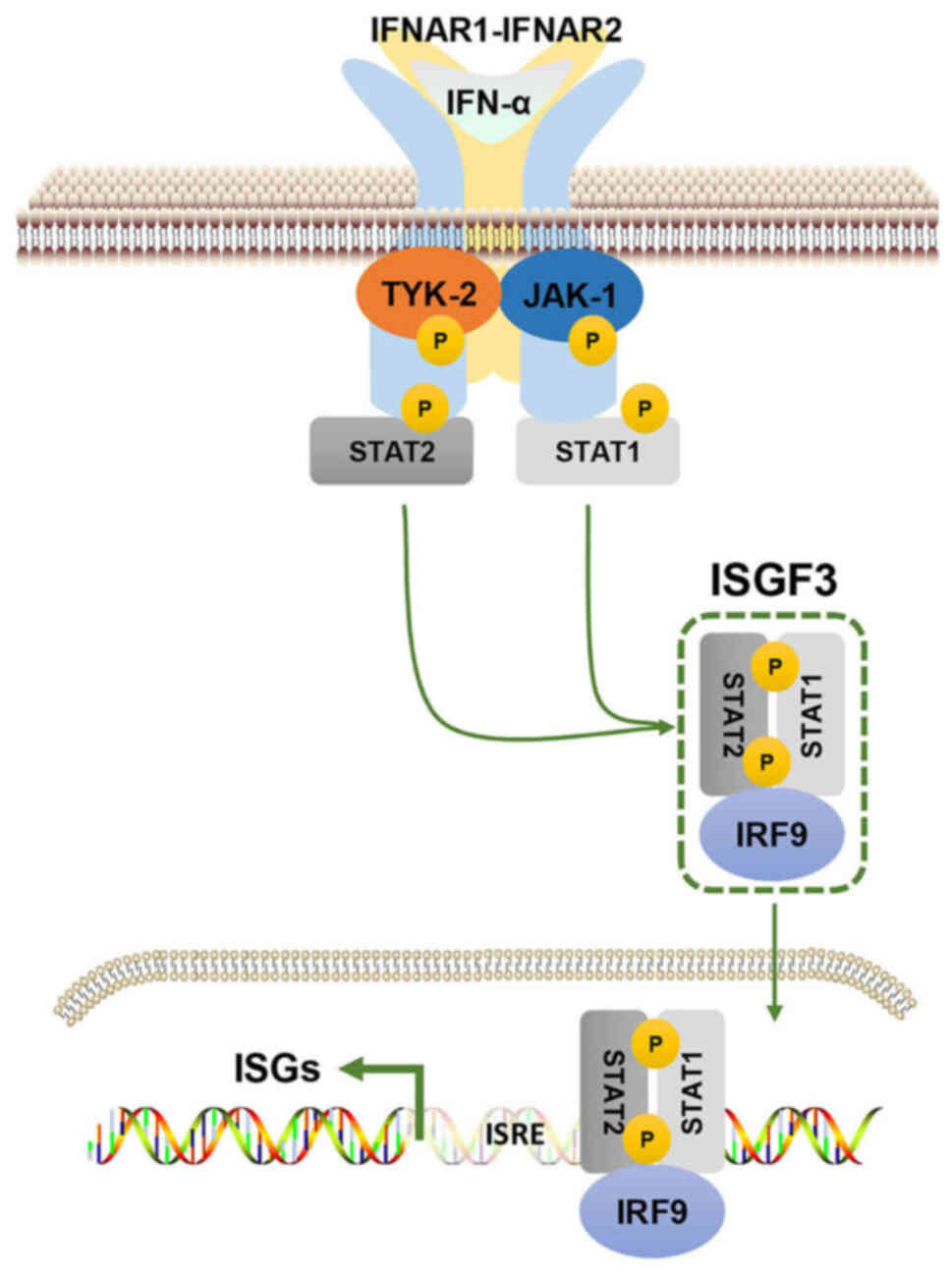
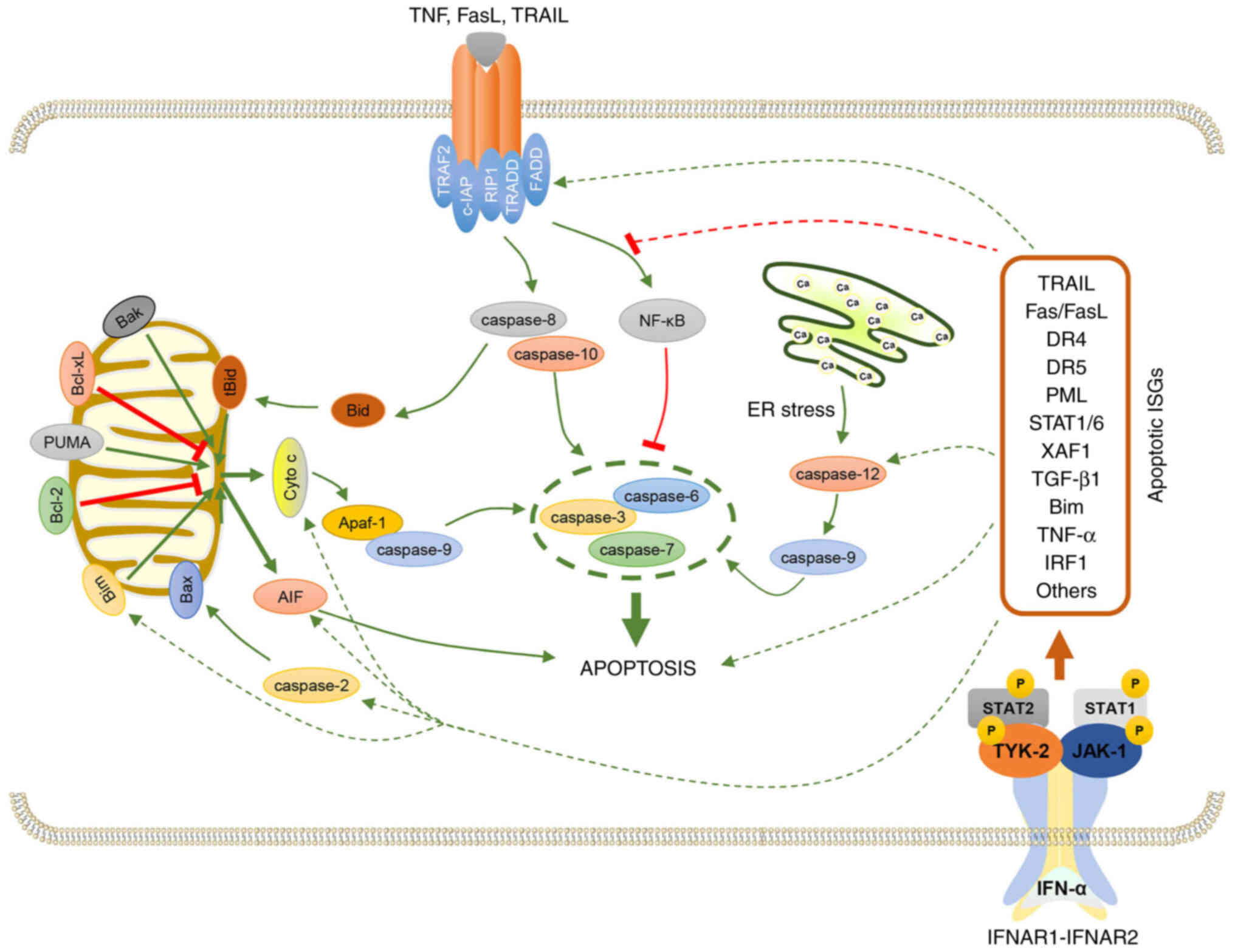
|
1
|
Cheon H, Borden EC and Stark GR:
Interferons and their stimulated genes in the tumor
microenvironment. Semin Oncol. 41:156–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bekisz J, Schmeisser H, Hernandez J,
Goldman ND and Zoon KC: Human interferons alpha, beta and omega.
