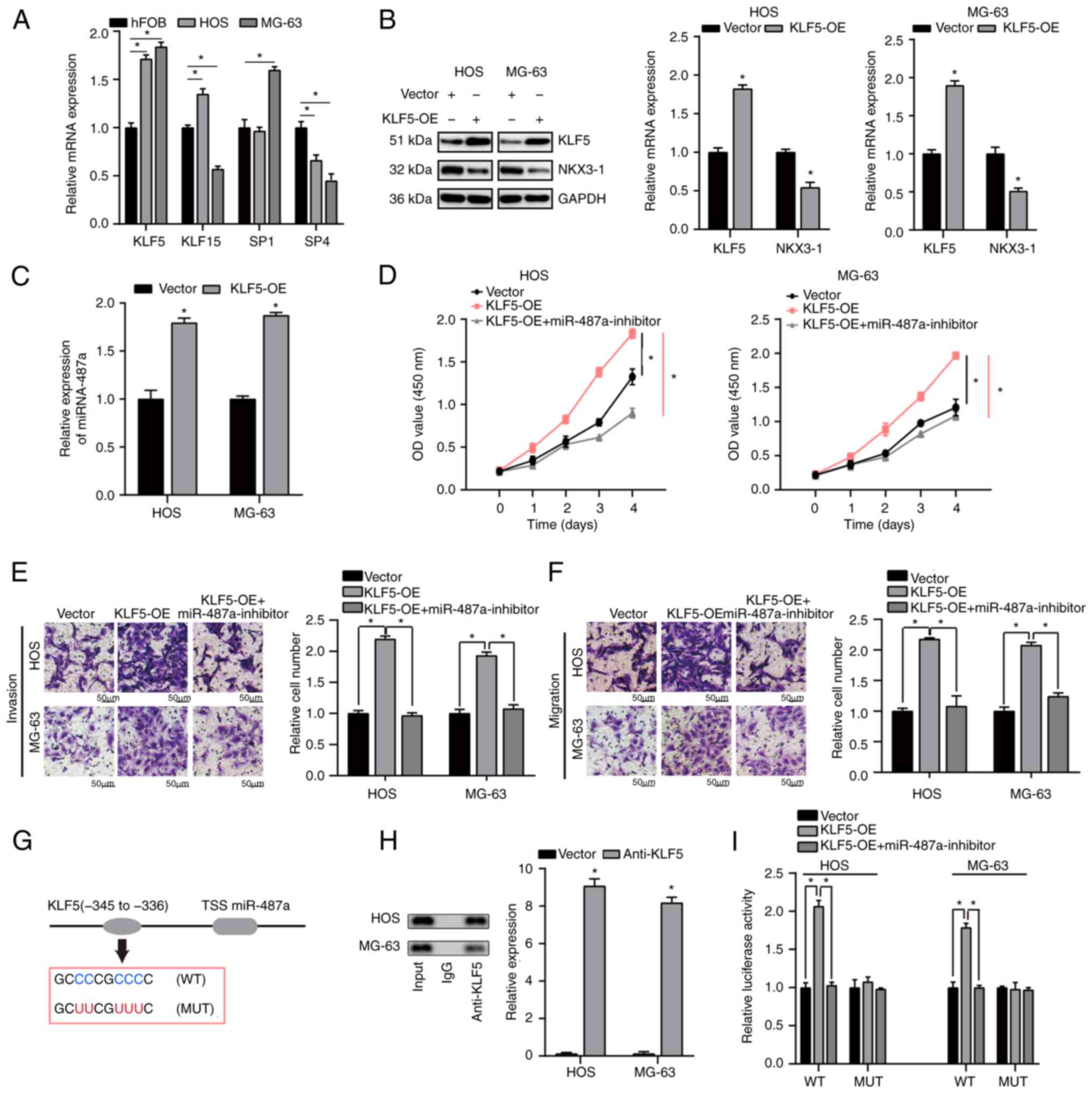
|
1
|
Lindsey BA, Markel JE and Kleinerman ES:
Osteosarcoma overview. Rheumatol Ther. 4:25–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang J and Zhang W: New molecular insights
into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:398–406.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ritter J and Bielack SS: Osteosarcoma. Ann
Oncol. 21 (Suppl 7):vii320–vii325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bernthal NM, Federman N, Eilber FR, Nelson
SD, Eckardt JJ, Eilber FC and Tap WD: Long-term results (>25
years) of a randomized, prospective clinical trial evaluating
chemotherapy in patients with high-grade, operable osteosarcoma.
