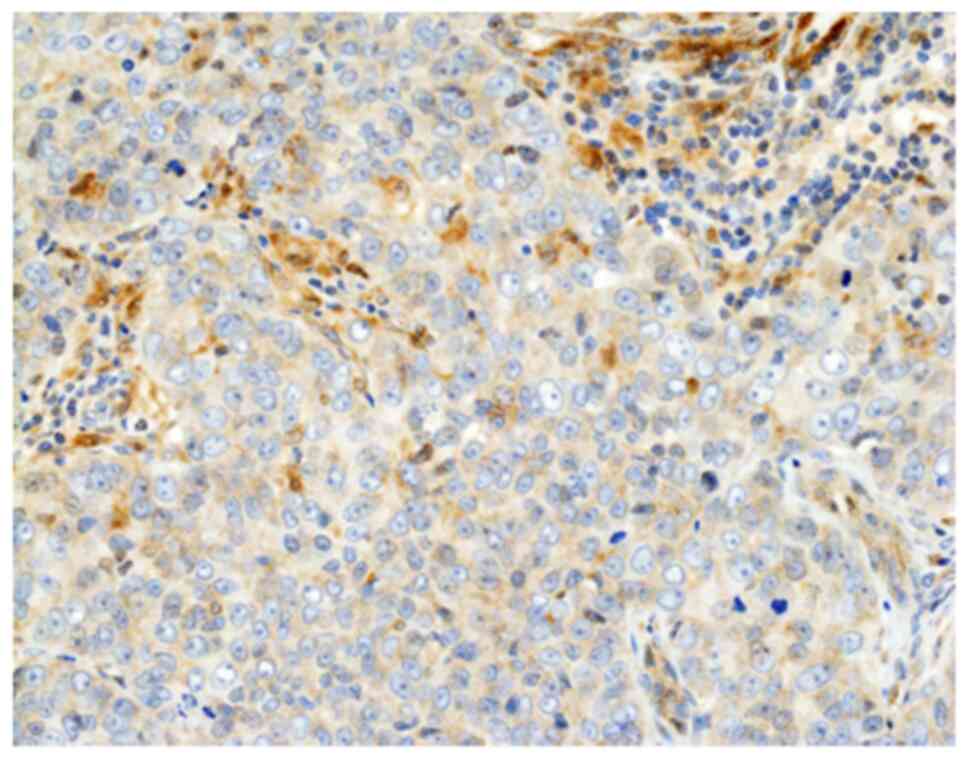
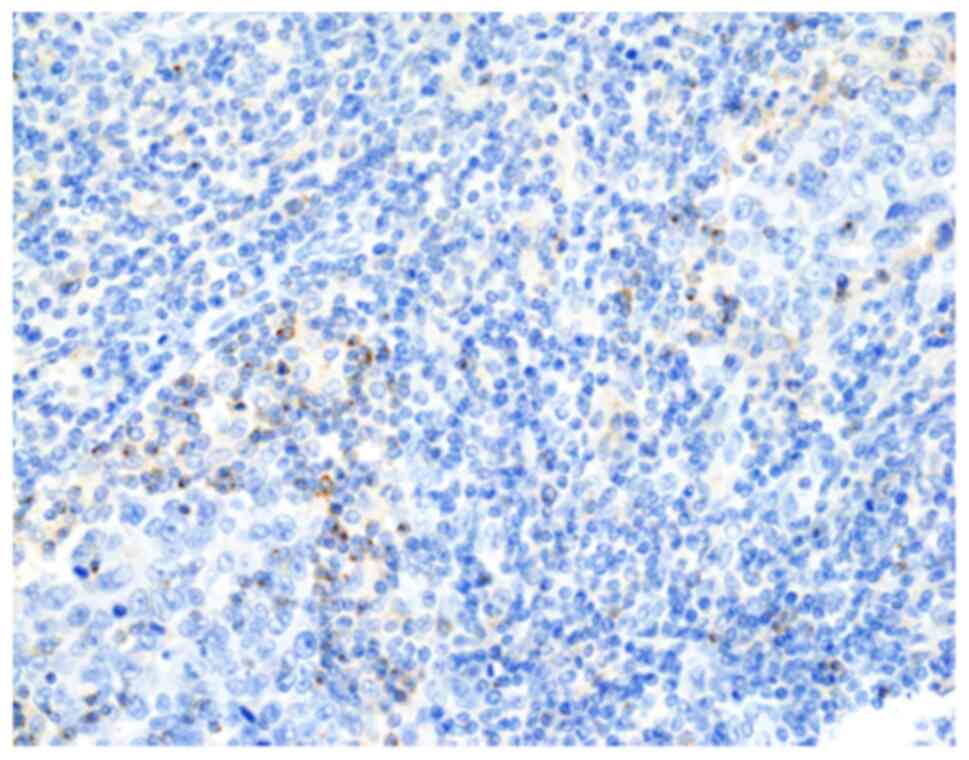
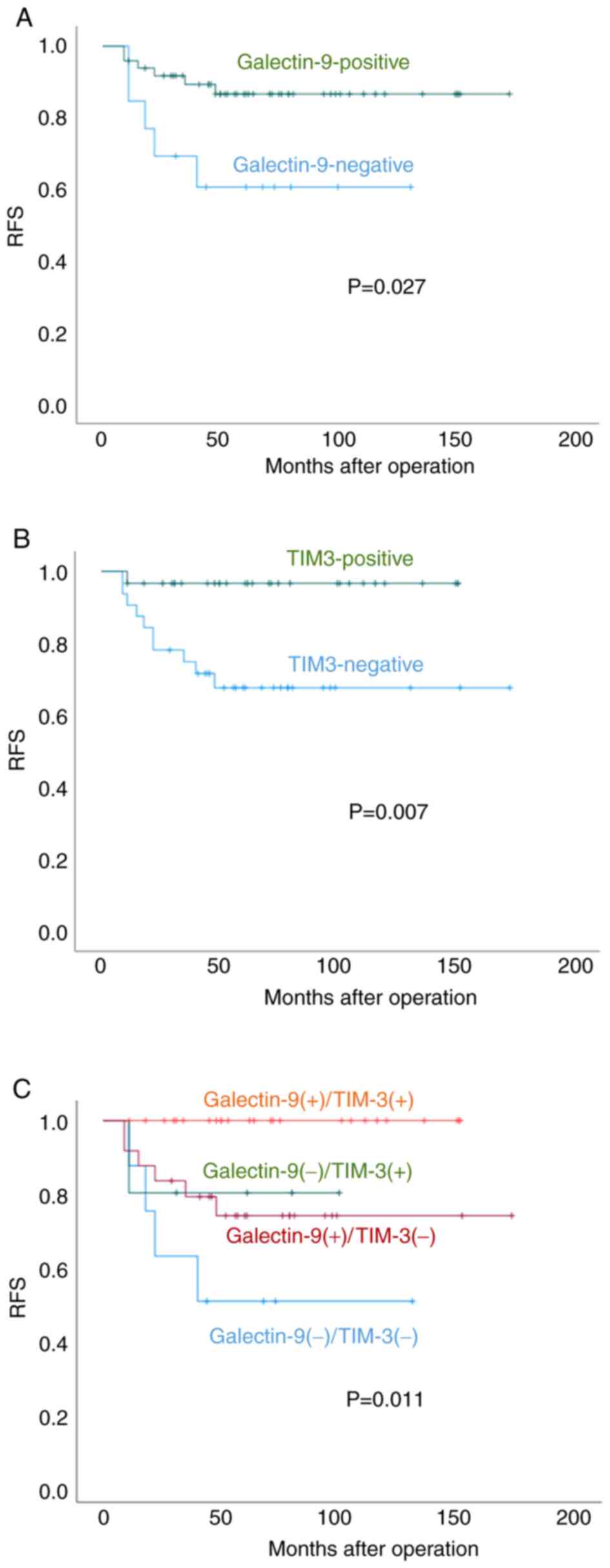
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cleator S, Heller W and Coombes RC:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Therapeutic options. Lancet Oncol.
