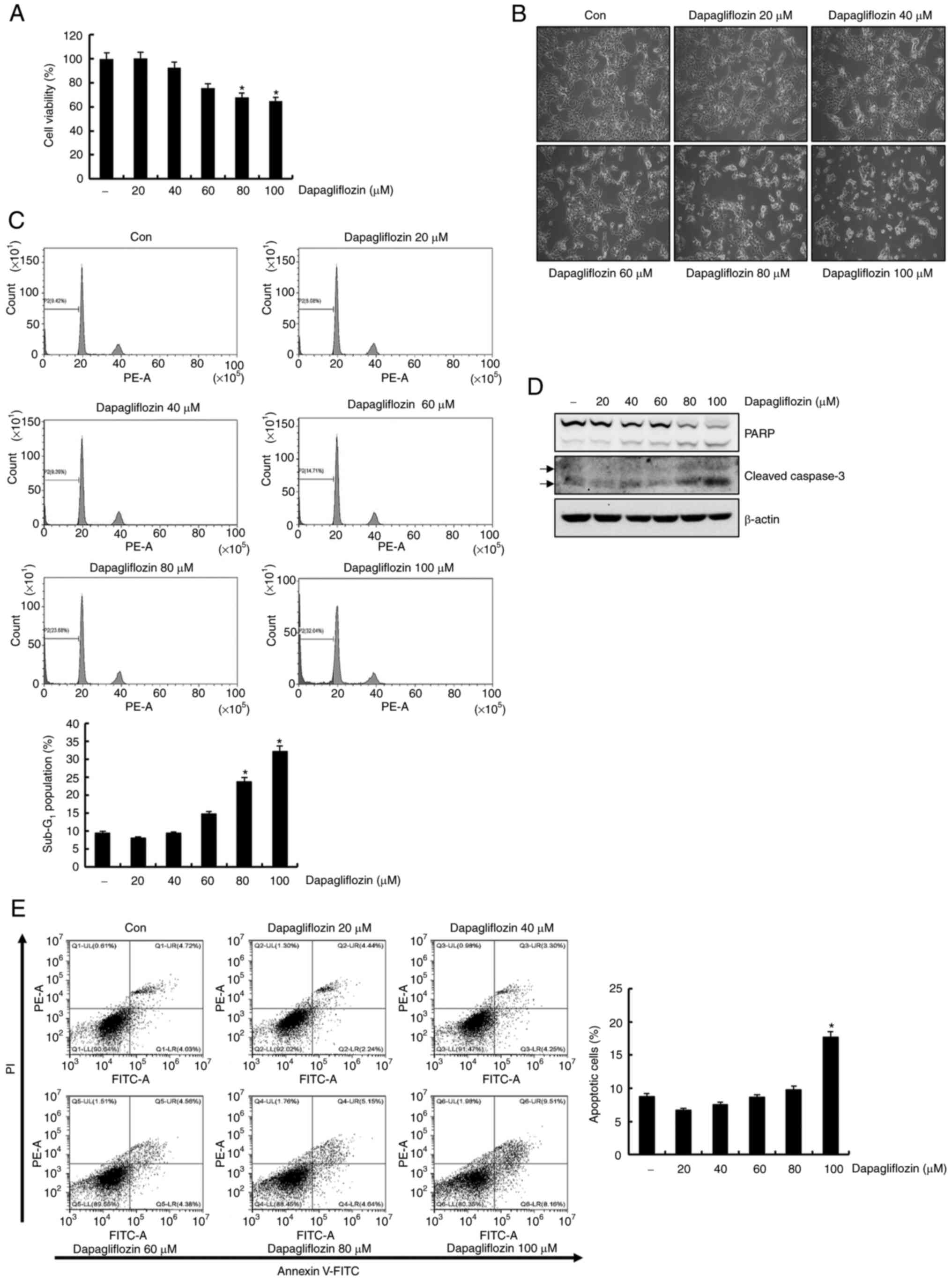
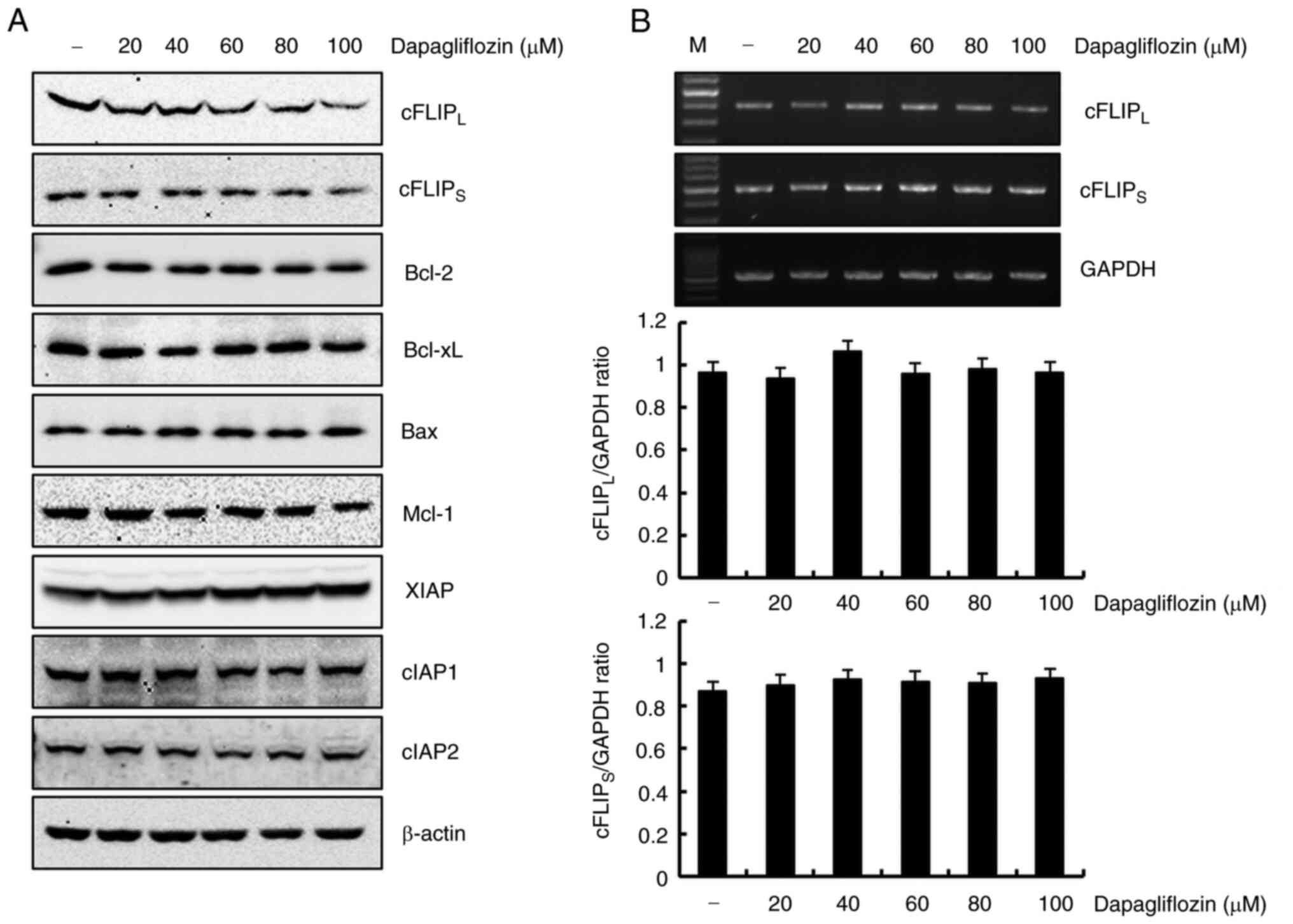
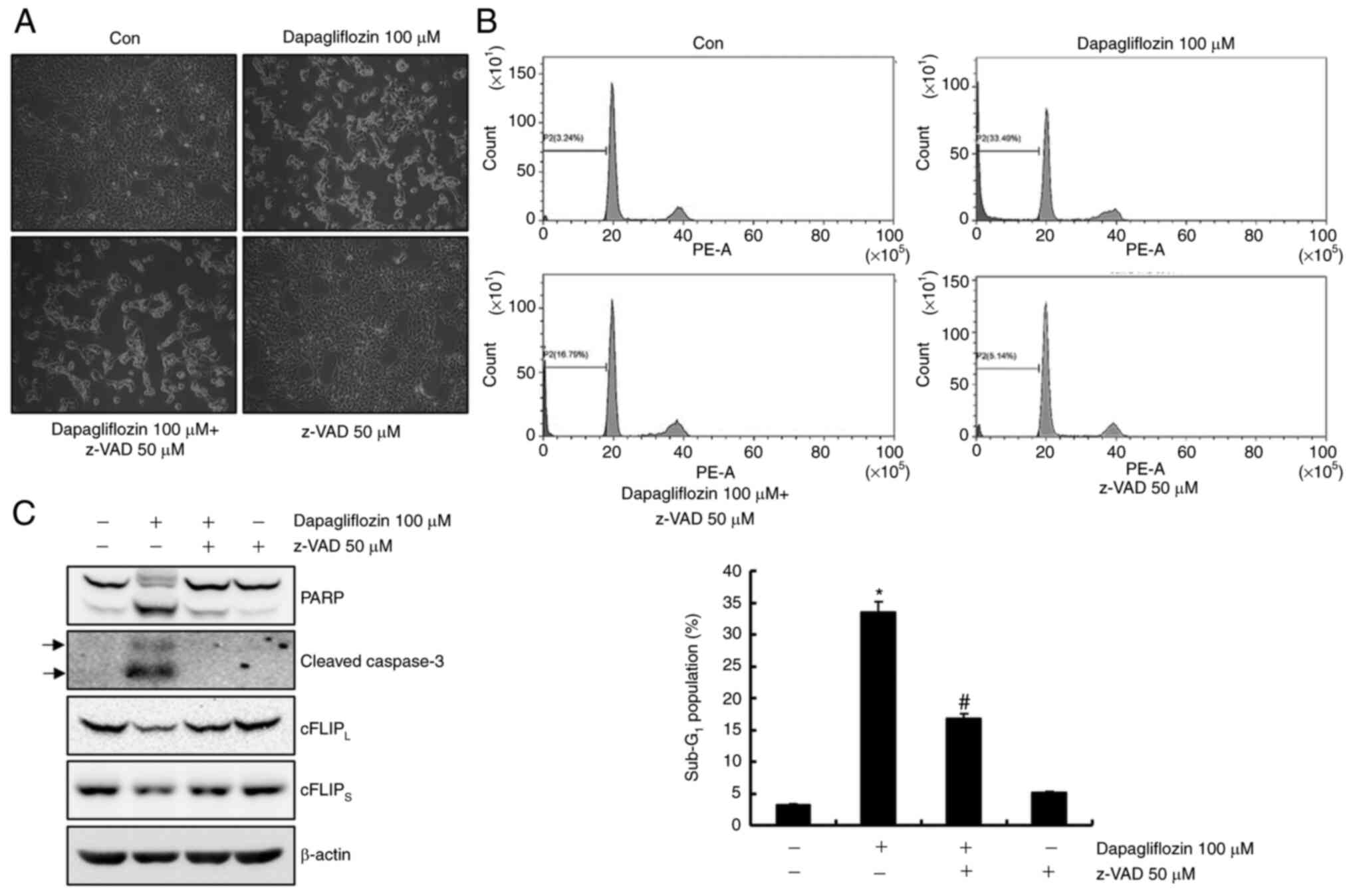
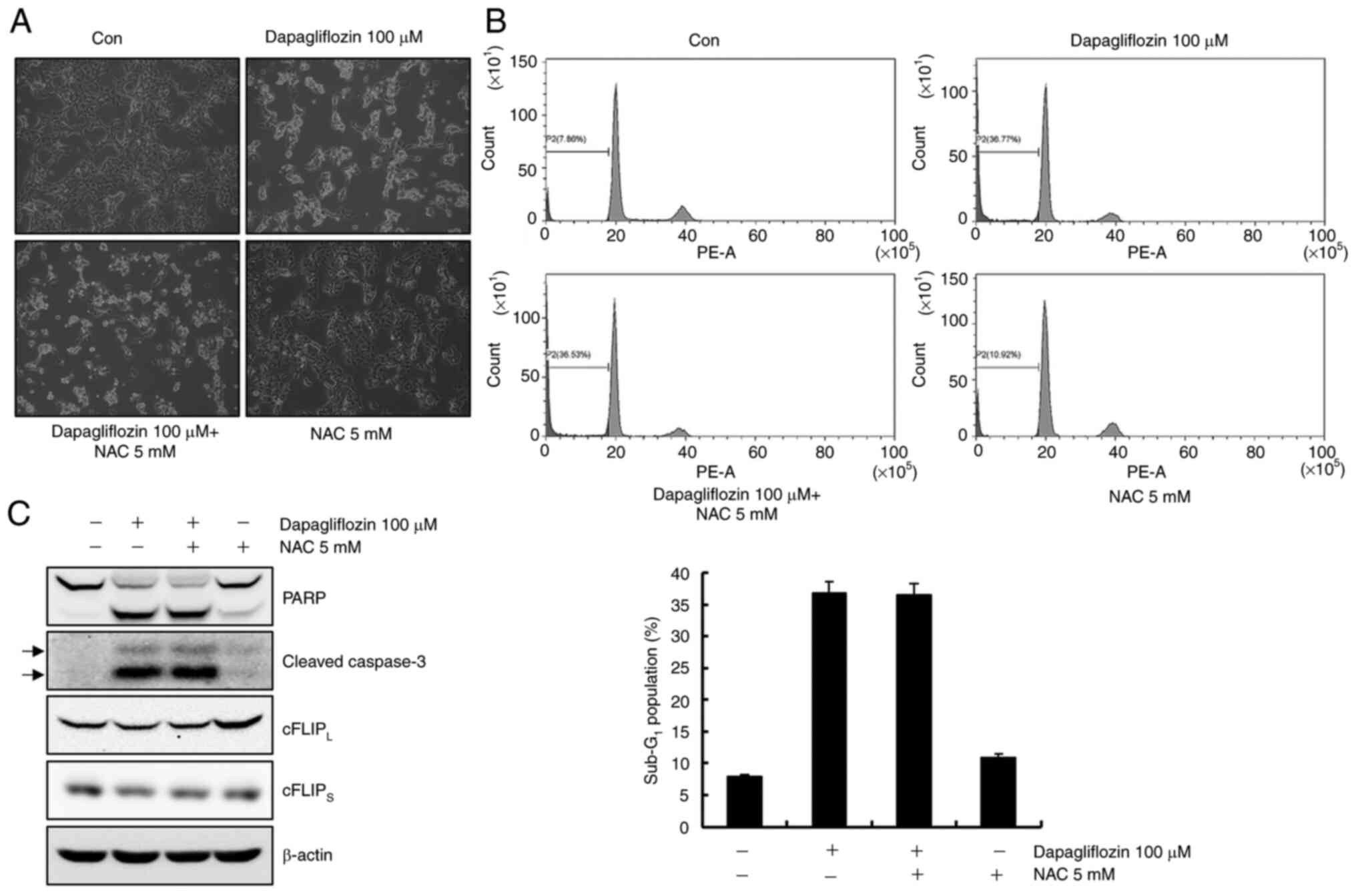
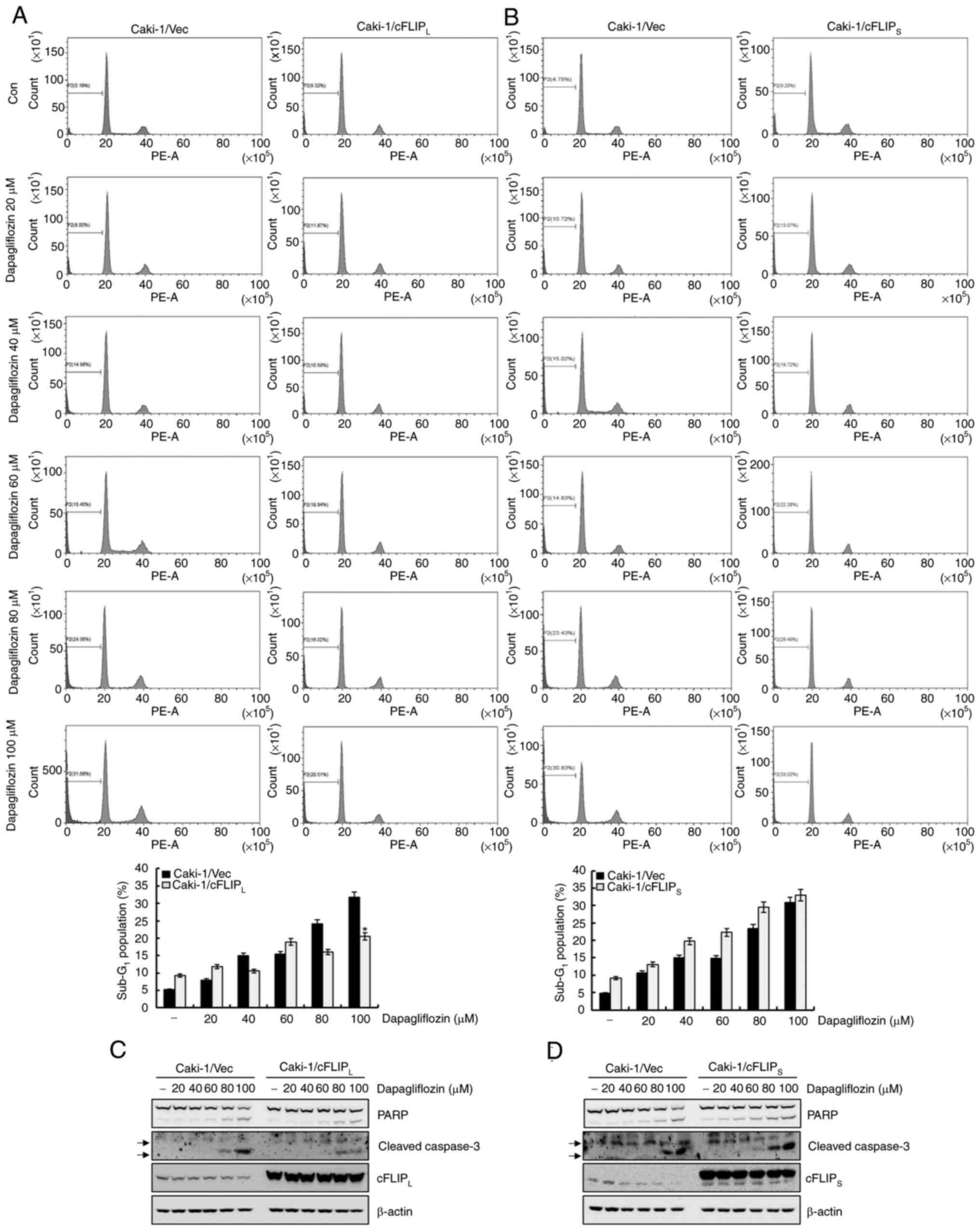
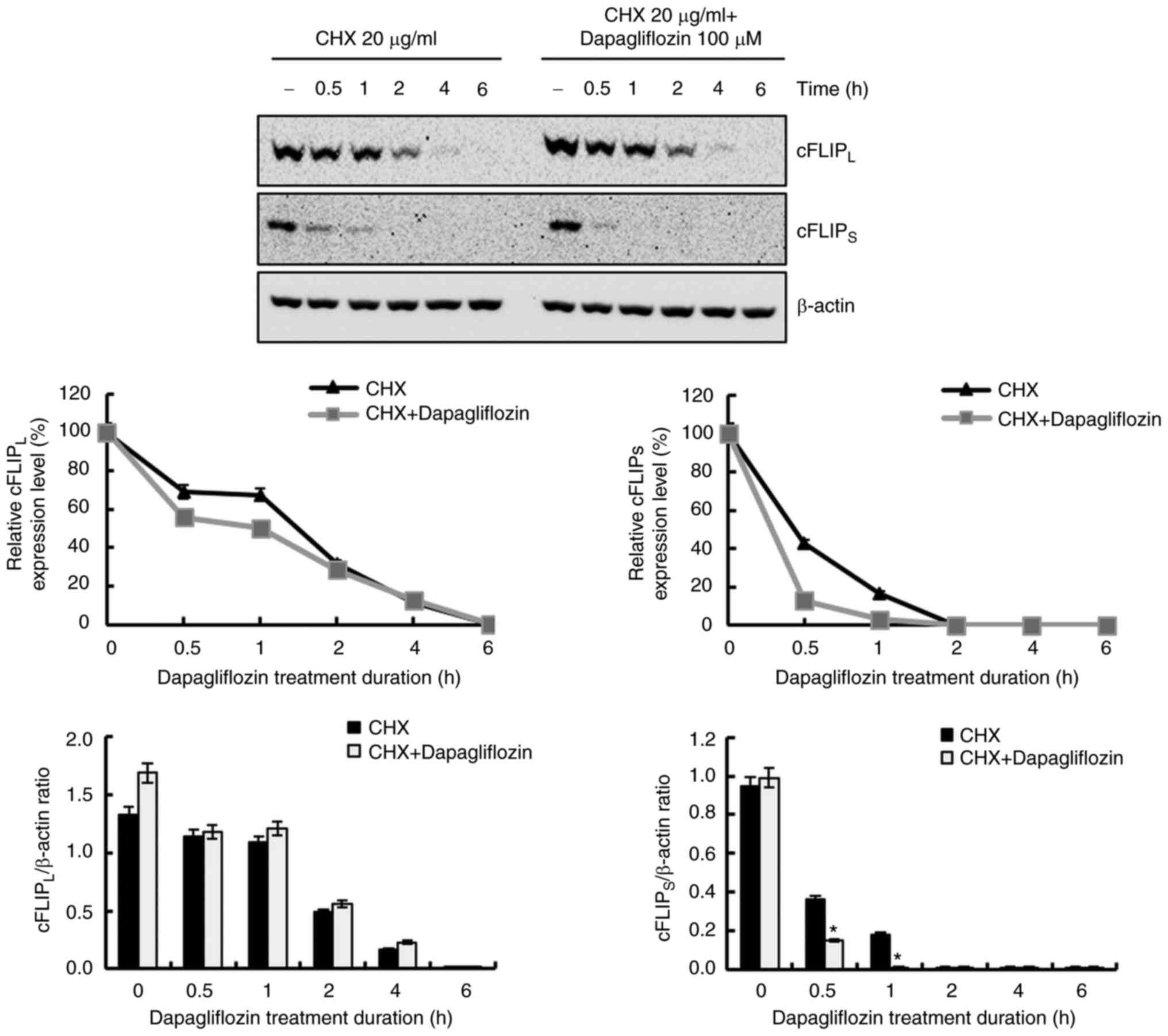
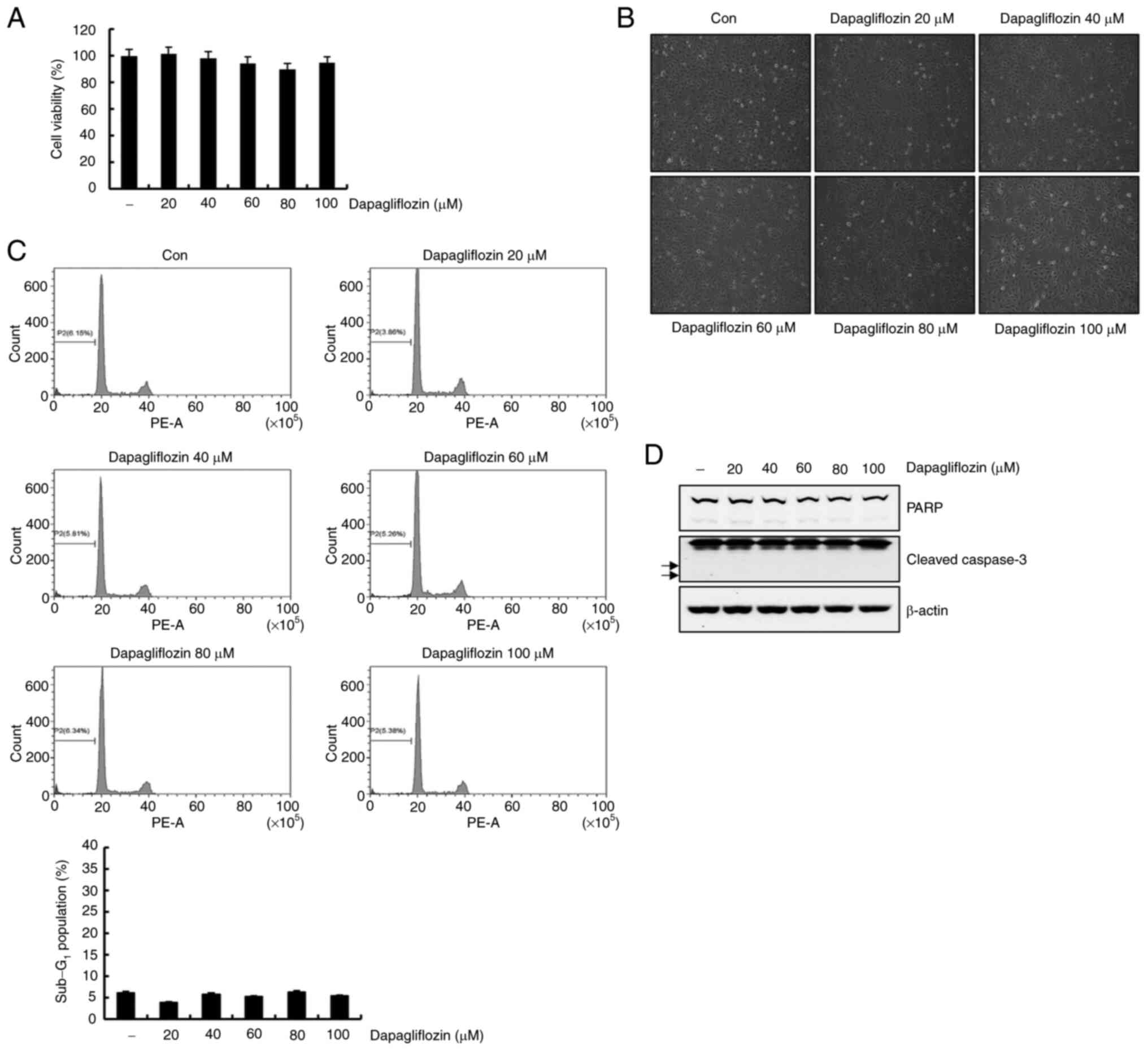
|
1
|
Low G, Huang G, Fu W, Moloo Z and Girgis
S: Review of renal cell carcinoma and its common subtypes in
radiology. World J Radiol. 8:484–500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ray RP, Mahapatra RS, Khullar S, Pal DK
and Kundu AK: Clinical characteristics of renal cell carcinoma:
Five years review from a tertiary hospital in Eastern India. Indian
J Cancer. 53:114–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jonasch E, Gao J and Rathmell WK: Renal
cell carcinoma. BMJ. 349:g47972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cohen HT and McGovern FJ: Renal-cell
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 353:2477–2490. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rabinovitch RA, Zelefsky MJ, Gaynor JJ and
Fuks Z: Patterns of failure following surgical resection of renal
cell carcinoma: Implications for adjuvant local and systemic
therapy. J Clin Oncol. 12:206–212. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang X, Zhang H and Chen X: Drug
resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug
Resist. 2:141–160. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bakris GL, Fonseca VA, Sharma K and Wright
EM: Renal sodium-glucose transport: Role in diabetes mellitus and
potential clinical implications. Kidney Int. 75:1272–1277. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mosley JF II, Smith L, Everton E and
Fellner C: Sodium-glucose linked transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors
in the management of type-2 diabetes: A drug class overview. P T.