Cancer. 118:5888–5893. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anderson ME: Update on survival in
osteosarcoma. Orthop Clin North Am. 47:283–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chu Y, Hu X, Wang G, Wang Z and Wang Y:
Downregulation of miR-136 promotes the progression of osteosarcoma
and is associated with the prognosis of patients with osteosarcoma.
Oncol Lett. 17:5210–5218. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang H, Zhao F, Cai S and Pu Y: MiR-193a
regulates chemoresistance of human osteosarcoma cells via
repression of IRS2. J Bone Oncol. 17:1002412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nishikawa R, Goto Y, Kurozumi A,
Matsushita R, Enokida H, Kojima S, Naya Y, Nakagawa M, Ichikawa T
and Seki N: MicroRNA-205 inhibits cancer cell migration and
invasion via modulation of centromere protein F regulating pathways
in prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 22:867–877. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen X and Zhang Y: BMP-2 and miR-29c in
osteosarcoma tissues on proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma
cells. Oncol Lett. 17:5389–5394. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen T, Xu C, Chen J, Ding C, Xu Z, Li C
and Zhao J: MicroRNA-203 inhibits cellular proliferation and
invasion by targeting Bmi1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol
Lett. 9:2639–2646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qin C, Zhao Y, Gong C and Yang Z:
MicroRNA-154/ADAM9 axis inhibits the proliferation, migration and
invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 14:6969–6975.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hannafon BN, Cai A, Calloway CL, Xu YF,
Zhang R, Fung KM and Ding WQ: miR-23b and miR-27b are oncogenic
microRNAs in breast cancer: Evidence from a CRISPR/Cas9 deletion
study. BMC Cancer. 19:6422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xia P, Gu R, Zhang W, Shao L, Li F, Wu C
and Sun Y: MicroRNA-377 exerts a potent suppressive role in
osteosarcoma through the involvement of the histone
acetyltransferase 1-mediated Wnt axis. J Cell Physiol.
234:22787–22798. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang G, Zhu Y, Jin C, Shi Q, An X, Song
L, Gao F and Li S: CircRNA_0078767 promotes osteosarcoma
progression by increasing CDK14 expression through sponging
microRNA-330-3p. Chem Biol Interact. 360:1099032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang X, Wang M, Lin B, Yao D, Li J, Tang
X, Li S, Liu Y, Xie R and Yu S: miR-487a promotes progression of
gastric cancer by targeting TIA1. Biochimie. 154:119–126. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma M, He M, Jiang Q, Yan Y, Guan S, Zhang
J, Yu Z, Chen Q, Sun M, Yao W, et al: MiR-487a promotes
TGF-β1-induced EMT, the migration and invasion of breast cancer
cells by directly targeting MAGI2. Int J Biol Sci. 12:397–408.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li XL, Jones MF, Subramanian M and Lal A:
Mutant p53 exerts oncogenic effects through microRNAs and their
target gene networks. FEBS Lett. 588:2610–2615. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liao JM, Cao B, Zhou X and Lu H: New
insights into p53 functions through its target microRNAs. J Mol
Cell Biol. 6:206–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Varet H, Brillet-Guéguen L, Coppée JY and
Dillies MA: SARTools: A DESeq2- and EdgeR-based R pipeline for
comprehensive differential analysis of RNA-Seq data. PLoS One.