8:235–244. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kakimi K, Karasaki T, Matsushita H and
Sugie T: Advances in personalized cancer immunotherapy. Breast
Cancer. 24:16–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma P and Allison JP: The future of
immune checkpoint therapy. Science. 348:56–61. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, Schneeweiss A,
Barrios CH, Iwata H, Diéras V, Hegg R, Im SA, Shaw Wright G, et al:
Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast
cancer. N Engl J Med. 379:2108–2121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cortes J, Cescon DW, Rugo HS, Nowecki Z,
Im SA, Yusof MM, Gallardo C, Lipatov O, Barrios CH, Holgado E, et
al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus
chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable
or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-355): A
randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical
trial. Lancet. 396:1817–1828. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mittendorf EA, Philips AV, Meric-Bernstam
F, Qiao N, Wu Y, Harrington S, Su X, Wang Y, Gonzalez-Angulo AM,
Akcakanat A, et al: PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast
cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:361–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tung N, Garber JE, Hacker MR, Torous V,
Freeman GJ, Poles E, Rodig S, Alexander B, Lee L, Collins LC and
Schnitt SJ: Prevalence and predictors of androgen receptor and
programmed death-ligand 1 in BRCA1-associated and sporadic
triple-negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2:160022016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ali HR, Glont SE, Blows FM, Provenzano E,
Dawson SJ, Liu B, Hiller L, Dunn J, Poole CJ, Bowden S, et al:
PD-L1 protein expression in breast cancer is rare, enriched in
basal-like tumours and associated with infiltrating lymphocytes.
Ann Oncol. 26:1488–1493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang C, Zhu H, Zhou Y, Mao F, Lin Y, Pan
B, Zhang X, Xu Q, Huang X and Sun Q: Prognostic value of PD-L1 in
breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast J. 23:436–443. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dill EA, Gru AA, Atkins KA, Friedman LA,
Moore ME, Bullock TN, Cross JV, Dillon PM and Mills AM: PD-L1
expression and intratumoral heterogeneity across breast cancer
subtypes and stages: An assessment of 245 primary and 40 metastatic
tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 41:334–342. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mori H, Kubo M, Yamaguchi R, Nishimura R,
Osako T, Arima N, Okumura Y, Okido M, Yamada M, Kai M, et al: The
combination of PD-L1 expression and decreased tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes is associated with a poor prognosis in triple-negative
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:15584–15592. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li Z, Dong P, Ren M, Song Y, Qian X, Yang
Y, Li S, Zhang X and Liu F: PD-L1 expression is associated with
tumor FOXP3 (+) regulatory T-cell infiltration of breast cancer and
poor prognosis of patient. J Cancer. 7:784–793. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gong B, Kiyotani K, Sakata S, Nagano S,
Kumehara S, Baba S, Besse B, Yanagitani N, Friboulet L, Nishio M,
et al: Secreted PD-L1 variants mediate resistance to PD-L1 blockade
therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Med. 216:982–1000.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wolf Y, Anderson AC and Kuchroo VK: TIM3
comes of age as an inhibitory receptor. Nat Rev Immunol.
20:173–185. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Monney L, Sabatos CA, Gaglia JL, Ryu A,
Waldner H, Chernova T, Manning S, Greenfield EA, Coyle AJ, Sobel
RA, et al: Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates
macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease.
Nature. 415:536–541. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Mingo Pulido A, Gardner A, Hiebler S,
Soliman H, Rugo HS, Krummel MF, Coussens LM and Ruffell B: TIM-3
regulates CD103+ dendritic cell function and response to
chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 33:60–74.e6. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yan W, Liu X, Ma H, Zhang H, Song X, Gao
L, Liang X and Ma C: Tim-3 fosters HCC development by enhancing
TGF-β-mediated alternative activation of macrophages. Gut.
64:1593–1604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong H,
Imitola J, Khoury SJ, Zheng XX, Strom TB and Kuchroo VK: The Tim-3
ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity.
