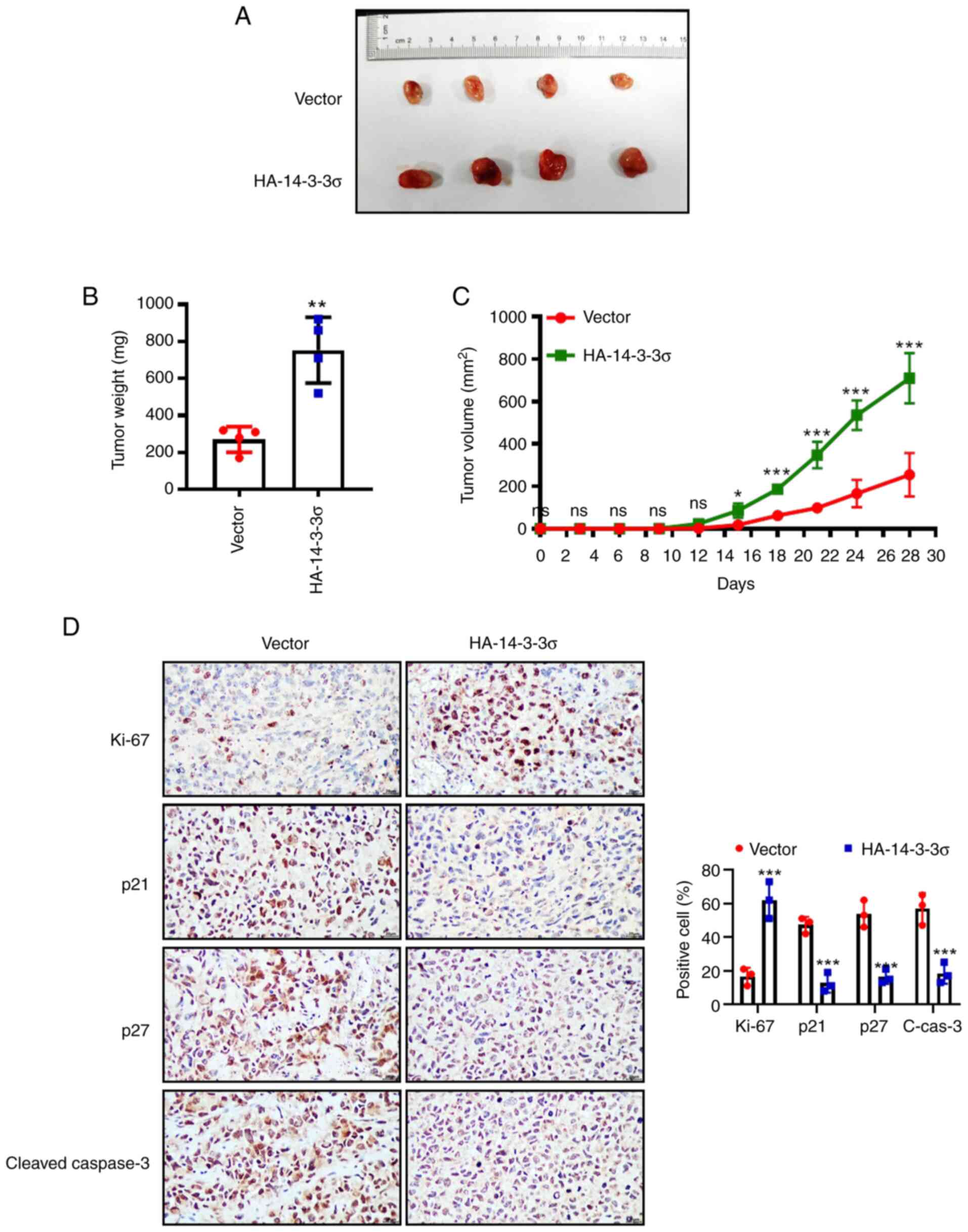
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Robinson KW and Sandler AB: The role of
MET receptor tyrosine kinase in non-small cell lung cancer and
clinical development of targeted anti-MET agents. Oncologist.
18:115–122. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kobayashi Y and Mitsudomi T: Not all
epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are
created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy.
Cancer Sci. 107:1179–1186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Karachaliou N, Santarpia M, Cao MZ,
Teixido C, Sosa AE, Berenguer J, Capote AR, Altavilla G and Rosell
R: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors in phase I and phase II
clinical trials for non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 26:713–722. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roviello G: The distinctive nature of
adenocarcinoma of the lung. Onco Targets Ther. 8:2399–2406. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sacco JJ, Al-Akhrass H and Wilson CM:
Challenges and strategies in precision medicine for non-small-cell
lung cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 22:4374–4385. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gainor JF, Dardaei L, Yoda S, Friboulet L,
Leshchiner I, Katayama R, Dagogo-Jack I, Gadgeel S, Schultz K,
Singh M, et al: Molecular mechanisms of resistance to first- and
second-generation ALK inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer.
