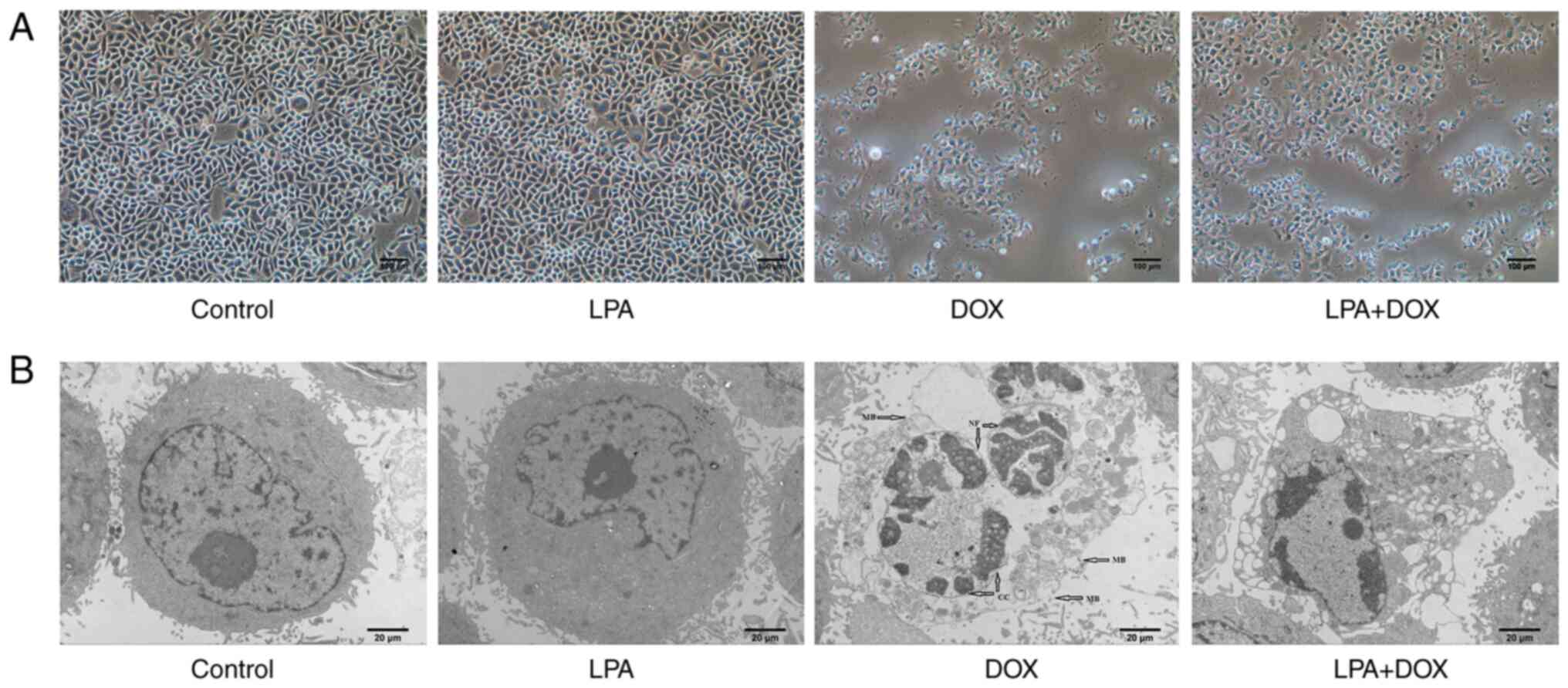
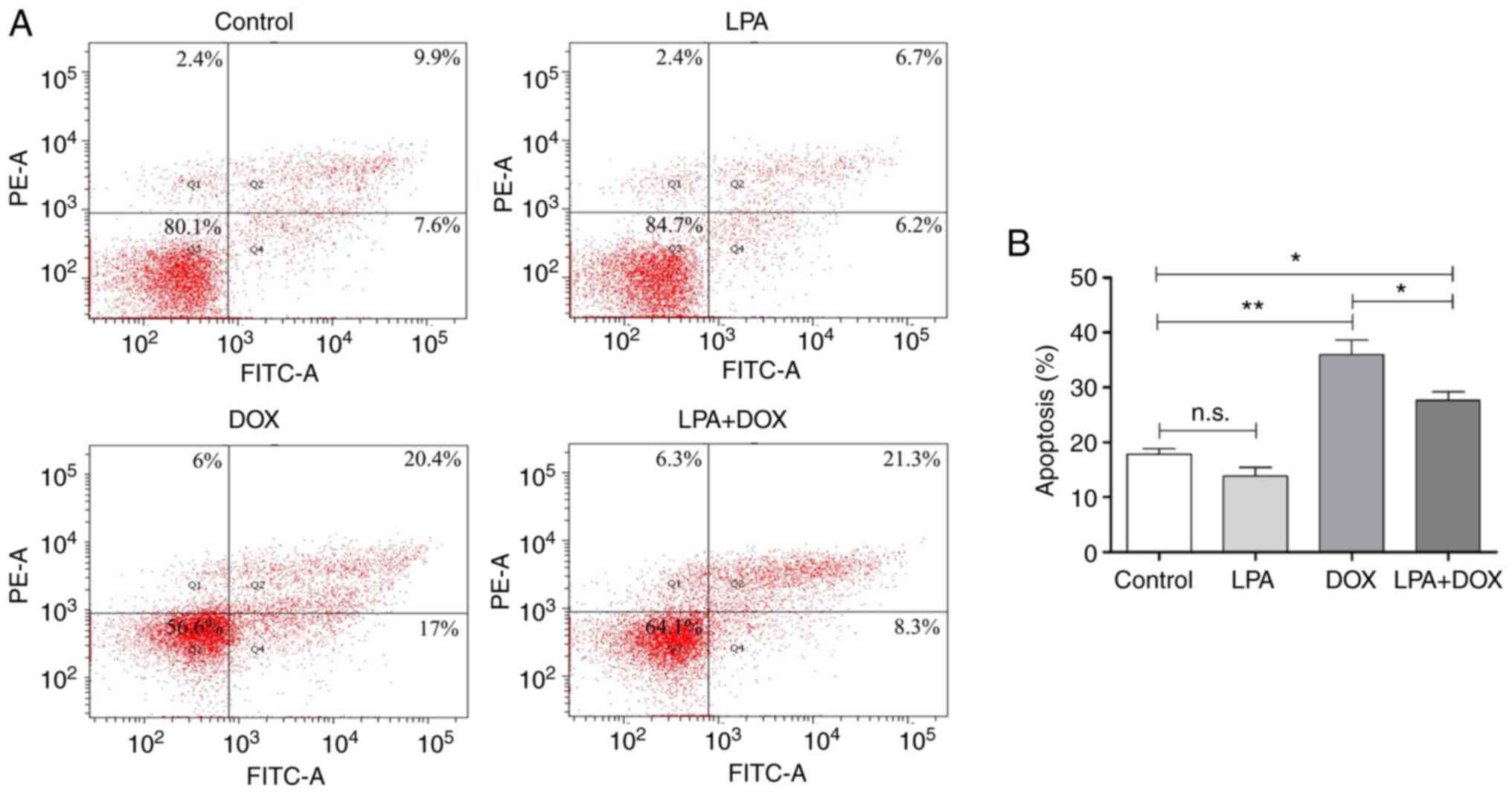
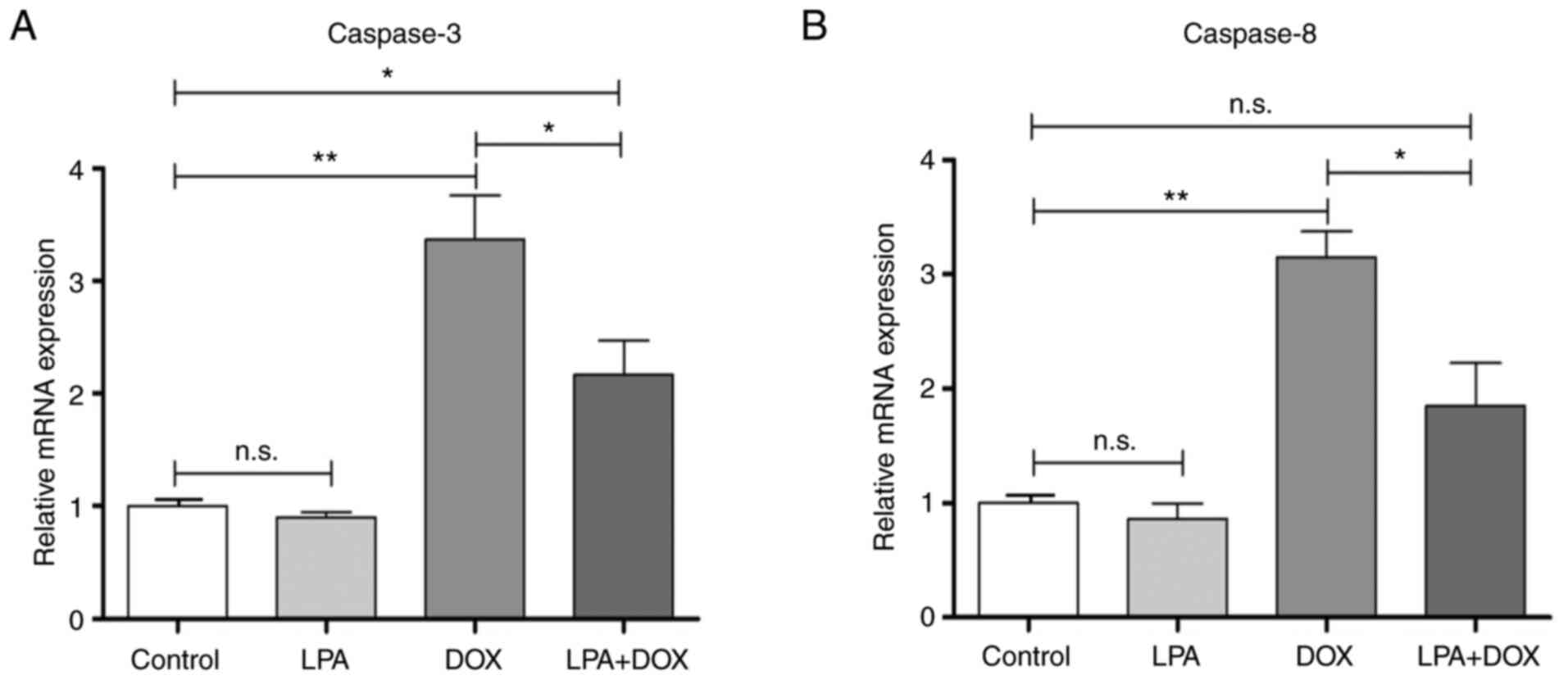
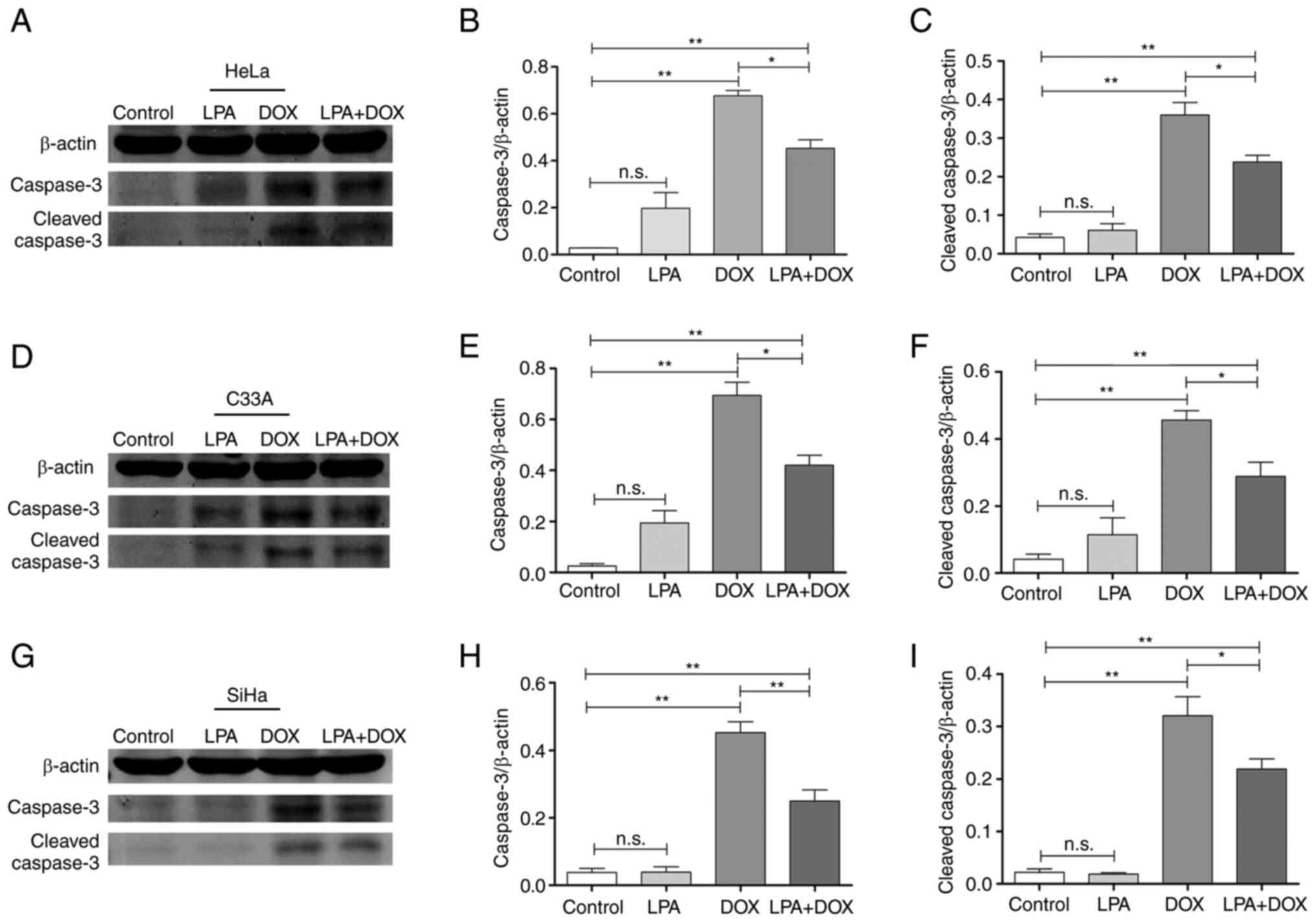
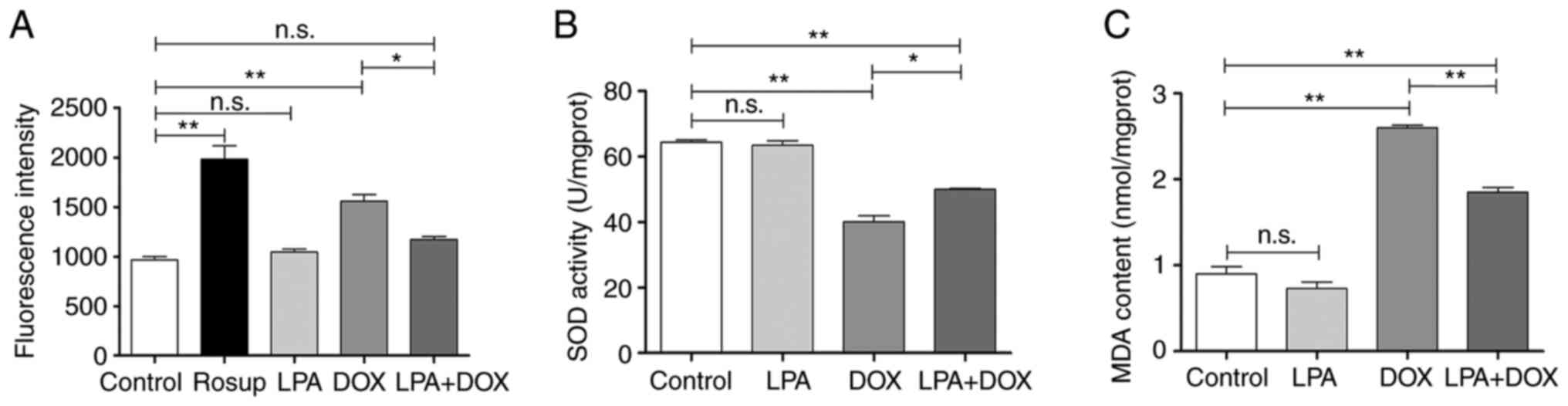
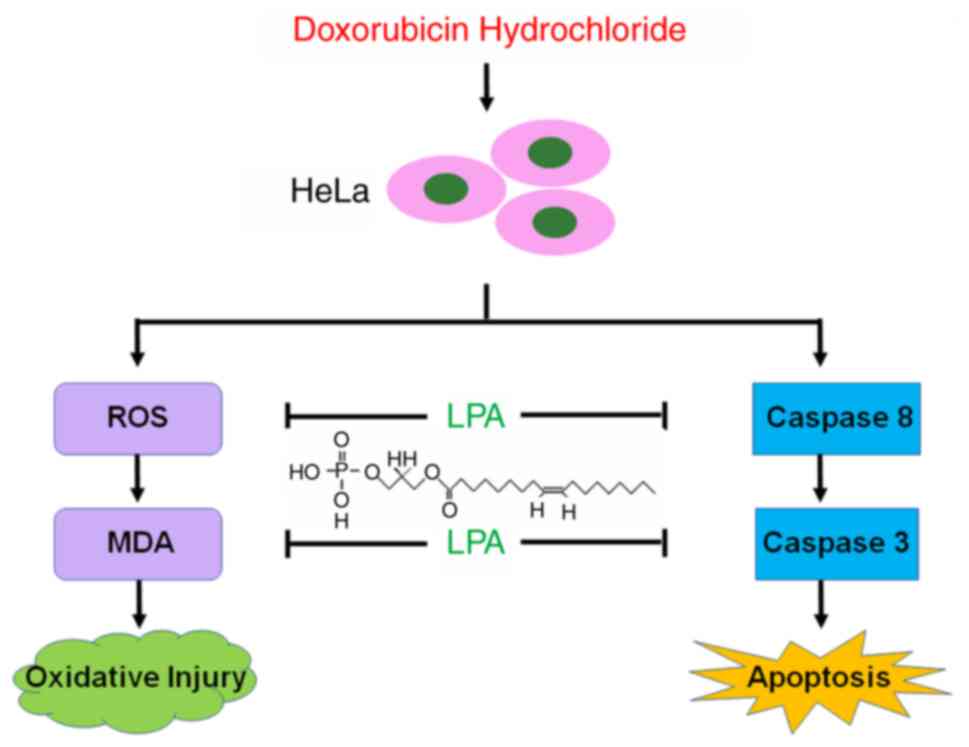
|
1
|
Murph MM, Scaccia LA, Volpicelli LA and
Radhakrishna H: Agonist-induced endocytosis of lysophosphatidic
acid-coupled LPA1/EDG-2 receptors via a dynamin2- and
Rab5-dependent pathway. J Cell Sci. 116:1969–1980. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Minis E, Holcomb K, Sisti G, Nasioudis D,
Kanninen TT, Athanasiou A, Frey MK, Chapman-Davis E, Caputo TA and
Witkin SS: Evaluation of lysophosphatidic acid in vaginal fluid as