Growth Factors. 22:243–251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pestka S: The human interferon-alpha
species and hybrid proteins. Semin Oncol. 24 (Suppl 9):S9-4-S9-17.
1997.
|
|
4
|
El-Baky NA and Redwan EM: Therapeutic
alpha-interferons protein: Structure, production, and biosimilar.
Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 45:109–127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lazear HM, Schoggins JW and Diamond MS:
Shared and distinct functions of type I and type III interferons.
Immunity. 50:907–923. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blaauboer A, Sideras K, van Eijck CHJ and
Hofland LJ: Type I interferons in pancreatic cancer and development
of new therapeutic approaches. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
159:1032042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grilo AL and Mantalaris A: Apoptosis: A
mammalian cell bioprocessing perspective. Biotechnol Adv.
37:459–475. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McNab F, Mayer-Barber K, Sher A, Wack A
and O'Garra A: Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat Rev
Immunol. 15:87–103. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Smyth MJ
and Kroemer G: Type I interferons in anticancer immunity. Nat Rev
Immunol. 15:405–414. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bekisz J, Baron S, Balinsky C, Morrow A
and Zoon KC: Antiproliferative properties of type I and type II
interferon. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 3:994–1015. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Haji Abdolvahab M, Mofrad MR and
Schellekens H: Interferon beta: From molecular level to therapeutic
effects. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 326:343–372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sin WX, Li P, Yeong JP and Chin KC:
Activation and regulation of interferon-β in immune responses.
Immunol Res. 53:25–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Markowitz CE: Interferon-beta: Mechanism
of action and dosing issues. Neurology. 68 (Suppl 4):S8–S11. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kali SK, Dröge P and Murugan P: Interferon
β, an enhancer of the innate immune response against SARS-CoV-2
infection. Microb Pathog. 158:1051052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jakimovski D, Kolb C, Ramanathan M,
Zivadinov R and Weinstock-Guttman B: Interferon β for multiple
sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 8:a0320032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chawla-Sarkar M, Lindner DJ, Liu YF,
Williams BR, Sen GC, Silverman RH and Borden EC: Apoptosis and
interferons: Role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of
apoptosis. Apoptosis. 8:237–249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
De Groof A, Ducreux J, Aleva F, Long AJ,
Ferster A, van der Ven A, van de Veerdonk F, Houssiau FA and
Lauwerys BR: STAT3 phosphorylation mediates the stimulatory effects
of interferon alpha on B cell differentiation and activation in
SLE. Rheumatology (Oxford). 59:668–677. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Indraccolo S: Interferon-alpha as
angiogenesis inhibitor: Learning from tumor models. Autoimmunity.
43:244–247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kotredes KP and Gamero AM: Interferons as
inducers of apoptosis in malignant cells. J Interferon Cytokine
Res. 33:162–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pestka S, Krause CD and Walter MR:
Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors.
Immunol Rev. 202:8–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pestka S: Purification and cloning of
interferon alpha. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 316:23–37.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pestka S: The human interferon alpha
species and receptors. Biopolymers. 55:254–287. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wittling MC, Cahalan SR, Levenson EA and
Rabin RL: Shared and unique features of human interferon-beta and
interferon-alpha subtypes. Front Immunol. 11:6056732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gibbert K, Schlaak JF, Yang D and Dittmer
U: IFN-α subtypes: Distinct biological activities in anti-viral
therapy. Br J Pharmacol. 168:1048–1058. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ortaldo JR, Herberman RB, Harvey C,
Osheroff P, Pan YC, Kelder B and Pestka S: A species of human alpha
interferon that lacks the ability to boost human natural killer
activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 81:4926–4929. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schreiber G: The molecular basis for
differential type I interferon signaling. J Biol Chem.
