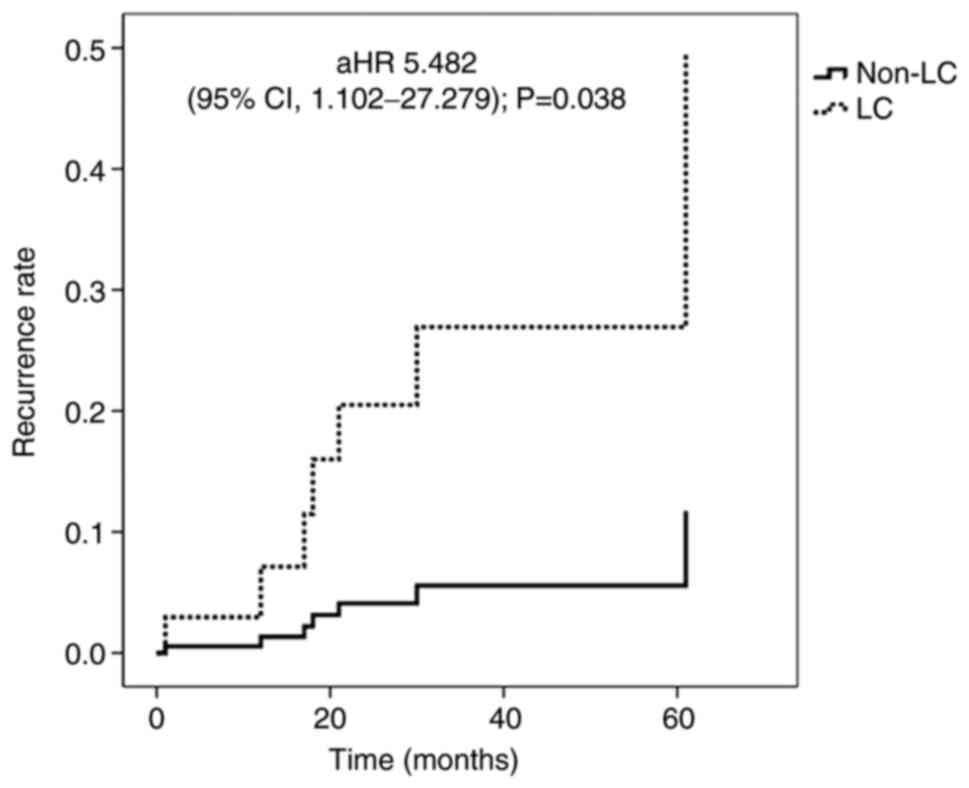
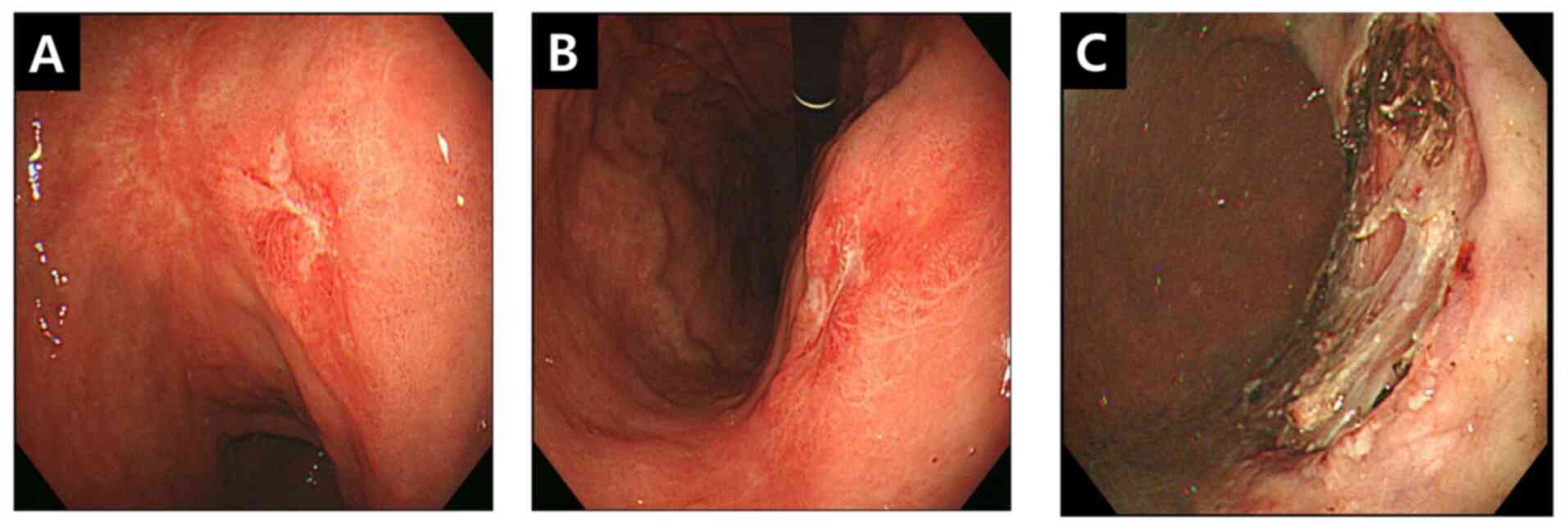
|
1
|
Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, Maciejewski
R and Sitarz R: Gastric cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors,
classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:40122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sugano K: Screening of gastric cancer in
Asia. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 29:895–905. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jun JK, Choi KS, Lee HY, Suh M, Park B,
Song SH, Jung KW, Lee CW, Choi IJ, Park EC and Lee D: Effectiveness
of the Korean national cancer screening program in reducing gastric
cancer mortality. Gastroenterology. 152:1319–1328.e1317. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gotoda T, Ho KY, Soetikno R, Kaltenbach T
and Draganov P: Gastric ES: Current status and future directions of
devices and training. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 24:213–233.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chu YN, Yu YN, Jing X, Mao T, Chen YQ,
Zhou XB, Song W, Zhao XZ and Tian ZB: Feasibility of endoscopic
treatment and predictors of lymph node metastasis in early gastric
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 25:5344–5355. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tate DJ, Klein A, Sidhu M, Desomer L,
Awadie H, Lee EY, Mahajan H, McLeod D and Bourke MJ: Endoscopic
submucosal dissection for suspected early gastric cancer: Absolute
versus expanded criteria in a large Western cohort (with video).
Gastrointest Endosc. 90:467–479. e4642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee J, Kim BW, Huh CW, Kim JS and Maeng
LS: Endoscopic factors that can predict histological ulcerations in
early gastric cancers. Clin Endosc. 53:328–333. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee SH, Kim MC, Jeon SW, Lee KN, Park JJ
and Hong SJ: Risk factors and clinical outcomes of non-curative
resection in patients with early gastric cancer treated with
endoscopic submucosal dissection: A retrospective multicenter study
in Korea. Clin Endosc. 53:196–205. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gotoda T, Yamamoto H and Soetikno RM:
Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J
Gastroenterol. 41:929–942. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda
E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Shiozawa J and Kohno
S: Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: A
large-scale feasibility study. Gut. 58:331–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang D, Kotzev AI and Draganov PV:
Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in the
West: The absolute but not final word. Gastrointest Endosc.
90:480–482. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, Ono H,
Nakanishi Y, Shimoda T and Kato Y: Incidence of lymph node
metastasis from early gastric cancer: Estimation with a large
number of cases at two large centers. Gastric Cancer. 3:219–225.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gotoda T: Endoscopic resection of early
gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 10:1–11. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goh LY, Leow AH and Goh KL: Observations
on the epidemiology of gastrointestinal and liver cancers in the
Asia-Pacific region. J Dig Dis. 15:463–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chung W: The cost of liver disease in
Korea: Methodology, data, and evidence. Clin Mol Hepatol. 21:14–21.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Eslam M, George J, Al
Mahtab M, Akbar SM, Jia J, Tian Q, Aggarwal R, Muljono DH, et al:
Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: A lancet
gastroenterology & hepatology commission. Lancet Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 5:167–228. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sorensen HT, Friis S, Olsen JH, Thulstrup
AM, Mellemkjaer L, Linet M, Trichopoulos D, Vilstrup H and Olsen J:
Risk of liver and other types of cancer in patients with cirrhosis:
A nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Hepatology. 28:921–925. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zullo A, Romiti A, Tomao S, Hassan C,
Rinaldi V, Giustini M, Morini S and Taggi F: Gastric cancer
prevalence in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur J Cancer Prev.
