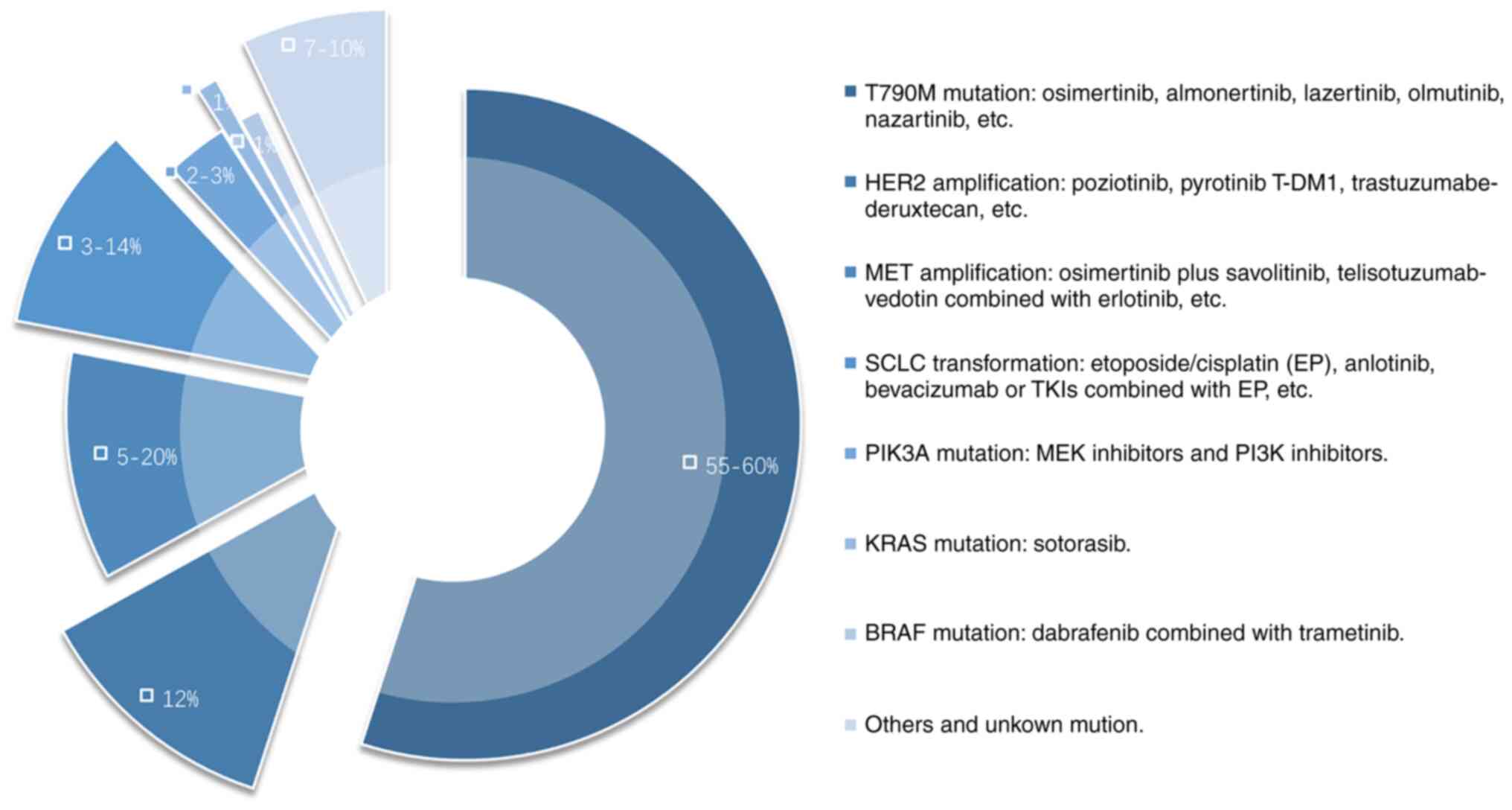
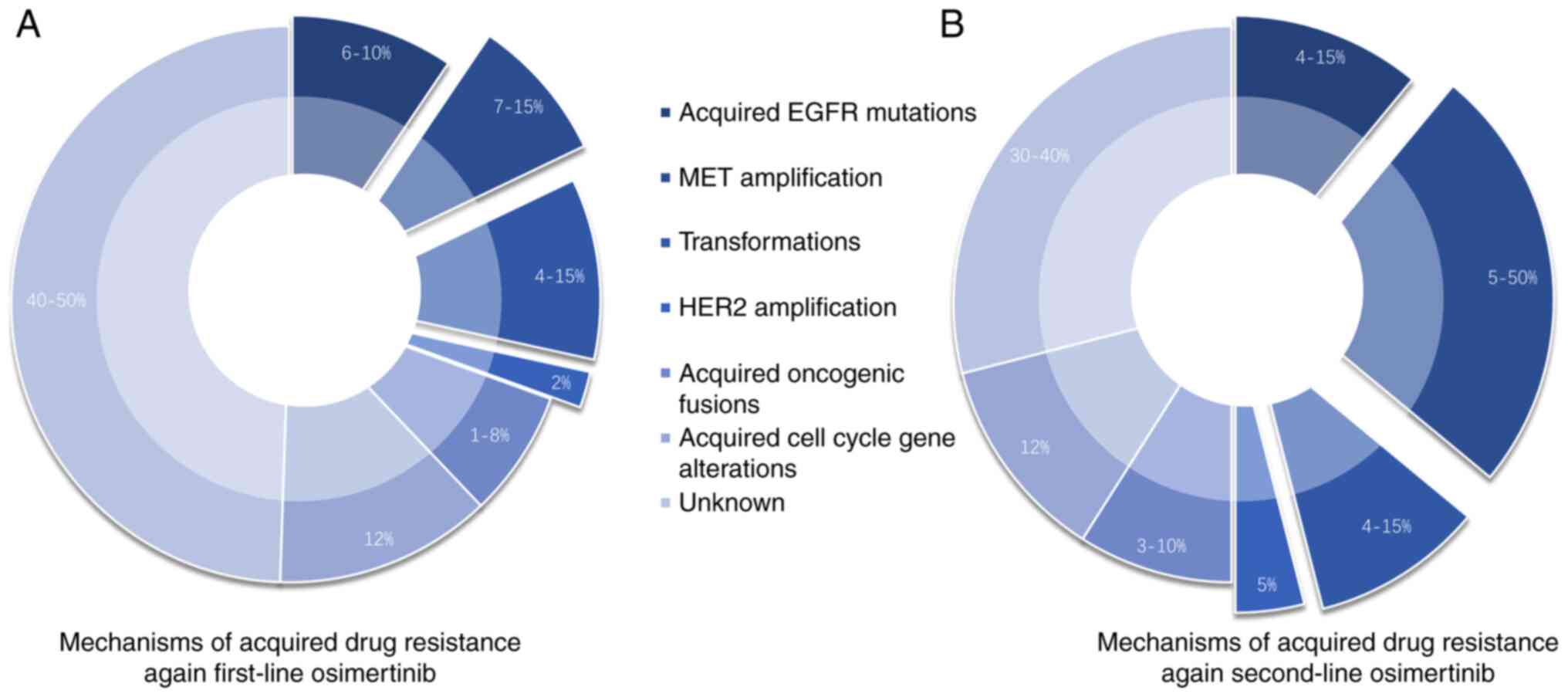
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao M, Li H, Sun D and Chen W: Cancer
burden of major cancers in China: A need for sustainable actions.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 40:205–210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Camidge DR, Doebele RC and Kerr KM:
Comparing and contrasting predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy
and targeted therapy of NSCLC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:341–355.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lee CK, Davies L, Wu YL, Mitsudomi T,
Inoue A, Rosell R, Zhou C, Nakagawa K, Thongprasert S, Fukuoka M,
et al: Gefitinib or erlotinib vs chemotherapy for EGFR
mutation-positive lung cancer: Individual patient data
meta-analysis of overall survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 109:2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rotow J and Bivona TG: Understanding and
targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:637–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kobayashi Y and Mitsudomi T: Not all
epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are
created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy.