292:7285–7294. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schreiber G and Piehler J: The molecular
basis for functional plasticity in type I interferon signaling.
Trends Immunol. 36:139–149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schneider WM, Chevillotte MD and Rice CM:
Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu
Rev Immunol. 32:513–545. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Furutani Y, Toguchi M, Shiozaki-Sato Y,
Qin XY, Ebisui E, Higuchi S, Sudoh M, Suzuki H, Takahashi N,
Watashi K, et al: An interferon-like small chemical compound
CDM-3008 suppresses hepatitis B virus through induction of
interferon-stimulated genes. PLoS One. 14:e02161392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Konishi H, Okamoto K, Ohmori Y, Yoshino H,
Ohmori H, Ashihara M, Hirata Y, Ohta A, Sakamoto H, Hada N, et al:
An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral
replication. Sci Rep. 2:2592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lightcap ES, Yu P, Grossman S, Song K,
Khattar M, Xega K, He X, Gavin JM, Imaichi H, Garnsey JJ, et al: A
small-molecule SUMOylation inhibitor activates antitumor immune
responses and potentiates immune therapies in preclinical models.
Sci Transl Med. 13:eaba77912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Krueger RE and Mayer GD: Tilorone
hydrochloride: An orally active antiviral agent. Science.
169:1213–1214. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Yao Q and Liu Z: An effective
synthesis method for tilorone dihydrochloride with obvious IFN-α
Inducing Activity. Molecules. 20:21458–21463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Manfrere KC, Torrealba MP, Miyashiro DR,
Oliveira LM, de Carvalho GC, Lima JF, Branco AC, Pereira NZ,
Pereira J, Sanches JA Jr and Sato MN: Toll-like receptor agonists
partially restore the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and
type I interferon in Sézary syndrome. Oncotarget. 7:74592–74601.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu D, Putta MR, Bhagat L, Dai M, Wang D,
Trombino AF, Sullivan T, Kandimalla ER and Agrawal S: Impact of
secondary structure of toll-like receptor 9 agonists on interferon
alpha induction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 52:4320–4325. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin L, Hutzen B, Zuo M, Ball S, Deangelis
S, Foust E, Pandit B, Ihnat MA, Shenoy SS, Kulp S, et al: Novel
STAT3 phosphorylation inhibitors exhibit potent growth-suppressive
activity in pancreatic and breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:2445–2454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin L, Deangelis S, Foust E, Fuchs J, Li
C, Li PK, Schwartz EB, Lesinski GB, Benson D, Lü J, et al: A novel
small molecule inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and DNA binding
activity and exhibits potent growth suppressive activity in human
cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 9:2172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aziz N, Son YJ and Cho JY: Thymoquinone
suppresses IRF-3-mediated expression of type I interferons via
suppression of TBK1. Int J Mol Sci. 19:13552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen K, Liu J and Cao X: Regulation of
type I interferon signaling in immunity and inflammation: A
comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 83:1–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vigneswara V and Ahmed Z: The role of
caspase-2 in regulating cell fate. Cells. 9:12592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Obeng E: Apoptosis (programmed cell death)
and its signals-A review. Braz J Biol. 81:1133–1143. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kashyap D, Garg VK and Goel N: Intrinsic
and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis: Role in cancer development and
prognosis. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 125:73–120. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tummers B and Green DR: Caspase-8:
Regulating life and death. Immunol Rev. 277:76–89. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sayers TJ: Targeting the extrinsic
apoptosis signaling pathway for cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 8:1173–1180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ashkenazi A: Targeting the extrinsic
apoptotic pathway in cancer: Lessons learned and future directions.
J Clin Invest. 125:487–489. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gibson CJ and Davids MS: BCL-2 antagonism
to target the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:5021–5029. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bock FJ and Tait SWG: Mitochondria as
multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:85–100. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Burke PJ: Mitochondria, bioenergetics and
apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cancer. 3:857–870. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xiong S, Mu T, Wang G and Jiang X:
Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mammals. Protein Cell.