40:451–462. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gnudi L, Coward RJM and Long DA: Diabetic
nephropathy: Perspective on novel molecular mechanisms. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 27:820–830. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xie Z, Wang F, Lin L, Duan S, Liu X, Li X,
Li T, Xue M, Cheng Y, Ren H and Zhu Y: An SGLT2 inhibitor modulates
SHH expression by activating AMPK to inhibit the migration and
induce the apoptosis of cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
495:200–210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kuang H, Liao L, Chen H, Kang Q, Shu X and
Wang Y: Therapeutic effect of sodium glucose Co-transporter 2
inhibitor dapagliflozin on renal cell carcinoma. Med Sci Monit.
23:3737–3745. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou J, Zhu J, Yu SJ, Ma HL, Chen J, Ding
XF, Chen G, Liang Y and Zhang Q: Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2
(SGLT-2) inhibition reduces glucose uptake to induce breast cancer
cell growth arrest through AMPK/mTOR pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
132:1108212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kabel AM, Arab HH and Elmaaboud MA: Effect
of dapagliflozin and/or L-arginine on solid tumor model in mice:
The interaction between nitric oxide, transforming growth
factor-beta 1, autophagy, and apoptosis. Fundam Clin Pharmacol.
35:968–978. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shirley S and Micheau O: Targeting c-FLIP
in cancer. Cancer Lett. 332:141–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ivanisenko NV, Seyrek K, Hillert-Richter
LK, König C, Espe J, Bose K and Lavrik IN: Regulation of extrinsic
apoptotic signaling by c-FLIP: Towards targeting cancer networks.
Trends Cancer. 8:190–209. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He MX and He YW: A role for c-FLIP(L) in
the regulation of apoptosis, autophagy, and necroptosis in T
lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ. 20:188–197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bagnoli M, Canevari S and Mezzanzanica D:
Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) signalling: A key
regulator of receptor-mediated apoptosis in physiologic context and
in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:210–213. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kataoka T: The caspase-8 modulator c-FLIP.
Crit Rev Immunol. 25:31–58. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Smyth P, Sessler T, Scott CJ and Longley
DB: FLIP(L): The pseudo-caspase. FEBS J. 287:4246–4260. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Poukkula M, Kaunisto A, Hietakangas V,
Denessiouk K, Katajamäki T, Johnson MS, Sistonen L and Eriksson JE:
Rapid turnover of c-FLIPshort is determined by its unique
C-terminal tail. J Biol Chem. 280:27345–27355. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Korkolopoulou P, Goudopoulou A, Voutsinas
G, Thomas-Tsagli E, Kapralos P, Patsouris E and Saetta AA: c-FLIP
expression in bladder urothelial carcinomas: Its role in resistance
to Fas-mediated apoptosis and clinicopathologic correlations.
Urology. 63:1198–1204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ullenhag GJ, Mukherjee A, Watson NF,
Al-Attar AH, Scholefield JH and Durrant LG: Overexpression of FLIPL
is an independent marker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
patients. Clin Cancer Res. 13:5070–5075. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ryu BK, Lee MG, Chi SG, Kim YW and Park
JH: Increased expression of cFLIP(L) in colonic adenocarcinoma. J
Pathol. 194:15–19. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Azad N and Iyer AKV: Reactive oxygen
species and apoptosis. Systems biology of free radicals and
antioxidants. Laher I: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; Berlin,
Heidelberg: pp. 113–135. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jan R and Chaudhry GE: Understanding
apoptosis and apoptotic pathways targeted cancer therapeutics. Adv
Pharm Bull. 9:205–218. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Plati J, Bucur O and Khosravi-Far R:
Apoptotic cell signaling in cancer progression and therapy. Integr
Biol (Camb). 3:279–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Plati J, Bucur O and Khosravi-Far R:
Dysregulation of apoptotic signaling in cancer: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Cell Biochem.
