|
1
|
Alvarez MC, Maso V, Torello CO, Ferro KP
and Saad STO: The polyphenol quercetin induces cell death in
leukemia by targeting epigenetic regulators of pro-apoptotic genes.
Clin Epigenetics. 10:1392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Casano K, Meddaugh H, Zambrano RM, Marble
M, Torres JI and Lacassie Y: Gorlin-like phenotype in a patient
with a PTCH2 variant of uncertain significance. Eur J Med Genet.
63:1038422020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hao BB, Li XJ, Jia XL, Wang YX, Zhai LH,
Li DZ, Liu J, Zhang D, Chen YL, Xu YH, et al: The novel cereblon
modulator CC-885 inhibits mitophagy via selective degradation of
BNIP3L. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 41:1246–1254. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei Y, Xiong X, Li X, Lu W, He X, Jin X,
Sun R, Lyu H, Yuan T, Sun T and Zhao M: Low-dose decitabine plus
venetoclax is safe and effective as post-transplant maintenance
therapy for high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic
syndrome. Cancer Sci. 112:3636–3644. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
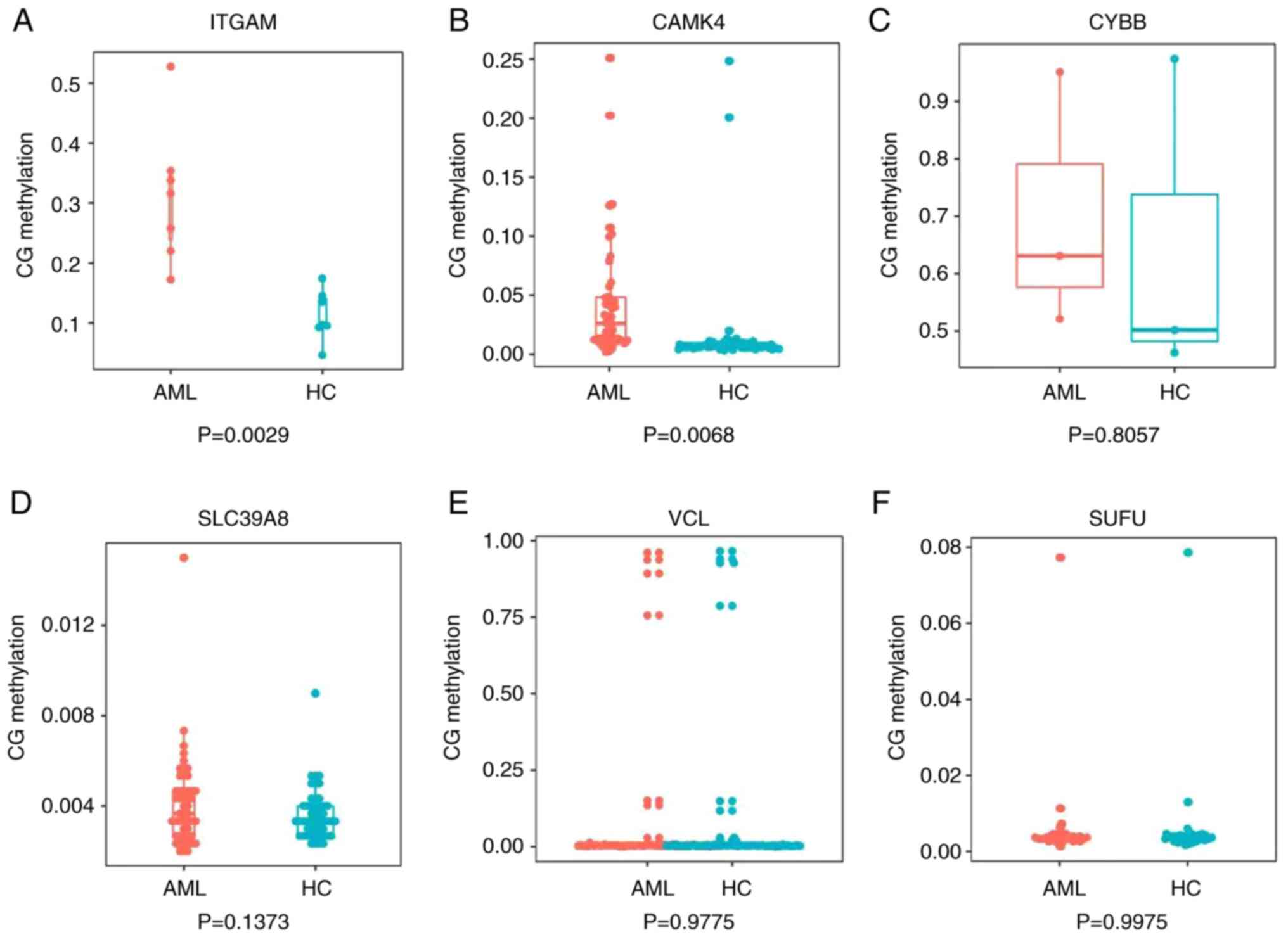
Hu L, Gao Y, Shi Z, Liu Y, Zhao J, Xiao Z,
Lou J, Xu Q and Tong X: DNA methylation-based prognostic biomarkers
of acute myeloid leukemia patients. Ann Transl Med. 7:7372019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Feng H, Li D, Liu S, Amizuka N
and Li M: Identification of differentially expressed genes induced
by aberrant methylation in oral squamous cell carcinomas using
integrated bioinformatic analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:16982018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xi Y, Lin Y, Guo W, Wang X, Zhao H, Miao
C, Liu W, Liu Y, Liu T, Luo Y, et al: Multi-omic characterization
of genome-wide abnormal DNA methylation reveals diagnostic and
prognostic markers for esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7:532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Itoh S, Yamazaki J, Iwahana M and
Tsukamoto A: Olsalazine inhibits cell proliferation and DNA
methylation in canine lymphoid tumor cell lines. Pol J Vet Sci.
