Introduction
An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a
borderline tumor with low malignant potential (1,2),
comprised of spindle cells and accompanied by an inflammatory
infiltrate of plasma cells, lymphocytes and/or eosinophils
(3,4). The lungs, abdominal cavity and
gastrointestinal tract are common sites of IMT, but primary hepatic
IMT is rare (5). The biological
behavior of the tumor remains unclear (6). IMTs are usually benign, but
sometimes, malignant biological behavior such as distant metastasis
and local recurrence may occur (6,7). The
anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene, encoding a receptor
tyrosine kinase belonging to the insulin receptor superfamily
(8), has been found to be
rearranged in ~50% of patients with IMT, which results in the
overexpression and hyperactivation of the receptor tyrosine kinase
(4,9). Therefore, ALK protein has important
value in the diagnosis of IMT; for ALK-negative patients, the novel
ETS variant transcription factor 6-neurotrophic receptor tyrosine
kinase 3 (ETV6-NTRK3) fusion gene, has important reference
value for diagnosis (4,10,11).
A biloma is a well-circumscribed intra-abdominal
bile accumulation outside the biliary tree (12); it can either be intrahepatic or
extrahepatic (12), with an
incidence of 0.3–2% (13). The
most common cause is choledocholithiasis, and other causes include
abdominal trauma and surgery, bile duct tumors, liver infarction,
percutaneous catheter drainage, transhepatic cholangiogram and
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, and fever, nausea,
vomiting and epigastralgia are common symptoms caused by biloma
(13).
To the best of our knowledge, there are no reported
cases of hepatic IMT manifesting with biloma. The present study
reports the case of a 45-year-old woman with hepatic IMT negative
for ALK upon immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ
hybridization (FISH) studies, in whom a biloma was identified
inside the hepatic IMT.
Case report
In March 2019, a 45-year-old woman presented to
Mianyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Mianyang, China)
with a solid, well-defined mass in the right upper quadrant of the
abdomen. The patient had no abdominal pain, fever, vomiting or
jaundice, and no history of hepatitis B or exposure to parasites.
Laboratory data showed a white blood cell count, a red blood cell
count and a platelet count of 5.17×109/l (reference
range, 3.5-9.5×109/l), 4.05×1012/l (reference
range, 4.3-5.8×1012/l) and 218×109/l
(reference range, 100–300×109/l), respectively, while
neutrophil, lymphocyte, eosinophil and basophil levels were 59.9%
(reference range, 50–70%), 32.3% (reference range, 20–40%), 1.0%
(reference range, 0–7%) and 0.4% (reference range, 0–2%),
respectively. Hemoglobin was recorded at 124 g/l (reference range,
120–170 g/l). Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate amino
transferase, alkaline phosphatase, glutamyl transpeptidase and
lactate dehydrogenase levels were 33 U/l (reference range, 0–50
U/l), 26.5 U/l (reference range, 0–40 U/l), 74.7 U/l (reference
range, 45–125 U/l), 17.4 U/l (reference range, 10–60 U/l) and 145.0
U/l (reference range, 120–250 U/l), respectively. Total bilirubin,
indirect bilirubin and direct bilirubin levels were 11.50 µmol/l
(reference range, 3.42-20.5 µmol/l), 1.30 µmol/l (reference range,
0–6.84 µmol/l) and 10.20 µmol/l (reference range, 0–18 µmol/l),
respectively. α-fetoprotein and carcinoembryonic antigen results
were 3.21 µg/ml (reference range, 0–20 µg/ml) and 1.30 µg/ml
(reference range, 0–5 µg/ml), and carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125),
CA153 and CA19-9 results were 7.50 KU/ml (reference range, 0–35
KU/ml), 10.60 KU/ml (reference range, 0–35 KU/ml) and 7.30 KU/ml
(reference range, 0–35 KU/ml), respectively.