Cancer Discov. 6:1118–1133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne
PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG and Halmos
B: EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 352:786–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Raungrut P, Wongkotsila A,
Lirdprapamongkol K, Svasti J, Geater SL, Phukaoloun M, Suwiwat S
and Thongsuksai P: Prognostic significance of 14-3-3gamma
overexpression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:3513–3518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Porter GW, Khuri FR and Fu H: Dynamic
14-3-3/client protein interactions integrate survival and apoptotic
pathways. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:193–202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Morrison DK: The 14-3-3 proteins:
Integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and
cancer development. Trends Cell Biol. 19:16–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huang Y, Yang M and Huang W: 14-3-3 σ: A
potential biomolecule for cancer therapy. Clin Chim Acta.
511:50–58. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ling C, Zuo D, Xue B, Muthuswamy S and
Muller WJ: A novel role for 14-3-3sigma in regulating epithelial
cell polarity. Genes Dev. 24:947–956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ling C, Su VM, Zuo D and Muller WJ: Loss
of the 14-3-3sigma tumor suppressor is a critical event in
ErbB2-mediated tumor progression. Cancer Discov. 2:68–81. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boudreau A, Tanner K, Wang D, Geyer FC,
Reis-Filho JS and Bissell MJ: 14-3-3sigma stabilizes a complex of
soluble actin and intermediate filament to enable breast tumor
invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E3937–E3944. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lodygin D and Hermeking H: The role of
epigenetic inactivation of 14-3-3sigma in human cancer. Cell Res.
15:237–246. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nacht M, Ferguson AT, Zhang W, Petroziello
JM, Cook BP, Gao YH, Maguire S, Riley D, Coppola G, Landes GM, et
al: Combining serial analysis of gene expression and array
technologies to identify genes differentially expressed in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 59:5464–5470. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ferguson AT, Evron E, Umbricht CB, Pandita
TK, Chan TA, Hermeking H, Marks JR, Lambers AR, Futreal PA,
Stampfer MR and Sukumar S: High frequency of hypermethylation at
the 14-3-3 sigma locus leads to gene silencing in breast cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:6049–6054. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lodygin D, Diebold J and Hermeking H:
Prostate cancer is characterized by epigenetic silencing of
14-3-3sigma expression. Oncogene. 23:9034–9041. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iwata N, Yamamoto H, Sasaki S, Itoh F,
Suzuki H, Kikuchi T, Kaneto H, Iku S, Ozeki I, Karino Y, et al:
Frequent hypermethylation of CpG islands and loss of expression of
the 14-3-3 sigma gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
19:5298–5302. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lodygin D, Epanchintsev A, Menssen A,
Diebold J and Hermeking H: Functional epigenomics identifies genes
frequently silenced in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 65:4218–4227.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okada T, Masuda N, Fukai Y, Shimura T,
Nishida Y, Hosouchi Y, Kashiwabara K, Nakajima T and Kuwano H:
Immunohistochemical expression of 14-3-3 sigma protein in
intraductal papillary-mucinous tumor and invasive ductal carcinoma
of the pancreas. Anticancer Res. 26((4B)): 3105–3110.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kuramitsu Y, Baron B, Yoshino S, Zhang X,
Tanaka T, Yashiro M, Hirakawa K, Oka M and Nakamura K: Proteomic
differential display analysis shows up-regulation of 14-3-3 sigma
protein in human scirrhous-type gastric carcinoma cells. Anticancer
Res. 30:4459–4465. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ito Y, Miyoshi E, Uda E, Yoshida H, Uruno
T, Takamura Y, Miya A, Kobayashi K, Matsuzuka F, Matsuura N, et al:
14-3-3 sigma possibly plays a constitutive role in papillary
carcinoma, but not in follicular tumor of the thyroid. Cancer Lett.
200:161–166. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Neal CL and Yu D: 14-3-3ζ as a prognostic
marker and therapeutic target for cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:1343–1354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guweidhi A, Kleeff J, Giese N, El Fitori
J, Ketterer K, Giese T, Büchler MW, Korc M and Friess H: Enhanced
expression of 14-3-3sigma in pancreatic cancer and its role in cell
cycle regulation and apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 25:1575–1585. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shiba-Ishii A, Kano J, Morishita Y, Sato
Y, Minami Y and Noguchi M: High expression of stratifin is a
universal abnormality during the course of malignant progression of
early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 129:2445–2453. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qi W, Liu X, Qiao D and Martinez JD:
Isoform-specific expression of 14-3-3 proteins in human lung cancer
tissues. Int J Cancer. 113:359–363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cetintas VB, Tetik A, Cok G, Kucukaslan
AS, Kosova B, Gunduz C, Veral A and Eroglu Z: Role of 14-3-3sigma
in resistance to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Cell Biol Int. 37:78–86. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Radhakrishnan VM, Jensen TJ, Cui H,
Futscher BW and Martinez JD: Hypomethylation of the 14-3-3sigma
promoter leads to increased expression in non-small cell lung
cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 50:830–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang R, Yan B, Li Z, Jiang Y, Mao C, Wang
X and Zhou X: Long non-coding RNA HOX transcript antisense RNA
promotes expression of 14-3-3sigma in non-small cell lung cancer.
