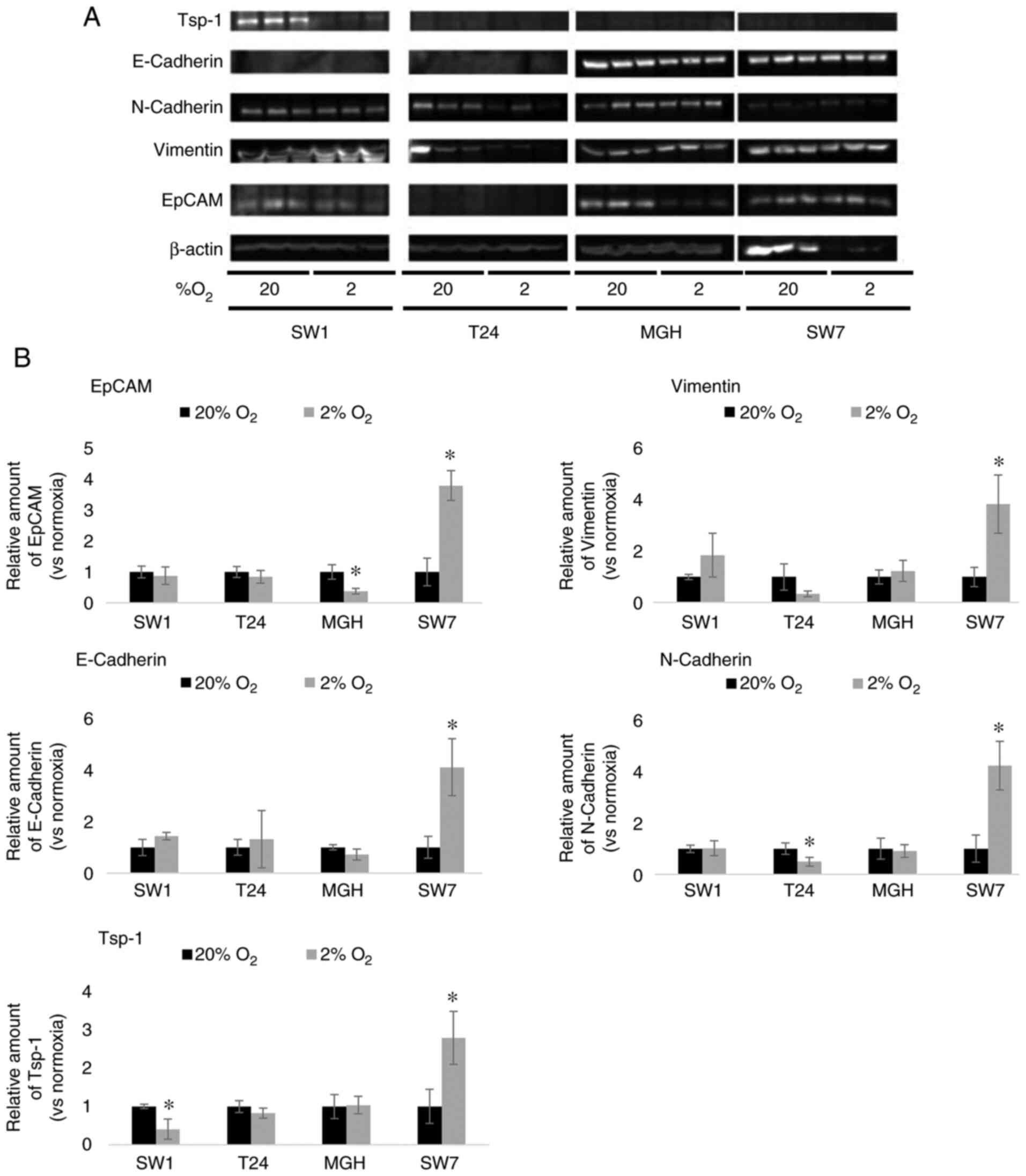
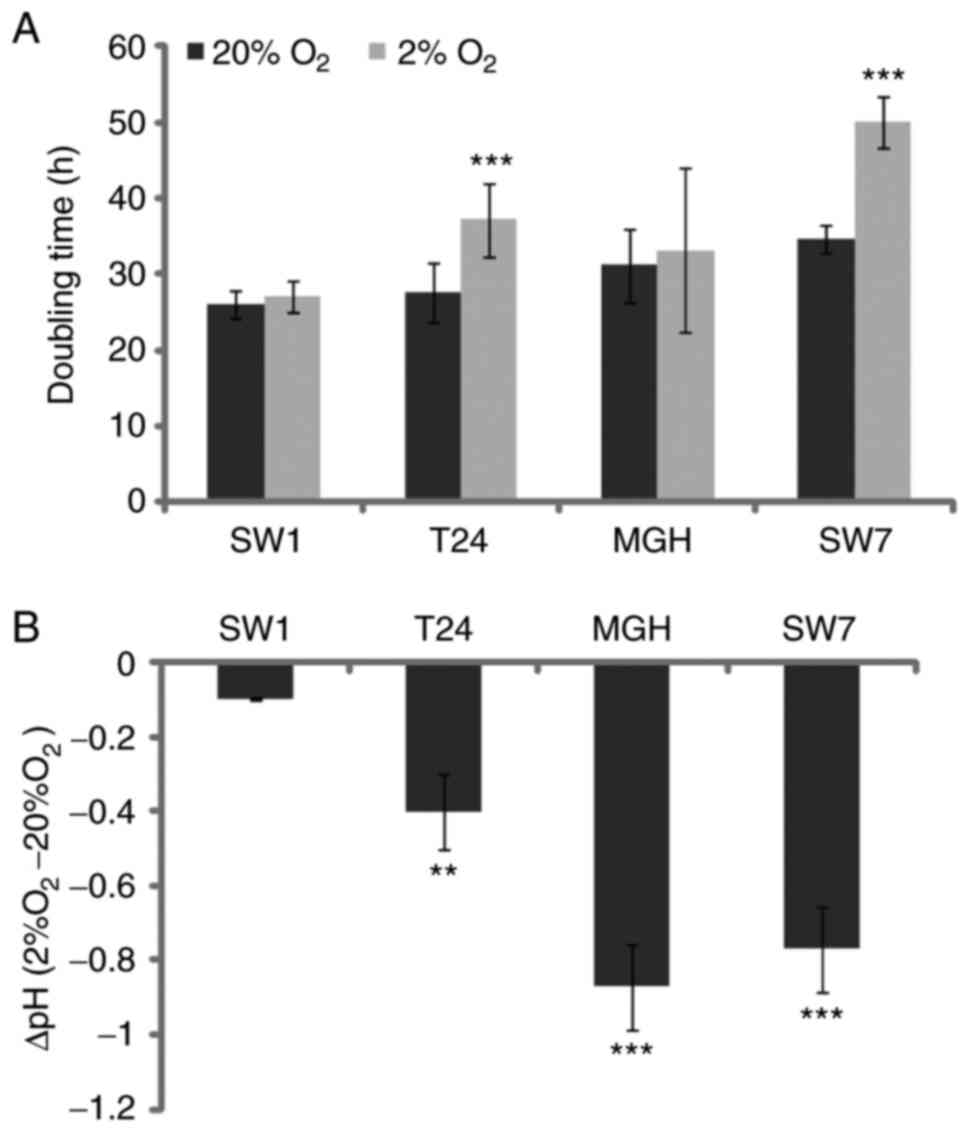
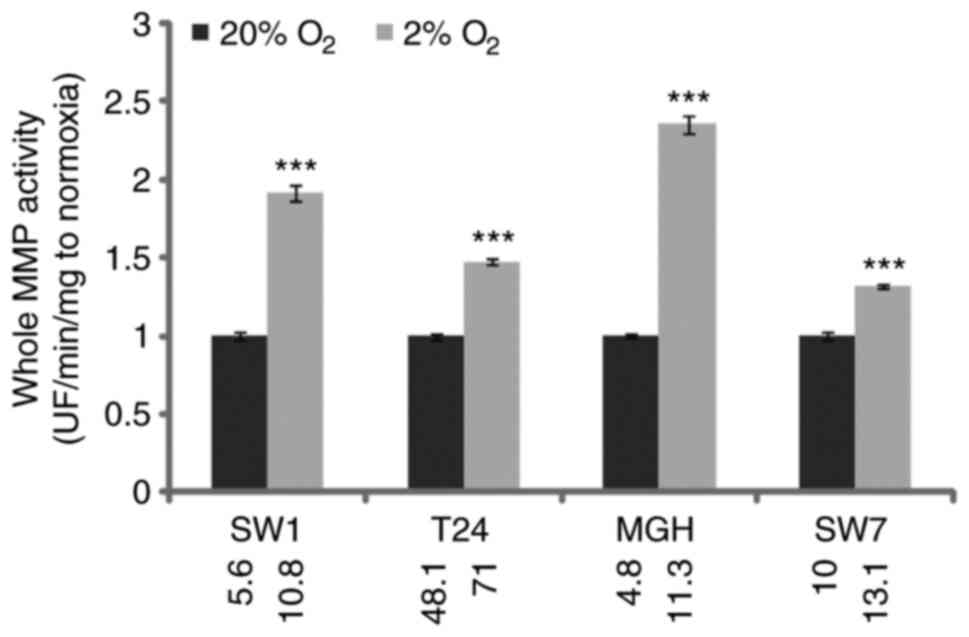
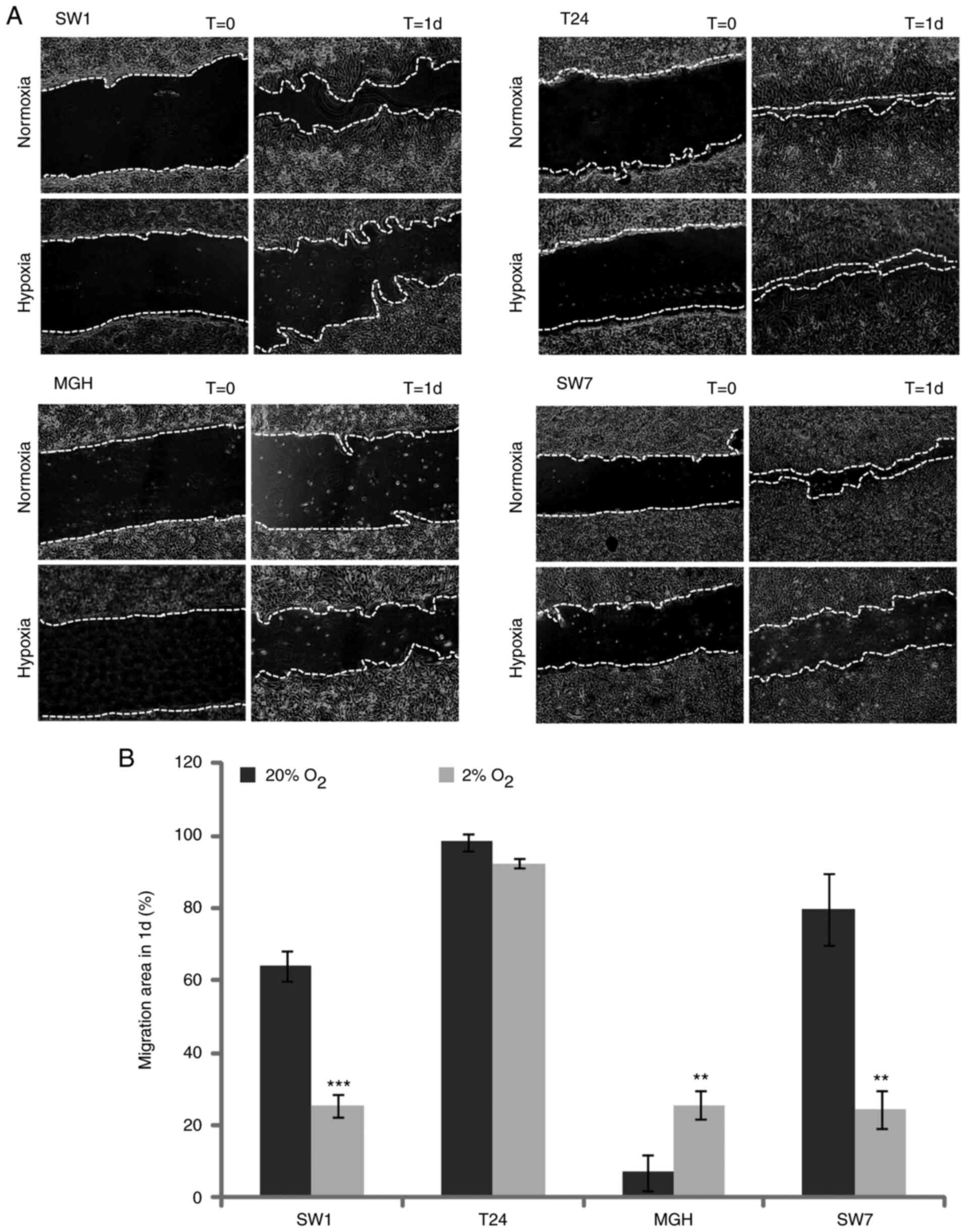
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feifer AH, Taylor JM, Tarin TV and Herr
HW: Maximizing cure for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Integration
of surgery and chemotherapy. Eur Urol. 59:978–984. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Folkman J: What is the evidence that
tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:4–6.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vaupel P, Kallinowski F and Okunief P:
Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic
microenvironment of human tumors: A review. Cancer Res.
49:6449–6465. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Evans SM, Hahn SM, Magarelli DP and Koch
CJ: Hypoxic heterogeneity in human tumors: EF5 binding,
vasculature, necrosis, and proliferation. Am J Clin Oncol.
24:467–472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu L and Hales CA: Long-term exposure to
hypoxia inhibits tumor progression of lung cancer in rats and mice.
BMC Cancer. 11:3312011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koh MY, Lemos R Jr, Liu X and Powis G: The
hypoxia-associated factor switches cells from HIF-1α- to
HIF-2α-dependent signaling promoting stem cell characteristics,
aggressive tumor growth and invasion. Cancer Res. 71:4015–4027.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin Q and Yun Z: Impact of the hypoxic
tumor microenvironment on the regulation of cancer stem cell
characteristics. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:949–956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peixoto A, Fernandes E, Gaiteiro C, Lima
L, Azevedo R, Soares J, Cotton S, Parreira B, Neves M, Amaro T, et
al: Hypoxia enhances the malignant nature of bladder cancer cells
and concomitantly antagonizes protein O-glycosylation extension.
Oncotarget. 7:63138–63157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue M, Chen W, Xiang A, Wang R, Chen H,
Pan J, Pang H, An H, Wang X, Hou H and Li X: Hypoxic exosomes
facilitate bladder tumor growth and development through
transferring long non-coding RNA-UCA1. Mol Cancer. 16:1432017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tátrai E, Bartal A, Gacs A, Paku S,
Kenessey I, Garay T, Hegedűs B, Molnár E, Cserepes MT, Hegedűs Z,
et al: Cell type-dependent HIF1 α-mediated effects of hypoxia on
proliferation, migration and metastatic potential of human tumor
cells. Oncotarget. 8:44498–44510. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pachmayr E, Treese C and Stein U:
Underlying mechanisms for distant metastasis-molecular biology.