Cancer Sci. 107:1179–1186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan
S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, Heeroma K, Itoh Y, Cornelio G and Yang PC: A
prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in
Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of
adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 9:154–162.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shi Y, Li J, Zhang S, Wang M, Yang S, Li
N, Wu G, Liu W, Liao G, Cai K, et al: Molecular Epidemiology of
EGFR mutations in asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer of adenocarcinoma histology-Mainland China Subset analysis
of the PIONEER study. PLoS One. 10:e01435152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH,
Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, et
al: Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu YL, Zhou C, Liam CK, Wu G, Liu X, Zhong
Z, Lu S, Cheng Y, Han B, Chen L, et al: First-line erlotinib versus
gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with advanced EGFR
mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Analyses from the
phase III, randomized, open-label, ENSURE study. Ann Oncol.
26:1883–1889. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schuler M, Paz-Ares L, Sequist LV, Hirsh
V, Lee KH, Wu YL, Lu S, Zhou C, Feng J, Ellis SH, et al: First-line
afatinib for advanced EGFRm+ NSCLC: Analysis of long-term
responders in the LUX-Lung 3, 6, and 7 trials. Lung Cancer.
133:10–19. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu YL, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Lee KH, Nakagawa
K, Niho S, Tsuji F, Linke R, Rosell R, Corral J, et al: Dacomitinib
versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with
EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:1454–1466.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard
D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, Zhou C, Reungwetwattana T, Cheng Y,
Chewaskulyong B, et al: Overall survival with osimertinib in
untreated, EGFR-Mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 382. pp.
41–50. 2020, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi YK, Wang L, Han BH, Li W, Yu P, Liu
YP, Ding CM, Song X, Ma ZY, Ren XL, et al: First-line icotinib
versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for
patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma
(CONVINCE): A phase 3, open-label, randomized study. Ann Oncol.
28:2443–2450. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rebuzzi SE, Alfieri R, La Monica S, Minari
R, Petronini PG and Tiseo M: Combination of EGFR-TKIs and
chemotherapy in advanced EGFR mutated NSCLC: Review of the
literature and future perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
146:1028202020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huang L and Fu L: Mechanisms of resistance
to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:390–401.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim
HR, Ramalingam SS, Shepherd FA, He Y, Akamatsu H, Theelen WS, et
al: Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 376:629–640. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thress KS, Paweletz CP, Felip E, Cho BC,
Stetson D, Dougherty B, Lai Z, Markovets A, Vivancos A, Kuang Y, et
al: Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in
non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat Med.
21:560–562. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang S, Tsui ST, Liu C, Song Y and Liu D:
EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to third-generation
inhibitors in T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer. J Hematol
Oncol. 9:592016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lim SM, Syn NL, Cho BC and Soo RA:
Acquired resistance to EGFR targeted therapy in non-small cell lung
cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cancer Treat Rev.
65:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nagano T, Tachihara M and Nishimura Y:
Mechanism of resistance to epidermal growth factor
receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and a potential treatment
strategy. Cells. 7:2122018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Park K, Tan EH, O'Byrne K, Zhang L, Boyer
M, Mok T, Hirsh V, Yang JC, Lee KH, Lu S, et al: Afatinib versus
gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR
mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase
2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol.
17:577–589. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jänne PA, Ou SI, Kim DW, Oxnard GR,
Martins R, Kris MG, Dunphy F, Nishio M, O'Connell J, Paweletz C, et
al: Dacomitinib as first-line treatment in patients with clinically
or molecularly selected advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A
multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:1433–1441.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu SG, Liu YN, Tsai MF, Chang YL, Yu CJ,
Yang PC, Yang JC, Wen YF and Shih JY: The mechanism of acquired
resistance to irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-afatinib
in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 7:12404–12413. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cabanero M, Sangha R, Sheffield BS, Sukhai
M, Pakkal M, Kamel-Reid S, Karsan A, Ionescu D, Juergens RA, Butts
C and Tsao MS: Management of EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung
cancer: Practical implications from a clinical and pathology
perspective. Curr Oncol. 24:111–119. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mok TS, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Lee KH, Nakagawa
K, Niho S, Chawla A, Rosell R, Corral J, Migliorino MR, et al:
Updated overall survival in a randomized study comparing
dacomitinib with gefitinib as first-line treatment in patients with
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR-Activating mutations.
Drugs. 81:257–266. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J,
Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura
F, Nogami N, Kurata T, et al: Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-Mutated
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 378:113–125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Han JY,
Katakami N, Kim HR, Hodge R, Kaur P, Brown AP, Ghiorghiu D, et al:
CNS efficacy of osimertinib in patients with T790M-Positive
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Data from a Randomized phase
III Trial (AURA3). J Clin Oncol. 36:2702–2709. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC,
Cobo M, Cho EK, Bertolini A, Bohnet S, Zhou C, Lee KH, Nogami N, et
al: CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with
untreated EGFR-Mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. Aug 28–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lu S, Wang Q, Zhang G, Dong X, Yang CT,
Song Y, Chang GC, Lu Y, Pan H, Chiu CH, et al: Efficacy of
aumolertinib (HS-10296) in patients with advanced EGFR T790M+
NSCLC: Updated post-national medical products administration
approval results from the APOLLO registrational trial. J Thorac
Oncol. 17:411–422. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lu S, Wang Q, Zhang G, Dong X, Yang C,
Song Y, Chang GC, LU Y, Pan H, Chiu CH, et al: 1208P Final results
of APOLLO study: Overall survival (OS) of aumolertinib in patients
with pretreated EGFR T790M-positive locally advanced or metastatic
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol. 32:S9622021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shi Y, Hu X, Zhang S, Lv D, Wu L, Yu Q,
Zhang Y, Liu L, Wang X, Cheng Y, et al: Efficacy, safety, and
genetic analysis of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR
T790M mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 2b, multicentre,
single-arm, open-label study. Lancet Respir Med. 9:829–839. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deeks ED: Furmonertinib: First approval.
Drugs. 81:1775–1780. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ahn MJ, Han JY, Kim SW, Ki Hyeong Lee5,
Kim DW, Lee YG, Cho EK, Lee GW, Lee JS, Kim JH, et al: Lazertinib,
a 3rd generation EGFR-TKI, in patients with EGFR-TKI resistant
NSCLC: Updated results of phase I/II Study. Abstract #9037. May
31-June 4. 2019.
|
|
35
|
Kim SW, Ahn MJ, Han JY, Lee KH, Cho EK,
Lee YG, Kim DW, Kim JH, Lee JS, Lee GW, et al: Intracranial
anti-tumor activity of lazertinib in patients with advanced NSCLC
who progressed after prior EGFR TKI therapy: Data from a phase I/II
study. Am Soc Clin Oncol. 38:95712020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dhillon S: Lazertinib: First approval.
Drugs. 81:1107–1113. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim ES: Olmutinib: First global approval.