5:737–749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sano R and Reed JC: ER stress-induced cell
death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3460–3470. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Obeng EA and Boise LH: Caspase-12 and
caspase-4 are not required for caspase-dependent endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 280:29578–29587.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hu H, Tian M, Ding C and Yu S: The C/EBP
homologous protein (CHOP) transcription factor functions in
endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and microbial
infection. Front Immunol. 9:30832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rozpedek W, Pytel D, Mucha B, Leszczynska
H, Diehl JA and Majsterek I: The role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP
signaling pathway in tumor progression during endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Curr Mol Med. 6:533–544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Thyrell L, Erickson S, Zhivotovsky B,
Pokrovskaja K, Sangfelt O, Castro J, Einhorn S and Grandér D:
Mechanisms of Interferon-alpha induced apoptosis in malignant
cells. Oncogene. 21:1251–1262. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shigeno M, Nakao K, Ichikawa T, Suzuki K,
Kawakami A, Abiru S, Miyazoe S, Nakagawa Y, Ishikawa H, Hamasaki K,
et al: Interferon-alpha sensitizes human hepatoma cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis through DR5 upregulation and NF-kappa B
inactivation. Oncogene. 22:1653–1662. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Herzer K, Hofmann TG, Teufel A, Schimanski
CC, Moehler M, Kanzler S, Schulze-Bergkamen H and Galle PR:
IFN-alpha-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma involves
promyelocytic leukemia protein and TRAIL independently of p53.
Cancer Res. 69:855–862. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zuo C, Qiu X, Liu N, Yang D, Xia M, Liu J,
Wang X, Zhu H, Xie H, Dan H, et al: Interferon-α and
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor cooperatively mediates TRAIL-induced
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 333:316–326.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li T, Dong ZR, Guo ZY, Wang CH, Tang ZY,
Qu SF, Chen ZT, Li XW and Zhi XT: Aspirin enhances IFN-α-induced
growth inhibition and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via
JAK1/STAT1 pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 20:366–374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Quiroga AD, Alvarez Mde L, Parody JP,
Ronco MT, Francés DE, Pisani GB, Carnovale CE and Carrillo MC:
Involvement of reactive oxygen species on the apoptotic mechanism
induced by IFN-alpha2b in rat preneoplastic liver. Biochem
Pharmacol. 73:1776–1785. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Parody JP, Ceballos MP, Quiroga AD,
Frances DE, Carnovale CE, Pisani GB, Alvarez ML and Carrillo MC:
FoxO3a modulation and promotion of apoptosis by interferon-α2b in
rat preneoplastic liver. Liver Int. 34:1566–1577. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Quiroga AD, Vera MC, Ferretti AC, Lucci A,
Comanzo CG, Lambertucci F, Ceballos MP and Carrillo MC: IFN-α-2b
induces apoptosis by decreasing cellular cholesterol levels in rat
preneoplastic hepatocytes. Cytokine. 133:1551722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lee SJ, Yang A, Wu TC and Hung CF:
Immunotherapy for human papillomavirus-associated disease and
cervical cancer: Review of clinical and translational research. J
Gynecol Oncol. 27:e512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Stewart C, Ralyea C and Lockwood S:
Ovarian cancer: An integrated review. Semin Oncol Nurs. 35:151–156.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shi WY, Cao C and Liu L: Interferon α
induces the apoptosis of cervical cancer HeLa cells by activating
both the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway and endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 17:18322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Miyake K, Bekisz J, Zhao T, Clark CR and
Zoon KC: Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is targeted in
IFN-α2a-induced Bid-mediated apoptosis through Bak activation in
ovarian cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:1378–1388. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Green DS, Husain SR, Johnson CL, Sato Y,
Han J, Joshi B, Hewitt SM, Puri RK and Zoon KC: Combination
immunotherapy with IL-4 Pseudomonas exotoxin and IFN-α and IFN-γ
mediate antitumor effects in vitro and in a mouse model of human
ovarian cancer. Immunotherapy. 11:483–496. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cai L, Liu J and Wang Y, Chen H, Ma Y and
Wang Y and Wang Y: Enhanced anti-melanoma efficacy of interferon
α-2b via overexpression of ING4 by enhanced Fas/FasL-mediated
apoptosis. Oncol Lett. 15:9577–9583. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lesinski GB, Raig ET, Guenterberg K, Brown
L, Go MR, Shah NN, Lewis A, Quimper M, Hade E, Young G, et al:
IFN-alpha and bortezomib overcome Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 overexpression in
melanoma cells by stimulating the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis.