Visc Med. 33:11–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morandi A, Taddei ML, Chiarugi P and
Giannoni E: Targeting the metabolic reprogramming that controls
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in aggressive tumors. Front
Oncol. 7:402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fitzgerald G, Soro-Arnaiz I and De Bock K:
The Warburg effect in endothelial cells and its potential as an
anti-angiogenic target in cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 6:1002018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Butturini E, Carcereri de Prati A, Boriero
D and Mariotto S: Tumor dormancy and interplay with hypoxic tumor
microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 20:43052019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen
H and Shu Y: Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the
tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 18:1572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Hushmandi K, Hashemi M,
Akbari ME, Kubatka P, Raei M, Koklesova L, Shahinozzaman M,
Mohammadinejad R, Najafi M, et al: Role of
microRNA/epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition axis in the
metastasis of bladder cancer. Biomolecules. 10:11592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakanishi K, Hiroi S, Tominaga S, Aida S,
Kasamatsu H, Matsuyama S, Matsuyama T and Kawai T: Expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein predicts survival in
patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary
tract. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2583–2590. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eltz S, Comperat E, Cussenot O and Rouprêt
M: Molecular and histological markers in urothelial carcinomas of
the upper urinary tract. BJU Int. 102:532–535. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wan W, Peng K, Li M, Qin L, Tong Z, Yan J,
Shen B and Yu C: Histone demethylase JMJD1A promotes urinary
bladder cancer progression by enhancing glycolysis through
coactivation of hypoxia inducible factor 1α. Oncogene.
36:3868–3877. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP,
Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW and
Kurth K: Predicting recurrence and progression in individual
patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A
combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur
Urol. 49:466–477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reiterer M, Colaço R, Emrouznejad P,
Jensen A, Rundqvist H, Johnson RS and Branco C: Acute and chronic
hypoxia differentially predispose lungs for metastases. Sci Rep.
9:102462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nobre AR, Entenberg D, Wang Y, Condeelis J
and Aguirre-Ghiso JA: The different routes to metastasis via
hypoxia-regulated programs. Trends Cell Biol. 28:941–956. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Committee on toxicity testing and
assessment of environmental agents, N.R.C., toxicity testing in the
21st century. A Vision and a Strategy The National Academies Press;
2015
|
|
26
|
Lin CW, Lin JC and Prout GR Jr:
Establishment and characterization of four human bladder tumor cell
lines and sublines with different degrees of malignancy. Cancer
Res. 45:5070–5079. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chabaud S, Saba I, Baratange C, Boiroux B,
Leclerc M, Rousseau A, Bouhout S and Bolduc S: Urothelial cell
expansion and differentiation are improved by exposure to hypoxia.
J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 11:3090–3099. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ivanovic Z: Hypoxia or in situ normoxia:
The stem cell paradigm. J Cell Physiol. 219:271–275. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Keeley TP and Mann GE: Defining
physiological normoxia for improved translation of cell physiology
to animal models and humans. Physiol Rev. 99:161–234. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dyson A, Simon F, Seifritz A, Zimmerling
O, Matallo J, Calzia E, Radermacher P and Singer M: Bladder tissue
oxygen tension monitoring in pigs subjected to a range of
cardiorespiratory and pharmacological challenges. Intensive Care
Med. 38:1868–1876. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McKeown SR: Defining normoxia, physoxia
and hypoxia in tumours-implications for treatment response. Br J
Radiol. 87:201306762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abou Khouzam R, Zaarour RF, Brodaczewska
K, Azakir B, Venkatesh GH, Thiery J, Terry S and Chouaib S: The
effect of hypoxia and hypoxia-associated pathways in the regulation
of antitumor response: Friends or foes? Front Immunol.
13:8288752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Afonso J, Santos LL, Morais A, Amaro T,
Longatto-Filho A and Baltazar F: Metabolic coupling in urothelial
bladder cancer compartments and its correlation to tumor
aggressiveness. Cell Cycle. 15:368–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Marquis L, Martin F,
Williams MB, Shah J, Svatek R, Das A, Adam L, Kamat A, et al: Role
of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in drug sensitivity
and metastasis in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:335–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vaupel P and Mayer A: Hypoxia in cancer:
Significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:225–239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yoo YG, Christensen J, Gu J and Huang LE:
HIF-1α mediates tumor hypoxia to confer a perpetual mesenchymal
phenotype for malignant progression. Sci Signal.