Drugs. 76:1153–1157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim DW, Lee DH, Han JY, Lee J, Cho BC,
Kang JH, Lee KH, Cho EK, Kim JS, Min YJ, et al: Safety,
tolerability, and anti-tumor activity of olmutinib in non-small
cell lung cancer with T790M mutation: A single arm, open label,
phase 1/2 trial. Lung Cancer. 135:66–72. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Park K, Jӓnne PA, Kim DW, Han JY, Wu MF,
Lee JS, Kang JH, Lee DH, Cho BC, Yu CJ, et al: Olmutinib in
T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer after failure of
first-line epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase
inhibitor therapy: A global, phase 2 study. Cancer. 127:1407–1416.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tan DS, Leighl NB, Riely GJ, Yang JC,
Sequist LV, Wolf J, Seto T, Felip E, Aix SP, Jonnaert M, et al:
Safety and efficacy of nazartinib (EGF816) in adults with
EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung carcinoma: A multicentre,
open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Respir Med. 8:561–572. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Costa DB, Schumer ST, Tenen DG and
Kobayashi S: Differential responses to erlotinib in epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung cancers with acquired
resistance to gefitinib carrying the L747S or T790M secondary
mutations. J Clin Oncol. 26:1182–1184; author reply 1184–1186.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Balak MN, Gong Y, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Li
AR, Zakowski MF, Chiang A, Yang G, Ouerfelli O, Kris MG, et al:
Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal
growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired
resistance to kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6494–6501.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bean J, Riely GJ, Balak M, Marks JL,
Ladanyi M, Miller VA and Pao W: Acquired resistance to epidermal
growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors associated with a novel
T854A mutation in a patient with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:7519–7525. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Grolleau E, Haddad V, Boissière L,
Falchero L and Arpin D: Clinical efficacy of osimertinib in a
patient presenting a double EGFR L747S and G719C mutation. J Thorac
Oncol. 14:e151–e153. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chiba M, Togashi Y, Bannno E, Kobayashi Y,
Nakamura Y, Hayashi H, Terashima M, De Velasco MA, Sakai K, Fujita
Y, et al: Efficacy of irreversible EGFR-TKIs for the uncommon
secondary resistant EGFR mutations L747S, D761Y, and T854A. BMC
Cancer. 17:2812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhu Y, Tang J, Li X, Qin T and Wei Y:
Durable response to osimertinib in a Chinese patient with
metastatic lung adenocarcinoma harboring a rare EGFR L858R/D761Y
compound mutation. Onco Targets Ther. 13:10447–10451. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang L, Yang X, Ming Z, Shi J, Lv X, Li
W, Yuan B, Chen Y, Liu B, Qin K, et al: Molecular characteristics
of the uncommon EGFR Exon 21 T854A Mutation and response to
osimertinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Lung
Cancer. 23:311–319. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Patil T, Mushtaq R, Marsh S, Azelby C,
Pujara M, Davies KD, Aisner DL, Purcell WT, Schenk EL, Pacheco JM,
et al: Clinicopathologic characteristics, treatment outcomes, and
acquired resistance patterns of atypical EGFR mutations and HER2
alterations in stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung
Cancer. 21:e191–e204. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Riudavets M, Sullivan I, Abdayem P and
Planchard D: Targeting HER2 in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
A glimpse of hope? An updated review on therapeutic strategies in
NSCLC harbouring HER2 alterations. ESMO Open. 6:1002602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Takezawa K, Pirazzoli V, Arcila ME, Nebhan
CA, Song X, de Stanchina E, Ohashi K, Janjigian YY, Spitzler PJ,
Melnick MA, et al: HER2 amplification: A potential mechanism of
acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers
that lack the second-site EGFRT790M mutation. Cancer Discov.
2:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Elamin YY, Robichaux JP, Carter BW, Altan
M, Gibbons DL, Fossella FV, Lam VK, Patel AB, Negrao MV, Le X, et
al: Poziotinib for patients With HER2 Exon 20 mutant non-small-cell
lung cancer: Results from a phase II Trial. J Clin Oncol.
40:702–709. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Song Z, Lv D, Chen SQ, Huang J, Li Y, Ying
S, Wu X, Hua F, Wang W, Xu C, et al: Pyrotinib in patients with
HER2-Amplified advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective,
multicenter, single-arm trial. Clin Cancer Res. 28:461–467. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhou C, Li X, Wang Q, Gao G, Zhang Y, Chen
J, Shu Y, Hu Y, Fan Y, Fang J, et al: Pyrotinib in HER2-Mutant
advanced lung adenocarcinoma after platinum-based chemotherapy: A
multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase II Study. J Clin Oncol.
38:2753–2761. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li BT, Shen R, Buonocore D, Olah ZT, Ni A,
Ginsberg MS, Ulaner GA, Offin M, Feldman D, Hembrough T, et al:
Ado-Trastuzumab emtansine for patients with HER2-Mutant lung
cancers: Results from a phase II basket trial. J Clin Oncol.
36:2532–2537. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li BT, Smit EF, Goto Y, Nakagawa K,
Udagawa H, Mazières J, Nagasaka M, Bazhenova L, Saltos AN, Felip E,
et al: Trastuzumab deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 386:241–251. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Koch JP, Aebersold DM, Zimmer Y and Medová
M: MET targeting: Time for a rematch. Oncogene. 39:2845–2862. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Pasquini G and Giaccone G: C-MET
inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 27:363–375. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T,
Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen
J, et al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung
cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, Riely G, Viale
A, Wang L, Chitale D, Motoi N, Szoke J, Broderick S, et al: MET
amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant
lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:20932–20937. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger
S, Cosper AK, et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung
cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS,
Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M and Riely GJ:
Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to
EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:2240–2247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lai GG, Lim TH, Lim J, Liew PJ, Kwang XL,
Nahar R, Aung ZW, Takano A, Lee YY, Lau DP, et al: Clonal MET
amplification as a determinant of tyrosine kinase inhibitor
resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 37:876–884. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Dulak AM, Gubish CT, Stabile LP, Henry C
and Siegfried JM: HGF-independent potentiation of EGFR action by
c-Met. Oncogene. 30:3625–3635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dong Y, Xu J, Sun B, Wang J and Wang Z:
MET-Targeted therapies and clinical outcomes: A systematic
literature review. Mol Diagn Ther. 26:203–227. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wu YL, Zhang L, Kim DW, Liu X, Lee DH,
Yang JC, Ahn MJ, Vansteenkiste JF, Su WC, Felip E, et al: Phase
Ib/II study of capmatinib (INC280) plus gefitinib after failure of
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor therapy in
patients with EGFR-Mutated, MET factor-dysregulated non-small-cell
lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:3101–3109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wu YL, Cheng Y, Zhou J, Lu S, Zhang Y,
Zhao J, Kim DW, Soo RA, Kim SW, Pan H, et al: Tepotinib plus
gefitinib in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer
with MET overexpression or MET amplification and acquired
resistance to previous EGFR inhibitor (INSIGHT study): An
open-label, phase 1b/2, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet
Respir Med. 8:1132–1143. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sequist LV, Han JY, Ahn MJ, Cho BC, Yu H,
Kim SW, Yang JC, Lee JS, Su WC, Kowalski D, et al: Osimertinib plus
savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified,
non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitors: Interim results from a multicentre, open-label,
phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 21:373–386. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Camidge D, Barlesi F, Goldman J,
Morgensztern D, Heist R, Vokes E, Spira A, Angevin E, Su W, Hong D,
Strickler J, Motwani M, Sun Z, et al: MA14. 03 EGFR M+ Subgroup of
Phase 1b study of telisotuzumab vedotin (Teliso-V) plus erlotinib
in c-Met+ non-small cell lung cancer. J Thor Oncol. 14:S305–S306.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
McCoach CE, Yu A, Gandara DR, Riess JW,
Vang DP, Li T, Lara PN, Gubens M, Lara F, Mack PC, et al: Phase
I/II study of capmatinib plus erlotinib in patients with
MET-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. JCO Precis Oncol.
1:PO.20.00279. 2021.
|
|
70
|
Camidge DR, Moran T, Demedts I, Grosch H,
Mileham K, Molina J, Juan-Vidal O, Bepler G, Goldman JW, Park K, et
al: A Randomized, open-label phase II study evaluating emibetuzumab
plus erlotinib and emibetuzumab monotherapy in MET
immunohistochemistry positive NSCLC patients with acquired
resistance to erlotinib. Clin Lung Cancer. 23:300–310. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Alqahtani A, Ayesh HSK and Halawani H:
PIK3CA gene mutations in solid malignancies: Association with
clinicopathological parameters and prognosis. Cancers (Basel).
12:932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Li J and Che G:
Clinical significance of PIK3CA gene in non-small-cell lung cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int.