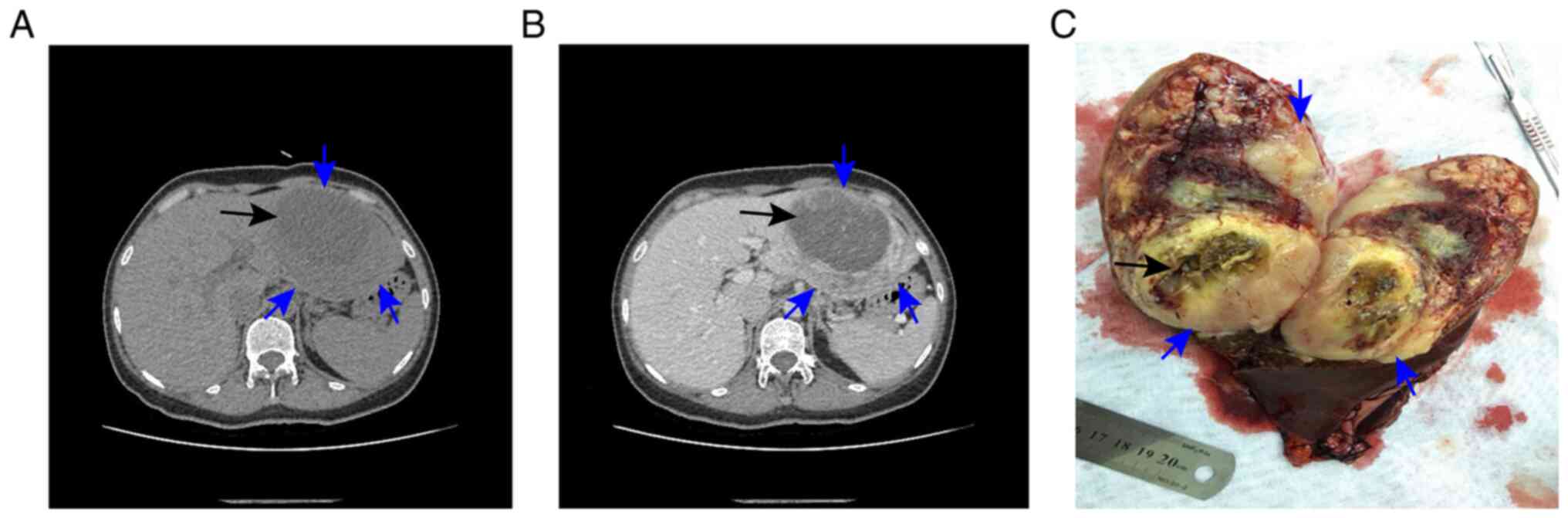
Computed tomography of the abdomen confirmed the
presence of the lesion, revealing a low-density mass measuring
11.2×8.5×10.5 cm in the left lobe of the liver, with a
lower-density mass measuring 8.5×6.1×5.9 cm in the interior of the
tumor (Fig. 1A and B). Based on
the analysis of patient history, laboratory data and imaging data,
the characteristics of the lesion were different from hepatocelluar
carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma,
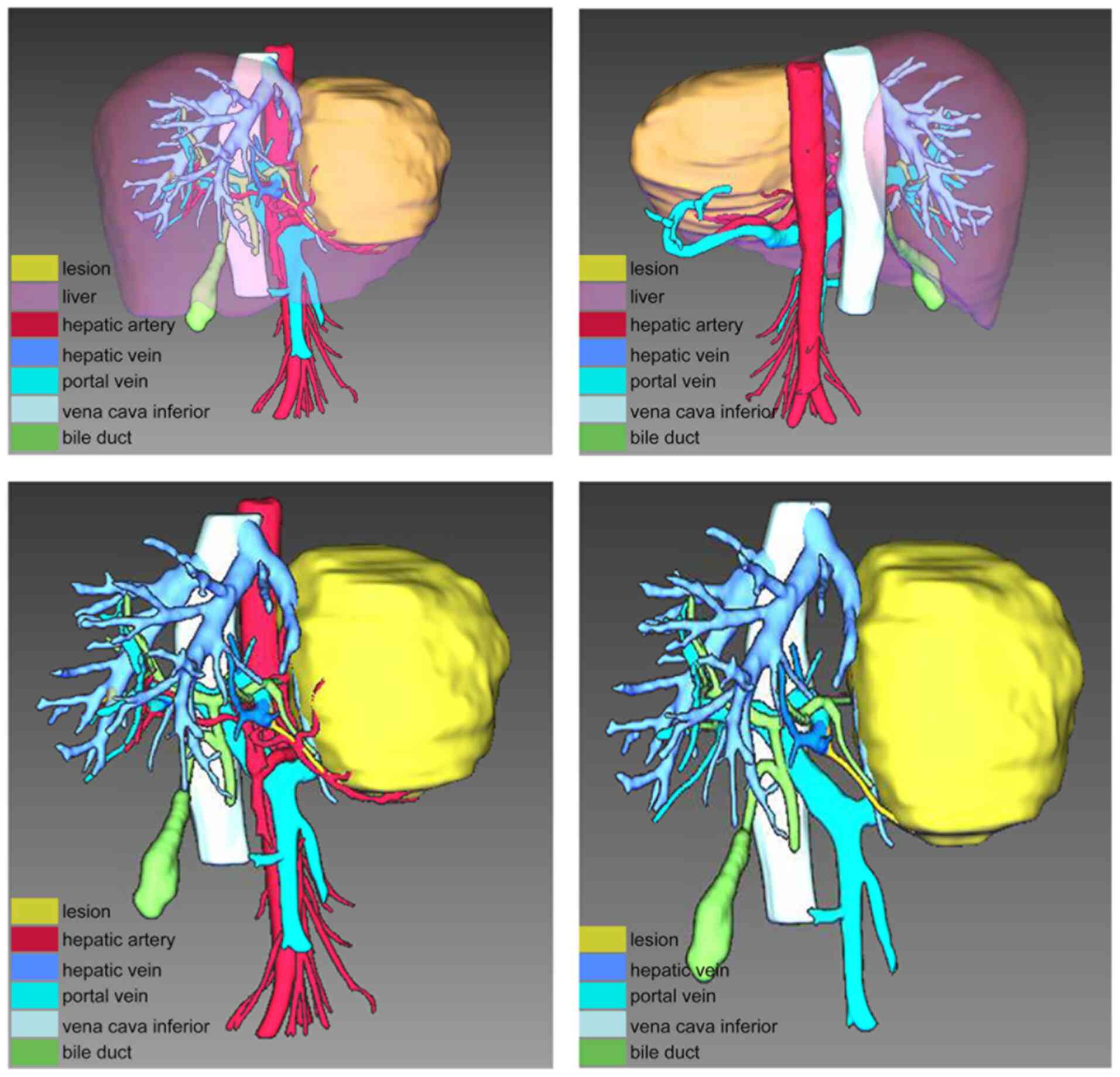
liver abscess and hepatic echinococcosis. Furthermore, IQQA-3D
(EDDA Technology, Inc.) imaging of the neoplastic area was
performed for precise preoperative evaluation (Fig. 2), and the lesion could be easily
removed by radical resection. As suspicion of a malignancy remained
high, surgical resection of the left hepatic lobe, including the
tumor, was undertaken. Intraoperatively, a tumor (12×10×9 cm), with
an unclear boundary, incomplete capsule and fish-like texture, was
found in the left lateral lobe of the liver, and a biloma,
measuring 8×6 cm, was identified inside the tumor (Fig. 1C). The resection margins were
clear.
The histopathological review of the sections
(4-µm-thick) was performed using hematoxylin and eosin staining.
The tumor excision tissue was stored as wax blocks in routine
storage at ambient temperature prior to staining. The fixation
protocol involved the use of 10% neutral buffered formalin as the
fixant, with the duration of fixation being 24 h at room
temperature. Following dehydration in a series of ethanol
solutions, the tumor excision tissues were paraffin-embedded and
sliced into 4-µm-thick sections. Firstly, the sections were
deparaffinized in xylene (10 min three times) and rehydrated by
serial soaking in 100% ethanol for 10 min, and 95, 85 and 75%
ethanol for 5 min each at 25°C. Secondly, sections were stained in
0.1% hematoxylin solution (10 min at 25°C) and differentiated in 1%
hydrochloric alcohol, then rinsed with tap water and with distilled
water until the nuclei became blue, and dehydrated in 95% ethanol.
