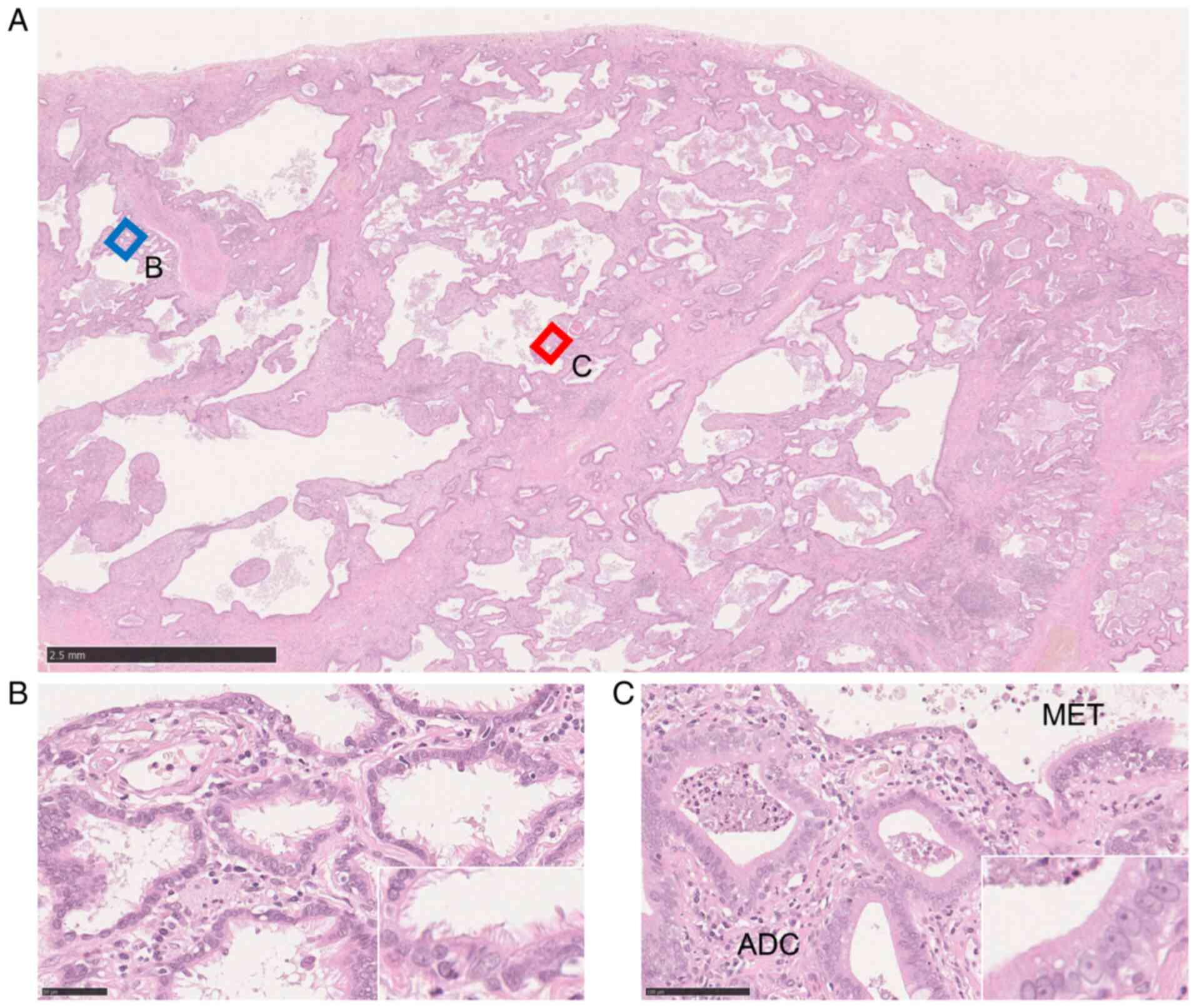
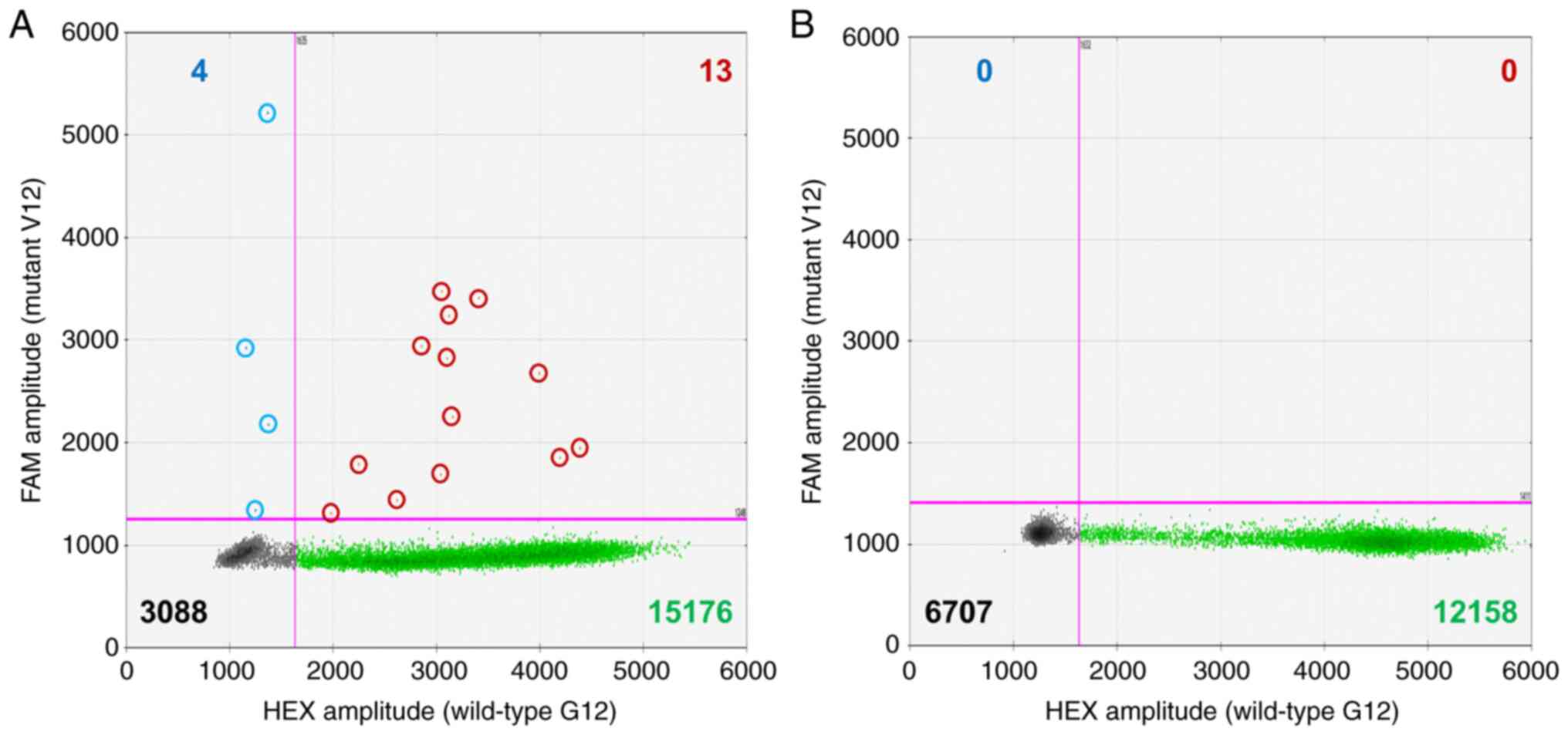
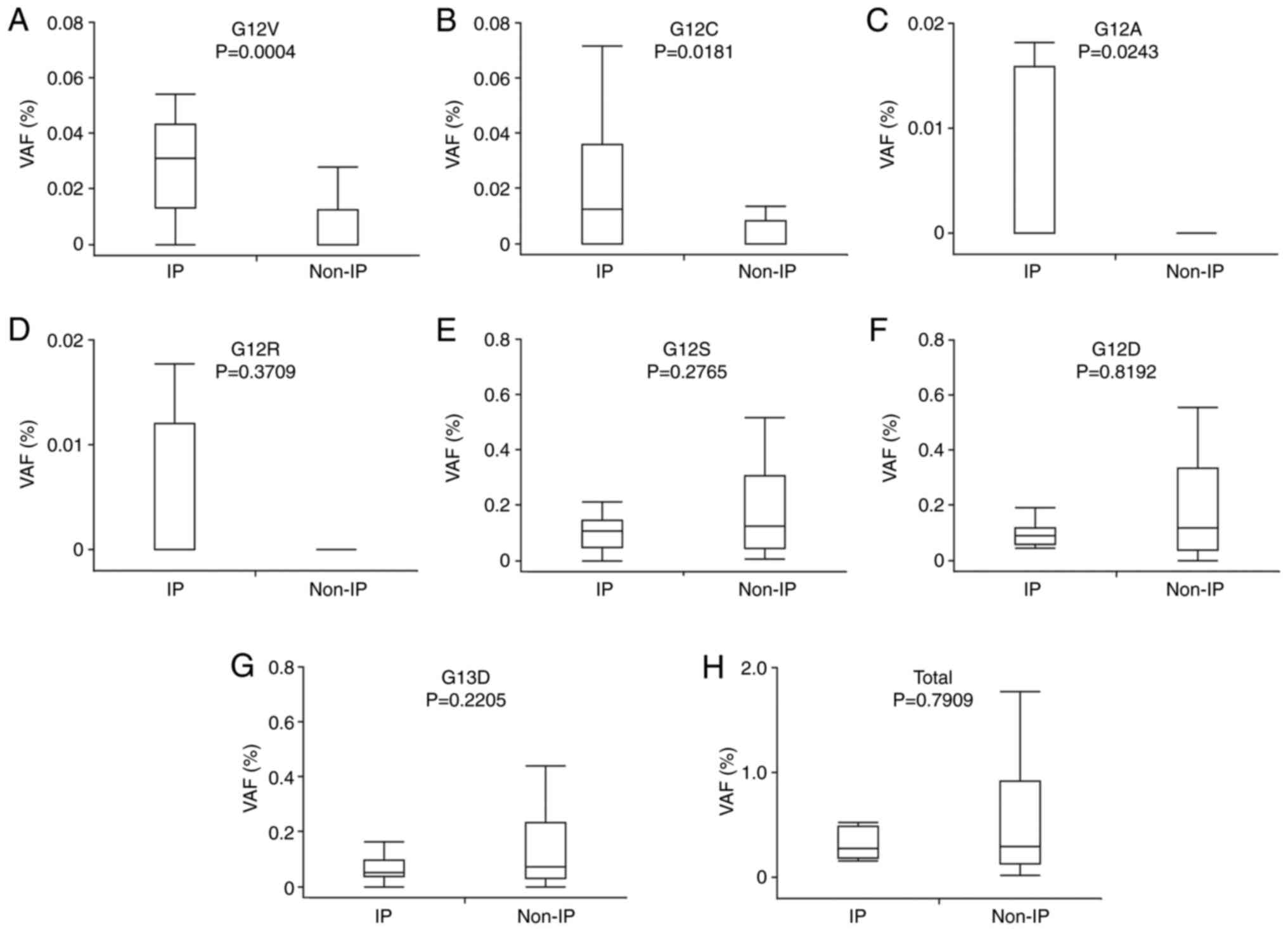
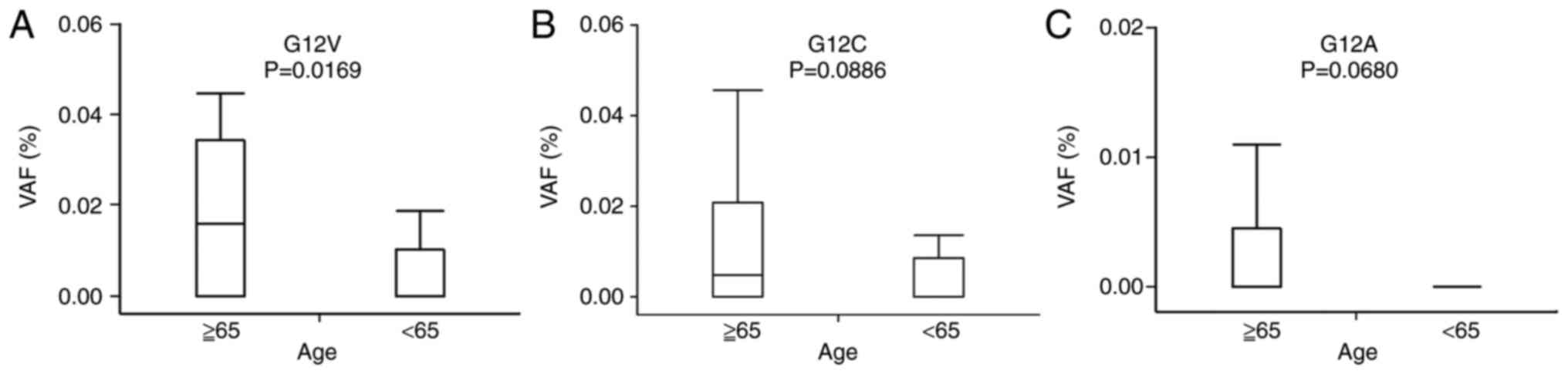
|
1
|
Yamaguchi M, Hirai S, Tanaka Y, Sumi T,
Miyajima M, Mishina T, Yamada G, Otsuka M, Hasegawa T, Kojima T, et
al: Fibroblastic foci, covered with alveolar epithelia exhibiting
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, destroy alveolar septa by
disrupting blood flow in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lab Invest.