11:e01570222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Castro-Mondragon JA, Riudavets-Puig R,
Rauluseviciute I, Lemma RB, Turchi L, Blanc-Mathieu R, Lucas J,
Boddie P, Khan A, Manosalva Pérez N, et al: JASPAR 2022: The 9th
release of the open-access database of transcription factor binding
profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 50(D1): D165–D173. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dweep H, Gretz N and Sticht C: miRWalk
database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1182:289–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C and
Leslie C: Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts
functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol.
11:R902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu X and Liu M: miR-522 stimulates
TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway and promotes osteosarcoma
tumorigenesis by targeting PPM1A. J Cell Biochem. 120:18425–18434.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang RM, Xiao S, Lei X, Yang H, Fang F
and Yang LY: miRNA-487a promotes proliferation and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 23:2593–2604. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang X, Cai S, Shu Y, Deng X, Zhang Y, He
N, Wan L, Chen X, Qu Y and Yu S: Exosomal miR-487a derived from m2
macrophage promotes the progression of gastric cancer. Cell Cycle.
20:434–444. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang J, Liu Z, Ge C, Chen C, Zhao F, Li
H, Chen T, Yao M and Li J: NK3 homeobox 1 (NKX3.1) up-regulates
forkhead box O1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and thereby
suppresses tumor proliferation and invasion. J Biol Chem.
292:19146–19159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miyaguchi K, Uzawa N, Mogushi K, Takahashi
K, Michikawa C, Nakata Y, Sumino J, Okada N, Mizushima H, Fukuoka Y
and Tanaka H: Loss of NKX3-1 as a potential marker for an increased
risk of occult lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 40:1907–1914. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren W and Gu G: Prognostic implications of
RB1 tumour suppressor gene alterations in the clinical outcome of
human osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl).
26:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li Z, Xu D, Chen X, Li S, Chan MTV and Wu
WKK: LINC01133: An emerging tumor-associated long non-coding RNA in
tumor and osteosarcoma. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 27:32467–32473.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen S, Zhou L and Wang Y: ALKBH5-mediated
m6A demethylation of lncRNA PVT1 plays an oncogenic role
in osteosarcoma. Cancer Cell Int. 20:342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takeuchi H, Taoka R, Mmeje CO, Jinesh GG,
Safe S and Kamat AM: CDODA-Me decreases specificity protein
transcription factors and induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
through induction of reactive oxygen species. Urol Oncol.
34:337.e11–e18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jia F, Liu Y, Dou X, Du C, Mao T and Liu
X: Liensinine inhibits osteosarcoma growth by ROS-mediated
suppression of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2022:82456142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rawat L and Nayak V: Piperlongumine
induces ROS mediated apoptosis by transcriptional regulation of
SMAD4/P21/P53 genes and synergizes with doxorubicin in osteosarcoma
cells. Chem Biol Interact. 354:1098322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gu Z, Wu S, Xu G, Wu W, Mao B and Zhao S:
miR-487a performs oncogenic functions in osteosarcoma by targeting
BTG2 mRNA. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 52:631–637. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao W, Sun M, Li S, Chen Z and Geng D:
Transcription factor ATF3 mediates the radioresistance of breast
cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4664–4675. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu M, Zhang N and He S: Transcription
factor KLF4 modulates microRNA-106a that targets Smad7 in gastric
cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 215:1524672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang T, Wang G, Yang L, Peng B, Wen Y,
Ding G and Wang Z: Transcription factor YY1 modulates lung cancer
progression by activating lncRNA-PVT1. DNA Cell Biol. 36:947–958.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Takeuchi H, Tanaka M, Tanaka A, Tsunemi A
and Yamamoto H: Predominance of M2-polarized macrophages in bladder
cancer affects angiogenesis, tumor grade and invasiveness. Oncol
Lett. 11:3403–3408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|