Thirdly, sections were counterstained in 0.5% eosin solution (3 min
at 25°C), and incubated in 95% anhydrous ethanol for 5 min twice
and in xylene solution for 10 min at 25°C. Lastly, the sections
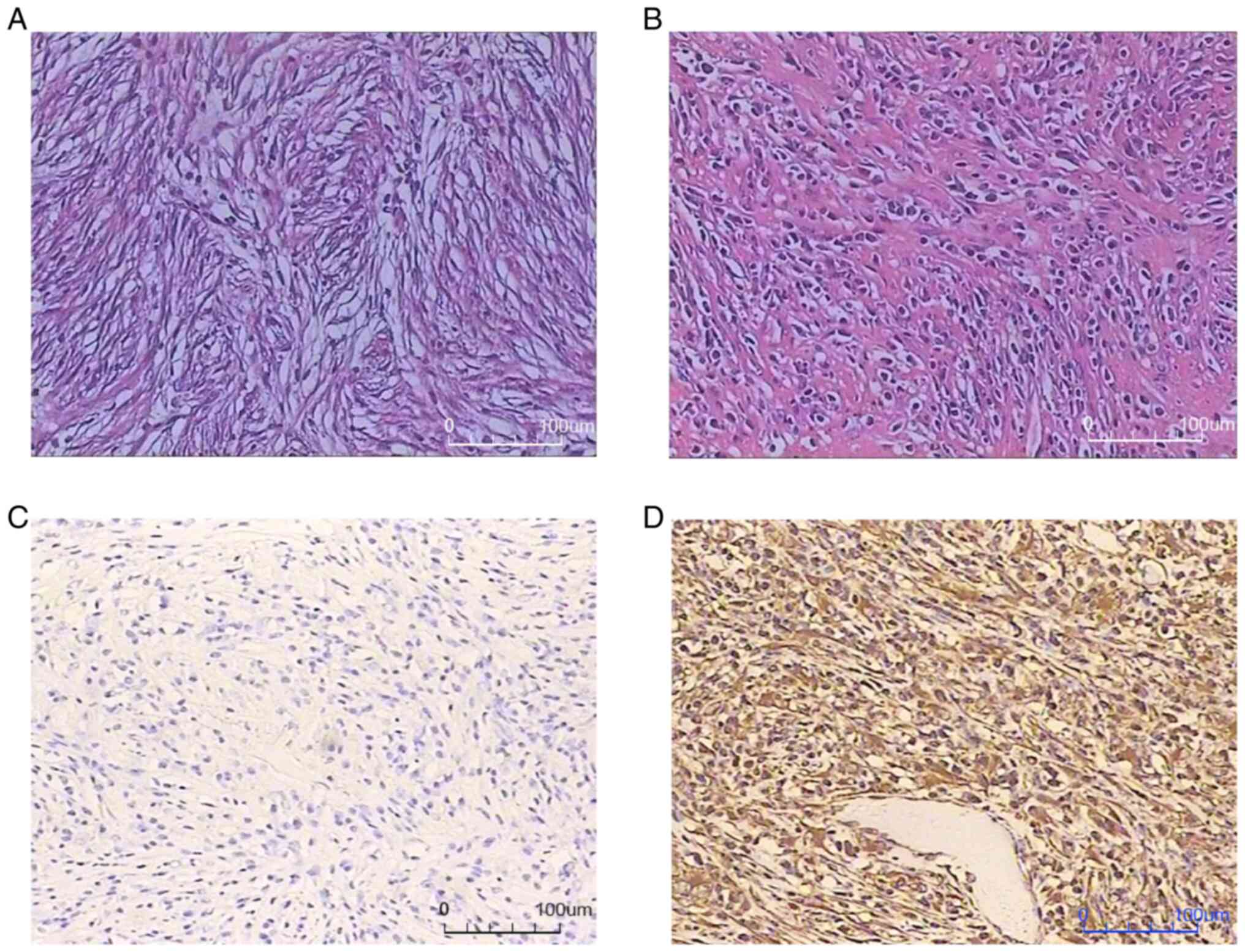
were sealed with Canada gum. Normal light microscopy was used to
image the H&E staining at a magnification of ×200. Spindle cell
proliferation with infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells and
mucinous degeneration were found (Fig.
3).
For immunostaining, the streptavidin-peroxidase
method was adapted to detect protein expression using paraffin
sections. The tumor excision tissue was stored as wax blocks in
routine storage at room temperature. The fixation protocol involved
the use of 10% neutral buffered formalin as the fixant, with the
duration of fixation being 24 h at room temperature. Tissue
sections (4-µm-thick) were dried at 60°C for 2.5 h, deparaffinized
with two 10-min washes in xylene, and rehydrated in decreasing
concentrations of ethanol in distilled water (100, 95, 85 and 75%;
5 min each). Next, sections were soaked in boiling sodium citrate
buffer (20140006; Henan Celnovte Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.) for 2.5
min in a microwave oven. When cooled to room temperature, the
sections were washed for 5 min in distilled water two times and for
5 min in PBS (20140002; 0.01 M pH 7.2-7.4; Henan Celnovte
Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.) one time. Subsequently, sections were
treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide at room temperature for 5 min to
block endogenous peroxidase activity. After washing for 5 min in
PBS two times, the sections were incubated for 60 min at 18–25°C
with ALK (rat anti-human) antibody (202011001; clone 5A4; dilution,
1:100; Henan Celnovte Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.) and washed for 5
min in PBS two times, followed by incubation with HRP-labeled goat
anti-rat IgG antibody (20170011; dilution, 1:100; Henan Celnovte
Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.) for 20 min at 18–25°C, washing with PBS