24:515–523. 2021.
|
|
9
|
Shen S, Wang G, Shi Q, Zhang R, Zhao Y,
Wei Y, Chen F and Christiani DC: Seven-CpG-based prognostic
signature coupled with gene expression predicts survival of oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Epigenetics. 9:882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grencewicz DJ, Romigh T, Thacker S, Abbas
A, Jaini R, Luse D and Eng C: Redefining the PTEN promoter:
Identification of novel upstream transcription start regions. Hum
Mol Genet. 30:2135–2148. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pramodh S, Raina R, Hussain A, Bagabir SA,
Haque S, Raza ST, Ajmal MR, Behl S and Bhagavatula D: Luteolin
causes 5′CpG demethylation of the promoters of TSGs and modulates
the aberrant histone modifications, restoring the expression of
TSGs in human cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 23:40672022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huang S, Zhang B, Fan W, Zhao Q, Yang L,
Xin W and Fu D: Identification of prognostic genes in the acute
myeloid leukemia microenvironment. Aging (Albany NY).
11:10557–10580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
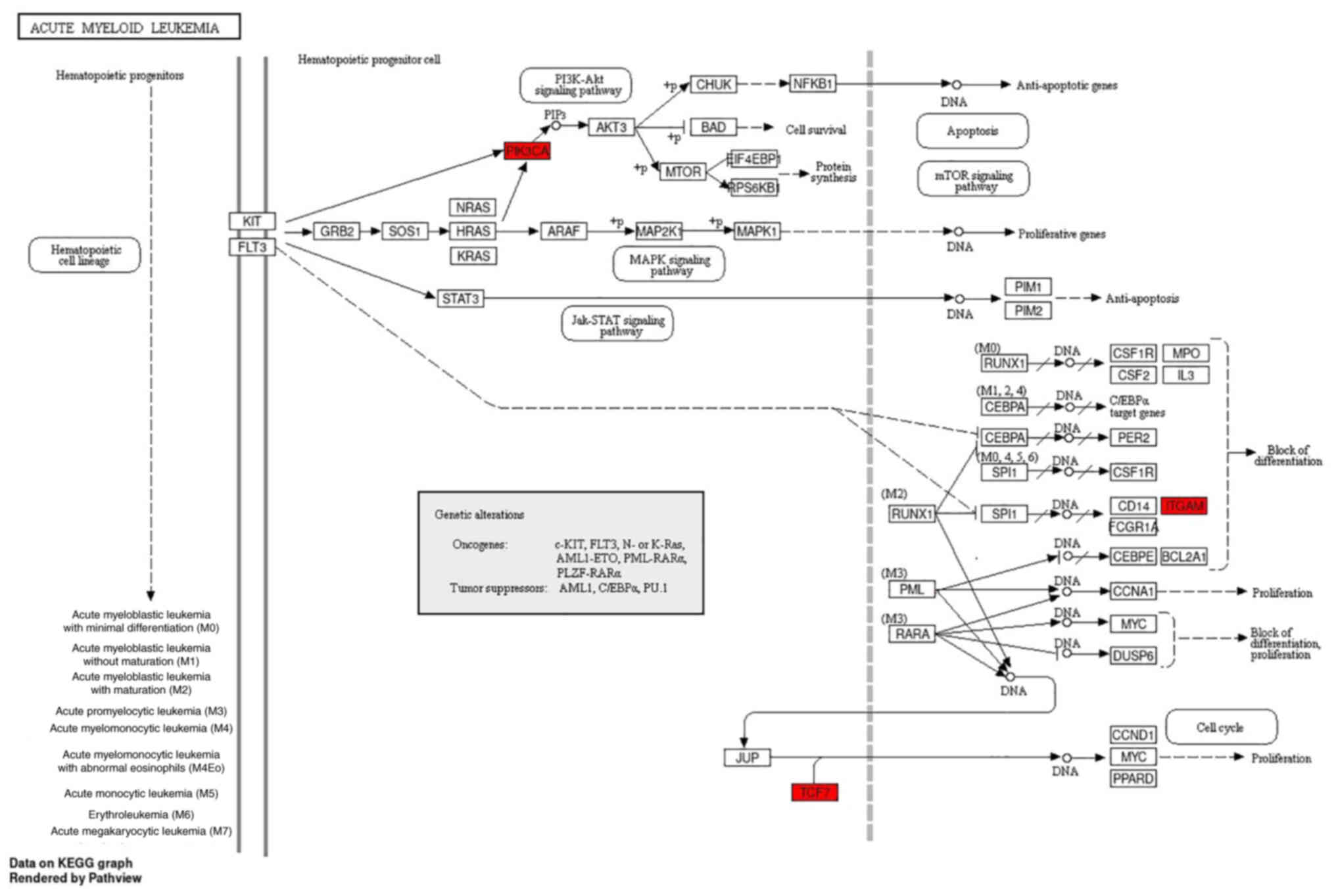
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
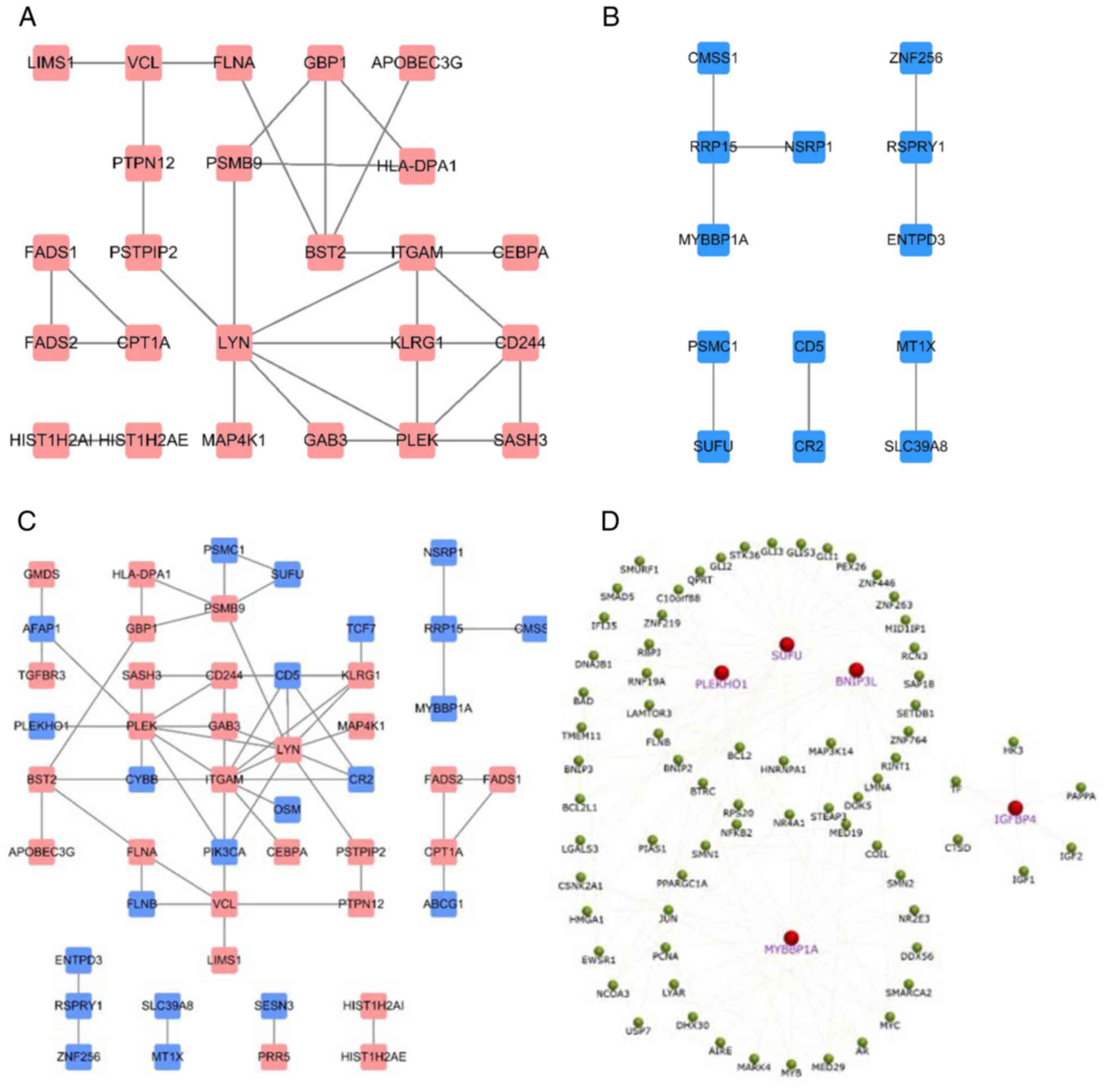
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shen Y, Pan X and Yang J: Gene regulation
and prognostic indicators of lung squamous cell carcinoma:
TCGA-derived miRNA/mRNA sequencing and DNA methylation data. J Cell
Physiol. 234:22896–22910. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Knaus HA, Berglund S, Hackl H, Blackford
AL, Zeidner JF, Montiel-Esparza R, Mukhopadhyay R, Vanura K, Blazar
BR, Karp JE, et al: Signatures of CD8+ T cell dysfunction in AML
patients and their reversibility with response to chemotherapy. JCI
Insight. 3:e1209742018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rommer A, Steinleitner K, Hackl H,
Schneckenleithner C, Engelmann M, Scheideler M, Vlatkovic I,
Kralovics R, Cerny-Reiterer S, Valent P, et al: Overexpression of
primary microRNA 221/222 in acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer.