4:pt42011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gao T, Li JZ, Lu Y, Zhang CY, Li Q, Mao J
and Li LH: The mechanism between epithelial mesenchymal transition
in breast cancer and hypoxia microenvironment. Biomed Pharmacother.
80:393–405. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fu Y, Ning L, Feng J, Yu X, Guan F and Li
X: Dynamic regulation of O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation on
STAT3 under hypoxia-induced EMT. Cell Signal. 93:1102772022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lv WL, Liu Q, An JH and Song XY:
Scutellarin inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in bladder cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
234:23169–23175. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Imrich S, Hachmeister M and Gires O: EpCAM
and its potential role in tumor-initiating cells. Cell Adh Migr.
6:30–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Trzpis M, McLaughlin PM, de Leij LM and
Harmsen MC: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule: More than a
carcinoma marker and adhesion molecule. Am J Pathol. 171:386–395.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brown TC, Sankpal NV and Gillanders WE:
Functional implications of the dynamic regulation of EpCAM during
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomolecules. 11:9562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fagotto F: EpCAM as modulator of tissue
plasticity. Cells. 9:21282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Usman S, Waseem NH, Nguyen TKN, Mohsin S,
Jamal A, Teh MT and Waseem A: Vimentin is at the heart of
epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) mediated metastasis.
Cancers (Basel). 13:49852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yun SJ and Kim WJ: Role of the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer: From prognosis
to therapeutic target. Korean J Urol. 54:645–650. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
DeBerardinis RJ: Is cancer a disease of
abnormal cellular metabolism? New angles on an old idea. Genet Med.
10:767–777. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bose S and Le A: Glucose metabolism in
cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1063:3–12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pérez-Tomás R and Pérez-Guillén I: Lactate
in the tumor microenvironment: An essential molecule in cancer
progression and treatment. Cancers (Basel). 12:32442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu L and Simon MC: Regulation of
transcription and translation by hypoxia. Cancer Biol Ther.
3:492–497. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Potter M, Newport E and Morten KJ: The
Warburg effect: 80 Years on. Biochem Soc Trans. 44:1499–1505. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zheng T, Jäättelä M and Liu B: pH gradient
reversal fuels cancer progression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
125:1057962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rodrigues D, Pinto J, Araújo AM, Jerónimo
C, Henrique R, Bastos ML, Guedes de Pinho P and Carvalho M: GC-MS
metabolomics reveals distinct profiles of low- and high-grade
bladder cancer cultured cells. Metabolites. 9:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang F, Ma S, Xue Y, Hou J and Zhang Y:
LDH-A promotes malignant progression via activation of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and conferring stemness in
muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
469:985–992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yuan D, Zheng S, Wang L, Li J, Yang J,
Wang B, Chen X and Zhang X: MiR-200c inhibits bladder cancer
progression by targeting lactate dehydrogenase A. Oncotarget.
8:67663–67669. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Goto M, Miwa H, Suganuma K, Tsunekawa-Imai
N, Shikami M, Mizutani M, Mizuno S, Hanamura I and Nitta M:
Adaptation of leukemia cells to hypoxic condition through switching
the energy metabolism or avoiding the oxidative stress. BMC Cancer.
14:762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lamonte G, Tang X, Chen JL, Wu J, Ding CK,
Keenan MM, Sangokoya C, Kung HN, Ilkayeva O, Boros LG, et al:
Acidosis induces reprogramming of cellular metabolism to mitigate
oxidative stress. Cancer Metab. 1:232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wanandi SI, Ningsih SS, Asikin H, Hosea R
and Neolaka GMG: Metabolic interplay between tumour cells and
cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) under hypoxia versus normoxia.