for 5 min (two times), incubation for 3–5 min at 18–25°C with
diaminobenzidine (DAB; DAB substrate:DAB buffer=1:20; 20170011;
Henan Celnovte Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.), washing for 5 min in
distilled water two times, and counterstaining with 5% hematoxylin
(20170011; Henan Celnovte Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.) for 5 min.
Finally, the sections were stained blue in 1% hydrochloric-acid
alcohol at room temperature, dehydrated in increasing
concentrations of ethanol (85, 95 and 100%), cleared with xylene,
and were sealed with Canada gum.
In order to ensure the accuracy and reliability of
the staining conclusion, both positive control and negative control
experiments were set up for each section to be detected according
to the manufacturer's instructions during the experiment. A blank
control was used as a negative control and an anaplastic lymphoma
tissue section was used as a positive control. Analysis was
performed using an Olympus BX 53 light microscope (magnification,
×200; Olympus Corporation). The aforementioned steps were repeated
for CD117 (clone EP10), CD34 (clone QBEnd/10 mouse), discovered on
GIST-1 (clone RBT-DOG-1), desmin (clone EP15), smooth muscle actin
(clone IA4), S-100 (clone poly), CD21 (clone EP64), pan-cytokeratin
(clone AE1/AE3), epithelial membrane antigen (clone aP1.4), CD23
(clone, aR013), vimentin (clone V9) and CD35 (clone RLB25 mouse)
(all Henan Celnovte Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.) according to the
manufacturer's instructions for each antibody. This revealed
negativity for ALK (clone 5A4), CD117 (clone EP10), CD34 (clone
QBEnd/10 mouse), discovered on GIST-1 (clone RBT-DOG-1), desmin
(clone EP15), smooth muscle actin (clone IA4), S-100 (clone poly),
CD21 (clone EP64), pan-cytokeratin (clone AE1/AE3), epithelial
membrane antigen (clone aP1.4), CD23 (clone, aR013) and CD35 (clone
RLB25 mouse) (all Henan Celnovte Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.), and
positive staining for vimentin (clone V9), with 5% Ki-67-positive
cells (Fig. 3).