13:3642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tanaka M, Oikawa K, Takanashi M, Kudo M,
Ohyashiki J, Ohyashiki K and Kuroda M: Down-regulation of miR-92 in
human plasma is a novel marker for acute leukemia patients. PLoS
One. 4:e55322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pérez C, Pascual M, Martín-Subero JI,
Bellosillo B, Segura V, Delabesse E, Álvarez S, Larrayoz MJ, Rifón
J, Cigudosa JC, et al: Aberrant DNA methylation profile of chronic
and transformed classic Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative
neoplasms. Haematologica. 98:1414–1420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu F, Wei T, Liu L, Hou F, Xu C, Guo H,
Zhang W, Ma M, Zhang Y, Yu Q and Wang J: Role of necroptosis and
immune infiltration in human stanford type A aortic dissection:
Novel insights from bioinformatics analyses. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022:61848022022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
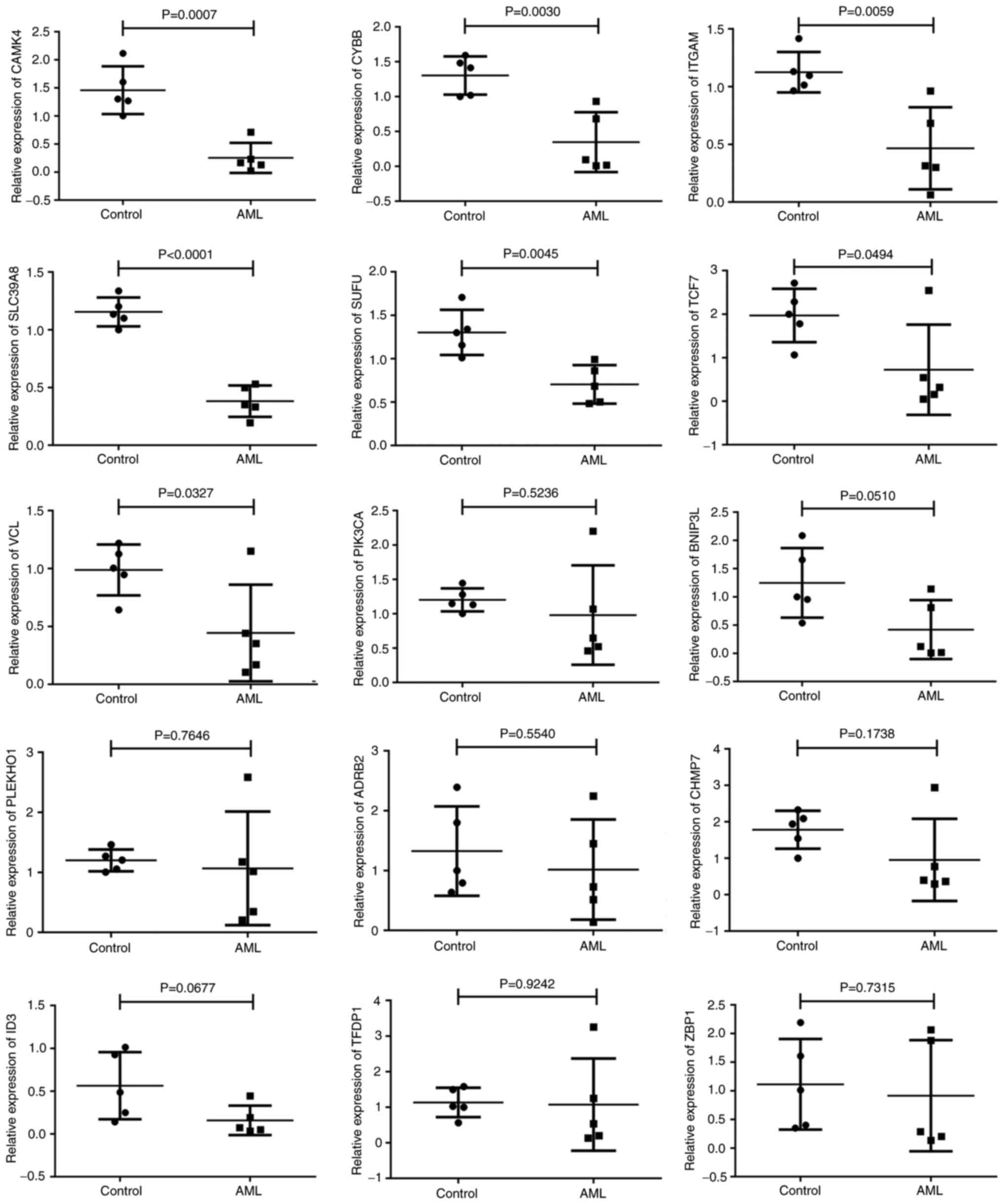
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abd ElHafeez S, D'Arrigo G, Leonardis D,
Fusaro M, Tripepi G and Roumeliotis S: Methods to analyze
time-to-event data: The cox regression analysis. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2021:13028112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo Y, Sun F, Peng X, Dong D, Ou W, Xie Y
and Luo Y: Integrated bioinformatics analysis to identify abnormal
methylated differentially expressed genes for predicting prognosis
of human colon cancer. Int J Gen Med. 14:4745–4756. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Jiang W, Wang J, Xie Y and Wang W:
Puerarin inhibits FUNDC1-mediated mitochondrial autophagy and
CSE-induced apoptosis of human bronchial epithelial cells by
activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY).