2020:36082412020.
|
|
73
|
Qiu X, Wang Y, Liu F, Peng L, Fang C, Qian
X, Zhang X, Wang Q, Xiao Z, Chen R, et al: Survival and prognosis
analyses of concurrent PIK3CA mutations in EGFR mutant non-small
cell lung cancer treated with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am J
Cancer Res. 11:3189–3200. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Song Z, Yu X and Zhang Y: Mutation and
prognostic analyses of PIK3CA in patients with completely resected
lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 5:2694–2700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Westover D, Zugazagoitia J, Cho BC, Lovly
CM and Paz-Ares L: Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and
second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Oncol. 29
(Suppl 1):i10–i19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Qu GP, Shi M, Wang D, Wu JH, Wang P, Gong
ML and Zhang ZJ: Dual targeting of MEK and PI3K effectively
controls the proliferation of human EGFR-TKI resistant non-small
cell lung carcinoma cell lines with different genetic backgrounds.
BMC Pulm Med. 21:2082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Markham AJD: Alpelisib: First global
approval. Drugs. 79:1249–1253. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Skoulidis F, Li BT, Dy GK, Price TJ,
Falchook GS, Wolf J, Italiano A, Schuler M, Borghaei H, Barlesi F,
et al: Sotorasib for lung cancers with KRAS p.G12C Mutation. N Engl
J Med. 384:2371–2381. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tanaka N, Lin JJ, Li C, Ryan MB, Zhang J,
Kiedrowski LA, Michel AG, Syed MU, Fella KA, Sakhi M, et al:
Clinical acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibition
through a Novel KRAS Switch-II pocket mutation and polyclonal
alterations converging on RAS-MAPK Reactivation. Cancer Discov.
11:1913–1922. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang SS; Nagasaka MJLCT and Therapy, :
Spotlight on Sotorasib (AMG 510) for KRASG12C positive
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 12:115–122.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Pratilas CA, Hanrahan AJ, Halilovic E,
Persaud Y, Soh J, Chitale D, Shigematsu H, Yamamoto H, Sawai A,
Janakiraman M, et al: Genetic predictors of MEK dependence in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 68:9375–9383. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ai X, Li Y, Chen R, Gu D and Mao Y: P59.
07 mutation profile of BRAF in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer
patients. J Thorac Oncol. 16:S11492021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Ohashi K, Sequist LV, Arcila ME, Moran T,
Chmielecki J, Lin YL, Pan Y, Wang L, de Stanchina E, Shien K, et
al: Lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors
occasionally harbor BRAF gene mutations but lack mutations in KRAS,
NRAS, or MEK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E2127–E2133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Odogwu L, Mathieu L, Blumenthal G, Larkins
E, Goldberg KB, Griffin N, Bijwaard K, Lee EY, Philip R, Jiang X,
et al: FDA approval summary: Dabrafenib and trametinib for the
treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancers harboring BRAF
V600E mutations. Oncologist. 23:740–745. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Zhu C, Wei Y and Wei X: AXL receptor
tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: Functions,
molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol Cancer.
18:1532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Goyette MA and Côté JF: AXL receptor
tyrosine kinase as a promising therapeutic target directing
multiple aspects of cancer progression and metastasis. Cancers
(Basel). 14:4662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhang Z, Lee JC, Lin L, Olivas V, Au V,
LaFramboise T, Abdel-Rahman M, Wang X, Levine AD, Rho JK, et al:
Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted
therapy in lung cancer. Nat Genet. 44:852–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Sang YB, Kim JH, Kim CG, Hong MH, Kim HR,
Cho BC and Lim SM: The Development of AXL inhibitors in lung
cancer: Recent progress and challenges. Front Oncol. 12:8112472022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Nishio M, Okamoto I, Murakami H,
Horinouchi H, Toyozawa R, Takeda M, Uno M, Crawford N, Jimbo T,
Ishigami M, et al: 570P A first-in-human phase I study of the AXL
inhibitor DS-1205c in combination with gefitinib in subjects with
EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 31:S4882020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Byers LA, Gold KA and Peguero JA: Ph I/II
study of oral selective AXL inhibitor bemcentinib (BGB324) in
combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced EGFRm NSCLC:
End of trial update. Wolters Kluwer Health; 2021, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Xun G, Hu W and Li B: PTEN loss promotes
oncogenic function of STMN1 via PI3K/AKT pathway in lung cancer.
Sci Rep. 11:143182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ferrara MG, Martini M, D'Argento E,
Forcella C, Vita E, Di Noia V, Sperduti I, Bilotta M, Ribelli M,
Damiano P, et al: PTEN loss as a predictor of tumor heterogeneity
and poor prognosis in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Clin Lung Cancer. 22:351–360. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Redig AJ, Capelletti M, Dahlberg SE, Sholl
LM, Mach S, Fontes C, Shi Y, Chalasani P and Jänne PA: Clinical and
molecular characteristics of NF1-mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:3148–3156. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Cheung HW, Du J, Boehm JS, He F, Weir BA,
Wang X, Butaney M, Sequist LV, Luo B, Engelman JA, et al:
Amplification of CRKL induces transformation and epidermal growth
factor receptor inhibitor resistance in human non-small cell lung
cancers. Cancer Discov. 1:608–625. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Cortot AB, Repellin CE, Shimamura T,
Capelletti M, Zejnullahu K, Ercan D, Christensen JG, Wong KK, Gray
NS and Jänne PA: Resistance to irreversible EGF receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitors through a multistep mechanism involving the IGF1R
pathway. Cancer Res. 73:834–843. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ware KE, Hinz TK, Kleczko E, Singleton KR,
Marek LA, Helfrich BA, Cummings CT, Graham DK, Astling D, Tan AC
and Heasley LE: A mechanism of resistance to gefitinib mediated by
cellular reprogramming and the acquisition of an FGF2-FGFR1
autocrine growth loop. Oncogenesis. 2:e392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Attili I, Passaro A, Pisapia P, Malapelle
U and de Marinis F: Uncommon EGFR compound mutations in non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A systematic review of available
evidence. Curr Oncol. 29:255–266. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Hayashi T, Kohsaka S, Takamochi K, Hara K,
Kishikawa S, Sano K, Takahashi F, Suehara Y, Saito T, Takahashi K,
et al: Clinicopathological characteristics of lung adenocarcinoma
with compound EGFR mutations. Hum Pathol. 103:42–51. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Rossi S, Damiano P, Toschi L, Finocchiaro
G, Giordano L, Marinello A, Bria E, D'Argento E and Santoro A:
Uncommon single and compound EGFR mutations: Clinical outcomes of a
heterogeneous subgroup of NSCLC. Curr Probl Cancer. 46:1007872022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Jiang D, Fu Y, Zhou X, Li Y, Cui Y, Hong
L, Jin H, Shi K, Huang F, Zhang X, et al: The prognosis of EGFR
complex mutation or co-mutation with tyrosine kinase inhibitor
treatment in non-small cell lung cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol.
40:e210862022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Wang R, Pan S and Song X: Research
Advances of EGFR-TP53 Co-mutation in advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 25:174–182. 2022.(In Chinese).
|
|
103
|
Wang F, Zhao N, Gao G, Deng HB, Wang ZH,
Deng LL, Yang Y and Lu C: Prognostic value of TP53 co-mutation
status combined with EGFR mutation in patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:2851–2859. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Cheng Y, Ma L, Liu Y, Zhu J, Xin Y, Liu X,
Wang Y, Zhang T, Yang C, Wang S, et al: Comprehensive
characterization and clinical impact of concomitant genomic
alterations in EGFR-mutant NSCLCs treated with EGFR kinase
inhibitors. Lung Cancer. 145:63–70. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zhang Y, Li S, Lyu Z, Cai J, Zheng N, Li
Y, Xu T and Zeng H: The co-mutation of EGFR and tumor-related genes
leads to a worse prognosis and a higher level of tumor mutational
burden in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Thorac
Dis. 14:185–193. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Li HS, Liu CM and Wang Y: Limited role of
KRAS mutation in guiding immunotherapy in advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer. Future Oncol. 18:2433–2443. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Marcoux N, Gettinger SN, O'Kane G, Arbour
KC, Neal JW, Husain H, Evans TL, Brahmer JR, Muzikansky A, Bonomi
PD, et al: EGFR-Mutant adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell
lung cancer and other neuroendocrine carcinomas: Clinical outcomes.