97:232–242. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Turner-Warwick M, Lebowitz M, Burrows B
and Johnson A: Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and lung cancer.
Thorax. 35:496–499. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Bruke AP, Marx A
and Nicholson AG: Adenocarcinoma. World Health Organization
Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart.
International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: pp.
292015, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kojima Y, Okudela K, Matsumura M, Omori T,
Baba T, Sekine A, Woo T, Umeda S, Takemura T, Mitsui H, et al: The
pathological features of idiopathic interstitial
pneumonia-associated pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Histopathology.
70:568–578. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okudela K, Kojima Y, Matsumura M, Arai H,
Umeda S, Tateishi Y, Mitsui H, Suzuki T, Tajiri M, Ogura T and
Ohashi K: Relationship between non-TRU lung adenocarcinomas and
bronchiolar metaplasia-potential implication in their histogenesis.
Histol Histopathol. 33:317–326. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujita M, Matsubara N, Matsuda I, Maejima
K, Oosawa A, Yamano T, Fujimoto A, Furuta M, Nakano K, Oku-Sasaki
A, et al: Genomic landscape of colitis-associated cancer indicates
the impact of chronic inflammation and its stratification by
mutations in the Wnt signaling. Oncotarget. 9:969–981. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kiraly O, Gong G, Olipitz W, Muthupalani S
and Engelward BP: Inflammation-induced cell proliferation
potentiates DNA damage-induced mutations in vivo. PLOS Genet.
11:e10049012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leslie KO: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
may be a disease of recurrent, tractional injury to the periphery
of the aging lung: A unifying hypothesis regarding etiology and
pathogenesis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 136:591–600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP,
Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N and Sibley RK: Helicobacter
pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
325:1127–1131. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Lin CC and Chien CS:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study
of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 2:1129–1133. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hirao S, Sho M, Kanehiro H, Hisanaga M,
Ikeda N, Tsurui H, Nakajima Y and Nakano H: Pancreatic
adenocarcinoma in a patient with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: Report of
a case and literature review. Hepatogastroenterology. 47:1159–1161.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M and Adami HO:
Increased risk of large-bowel cancer in Crohn's disease with
colonic involvement. Lancet. 336:357–359. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Farrow B and Evers BM: Inflammation and
the development of pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol. 10:153–169. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chui MH, Xing D, Zeppernick F, Wang ZQ,
Hannibal CG, Frederiksen K, Kjaer SK, Cope L, Kurman RJ, Shih IM,
et al: Clinicopathologic and molecular features of paired cases of
metachronous ovarian serous borderline tumor and subsequent serous
carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 43:1462–1472. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Correa P and Shiao YH: Phenotypic and
genotypic events in gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 54 (Suppl
7):S1941–S1943. 1994.
|
|
17
|
Meyer EC and Liebow AA: Relationship of
interstitial pneumonia honeycombing and atypical epithelial
proliferation to cancer of the lung. Cancer. 18:322–351. 1965.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singhi AD, Arnold CA, Crowder CD,
Lam-Himlin DM, Voltaggio L and Montgomery EA: Esophageal
leukoplakia or epidermoid metaplasia: A clinicopathological study
of 18 patients. Mod Pathol. 27:38–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tretyakova N, Matter B, Jones R and
Shallop A: Formation of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-DNA adducts at
specific guanines within K-ras and p53 gene sequences: Stable
isotope-labeling mass spectrometry approach. Biochemistry.
41:9535–9544. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yokoyama A, Kakiuchi N, Yoshizato T,
Nannya Y, Suzuki H, Takeuchi Y, Shiozawa Y, Sato Y, Aoki K, Kim SK,
et al: Age-related remodeling of oesophageal epithelia by mutated
cancer drivers. Nature. 565:312–317. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hironaka M and Fukayama M: Pulmonary
fibrosis and lung carcinoma: A comparative study of metaplastic
epithelia in honeycombed areas of usual interstitial pneumonia with
or without lung carcinoma. Pathol Int. 49:1060–1066. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wistuba II, Berry J, Behrens C, Maitra A,
Shivapurkar N, Milchgrub S, Mackay B, Minna JD and Gazdar AF:
Molecular changes in the bronchial epithelium of patients with
small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 6:2604–2610.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vancheri C, Failla M, Crimi N and Raghu G:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A disease with similarities and
links to cancer biology. Eur Respir J. 35:496–504. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shyu S, Heath JE and Burke AP:
Neuroendocrine cell proliferations in lungs explanted for fibrotic
interstitial lung disease and emphysema. Pathology. 50:699–702.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|