12:179–182. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi YK, Ahn JY, Kim DH, Jung KW, Na HK,
Choi KD, Lee JH, Song HJ, Lee GH and Jung HY: Efficacy and safety
of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasms in
patients with compensated liver cirrhosis: A propensity
score-matched case-control study. Gastrointest Endosc.
87:1423–1431. e14232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ogura K, Okamoto M, Sugimoto T, Yahagi N,
Fujishiro M, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Kawabe T and Omata M:
Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric
cancer in patients with liver cirrhosis. Endoscopy. 40:443–445.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eom BW, Jung KW, Won YJ, Yang H and Kim
YW: Trends in gastric cancer incidence according to the
clinicopathological characteristics in Korea, 1999–2014. Cancer Res
Treat. 50:1343–1350. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsoris A and Marlar CA: Use of the child
pugh score in liver disease. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
(Treasure Island, FL). 2021.
|
|
23
|
Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, Mouri R, Hirata
M, Kawamura T, Yoshihara M and Chayama K: Advantage of endoscopic
submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer.
Gastrointest Endosc. 64:877–883. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zullo A, Hassan C and Morini S:
Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with liver cirrhosis:
Facts and fictions. Dig Liver Dis. 35:197–205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sonnenberg A and Wasserman IH:
Associations of peptic-ulcer and gastric-cancer with other diseases
in us veterans. Am J Public Health. 85:1252–1255. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jang HJ, Kim JH, Song HH, Woo KH, Kim M,
Kae SH, Lee J, Cho JW, Kang JH, Lee SI, et al: Clinical outcomes of
patients with liver cirrhosis who underwent curative surgery for
gastric cancer: A retrospective multi-center study. Dig Dis Sci.
53:399–404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nicoll A: Surgical risk in patients with
cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:1569–1575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choe WH, Kim JH, Park JH, Kim HU, Cho DH,
Lee SP, Lee TY, Lee SY, Sung IK, Park HS and Shim CS: Endoscopic
submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer in patients with
liver cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 63:466–473. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aytac S, Turkay C, Bavbek N and Kosar A:
Hemostasis and global fibrinolytic capacity in chronic liver
disease. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 18:623–626. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kato M, Nishida T, Hamasaki T, Kawai N,
Yoshio T, Egawa S, Yamamoto K, Ogiyama H, Komori M, Nakahara M, et
al: Outcomes of ESD for patients with early gastric cancer and
comorbid liver cirrhosis: A propensity score analysis. Surg Endosc.
29:1560–1566. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Anti M, Armuzzi A and Gasbarrini G:
Epithelial cell turnover and apoptosis. Ital J Gastroenterol. 30
(Suppl 3):S276–S278. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abnet CC, Lai B, Qiao YL, Vogt S, Luo XM,
Taylor PR, Dong ZW, Mark SD and Dawsey SM: Zinc concentration in
esophageal biopsy specimens measured by x-ray fluorescence and
esophageal cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97:301–306. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Becker U, Almdal T, Christensen E, Gluud
C, Farholt S, Bennett P, Svenstrup B and Hardt F: Sex-Hormones in
postmenopausal women with primary biliary-cirrhosis. Hepatology.
13:865–869. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hara K, Kohno S, Koga H, Kaku M, Tomono K,
Sakata S, Komatsu K and Omagari K: Infections in patients with
liver-cirrhosis and hepatocellular-carcinoma. Internal Med.
34:491–495. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|