J Clin Oncol. 37:278–285. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Poirier JT,
Mermel CH, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, Katayama R, Costa C, Ross KN,
Moran T, et al: RB loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung
adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer. Nat
Commun. 6:63772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Lee JK, Lee J, Kim S, Kim S, Youk J, Park
S, An Y, Keam B, Kim DW, Heo DS, et al: Clonal history and genetic
predictors of transformation into small-cell carcinomas from lung
adenocarcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 35:3065–3074. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Offin M, Chan JM, Tenet M, Rizvi HA, Shen
R, Riely GJ, Rekhtman N, Daneshbod Y, Quintanal-Villalonga A,
Penson A, et al: Concurrent RB1 and TP53 alterations define a
subset of EGFR-Mutant lung cancers at risk for histologic
transformation and inferior clinical outcomes. J Thorac Oncol.
14:1784–1793. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Mambetsariev I, Arvanitis L, Fricke J,
Pharaon R, Baroz AR, Afkhami M, Koczywas M, Massarelli E and Salgia
R: Small cell lung cancer transformation following treatment in
EGFR-Mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Med. 11:14292022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Mc Leer A, Foll M, Brevet M, Antoine M,
Novello S, Mondet J, Cadranel J, Girard N, Giaj Levra M, Demontrond
P, et al: Detection of acquired TERT amplification in addition to
predisposing p53 and Rb pathways alterations in EGFR-mutant lung
adenocarcinomas transformed into small-cell lung cancers. Lung
Cancer. 167:98–106. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Song KA, Niederst MJ, Lochmann TL, Hata
AN, Kitai H, Ham J, Floros KV, Hicks MA, Hu H, Mulvey HE, et al:
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition antagonizes response to
targeted therapies in lung cancer by suppressing BIM. Clin Cancer
Res. 24:197–208. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Shaurova T, Zhang L, Goodrich DW and
Hershberger PA: Understanding lineage plasticity as a path to
targeted therapy failure in EGFR-Mutant non-small cell lung cancer.
Front Genet. 11:2812020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Wang W, Xu C, Chen H, Jia J, Wang L, Feng
H, Wang H, Song Z, Yang N and Zhang Y: Genomic alterations and
clinical outcomes in patients with lung adenocarcinoma with
transformation to small cell lung cancer after treatment with EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A multicenter retrospective study. Lung
Cancer. 155:20–27. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zhang C, Zhang S, Yao Y, Huang J, Peng K,
Gao Q, Chen H, Xu C, Zhang X, Wu Y, Yang J, et al: MA12. 08
Chemotherapy plus EGFR TKIs or bevacizumab versus chemotherapy
alone in SCLC-transformed EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. J Thor
Oncol. 16:S178–S179. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Kuiper JL, Ronden MI, Becker A, Heideman
DA, van Hengel P, Ylstra B, Thunnissen E and Smit EF:
Transformation to a squamous cell carcinoma phenotype of an
EGFR-mutated NSCLC patient after treatment with an EGFR-tyrosine
kinase inhibitor. J Clin Pathol. 68:320–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Levin PA, Mayer M, Hoskin S, Sailors J,
Oliver DH and Gerber DE: Histologic transformation from
adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma as a mechanism of
resistance to EGFR inhibition. J Thorac Oncol. 10:e86–e88. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Longo L, Mengoli MC, Bertolini F, Bettelli
S, Manfredini S and Rossi G: Synchronous occurrence of
squamous-cell carcinoma ‘transformation’ and EGFR exon 20 S768I
mutation as a novel mechanism of resistance in EGFR-mutated lung
adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 103:24–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Roca E, Pozzari M, Vermi W, Tovazzi V,
Baggi A, Amoroso V, Nonnis D, Intagliata S and Berruti A: Outcome
of EGFR-mutated adenocarcinoma NSCLC patients with changed
phenotype to squamous cell carcinoma after tyrosine kinase
inhibitors: A pooled analysis with an additional case. Lung Cancer.
127:12–18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Liao J, Li Y, Liu C, Long Q and Wang J:
Case report: EGFR-Positive early-stage lung adenocarcinoma
transforming to squamous cell carcinoma after TKI treatment. Front
Oncol. 11:6968812021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Jukna A, Montanari G, Mengoli MC, Cavazza
A, Covi M, Barbieri F, Bertolini F and Rossi G: Squamous Cell
Carcinoma ‘Transformation’ concurrent with secondary T790M mutation
in resistant EGFR-Mutated Adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Oncol.
11:e49–e51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Bugano DDG, Kalhor N, Zhang J, Neskey M
and William WN Jr: Squamous-cell transformation in a patient with
lung adenocarcinoma receiving erlotinib: Co-occurrence with T790M
mutation. Cancer Treat Comm. 4:34–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Park S, Shim JH, Lee B, Cho I, Park WY,
Kim Y, Lee SH, Choi Y, Han J, Ahn JS, et al: Paired genomic
analysis of squamous cell carcinoma transformed from EGFR-mutated
lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 134:7–15. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Weng CH, Chen LY, Lin YC, Shih JY, Lin YC,
Tseng RY, Chiu AC, Yeh YH, Liu C, Lin YT, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) beyond EGFR mutations per
se is a common mechanism for acquired resistance to EGFR TKI.
Oncogene. 38:455–468. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Brabletz S, Schuhwerk H, Brabletz T and
Stemmler MP: Dynamic EMT: A multi-tool for tumor progression. EMBO
J. 40:e1086472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhu X, Chen L, Liu L and Niu X:
EMT-Mediated Acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC: Mechanisms and
strategies. Front Oncol. 9:10442019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Miralaei N, Majd A, Ghaedi K, Peymani M
and Safaei M: Integrated pan-cancer of AURKA expression and drug
sensitivity analysis reveals increased expression of AURKA is
responsible for drug resistance. Cancer Med. 10:6428–6441. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Nilsson MB, Sun H, Robichaux J, Pfeifer M,
McDermott U, Travers J, Diao L, Xi Y, Tong P, Shen L, et al: A
YAP/FOXM1 axis mediates EMT-associated EGFR inhibitor resistance
and increased expression of spindle assembly checkpoint components.
Sci Transl Med. 12:eaaz45892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Wang CY, Lee MH, Kao YR, Hsiao SH, Hong SY
and Wu CW: Alisertib inhibits migration and invasion of EGFR-TKI
resistant cells by partially reversing the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1868:1190162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Yeh CT, Chen TT, Satriyo PB, Wang CH, Wu
ATH, Chao TY, Lee KY, Hsiao M, Wang LS and Kuo KT: Bruton's
tyrosine kinase (BTK) mediates resistance to EGFR inhibition in
non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Oncogenesis. 10:562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Liao BC, Griesing S and Yang JC:
Second-line treatment of EGFR T790M-negative non-small cell lung
cancer patients. Ther Adv Med Oncol. Nov 25–2019.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Lee CK, Man J, Lord S, Links M, Gebski V,
Mok T and Yang JC: Checkpoint Inhibitors in Metastatic EGFR-Mutated
non-small cell lung cancer-A meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol.
12:403–407. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Lee CK, Man J, Lord S, Cooper W, Links M,
Gebski V, Herbst RS, Gralla RJ, Mok T and Yang JC: Clinical and
molecular characteristics associated with survival among patients
treated with checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung
carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol.