Nat Immunol. 6:1245–1252. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sabatos-Peyton CA, Nevin J, Brock A,
Venable JD, Tan DJ, Kassam N, Xu F, Taraszka J, Wesemann L, Pertel
T, et al: Blockade of Tim-3 binding to phosphatidylserine and
CEACAM1 is a shared feature of anti-Tim-3 antibodies that have
functional efficacy. Oncoimmunology. 7:e13856902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gitt MA and Barondes SH: Evidence that a
human soluble beta-galactoside-binding lectin is encoded by a
family of genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:7603–7607. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paroutaud P, Levi G, Teichberg VI and
Strosberg AD: Extensive amino acid sequence homologies between
animal lectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:6345–6348. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caron M, Bladier D and Joubert R: Soluble
galactoside-binding vertebrate lectins: A protein family with
common properties. Int J Biochem. 22:1379–1385. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kikushige Y, Miyamoto T, Yuda J,
Jabbarzadeh-Tabrizi S, Shima T, Takayanagi S, Niiro H, Yurino A,
Miyawaki K, Takenaka K, et al: A TIM-3/Gal-9 autocrine stimulatory
loop drives self-renewal of human myeloid leukemia stem cells and
leukemic progression. Cell Stem Cell. 17:341–352. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gonçalves Silva I, Yasinska IM, Sakhnevych
SS, Fiedler W, Wellbrock J, Bardelli M, Varani L, Hussain R,
Siligardi G, Ceccone G, et al: The Tim-3-galectin-9 secretory
pathway is involved in the immune escape of human acute myeloid
leukemia cells. EBioMedicine. 22:44–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sakhnevych SS, Yasinska IM, Bratt AM,
Benlaouer O, Gonçalves Silva I, Hussain R, Siligardi G, Fiedler W,
Wellbrock J, Gibbs BF, et al: Cortisol facilitates the immune
escape of human acute myeloid leukemia cells by inducing
latrophilin 1 expression. Cell Mol Immunol. 15:994–997. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gonçalves Silva I, Rüegg L, Gibbs BF,
Bardelli M, Fruehwirth A, Varani L, Berger SM, Fasler-Kan E and
Sumbayev VV: The immune receptor Tim-3 acts as a trafficker in a
Tim-3/galectin-9 autocrine loop in human myeloid leukaemia cells.
Oncoimmunology. 5:e11955352016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA and
Ribas A: Primary adaptive and acquired resistance to cancer
immunotherapy. Cell. 168:707–723. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang R, Sun L, Li CF, Wang YH, Yao J, Li
H, Yan M, Chang WC, Hsu JM, Cha JH, et al: Galectin-9 interacts
with PD-1 and TIM-3 to regulate T cell death and is a target for
cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 12:8322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cong Y, Liu J, Chen G and Qiao G: The
emerging role of T-cell immunoglobulin Mucin-3 in breast cancer: A
promising target for immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 11:7232382021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jikuya R, Kishida T, Sakaguchi M, Yokose
T, Yasui M, Hashizume A, Tatenuma T, Mizuno N, Muraoka K, Umemoto
S, et al: Galectin-9 expression as a poor prognostic factor in
patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
69:2041–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Irie A, Yamauchi A, Kontani K, Kihara M,
Liu D, Shirato Y, Seki M, Nishi N, Nakamura T, Yokomise H, et al:
Galectin-9 as a prognostic factor with antimetastatic potential in
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2962–2968. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen H, Wang M, Weng T, Wei Y, Liu C, Yang
L, Ren K, Tang Y, Tang Z and Gou X: The prognostic and
clinicopathological significance of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression in
the prognosis of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol
Oncol. 39:743–753. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cabioglu N, Onder S, Oner G, Karatay H,
Tukenmez M, Muslumanoglu M, İgci A, Eralp Y, Aydiner A, Saip P, et
al: TIM3 expression on TILs is associated with poor response to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced
triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 21:3572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burugu S, Gao D, Leung S, Chia SK and
Nielsen TO: TIM-3 expression in breast cancer. Oncoimmunology.
7:e15021282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Byun KD, Hwang HJ, Park KJ, Kim MC, Cho
SH, Ju MH, Lee JH and Jeong JS: T-cell immunoglobulin mucin 3
expression on tumor infiltrating lymphocytes as a positive
prognosticator in triple-negative breast cancer. J Breast Cancer.
21:406–414. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rakha EA, Allison KH, Bu H, Ellis IO,
Foschini MP, Horii R, et al: Invasive breast carcinoma of no
special type. WHO classification of tumours: Breast tumours. 5th
edition. Volume 2. IARC; Lyon: pp. 102–109. 2019
|
|
40
|
Yoshikawa K, Ishida M, Yanai H, Tsuta K,
Sekimoto M and Sugie T: Adipophilin expression is an independent
marker for poor prognosis of patients with triple-negative breast
cancer: An immunohistochemical study. PLoS One. 15:e02425632020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoshikawa K, Ishida M, Yanai H, Tsuta K,
Sekimoto M and Sugie T: Prognostic significance of PD-L1-positive
cancer-associated fibroblasts in patients with triple-negative
breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 21:2392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yoshikawa K, Ishida M, Yanai H, Tsuta K,
Sekimoto M and Sugie T: Immunohistochemical analysis of CD155
expression in triple-negative breast cancer patients. PLoS One.