This phenotype is not typical of IMT (11). To confirm the diagnosis, FISH
studies were conducted to assess characteristic genetic
rearrangements using ALK (Fracture rearrangement probe; cat.
no. F.01079; Guangzhou Anbiping Pharmaceutical Technology Co.,
Ltd.), RET (Fracture rearrangement probe; cat. no.
F.01104-01; Guangzhou Anbiping Pharmaceutical Technology Co.,
Ltd.), ROS1 (Fracture rearrangement probe; cat. no. F.01086;
Guangzhou Anbiping Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.),
MDM2 (Fracture rearrangement probe; cat. no. F.01017-01;
Guangzhou Anbiping Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.),
MGEA5 (Fracture rearrangement probe; cat. no. F.01275-01;
Guangzhou Anbiping Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.) and
ETV6 break-apart assays (Fusion probe; cat. no. F.01258-01;
Guangzhou Anbiping Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.). The tumor
excision tissue was stored as wax blocks in routine storage at room
temperature. The fixation protocol involved the use of 10% neutral
buffered formalin as the fixant, with the duration of fixation
being 24 h at room temperature. The tissues were embedded in
paraffin. Corresponding H&E sections were reviewed by a
pathologist who circled the area of tumor for testing.
ALK FISH was performed using 4-µm-thick FFPE
tissue sections. Sections were deparaffinized, rehydrated in 100,
90 and 70% ethanol, washed with 2× saline sodium citrate (SSC)
(UltraPure™ 20X SSC; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.),
incubated in pretreatment solution (deionized water; 25 min at
90°C), and digested with pepsin solution (1:10,000; Sigma-Aldrich;
Merck KGaA; 4 mg/ml pepsin; 0.02 mol/l HCL) for 6 min at 37°C.
Subsequently, sections were washed with 2× SSC (5 min at room
temperature), dehydrated in ethanol (70, 90 and 100%), dried at
room temperature and then exposed to 10 µl ALK gene probe
(Fracture rearrangement probe; cat. no. F.01079; batch number,
202110001; concentration, 60 ng/µl; Guangzhou Anbiping
Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.). Denaturation (5 min at 85°C)
and hybridization (10–18 h at 37°C) were performed using the
ThermoBrite System (Abbott Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.). After 24 h,
the specimens were treated with 2× SSC (36 ml pure water + 4 ml 20X
SSC) for 10 min at 37°C, 2× SSC containing 0.1% Nonidet P-40 (NP
40; Nacalai Tesque Inc.; 36 ml pure water + 4 ml 20X SSC + 40 µl
NP-40) for 5 min at 37°C, rehydrated in 70% ethanol (3 min, at room
temperature) and dried in the dark. Nuclei were counterstained with
DAPI using antifade reagent for 30 min at −20°C (VECTASHIELD
Mounting Medium; Vector Laboratories, Inc.). Analysis was performed
using a fluorescence microscope (magnification, ×1,000; Axio imager
Z1; Carl Zeiss AG) and data analysis was performed using ISIS
software (version 5.4.6; MetaSystems). FISH signal was classified
under two signal patterns: Normal (two yellow signals) and typical
positive signal pattern (one red, one green and one yellow signal),
and >100 tumor cells were assessed. The aforementioned steps
were repeated for RET, ROS1, MDM2 and MGEA5 genes and ETV6-NTRK3
fusion genes according to the manufacturer's instructions for each
gene. These studies found an ETV6 rearrangement, identified
as an ETV6-NTRK3 fusion oncogene. ALK, RET, ROS1,
MDM2 and MGEA5 were negative (Fig. 4).