4:210–216. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Yang CY, Liao WY, Ho CC, Chen KY, Tsai TH,
Hsu CL, Su KY, Chang YL, Wu CT, Hsu CC, et al: Association between
programmed death-ligand 1 expression, immune microenvironments, and
clinical outcomes in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung
adenocarcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Eur J Cancer. 124:110–122. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Isomoto K, Haratani K, Hayashi H, Shimizu
S, Tomida S, Niwa T, Yokoyama T, Fukuda Y, Chiba Y, Kato R, et al:
Impact of EGFR-TKI treatment on the tumor immune microenvironment
in EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 26:2037–2046. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Reck M, Mok TS, Nishio M, Jotte RM,
Cappuzzo F, Orlandi F, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, Rodríguez-Abreu
D, Moro-Sibilot D, et al: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and
chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): Key
subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver
metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir
Med. 7:387–401. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Wu SG, Ho CC, Yang JC, Lia BC, Yang CY,
Lin YT, Yu CJ, Liao WY and Shih JY: 12P A phase II study of
atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab, carboplatin or
cisplatin, and pemetrexed for EGFR-mutant metastatic NSCLC patients
after failure of EGFR TKIs. Ann Oncol. 33:S33–S34. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Lam TC, Tsang KC, Choi HC, Lee VH, Lam KO,
Chiang CL, So TH, Chan WW, Nyaw SF, Lim F, et al: Combination
atezolizumab, bevacizumab, pemetrexed and carboplatin for
metastatic EGFR mutated NSCLC after TKI failure. Lung Cancer.
159:18–26. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Ren S, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Zhou J, Fan Y, Shu
Y, Liu X, Zhang H, He J, Gao G, et al: A multi-center phase II
study of toripalimab with chemotherapy in patients with EGFR mutant
advanced NSCLC patients resistant to EGFR TKIs: Efficacy and
biomarker analysis. Am Soc Clin Oncol. 6:3552020.
|
|
141
|
Jiang T, Wang P, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Zhou J,
Fan Y, Shu Y, Liu X, Zhang H, He J, et al: Toripalimab plus
chemotherapy as second-line treatment in previously EGFR-TKI
treated patients with EGFR-mutant-advanced NSCLC: A multicenter
phase-II trial. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:3552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Lu S, Wu L, Jian H, Cheng Y, Wang Q, Fang
J, Wang Z, Hu Y, Sun M, Han L, et al: VP9-2021: ORIENT-31: Phase
III study of sintilimab with or without IBI305 plus chemotherapy in
patients with EGFR mutated nonsquamous NSCLC who progressed after
EGFR-TKI therapy. Ann Oncol. 33:112–113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Hayashi H, Sugawara S, Fukuda Y, Fujimoto
D, Miura S, Ota K, Ozawa Y, Hara S, Tanizaki J, Azuma K, et al: A
randomized phase II study comparing nivolumab with
carboplatin-pemetrexed for EGFR-mutated NSCLC with resistance to
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (WJOG8515L). Clin Cancer Res.
28:893–902. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
de Rouw N, Piet B, Derijks HJ, van den
Heuvel MM and Ter Heine R: Mechanisms, management and prevention of
pemetrexed-related toxicity. Drug Saf. 44:1271–1281. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Liang SK, Keng LT, Chang CH, Wen YF, Lee
MR, Yang CY, Wang JY, Ko JC, Shih JY and Yu CJ: Treatment options
of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors and subsequent systemic
chemotherapy agents for advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma
patients: Implications from Taiwan cancer registry cohort. Front
Oncol. 10:5903562021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Li Z, Guo H, Lu Y, Hu J, Luo H and Gu W:
Chemotherapy with or without pemetrexed as second-line regimens for
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients who have progressed
after first-line EGFR TKIs: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:3697–3703. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Yoo KH, Lee SJ, Cho J, Lee KH, Park KU,
Kim KH, Cho EK, Choi YH, Kim HR, Kim HG, et al: A randomized,
open-label, Phase II study comparing pemetrexed plus cisplatin
followed by maintenance pemetrexed versus pemetrexed alone in
patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant
non-small cell lung cancer after failure of first-line EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitor: KCSG-LU12-13. Cancer Res Treat.
51:718–726. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Le X, Nilsson M, Goldman J, Reck M,
Nakagawa K, Kato T, Ares LP, Frimodt-Moller B, Wolff K,
Visseren-Grul C, et al: Dual EGFR-VEGF Pathway inhibition: A
promising strategy for patients with EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J Thorac
Oncol. 16:205–215. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Lian Z, Du W, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Liu T, Wang
A, Cai T, Zhu J, Zeng Y, Liu Z and Huang JA: Anlotinib can overcome
acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs via FGFR1 signaling in non-small
cell lung cancer without harboring EGFR T790M mutation. Thorac
Cancer. 11:1934–1943. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Zhang C, Cao H, Cui Y, Jin S, Gao W, Huang
C and Guo R: Concurrent use of anlotinib overcomes acquired
resistance to EGFR-TKI in patients with advanced EGFR-mutant
non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. 12:2574–2584. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Hata A, Katakami N, Kaji R, Yokoyama T,
Kaneda T, Tamiya M, Inoue T, Kimura H, Yano Y, Tamura D, et al:
Afatinib plus bevacizumab combination after acquired resistance to
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung
cancer: Multicenter, single-arm, phase 2 trial (ABC Study). Cancer.
124:3830–3838. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Yang R, Wang D, Li X, Mao K, Wang J, Li P,
Shi X, Zhang S and Wang Y: An advanced non-small cell lung cancer
patient with EGFR and KRAS mutations, and PD-L1 positive, benefited
from immunotherapy: A case report. Ann Transl Med. 10:3812022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Bai M, Wang W, Gao X, Wu L, Jin P, Wu H,
Yu J and Meng X: Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in
patients with EGFR Mutated NSCLC and potential risk factors
associated with prognosis: A single institution experience. Front
Immunol. 13:8324192022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Mu Y, Hao X, Xing P, Hu X, Wang Y, Li T,
Zhang J, Xu Z and Li J: Acquired resistance to osimertinib in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and clinical
outcomes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:2427–2433. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Leonetti A, Sharma S, Minari R, Perego P,
Giovannetti E and Tiseo M: Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in
EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 121:725–737.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
He J, Huang Z, Han L, Gong Y and Xie C:
Mechanisms and management of 3rd-generation EGFR-TKI resistance in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer (Review). Int J Oncol.
59:902021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Papadimitrakopoulou V, Wu YL, Han JY, Ahn
MJ, Ramalingam SS, John T, Okamoto I, Yang JC, Bulusu K, Laus G, et
al: Analysis of resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients
with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 study. Annal Oncol.
29:viii7412018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Piotrowska Z, Nagy R, Fairclough S, Lanman
R, Marcoux N, Gettinger S, Owonikoko T, Ramalingam S and Sequist L:
Characterizing the genomic landscape of EGFR C797S in lung cancer
using ctDNA next-generation sequencing. J Thorac Oncol.
12:S17672017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Wang X, Zhou L, Yin JC, Wu X, Shao YW and
Gao B: Lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR 19del/C797S/T790M triple
mutations responds to brigatinib and Anti-EGFR antibody combination
therapy. J Thorac Oncol. 14:e85–e88. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Chang Y, Liu S, Jiang Y, Hua L and Wen L:
Effective treatment of pulmonary adenocarcinoma harboring triple
EGFR mutations of L858R, T790M, cis-G796s/cis-C797s by osimertinib,
brigatinib, and bevacizumab combination therapy: A case report.
Respir Med Case Rep. 36:1015822022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Zhou R, Song L, Zhang W, Shao L and Li X
and Li X: Combination of osimertinib and anlotinib may overcome the
resistance mediated by in cis EGFR T790M-C797S in NSCLC: A case
report. Onco Targets Ther. 14:2847–2851. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Yang Y, Xu H, Ma L, Yang L, Yang G, Zhang
S, Ai X, Zhang S and Wang Y: Possibility of brigatinib-based
therapy, or chemotherapy plus anti-angiogenic treatment after
resistance of osimertinib harboring EGFR T790M-cis-C797S mutations
in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Cancer Med. 10:8328–8337. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Zhao Y, Chen Y, Huang H, Li X, Shao L and
Ding H: Significant benefits of afatinib and apatinib in a
refractory advanced NSCLC patient resistant to osimertinib: A case
report. OncoTargets Ther. 14:3063–3067. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Yang Z, Yang N, Ou Q, Xiang Y, Jiang T, Wu
X, Bao H, Tong X, Wang X, Shao YW, et al: Investigating novel
resistance mechanisms to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 24:3097–3107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Zhang Y, He B, Zhou D, Li M and Hu C:
Newly emergent acquired EGFR exon 18 G724S mutation after
resistance of a T790M specific EGFR inhibitor osimertinib in
non-small-cell lung cancer: A case report. OncoTargets Ther.