16:e02531762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoshikawa K, Ishida M, Yanai H, Tsuta K,
Sekimoto M and Sugie T: Immunohistochemical comparison of three
programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) assays in triple-negative breast
cancer. PLoS One. 16:e02578602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Elston CW and Ellis IO: Pathological
prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological
grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with
long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 19:403–410. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wu Q, Ma G, Deng Y, Luo W, Zhao Y, Li W
and Zhou Q: Prognostic value of Ki-67 in patients with resected
triple-negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Front Oncol.
9:10682019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine
N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G, Wienert S, Van den Eynden G, Baehner FL,
Penault-Llorca F, et al: The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an
International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann Oncol. 26:259–271. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Darb-Esfahani
S, Lederer B, Heppner BI, Weber KE, Budczies J, Huober J, Klauschen
F, Furlanetto J, et al: Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and
prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: A pooled analysis
of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol.
19:40–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sideras K, Biermann K, Verheij J,
Takkenberg BR, Mancham S, Hansen BE, Schutz HM, de Man RA,
Sprengers D, Buschow SI, et al: PD-L1, galectin-9 and
CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with
survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncoimmunology.
6:e12733092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zang K, Hui L, Wang M, Huang Y, Zhu X and
Yao B: TIM-3 as a Prognostic marker and a potential immunotherapy
target in human malignant tumors: A meta-analysis and
bioinformatics validation. Front Oncol. 11:5793512021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Saleh R, Toor SM and Elkord E: Targeting
TIM-3 in solid tumors: Innovations in the preclinical and
translational realm and therapeutic potential. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 24:1251–1262. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang H, Xiang R, Wu B, Li J and Luo G:
T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 expression in invasive ductal breast
carcinoma: Clinicopathological correlations and association with
tumor infiltration by cytotoxic lymphocytes. Mol Clin Oncol.
7:557–563. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Solinas C, Garaud S, De Silva P, Boisson
A, Van den Eynden G, de Wind A, Risso P, Rodrigues Vitória J,
Richard F, Migliori E, et al: Immune checkpoint molecules on
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and their association with tertiary
lymphoid structures in human breast cancer. Front Immunol.
8:14122017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Yasinska IM, Sakhnevych SS, Pavlova L, Teo
Hansen Selnø A, Teuscher Abeleira AM, Benlaouer O, Gonçalves Silva
I, Mosimann M, Varani L, Bardelli M, et al: The Tim-3-Galectin-9
pathway and its regulatory mechanisms in human breast cancer. Front
Immunol. 10:15942019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yamauchi A, Kontani K, Kihara M, Nishi N,
Yokomise H and Hirashima M: Galectin-9, a novel prognostic factor
with antimetastatic potential in breast cancer. Breast J. 12 (5
Suppl 2):S196–S200. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li H, Wu K, Tao K, Chen L, Zheng Q, Lu X,
Liu J, Shi L, Liu C, Wang G and Zou W: Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling
pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in
patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 56:1342–1351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang ZY, Dong JH, Chen YW, Wang XQ, Li
CH, Wang J, Wang GQ, Li HL and Wang XD: Galectin-9 acts as a
prognostic factor with antimetastatic potential in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:2503–2509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lee MJ, Heo YM, Hong SH, Kim K and Park S:
The binding properties of glycosylated and non-glycosylated Tim-3
molecules on CD4CD25 T cells. Immune Netw. 9:58–63. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sato M, Nishi N, Shoji H, Seki M,
Hashidate T, Hirabayashi J, Kasai Ki K, Hata Y, Suzuki S, Hirashima
M and Nakamura T: Functional analysis of the carbohydrate
recognition domains and a linker peptide of galectin-9 as to
eosinophil chemoattractant activity. Glycobiology. 12:191–197.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Barjon C, Niki T, Vérillaud B, Opolon P,
Bedossa P, Hirashima M, Blanchin S, Wassef M, Rosen HR, Jimenez AS,
et al: A novel monoclonal antibody for detection of galectin-9 in
tissue sections: Application to human tissues infected by oncogenic
viruses. Infect Agent Cancer. 7:162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yoon HK, Kim TH, Park S, Jung H, Quan X,
Park SJ, Han J and Lee A: Effect of anthracycline and taxane on the
expression of programmed cell death ligand-1 and galectin-9 in
triple-negative breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 214:1626–1631.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|