a biomarker for ovarian cancer: A pilot study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol X. 2:1000122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ramachandran S, Ramaswamy S, Cho CH and
Parthasarathy S: Lysophosphatidic acid induces glycodelin gene
expression in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 177:197–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim NH, Sadra A, Park HY, Oh SM, Chun J,
Yoon JK and Huh SO: HeLa E-Box Binding protein, HEB, inhibits
promoter activity of the lysophosphatidic acid receptor gene Lpar1
in neocortical neuroblast cells. Mol Cells. 42:123–134.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu S, Jiang H, Min L, Ning T, Xu J, Wang
T, Wang X, Zhang Q, Cao R, Zhang S and Zhu S: Lysophosphatidic acid
mediated PI3K/AKT activation contributed to esophageal squamous
cell cancer progression. Carcinogenesis. 42:611–620. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Feng Y, Xiao M and Zhang Z, Cui R, Jiang
X, Wang S, Bai H, Liu C and Zhang Z: Potential interaction between
lysophosphatidic acid and tumor-associated macrophages in ovarian
carcinoma. J Inflamm (Lond). 17:232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Obol JH, Lin S, Obwolo MJ, Harrison R and
Richmond R: Knowledge, attitudes, and practice of cervical cancer
prevention among health workers in rural health centres of Northern
Uganda. BMC Cancer. 21:1102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sui Y, Yang Y, Wang J, Li Y, Ma H, Cai H,
Liu X, Zhang Y, Wang S, Li Z, et al: Lysophosphatidic acid inhibits
apoptosis induced by cisplatin in cervical cancer cells. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:5983862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nie H, Bu F, Xu J, Li T and Huang J: 29
immune-related genes pairs signature predict the prognosis of
cervical cancer patients. Sci Rep. 10:141522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abdoul-Azize S, Buquet C, Li H, Picquenot
JM and Vannier JP: Integration of Ca2+ signaling
regulates the breast tumor cell response to simvastatin and
doxorubicin. Oncogene. 37:4979–4993. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei T, Xiaojun X and Peilong C:
Magnoflorine improves sensitivity to doxorubicin (DOX) of breast
cancer cells via inducing apoptosis and autophagy through AKT/mTOR
and p38 signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 121:1091392020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jawad B, Poudel L, Podgornik R, Steinmetz
NF and Ching WY: Molecular mechanism and binding free energy of
doxorubicin intercalation in DNA. Phys Chem Chem Phys.