12:51–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Schoenfeld AJ, Chan JM, Kubota D, Sato H,
Rizvi H, Daneshbod Y, Chang JC, Paik PK, Offin M, Arcila ME, et al:
Tumor analyses reveal squamous transformation and off-target
alterations as early resistance mechanisms to first-line
osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
26:2654–2663. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Fairclough SR, Kiedrowski LA, Lin JJ,
Zelichov O, Tarcic G, Stinchcombe TE, Odegaard JI, Lanman RB, Shaw
AT and Nagy RJ: Identification of osimertinib-resistant EGFR L792
mutations by cfDNA sequencing: oncogenic activity assessment and
prevalence in large cfDNA cohort. Exp Hematol Oncol. 8:242019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Ma L, Chen R, Wang F, Ma LL, Yuan MM, Chen
RR and Liu J: EGFR L718Q mutation occurs without T790M mutation in
a lung adenocarcinoma patient with acquired resistance to
osimertinib. Ann Transl Med. 7:2072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Fang W, Huang Y, Gan J, Zheng Q and Zhang
L: Emergence of EGFR G724S after progression on osimertinib
responded to afatinib monotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. 15:e36–e37.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Zhang Y, Yang Q, Zeng X, Wang M, Dong S,
Yang B, Tu X, Wei T, Xie W, Zhang C, et al: MET amplification
attenuates lung tumor response to immunotherapy by inhibiting
STING. Cancer Discov. 11:2726–2737. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Syed YY: Amivantamab: First approval.
Drugs. 81:1349–1353. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Amivantamab OK'd for EGFR-Mutant NSCLC, .
Cancer Discov. 11:16042021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Neijssen J, Cardoso RM, Chevalier KM,
Wiegman L, Valerius T, Anderson GM, Moores SL, Schuurman J, Parren
PW, Strohl WR and Chiu ML: Discovery of amivantamab (JNJ-61186372),
a bispecific antibody targeting EGFR and MET. J Biol Chem.
296:1006412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Planchard D, Loriot Y, André F, Gobert A,
Auger N, Lacroix L and Soria JC: EGFR-independent mechanisms of
acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC
patients. Ann Oncol. 26:2073–2078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Ramalingam S, Cheng Y, Zhou C, Ohe Y,
Imamura F, Cho BC, Lin M, Majem M, Shah R, Rukazenkov Y, et al:
Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib:
preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. OncologyPro.
29:viii7402018.
|
|
176
|
Oxnard GR, Hu Y, Mileham KF, Husain H,
Costa DB, Tracy P, Feeney N, Sholl LM, Dahlberg SE, Redig AJ, et
al: Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications
in patients With EGFR T790M-Positive lung cancer and acquired
resistance to osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 4:1527–1534. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Qu F, Zhou Y and Yu WJA-CD: A review of
research progress on mechanisms and overcoming strategies of
acquired osimertinib resistance. Anticancer Drugs. 33:e76–e83.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Beenken A and Mohammadi M: The FGF family:
Biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:235–253. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Lu Y, Liu Y, Oeck S, Zhang GJ, Schramm A
and Glazer PM: Hypoxia induces resistance to EGFR inhibitors in
lung cancer cells via upregulation of FGFR1 and the MAPK pathway.
Cancer Res. 80:4655–4667. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Quintanal-Villalonga A, Molina-Pinelo S,
Cirauqui C, Ojeda-Márquez L, Marrugal Á, Suarez R, Conde E,
Ponce-Aix S, Enguita AB, Carnero A, et al: FGFR1 Cooperates with
EGFR in lung cancer oncogenesis, and their combined inhibition
shows improved efficacy. J Thorac Oncol. 14:641–655. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Hayakawa D, Takahashi F, Mitsuishi Y,
Tajima K, Hidayat M, Winardi W, Ihara H, Kanamori K, Matsumoto N,
Asao T, et al: Activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
confers acquired resistance to osimertinib in non-small cell lung
cancer with EGFR T790M mutation. Thorac Cancer. 11:140–149. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Zhao Y, Wang H and He C: Drug resistance
of targeted therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
harbored EGFR mutation: From mechanism analysis to clinical
strategy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 147:3653–3664. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Makimoto G, Ninomiya K, Kubo T, Sunami R,
Kato Y, Ichihara E, Ohashi K, Rai K, Hotta K, Tabata M, et al: A
novel osimertinib-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cell line
harbouring mutant EGFR and activated IGF1R. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
51:956–965. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Wang R, Yamada T, Kita K, Taniguchi H,
Arai S, Fukuda K, Terashima M, Ishimura A, Nishiyama A, Tanimoto A,
et al: Transient IGF-1R inhibition combined with osimertinib
eradicates AXL-low expressing EGFR mutated lung cancer. Nat Commun.
11:46072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Lin CC, Shih JY, Yu CJ, Ho CC, Liao WY,
Lee JH, Tsai TH, Su KY, Hsieh MS, Chang YL, et al: Outcomes in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and acquired Thr790Met
mutation treated with osimertinib: A genomic study. Lancet Respir
Med. 6:107–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Jia Y, Yun CH, Park E, Ercan D, Manuia M,
Juarez J, Xu C, Rhee K, Chen T, Zhang H, et al: Overcoming
EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective
allosteric inhibitors. Nature. 534:129–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
To C, Jang J, Chen T, Park E, Mushajiang
M, De Clercq DJH, Xu M, Wang S, Cameron MD, Heppner DE, et al:
Single and dual targeting of mutant EGFR with an allosteric
inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 9:926–943. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Tripathi SK and Biswal BK: Allosteric
mutant-selective fourth-generation EGFR inhibitors as an efficient
combination therapeutic in the treatment of non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Drug Discov Today. 26:1466–1472. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Kashima K, Kawauchi H, Tanimura H,
Tachibana Y, Chiba T, Torizawa T and Sakamoto H: CH7233163
overcomes osimertinib-resistant EGFR-Del19/T790M/C797S Mutation.
Mol Cancer Ther. 19:2288–2297. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Schalm S, Dineen T, Lim S, Park CW, Hsieh
J, Woessner R, Zhang Z, Wilson K, Eno M, Wilson D, et al: 1296P
BLU-945, a highly potent and selective 4th generation EGFR TKI for
the treatment of EGFR T790M/C797S resistant NSCLC. Ann Oncol.
31:S8392020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Conti C, Campbell J, Woessner R, Guo J,
Timsit Y, Iliou M, Wardwell S, Davis A, Chicklas S, Hsieh J, et al:
BLU-701 is a highly potent, brain-penetrant and WT-sparing
next-generation EGFR TKI for the treatment of sensitizing (ex19del,
L858R) and C797S resistance mutations in metastatic NSCLC. Cancer
Res. 81 (Suppl 13):12622021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Lim SM, Park CW, Zhang Z, Woessner R,
Dineen T, Stevison F, Hsieh J, Eno M, Wilson D, Campbell J, et al:
BLU-945, a fourth-generation, potent and highly selective epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with intracranial
activity, demonstrates robust in vivo anti-tumor activity in models
of osimertinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 81
(Suppl 13):14672021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Tavera L, Zhang Z, Wardwell S, Job E,
McGinn K, Chen M, Iliou M, Albayya F, Campbell J, Eno M, et al:
BLU-701 tumour suppression and intracranial activity as a single
agent and in combination with BLU-945 in models of non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) driven by EGFR mutations. Mol Cell Biol.
165:S372022.
|
|
194
|
Liu X, Zhang X, Yang L, Chen S, Tian X,
Dong T, Ding CZ, Hu L, Wu L, Zhao L, Mao J, et al: Preclinical
evaluation of TQB3804, a potent EGFR C797S inhibitor. Cancer Res.