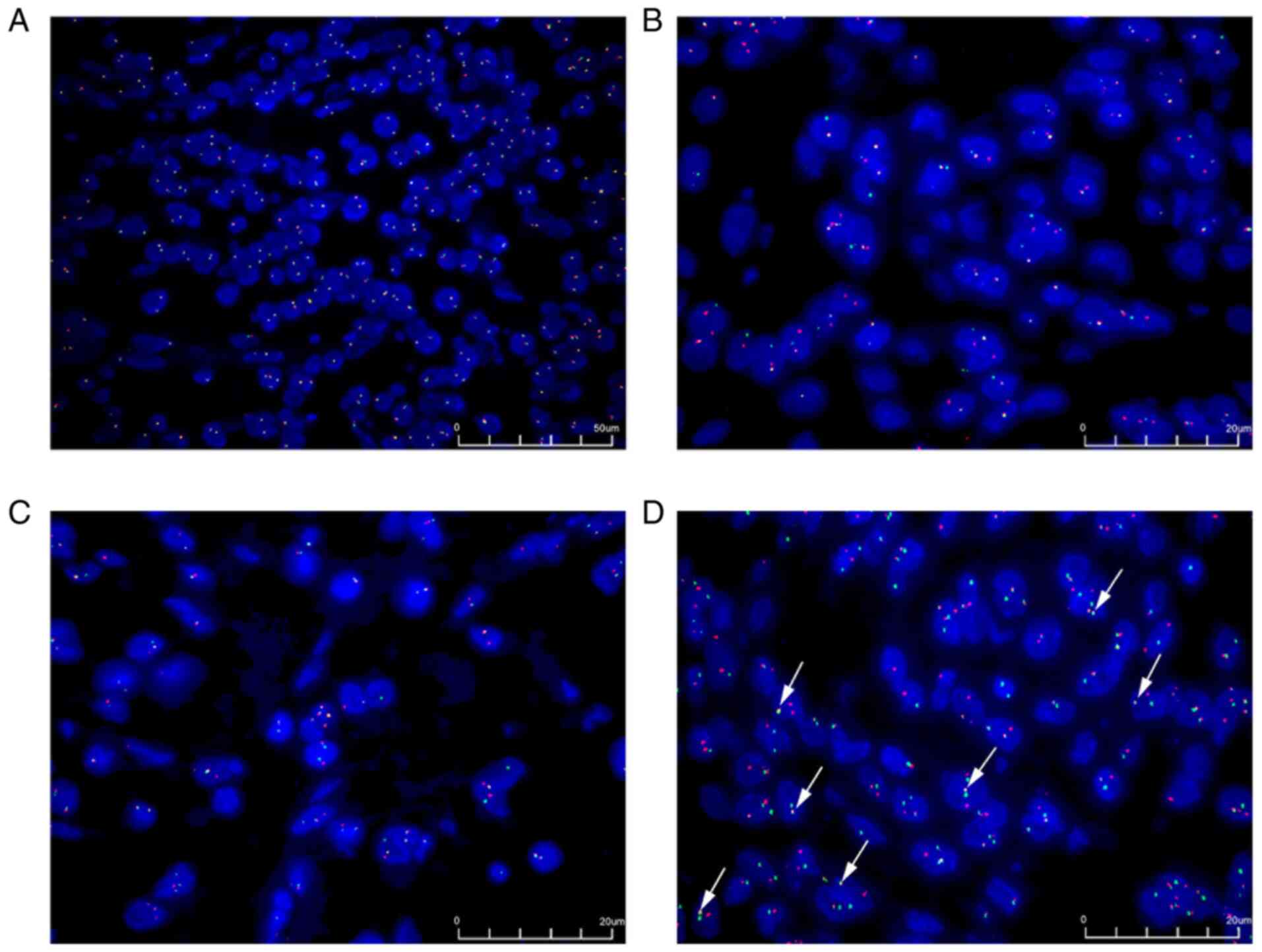 | Figure 4.Fluorescence in situ
hybridization. (A) The anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene was detected
using a broken rearrangement probe. The proportion of positive
cells was 3% (magnification, ×400). (B) The ETV6 gene was
detected using a broken rearrangement probe. The green signal
represents the GSP ETV6 (centromere) and the red signal
represents the GSP ETV6 (telomere) (magnification, ×1,000).
(C) The NTRK3 gene was detected using a broken rearrangement
probe. The green signal represents the GSP NTRK3 (telomere)
and the red signal represents the GSP NTRK3 (centromere)
(magnification, ×1,000). (D) The ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene was
detected using the fusion gene probes. The white arrow shows the
typical ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene, which is demonstrated by the
close proximity of the red signal (ETV6 from chromosome 12)
with the green signal (NTRK3 from chromosome 15) in multiple
tumor cells. ETV6, ETS variant transcription factor 6; NTRK3,
neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (magnification, ×1,000).
GSP, gene-specific primer. |
Finally, a diagnosis of hepatic IMT with biloma was
made, based on morphological and immunohistochemical findings, and
the characteristic genetic rearrangements. The postoperative course
was uneventful, and the patient was discharged at postoperative day
7. The patient was followed up every 3 months without adjuvant
treatment. No recurrence of symptoms was noted at the 3-year
follow-up and outpatient follow-up every 6 months will still be
performed.
Discussion
According to the World Health Organization
classification of soft-tissue tumors, IMT is a borderline tumor
with low malignant potential; it is a mesenchymal neoplasm
comprising myofibroblastic and fibroblastic spindle cells,
accompanied by an inflammatory infiltrate of plasma cells,
lymphocytes and/or eosinophils (4,5,14).
The lung is the most common site of IMT (15). In addition, IMTs originating from
female genital organs (4,16), the intra-abdominal region (17,18),
the retroperitoneum (19), the
ileocecal mesentery (20) and the
pancreas (21) have also been
reported. However, those located in the liver are even rarer
(5).