21:3877–3893. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu J, Liu D, Niu H, Zhu G, Xu Y, Ye D, Li
J and Zhang Q: Resveratrol reverses Doxorubicin resistance by
inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through
modulating PTEN/Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 36:192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pilco-Ferreto N and Calaf GM: Influence of
doxorubicin on apoptosis and oxidative stress in breast cancer cell
lines. Int J Oncol. 49:753–762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Islam MT: Oxidative stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction-linked neurodegenerative disorders.
Neurol Res. 39:73–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Prasad S, Gupta SC and Tyagi AK: Reactive
oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative
nutraceuticals. Cancer Lett. 387:95–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu R, Gang L, Shen X, Xu H, Wu F and
Sheng L: Binding characteristics and superimposed antioxidant
properties of caffeine combined with superoxide dismutase. ACS
Omega. 4:17417–17424. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saribal D, Hocaoglu-Emre FS, Karaman F,
Mırsal H and Akyolcu MC: Trace element levels and
oxidant/antioxidant status in patients with alcohol abuse. Biol
Trace Elem Res. 193:7–13. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu X, Lai Y and Hua ZC: Apoptosis and
apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials.
Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201809922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X and Li Y, Tang X, Shang X, Zhao Z,
Jiang Y and Li Y: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia outer membrane
protein A induces epithelial cell apoptosis via mitochondrial
pathways. J Microbiol. 58:868–877. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang M, Qi L, Li L and Li Y: The
caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and
pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 6:1122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma M, Wang X, Liu N, Shan F and Feng Y:
Low-dose naltrexone inhibits colorectal cancer progression and
promotes apoptosis by increasing M1-type macrophages and activating
the Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3/PARP pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
83:1063882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim JM, Ghosh SR, Weil AC and Zirkin BR:
Caspase-3 and caspase-activated deoxyribonuclease are associated
with testicular germ cell apoptosis resulting from reduced
intratesticular testosterone. Endocrinology. 142:3809–3816. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang C, Feng X, He L, Zhang Y and Shao L:
The interrupted effect of autophagic flux and lysosomal function
induced by graphene oxide in p62-dependent apoptosis of F98 cells.
J Nanobiotechnology. 18:522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wan T, Wang Z, Luo Y, Zhang Y, He W, Mei
Y, Xue J, Li M, Pan H, Li W, et al: FA-97, a New synthetic caffeic
acid phenethyl ester derivative, protects against oxidative
stress-mediated neuronal cell apoptosis and scopolamine-induced
cognitive impairment by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2019:82396422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nogueira V and Hay N: Molecular pathways:
Reactive oxygen species homeostasis in cancer cells and
implications for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4309–4314.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Peng N, Jin L, He A, Deng C and Wang X:
Effect of sulphoraphane on newborn mouse cardiomyocytes undergoing
ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Pharm Biol. 57:753–759. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song S, Chu L, Liang H, Chen J, Liang J,
Huang Z, Zhang B and Chen X: Protective effects of dioscin against
doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via regulation of
Sirt1/FOXO1/NF-κb Signal. Front Pharmacol. 10:10302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rasool M, Malik A, Basit Ashraf MA,
Parveen G, Iqbal S, Ali I, Qazi MH, Asif M, Kamran K, Iqbal A, et
al: Evaluation of matrix metalloproteinases, cytokines and their
potential role in the development of ovarian cancer. PLoS One.
11:e01671492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wei LF, Zhang HM, Wang SS, Jing JJ, Zheng
ZC, Gao JX, Liu Z and Tian J: Changes of MDA and SOD in brain
tissue after secondary brain injury with seawater immersion in
rats. Turk Neurosurg. 26:384–288. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|