Malays J Med Sci. 25:7–16. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xue M, Li X, Li Z and Chen W: Urothelial
carcinoma associated 1 is a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-targeted
long noncoding RNA that enhances hypoxic bladder cancer cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion. Tumour Biol. 35:6901–6912.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ioachim E, Michael MC, Salmas M, Damala K,
Tsanou E, Michael MM, Malamou-Mitsi V and Stavropoulos NE:
Thrombospondin-1 expression in urothelial carcinoma: Prognostic
significance and association with p53 alterations, tumour
angiogenesis and extracellular matrix components. BMC Cancer.
6:1402006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Firlej V, Mathieu JR, Gilbert C, Lemonnier
L, Nakhlé J, Gallou-Kabani C, Guarmit B, Morin A, Prevarskaya N,
Delongchamps NB and Cabon F: Thrombospondin-1 triggers cell
migration and development of advanced prostate tumors. Cancer Res.
71:7649–7658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zeeshan R and Mutahir Z: Cancer
metastasis-tricks of the trade. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 17:172–182.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Majidpoor J and Mortezaee K: Steps in
metastasis: An updated review. Med Oncol. 38:32021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nguyen DX, Bos PD and Massagué J:
Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:274–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kanayama H: Matrix metalloproteinases and
bladder cancer. J Med Invest. 48:31–43. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Alfano M, Nebuloni M, Allevi R, Zerbi P,
Longhi E, Lucianò R, Locatelli I, Pecoraro A, Indrieri M, Speziali
C, et al: Linearized texture of three-dimensional extracellular
matrix is mandatory for bladder cancer cell invasion. Sci Rep.
6:361282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1
(HIF-1) pathway. Sci STKE. 2007:cm82007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1 and mechanisms of
hypoxia sensing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:167–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lee DH and Goldberg AL: Selective
inhibitors of the proteasome-dependent and vacuolar pathways of
protein degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem.
271:27280–24284. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Piret JP, Mottet D, Raes M and Michiels C:
CoCl2, a chemical inducer of hypoxia-inducible factor-1,
and hypoxia reduce apoptotic cell death in hepatoma cell line
HepG2. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 973:443–447. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ke Q and Costa M: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol. 70:1469–1480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Razorenova OV, Finger EC, Colavitti R,
Chernikova SB, Boiko AD, Chan CK, Krieg A, Bedogni B, LaGory E,
Weissman IL, et al: VHL loss in renal cell carcinoma leads to
up-regulation of CUB domain-containing protein 1 to stimulate
PKC{delta}-driven migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1931–1936.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Xia J, Ozaki I, Matsuhashi S, Kuwashiro T,
Takahashi H, Anzai K and Mizuta T: Mechanisms of PKC-mediated
enhancement of HIF-1α activity and its inhibition by vitamin K2 in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20:10222019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Leong HS and Chambers AF: Hypoxia promotes
tumor cell motility via RhoA and ROCK1 signaling pathways. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:887–888. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gilloteaux J, Jamison JM, Neal DR, Loukas
M, Doberzstyn T and Summers JL: Cell damage and death by
autoschizis in human bladder (RT4) carcinoma cells resulting from
treatment with ascorbate and menadione. Ultrastruct Pathol.
34:140–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Krishna MC, Mitchell JB,
Corpe CP, Buettner GR, Shacter E and Levine M: Pharmacologic
ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer cells: Action
as a pro-drug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to tissues. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13604–13609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hussein D, Estlin EJ, Dive C and Makin GW:
Chronic hypoxia promotes hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-dependent
resistance to etoposide and vincristine in neuroblastoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:2241–2250. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Poulsen RC, Knowles HJ, Carr AJ and Hulley
PA: Cell differentiation versus cell death: Extracellular glucose
is a key determinant of cell fate following oxidative stress
exposure. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ringuette Goulet C, Bernard G, Chabaud S,
Couture A, Langlois A, Neveu B, Pouliot F and Bolduc S:
Tissue-engineered human 3D model of bladder cancer for invasion
study and drug discovery. Biomaterials. 145:233–241. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|