Exp Ther Med. 14:4503–4508. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carbone L: Pain management standards in
the eighth edition of the guide for the care and use of laboratory
animals. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51:322–328. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Xu J, Zhou W, Yang F, Chen G, Li H, Zhao
Y, Liu P, Li H, Tan M, Xiong X and Sun Y: The β-TrCP-FBXW2-SKP2
axis regulates lung cancer cell growth with FBXW2 acting as a
tumour suppressor. Nat Commun. 8:140022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu Q, Tan M and Sun Y: SAG/ROC2/Rbx2 is a
novel activator protein-1 target that promotes c-Jun degradation
and inhibits 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced
neoplastic transformation. Cancer Res. 67:3616–3625. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shang W, Liang X, Li S, Li T, Zheng L,
Shao W, Wang Y, Liu F, Ma L and Jia J: Orphan nuclear receptor
Nurr1 promotes Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric
carcinogenesis by directly enhancing CDK4 expression. EBioMedicine.
53:1026722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou WH, Tang F, Xu J, Wu X, Yang SB, Feng
ZY, Ding YG, Wan XB, Guan Z, Li HG, et al: Low expression of Beclin
1, associated with high Bcl-xL, predicts a malignant phenotype and
poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Autophagy. 8:389–400. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou W, Xu J, Tan M, Li H, Li H, Wei W and
Sun Y: UBE2M is a stress-inducible dual E2 for neddylation and
ubiquitylation that promotes targeted degradation of UBE2F. Mol
Cell. 70:1008–1024. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A
and Nicholson AG: Introduction to The 2015 world health
organization classification of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus,
and heart. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1240–1242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Yuan Y, Li Y, Zhang P, Chen P and
Sun S: An inverse interaction between HOXA11 and HOXA11-AS is
associated with cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma.
Epigenetics. 14:949–960. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jin CY, Du L, Nuerlan AH, Wang XL, Yang YW
and Guo R: High expression of RRM2 as an independent predictive
factor of poor prognosis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.
Aging (Albany NY). 13:3518–3535. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yu Y and Tian X: Analysis of genes
associated with prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma based on GEO and
TCGA databases. Medicine (Baltimore). 99:e201832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Liu X, Liu L, Li J, Hu Q and Sun
R: Expression and prognostic significance of m6A-related genes in
lung adenocarcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 26:e9196442020.
|
|
43
|
Dellinger RW, Karjian PL and Neuteboom ST:
NB1011 induces Ser15 phosphorylation of p53 and activates the G2/M
checkpoint. Anticancer Drugs. 14:449–455. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Holm R, Ali T, Svendsrud DH, Nesland JM,
Kristensen GB and Lyng H: Expression of 14-3-3sigma in cervical
squamous cell carcinomas: Relationship with clinical outcome. Oncol
Rep. 22:11–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Horie-Inoue K and Inoue S: Epigenetic and
proteolytic inactivation of 14-3-3sigma in breast and prostate
cancers. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:235–239. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Simpson PT, Gale T, Reis-Filho JS, Jones
C, Parry S, Steele D, Cossu A, Budroni M, Palmieri G and Lakhani
SR: Distribution and significance of 14-3-3sigma, a novel
myoepithelial marker, in normal, benign, and malignant breast
tissue. J Pathol. 202:274–285. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Neal CL, Yao J, Yang W, Zhou X, Nguyen NT,
Lu J, Danes CG, Guo H, Lan KH, Ensor J, et al: 14-3-3zeta
overexpression defines high risk for breast cancer recurrence and
promotes cancer cell survival. Cancer Res. 69:3425–3432. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nakayama H, Sano T, Motegi A, Oyama T and
Nakajima T: Increasing 14-3-3 sigma expression with declining
estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen-responsive finger protein
expression defines malignant progression of endometrial carcinoma.
Pathol Int. 55:707–715. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Akahira J, Sugihashi Y, Suzuki T, Ito K,
Niikura H, Moriya T, Nitta M, Okamura H, Inoue S, Sasano H, et al:
Decreased expression of 14-3-3 sigma is associated with advanced
disease in human epithelial ovarian cancer: Its correlation with
aberrant DNA methylation. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2687–2693. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li Z, Dong Z, Myer D, Yip-Schneider M, Liu
J, Cui P, Schmidt CM and Zhang JT: Role of 14-3-3sigma in poor
prognosis and in radiation and drug resistance of human pancreatic
cancers. BMC Cancer. 10:5982010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Perathoner A, Pirkebner D, Brandacher G,
Spizzo G, Stadlmann S, Obrist P, Margreiter R and Amberger A:
14-3-3sigma expression is an independent prognostic parameter for
poor survival in colorectal carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res.
11:3274–3279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|