79 (Suppl 13):13202019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
195
|
Huang J and Wang H: Targeted therapy and
mechanism of drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer with
epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za
Zhi. 25:183–192. 2022.(In Chinese).
|
|
196
|
Lim S, Kim DW, Jung JE, Lee G, Ryou JH,
Kang SU, Lee YH, Shin HJ, Yum SY and Yim Ε: A Phase 1/2, open-label
study of BBT-176, a triple mutation targeting EGFR TKI, in patients
with NSCLC who progressed after prior EGFR TKI therapy. Ann Oncol.
32:S949–S1039. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Lim S, Kim D and Jung J: A phase I/II,
open-label study of BBT-176, a triple mutation targeting EGFR TKI,
in patients with NSCLC who progressed after prior EGFR TKI therapy.
Ann Oncol. 32:S1035(Suppl 5):2021.
|
|
198
|
Park K, Haura EB, Leighl NB, Mitchell P,
Shu CA, Girard N, Viteri S, Han JY, Kim SW, Lee CK, et al:
Amivantamab in EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated non-small-cell lung
cancer progressing on platinum chemotherapy: Initial results from
the CHRYSALIS phase I study. J Clin Oncol. 39:3391–3402. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Cho B, Lee K, Cho E, Kim DW, Lee JS, Han
JY, Kim SW, Spira A, Haura EB, Sabari JK, et al: 1258O Amivantamab
(JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in combination
with lazertinib, a 3rd-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI),
in advanced EGFR NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 31:S813(Suppl 4):2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Yu H, Johnson M, Steuer C, Vigliotti M,
Chen S, Kamai Y, Yu C and Jänne P: Preliminary phase 1 results of
U3-1402-A novel HER3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate-in EGFR
TKI-resistant, EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Mol Cell Biol. 14:S336–S337.
2019.
|
|
201
|
Jänne PA, Baik C, Su WC, Johnson ML,
Hayashi H, Nishio M, Kim DW, Koczywas M, Gold KA, Steuer CE, et al:
Efficacy and safety of patritumab deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in EGFR
inhibitor-resistant, EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Discov. 12:74–89. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
202
|
Soo RA, Han JY, Dafni U, Cho BC, Yeo CM,
Nadal E, Carcereny E, de Castro J, Sala MA, Bernabé R, et al: A
randomised phase II study of osimertinib and bevacizumab versus
osimertinib alone as second-line targeted treatment in advanced
NSCLC with confirmed EGFR and acquired T790M mutations: The
European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP 10–16) BOOSTER trial. Ann
Oncol. 33:181–192. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Cui Q, Hu Y, Cui Q, Wu D, Mao Y, Ma D and
Liu H: Osimertinib rechallenge with bevacizumab vs. chemotherapy
plus bevacizumab in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC patients with osimertinib
resistance. Front Pharmacol. 12:7467072022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Sequist L, Peled N, Tufman A, Servidio L,
Li J, Taylor R and Zhao J: COMPEL: Chemotherapy with/without
osimertinib in patients with EGFRm advanced NSCLC and progression
on first-line osimertinib. J Thor Oncol. 16:S11012021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Han B, Li K, Wang Q, Zhang L, Shi J, Wang
Z, Cheng Y, He J, Shi Y, Zhao Y, et al: Effect of anlotinib as a
third-line or further treatment on overall survival of patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The ALTER 0303 phase 3
Randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 4:1569–1575. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Tamiya M, Kunimasa K, Nishino K, Matsumoto
S, Kawachi H, Kuno K, Inoue T, Kuhara H, Imamura F, Goto K and
Kumagai T: Successful treatment of an osimertinib-resistant lung
adenocarcinoma with an exon 18 EGFR mutation (G719S) with afatinib
plus bevacizumab. Invest New Drugs. 39:232–236. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Blakely CM, Watkins TBK, Wu W, Gini B,
Chabon JJ, McCoach CE, McGranahan N, Wilson GA, Birkbak NJ, Olivas
VR, et al: Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic
alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat Genet.
49:1693–1704. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Dagogo-Jack I and Shaw AT: Tumour
heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 15:81–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
209
|
Assaraf YG, Brozovic A, Gonçalves AC,
Jurkovicova D, Linē A, Machuqueiro M, Saponara S, Sarmento-Ribeiro
AB, Xavier CPR and Vasconcelos MH: The multi-factorial nature of
clinical multidrug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Updat.
46:1006452019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Zhang Y, Wang D, Peng M, Tang L, Ouyang J,
Xiong F, Guo C, Tang Y, Zhou Y, Liao Q, et al: Single-cell RNA
sequencing in cancer research. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:812021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Maynard A, McCoach CE, Rotow JK, Harris L,
Haderk F, Kerr DL, Yu EA, Schenk EL, Tan W, Zee A, et al:
Therapy-Induced evolution of human lung cancer revealed by
single-cell RNA sequencing. Cell. 182:1232–1251.e22. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
212
|
Kim DW and Cho JY: Recent advances in
allogeneic CAR-T cells. Biomolecules. 10:2632020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
213
|
Patel AJ, Richter A, Drayson MT and
Middleton GW: The role of B lymphocytes in the immuno-biology of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 69:325–342.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Hung LVM, Ngo HT and Van Pham P: Clinical
trials with cytokine-induced killer cells and CAR-T cell
transplantation for non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 1292:113–130. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Johnson LA and June CH: Driving
gene-engineered T cell immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Res. 27:38–58.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Xu J, Zhang Q, Tian K, Wang H, Yin H and
Zheng J: Current status and future prospects of the strategy of
combining CAR-T with PD-1 blockade for antitumor therapy (Review).
Mol Med Rep. 17:2083–2088. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Kandra P, Nandigama R, Eul B, Huber M,
Kobold S, Seeger W, Grimminger F and Savai R: Utility and drawbacks
of chimeric antigen receptor T Cell (CAR-T) therapy in lung cancer.
Front Immunol. 13:9035622022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
218
|
Xu C, Ju D and Zhang X: Chimeric antigen
receptor T-cell therapy: Challenges and opportunities in lung
cancer. Antib Ther. 5:73–83. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Yang P, Qiao Y, Meng M and Zhou Q:
Cancer/Testis antigens as biomarker and target for the diagnosis,
prognosis, and therapy of lung cancer. Front Oncol. 12:8641592022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
220
|
Yeku O, Li X and Brentjens RJ: Adoptive
T-Cell therapy for solid tumors. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book.
37:193–204. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Reppel L, Tsahouridis O, Akulian J, Davis
IJ, Lee H, Fucà G, Weiss J, Dotti G, Pecot CV and Savoldo B:
Targeting disialoganglioside GD2 with chimeric antigen
receptor-redirected T cells in lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer.
10:e0038972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Min J, Long C, Zhang L, Duan J, Fan H, Chu
F and Li Z: c-Met specific CAR-T cells as a targeted therapy for
non-small cell lung cancer cell A549. Bioengineered. 13:9216–9232.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Feng K, Guo Y, Dai H, Wang Y, Li X, Jia H
and Han W: Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for the
immunotherapy of patients with EGFR-expressing advanced
relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Sci China Life Sci.
59:468–479. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
224
|
Xiao BF, Zhang JT, Zhu YG, Cui XR, Lu ZM,
Yu BT and Wu N: Chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell therapy in lung
cancer: Potential and challenges. Front Immunol. 12:7827752021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Qu J, Mei Q, Chen L and Zhou J: Chimeric
antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): Current status and future Aperspectives. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 70:619–631. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Chen L, Chen F, Li J, Pu Y, Yang C, Wang
Y, Lei Y and Huang Y: CAR-T cell therapy for lung cancer: Potential
and perspective. Thorac Cancer. 13:889–899. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Vasic D, Lee JB, Leung Y, Khatri I, Na Y,
Abate-Daga D and Zhang L: Allogeneic double-negative CAR-T cells
inhibit tumor growth without off-tumor toxicities. Sci Immunol.
7:eabl36422022. View Article : Google Scholar
|