The ALK gene was first discovered in 1994 in
a subtype of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (22), located on chromosome 2p23, encoding
ALK (22). Previous studies have
confirmed that ALK gene rearrangements are found in nearly
one-half of patients with IMT, which leads to ALK
overexpression (4,11,23).
Therefore, the ALK protein is considered to be an important feature
for identifying IMT (4).
For ALK-negative patients, recent studies have
identified some new fusion genes, mainly including the ROS1,
ETV6, PDGFRβ, RET and NTRK3 genes (10,11,24).
A case of ALK-negative uterine IMT harboring the ETV6-NTRK3
fusion gene was reported by Takahashi et al (4). Alassiri et al (11) also found that ETV6-NTRK3 is
expressed in a subset of ALK-negative IMTs. These findings are
consistent with the characteristic genetic rearrangements of the
present patient.
The biological behavior of the tumor is an important
factor affecting the prognosis of the patient, as well as an
important reference for developing a treatment plan. However, the
biological behavior of IMT is unclear. ALK is more commonly
expressed in children and is associated with tumor aggressiveness
and high recurrence rates (2). By
comparison, ALK-negative IMT may have a higher risk of metastasis
(2,10).
As is well known, biliary injury is a direct cause
of the formation of biloma (25–27).
Sakamoto et al (28) found
that the incidence of intrahepatic biloma formation in patients
with a metastatic liver tumor was higher than that in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. In the present patient, a biloma,
measuring 8×6 cm, was found inside the ALK-negative IMT. We
hypothesized that in this case, the formation of the biloma was
associated with the lack of expression of the ALK gene and the
formation of the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first
report of a case of ALK-negative hepatic IMT harboring the
ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene and manifesting with biloma. However,
the underlying mechanism of this disease remains unclear. von der
Thüsen et al (29) found
that the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene encodes an activated
membrane receptor kinase protein, which can promote cell
proliferation and survival through the activation of the Ras-MAP
kinase and PI3K-Akt pathways. The ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene is
also associated with secretory carcinoma (30,31).
Tang et al (32) reported a
case of secretory carcinoma of the breast harboring the
ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene, which showed chemo-resistance to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy and multiple distant metastases.
Accordingly, we hypothesize that the ALK-negative hepatic IMT with
an ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene in the present case was
significantly more likely to invade and damage the biliary tract,
which eventually led to the formation of the biloma. As no similar
cases have been reported in the past, it remains uncertain as to
whether this is a significant observation, and further research
will be required to illuminate the mechanism of this disease.
In conclusion, the present case is of particular
interest for two reasons. First, it is not a typical case of
hepatic IMT owing to the ALK-negativity of the tumor upon
immunohistochemistry and FISH, as well as the presence of an
ETV6-NTRK3 fusion. Secondly, the report provides the first
demonstration of a biloma in an ALK-negative IMT of the liver.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Authors' contributions
KH and JY designed the study and wrote the
manuscript. PWZ, JYZ, PZ and KH performed all the experiments. JY,
PWZ and KH confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All
authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
This study has been approved by The Mianyang
Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Mianyang, China; approval
number, 2020LL-12). Written informed consent was obtained.
Patient consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was
obtained.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Zhou P, Chen YH, Lu JH, Jin CC, Xu XH and
Gong XH: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor after breast
prosthesis: A case report and literature review. World J Clin
Cases. 10:1432–1440. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang GH, Guo XY, Liang GZ and Wang Q:
Kidney inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor masquerading as
metastatic malignancy: A case report and literature review. World J
Clin Cases. 7:4366–4376. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thompson LDR: Inflammatory myofibroblastic
tumor. Ear Nose Throat J. 100 (5_suppl):520S–521S. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takahashi A, Kurosawa M, Uemura M,
Kitazawa J and Hayashi Y: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative
uterine inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor containing the
ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene: A case report. J Int Med Res. 46:3498–3503.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beauchamp A, Villanueva A, Feliciano W and
Reymunde A: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the liver in an
elderly woman following a second liver biopsy: A case report. Bol
Asoc Med P R. 103:60–64. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Zheng G, Meng X, Li Y, Shi D and
Yu J: Microwave ablation for the management of pulmonary
inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: A case report and literature
review. Transl Cancer Res. 10:4582–4590. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao HD, Wu T, Wang JQ, Zhang WD, He XL,
Bao GQ, Li Y, Gong L and Wang Q: Primary inflammatory
myofibroblastic tumor of the breast with rapid recurrence and
metastasis: A case report. Oncol Lett. 5:97–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mariño-Enríquez A, Wang WL, Roy A,
Lopez-Terrada D, Lazar AJ, Fletcher CD, Coffin CM and Hornick JL:
Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: An aggressive
intra-abdominal variant of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor with
nuclear membrane or perinuclear ALK. Am J Surg Pathol. 35:135–144.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamamoto H, Yoshida A, Taguchi K, Kohashi
K, Hatanaka Y, Yamashita A, Mori D and Oda Y: ALK, ROS1 and NTRK3
gene rearrangements in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumours.