Cancer Res. 68:8351–8360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Minnie SA and Hill GR: Immunotherapy of
multiple myeloma. J Clin Invest. 130:1565–1575. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Gómez-Benito M, Balsas P, Carvajal-Vergara
X, Pandiella A, Anel A, Marzo I and Naval J: Mechanism of apoptosis
induced by IFN-alpha in human myeloma cells: Role of Jak1 and Bim
and potentiation by rapamycin. Cell Signal. 19:844–854. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Deleuze A, Saout J, Dugay F, Peyronnet B,
Mathieu R, Verhoest G, Bensalah K, Crouzet L, Laguerre B,
Belaud-Rotureau MA, et al: Immunotherapy in renal cell carcinoma:
The future is now. Int J Mol Sci. 21:25322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Clark PE, Polosukhina DA, Gyabaah K, Moses
HL, Thorburn A and Zent R: TRAIL and interferon-alpha act
synergistically to induce renal cell carcinoma apoptosis. J Urol.
184:1166–1174. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Reiter M, Eckhardt I, Haferkamp A and
Fulda S: Smac mimetic sensitizes renal cell carcinoma cells to
interferon-α-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 375:1–8. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bake V, Roesler S, Eckhardt I, Belz K and
Fulda S: Synergistic interaction of Smac mimetic and IFNα to
trigger apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Lett.
355:224–231. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cowling V and Downward J: Caspase-6 is the
direct activator of caspase-8 in the cytochrome c-induced apoptosis
pathway: Absolute requirement for removal of caspase-6 prodomain.
Cell Death Diff. 9:1046–1056. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Inoue S, Browne G, Melino G and Cohen GM:
Ordering of caspases in cells undergoing apoptosis by the intrinsic
pathway. Cell Death Differ. 16:1053–1061. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB,
Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD, Wang HG, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Alnemri
ES, et al: Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade:
Hierarchical activation of caspases-2, −3, −6, −7, −8, and −10 in a
caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol. 144:281–292. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Aricò E, Castiello L, Capone I, Gabriele L
and Belardelli F: Type I interferons and cancer: An evolving story
demanding novel clinical applications. Cancers (Basel).
11:19432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Muñoz de Escalona Rojas JE, García Serrano
JL, Cantero Hinojosa J, Padilla Torres JF and Bellido Muñoz RM:
Application of interferon alpha 2b in conjunctival intraepithelial
neoplasia: Predictors and prognostic factors. J Ocul Pharmacol
Ther. 30:489–494. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Yoon SY and Won JH: The clinical role of
interferon alpha in Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative
neoplasms. Blood Res. 56:S44–S50. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ghosh D, Ghosh D and Parida P:
Physiological proteins in therapeutics: A current review on
interferons. Mini Rev Med Chem. 12:947–952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Di Trolio R, Simeone E, Di Lorenzo G,
Buonerba C and Ascierto PA: The use of interferon in melanoma
patients: A systematic review. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
2:203–312. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hauschild A, Kähler KC, Schäfer M and
Fluck M: Interdisciplinary management recommendations for toxicity
associated with interferon-alfa therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges.
6:829–838. 2008.(In English, German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Conlon KC, Miljkovic MD and Waldmann TA:
Cytokines in the treatment of cancer. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
39:6–21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|