104:1124–1149. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goldar S, Khaniani MS, Derakhshan SM and
Baradaran B: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer
development and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2129–2144.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Longley DB, Wilson TR, McEwan M, Allen WL,
McDermott U, Galligan L and Johnston PG: c-FLIP inhibits
chemotherapy–induced colorectal cancer cell death. Oncogene.
25:838–848. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Safa AR, Day TW and Wu CH: Cellular
FLICE-like inhibitory protein (C-FLIP): A novel target for cancer
therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:37–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oztürk S, Schleich K and Lavrik IN:
Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory proteins (c-FLIPs): Fine-tuners of
life and death decisions. Exp Cell Res. 318:1324–1331. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kiraz Y, Adan A, Yandim MK and Baran Y:
Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis. Tumour
Biol. 37:8471–8486. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pfeffer CM and Singh ATK: Apoptosis: A
target for anticancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 19:4482018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Saito T, Okada S, Yamada E, Shimoda Y,
Osaki A, Tagaya Y, Shibusawa R, Okada J and Yamada M: Effect of
dapagliflozin on colon cancer cell [Rapid Communication]. Endocr J.
62:1133–1137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu X, Yue P, Schönthal AH, Khuri FR and
Sun SY: Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein down-regulation
contributes to celecoxib-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 66:11115–11119. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen S, Liu X, Yue P, Schönthal AH, Khuri
FR and Sun SY: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous
protein-dependent death receptor 5 induction and
ubiquitin/proteasome-mediated cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein
down-regulation contribute to enhancement of tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by
dimethyl-celecoxib in human non small-cell lung cancer cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 72:1269–1279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin Y, Liu X, Yue P, Benbrook DM, Berlin
KD, Khuri FR and Sun SY: Involvement of c-FLIP and survivin
down-regulation in flexible heteroarotinoid-induced apoptosis and
enhancement of TRAIL-initiated apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:3556–3565. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mora-Molina R, Stöhr D, Rehm M and
López-Rivas A: cFLIP downregulation is an early event required for
endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in tumor cells. Cell
Death Dis. 13:1112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yodkeeree S, Sung B, Limtrakul P and
Aggarwal BB: Zerumbone enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the
induction of death receptors in human colon cancer cells: Evidence
for an essential role of reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res.
69:6581–6589. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sheikh BY, Sarker MMR, Kamarudin MNA and
Mohan G: Antiproliferative and apoptosis inducing effects of citral
via p53 and ROS-induced mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human
colorectal HCT116 and HT29 cell lines. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:834–846. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kanayama A and Miyamoto Y: Apoptosis
triggered by phagocytosis-related oxidative stress through FLIPS
down-regulation and JNK activation. J Leukoc Biol. 82:1344–1352.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nitobe J, Yamaguchi S, Okuyama M, Nozaki
N, Sata M, Miyamoto T, Takeishi Y, Kubota I and Tomoike H: Reactive
oxygen species regulate FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP) and
susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis in cardiac myocytes.
Cardiovasc Res. 57:119–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Uthman L, Homayr A, Juni RP, Spin EL,
Kerindongo R, Boomsma M, Hollmann MW, Preckel B, Koolwijk P, van
Hinsbergh VWM, et al: Empagliflozin and dapagliflozin reduce ROS
generation and restore NO bioavailability in tumor necrosis factor
α-stimulated human coronary arterial endothelial cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 53:865–886. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu Y, Xu Q, Li H, Meng Z, Hao M, Ma X, Lin
W and Kuang H: Dapagliflozin reduces apoptosis of diabetic retina
and human retinal microvascular endothelial cells through
ERK1/2/cPLA2/AA/ROS pathway independent of hypoglycemic. Front
Pharmacol. 13:8278962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Leng W, Wu M, Pan H, Lei X, Chen L, Wu Q,
Ouyang X and Liang Z: The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin attenuates
the activity of ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome axis in steatohepatitis with
diabetes mellitus. Ann Transl Med. 7:4292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shibusawa R, Yamada E, Okada S, Nakajima
Y, Bastie CC, Maeshima A, Kaira K and Yamada M: Dapagliflozin
rescues endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death. Sci Rep.
9:98872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|