Histopathology. 69:72–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alassiri AH, Ali RH, Shen Y, Lum A,
Strahlendorf C, Deyell R, Rassekh R, Sorensen PH, Laskin J, Marra
M, et al: ETV6-NTRK3 is expressed in a subset of ALK-Negative
inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors. Am J Surg Pathol.
40:1051–1061. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balfour J and Ewing A: Hepatic Biloma.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL) StatPearls Publishing
2022; Jan. 2021
|
|
13
|
FaisalUddin M, Bansal R, Iftikhar PM, Khan
J and Arastu AH: A rare case report of biloma after
cholecystectomy. Cureus. 11:e54592019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jo VY and Fletcher CD: WHO classification
of soft tissue tumours: An update based on the 2013 (4th) edition.
Pathology. 46:95–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Coffin CM, Watterson J, Priest JR and
Dehner LP: Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
(inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and
immunohistochemical study of 84 cases. Am J Surg Pathol.
19:859–872. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shukla PS and Mittal K: Inflammatory
myofibroblastic tumor in female genital tract. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
143:122–129. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao JJ, Ling JQ, Fang Y, Gao XD, Shu P,
Shen KT, Qin J, Sun YH and Qin XY: Intra-abdominal inflammatory
myofibroblastic tumor: Spontaneous regression. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:13625–13631. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SH, Cho YH and Kim HY: Two cases of
infantile intra-abdominal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor.
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 17:116–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koirala R, Shakya VC, Agrawal CS, Khaniya
S, Pandey SR, Adhikary S and Pathania OP: Retroperitoneal
inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Am J Surg. 199:e17–19. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Corapçioğlu F, Kargi A, Olgun N, Ozer E,
Olguner M and Sarialioğlu F: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of
the ileocecal mesentery mimicking abdominal lymphoma in childhood:
Report of two cases. Surg Today. 35:687–691. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakamura Y, Inui K, Yoshino J, Tokoro T,
Sabater L, Takeda S, Yamashita K, Okochi O and Nakao A:
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory fibrosarcoma) of
the pancreas: A case report. Hepatogastroenterology. 52:625–628.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB,
Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL and Look AT: Fusion of a kinase
gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's
lymphoma. Science. 263:1281–1284. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coffin CM, Patel A, Perkins S,
Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Perlman E and Griffin CA: ALK1 and p80
expression and chromosomal rearrangements involving 2p23 in
inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Mod Pathol. 14:569–576. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lovly CM, Gupta A, Lipson D, Otto G,
Brennan T, Chung CT, Borinstein SC, Ross JS, Stephens PJ, Miller VA
and Coffin CM: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors harbor multiple
potentially actionable kinase fusions. Cancer Discov. 4:889–895.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bhagat N, Reyes DK, Lin M, Kamel I, Pawlik
TM, Frangakis C and Geschwind JF: Phase II study of
chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatic
neuroendocrine metastases: High incidence of biliary injury.
Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 36:449–459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Suzuki K, Hashimoto T, Osugi S, Toyota N,
Omagari K and Tamura A: Spontaneous biloma resulting from
intrahepatic bile duct perforation coexisting with intrahepatic
cholelithiasis and cholangiocarcinoma: A case report and literature
review. Am J Case Rep. 21:e9262702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stonelake S, Ali S, Pinkey B, Ong E,
Anbarasan R, McGuirk S, Perera T, Mirza D, Muiesan P and Sharif K:
Fifteen-year single-center experience of biliary complications in
liver trauma patients: Changes in the management of posttraumatic
bile leak. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 31:245–251. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sakamoto I, Iwanaga S, Nagaoki K, Matsuoka
Y, Ashizawa K, Uetani M, Fukuda T, Okimoto T, Okudaira S, Omagari
K, et al: Intrahepatic biloma formation (bile duct necrosis) after
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
181:79–87. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
von der Thüsen JH, Dumoulin DW, Maat APWM,
Wolf J, Sadeghi AH, Aerts JGJV and Cornelissen R: ETV6-NTRK3
translocation-associated low-grade mucinous bronchial
adenocarcinoma: A novel bronchial salivary gland-type non-small
cell lung cancer subtype. Lung Cancer. 156:72–75. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laé M, Fréneaux P, Sastre-Garau X,
Chouchane O, Sigal-Zafrani B and Vincent-Salomon A: Secretory
breast carcinomas with ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene belong to the
basal-like carcinoma spectrum. Mod Pathol. 22:291–298. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Osako T, Takeuchi K, Horii R, Iwase T and
Akiyama F: Secretory carcinoma of the breast and its
histopathological mimics: Value of markers for differential
diagnosis. Histopathology. 63:509–519. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang H, Zhong L, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Liang
G, Chen G and Xie G: Secretory carcinoma of the breast with
multiple distant metastases in the brain and unfavorable prognosis:
A case report and literature review. Diagn Pathol. 16:562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|