14:1253–1264. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alhadidi Q and Shah ZA: Cofilin Mediates
LPS-induced microglial cell activation and associated neurotoxicity
through activation of NF-κB and JAK-STAT pathway. Mol Neurobiol.
55:1676–1691. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Silverbush D, Grosskurth S, Wang D, Powell
F, Gottgens B, Dry J and Fisher J: Cell-specific computational
modeling of the PIM pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res.
77:827–838. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stranahan AW, Berezniuk I, Chakraborty S,
Feller F, Khalaj M and Park CY: Leukotrienes promote stem cell
self-renewal and chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 36:1575–1584. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Malik B, Devine H, Patani R, La Spada AR,
Hanna MG and Greensmith L: Gene expression analysis reveals early
dysregulation of disease pathways and links Chmp7 to pathogenesis
of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Sci Rep. 9:35392019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Garcia-Manero G, Tambaro FP, Bekele NB,
Yang H, Ravandi F, Jabbour E, Borthakur G, Kadia TM, Konopleva MY,
Faderl S, et al: Phase II trial of vorinostat with idarubicin and
cytarabine for patients with newly diagnosed acute myelogenous
leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 30:2204–2210.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Park JS, Kim SM, Choi J, Jung KA, Hwang
SH, Yang S, Kwok SK, Cho ML and Park SH: Interleukin-21-mediated
suppression of the Pax3-Id3 pathway exacerbates the development of
Sjögren's syndrome via follicular helper T cells. Cytokine.
125:1548342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
May AM, Frey AV, Bogatyreva L,
Benkisser-Petersen M, Hauschke D, Lübbert M, Wäsch R, Werner M,
Hasskarl J and Lassmann S: ID2 and ID3 protein expression mirrors
granulopoietic maturation and discriminates between acute leukemia
subtypes. Histochem Cell Biol. 141:431–440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li Z, Lu J, Zeng G, Pang J, Zheng X, Feng
J and Zhang J: MiR-129-5p inhibits liver cancer growth by targeting
calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CAMK4). Cell Death
Dis. 10:7892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang XT, Fang R, Ye SB, Zhang RS, Li R,
Wang X, Ji RH, Lu ZF, Ma HH, Zhou XJ, et al: Targeted
next-generation sequencing revealed distinct clinicopathologic and
molecular features of VCL-ALK RCC: A unique case from an older
patient without clinical evidence of sickle cell trait. Pathol Res
Pract. 215:1526512019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kesavardhana S, Malireddi RKS, Burton AR,
Porter SN, Vogel P, Pruett-Miller SM and Kanneganti TD: The Zα2
domain of ZBP1 is a molecular switch regulating influenza-induced
PANoptosis and perinatal lethality during development. J Biol Chem.
295:8325–8330. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Morimoto Y, Mizushima T, Wu X, Okuzaki D,
Yokoyama Y, Inoue A, Hata T, Hirose H, Qian Y, Wang J, et al:
miR-4711-5p regulates cancer stemness and cell cycle progression
via KLF5, MDM2 and TFDP1 in colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
122:1037–1049. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng S, Li M, Miao K and Xu H: lncRNA
GAS5-promoted apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer by
targeting miR-378a-5p/SUFU signaling. J Cell Biochem.
121:2225–2235. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang P, Zhou C, Lu C, Li W, Li W, Jing B,
Chen W, Zha Y, Zhang P, Bai C, et al: PLEKHO2 is essential for
M-CSF-dependent macrophage survival. Cell Signal. 37:115–122. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Rodrigo R, Mendis N, Ibrahim M, Ma C,
Kreinin E, Roma A, Berg S, Blay J and Spagnuolo PA: Knockdown of
BNIP3L or SQSTM1 alters cellular response to mitochondria target
drugs. Autophagy. 15:900–907. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|