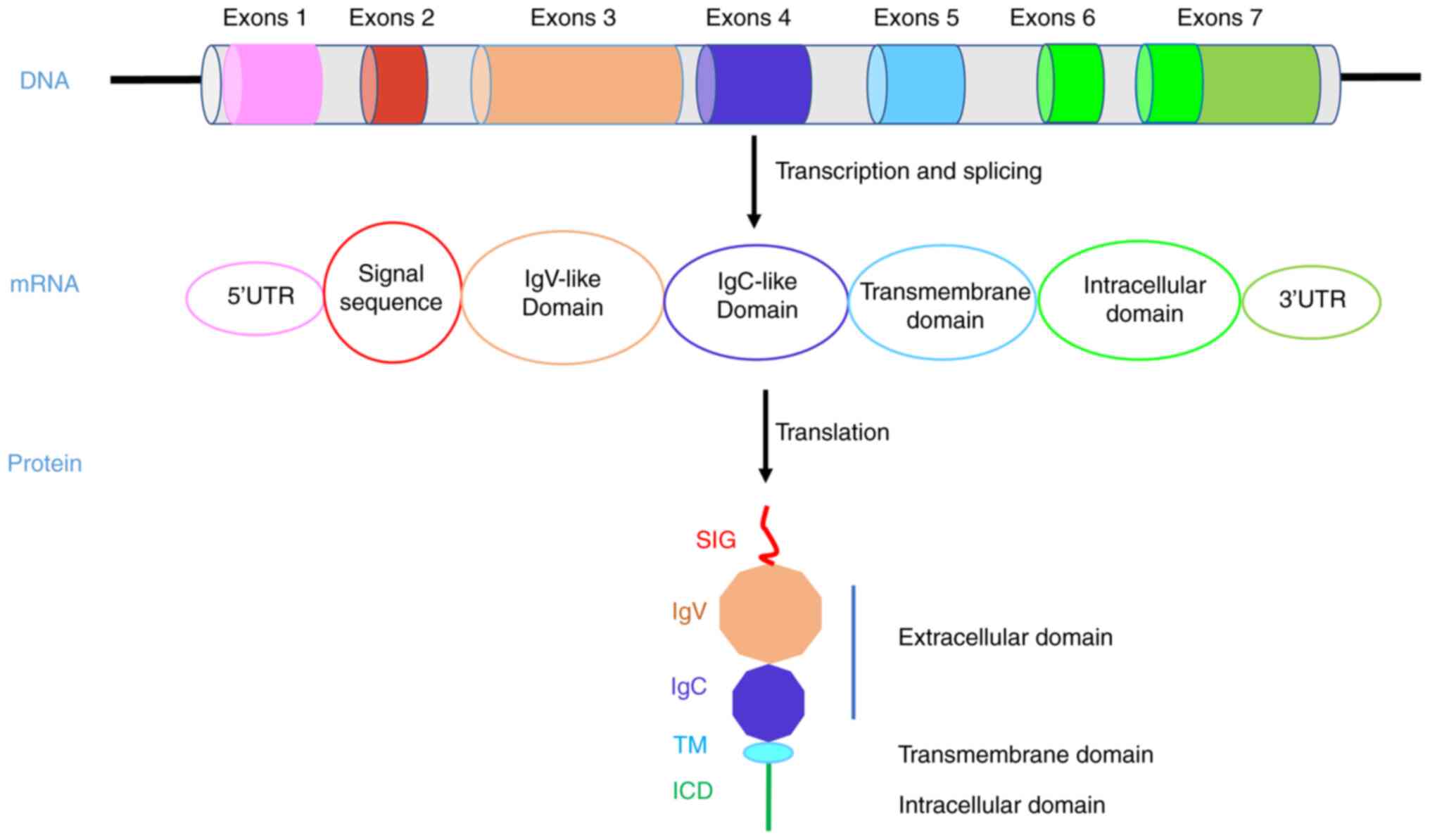
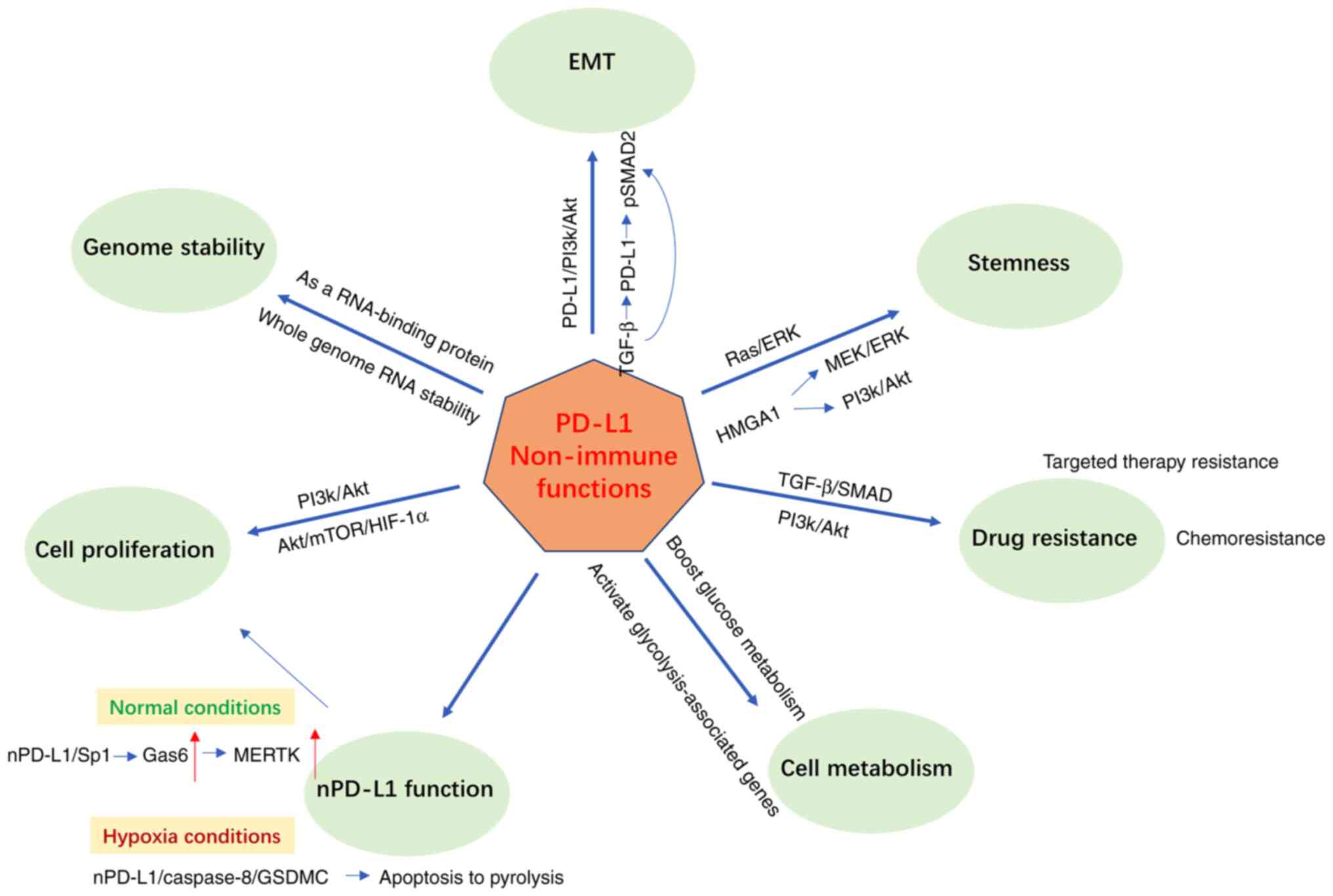
|
1
|
Sun C, Mezzadra R and Schumacher TN:
Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity.
48:434–452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thompson RH, Gillett MD, Cheville JC,
Lohse CM, Dong H, Webster WS, Krejci KG, Lobo JR, Sengupta S, Chen
L, et al: Costimulatory B7-H1 in renal cell carcinoma patients:
Indicator of tumor aggressiveness and potential therapeutic target.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:17174–17179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Muenst S, Schaerli AR, Gao F, Däster S,
Trella E, Droeser RA, Muraro MG, Zajac P, Zanetti R, Gillanders WE,
et al: Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is
associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 146:15–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kraft S, Fernandez-Figueras MT, Richarz
NA, Flaherty KT and Hoang MP: PDL1 expression in desmoplastic
melanoma is associated with tumor aggressiveness and progression. J
Am Acad Dermatol. 77:534–542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nduom EK, Wei J, Yaghi NK, Huang N, Kong
LY, Gabrusiewicz K, Ling X, Zhou S, Ivan C, Chen JQ, et al: PD-L1
expression and prognostic impact in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol.
18:195–205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xia H, Shen J, Hu F, Chen S, Huang H, Xu Y
and Ma H: PD-L1 over-expression is associated with a poor prognosis
in Asian non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta.
469:191–194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang S, Yuan B, Wang Y, Li M, Liu X, Cao
J, Li C and Hu J: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance
of PD-L1 expression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 36:117–130. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cha JH, Chan LC, Li CW, Hsu JL and Hung
MC: Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer. Mol Cell.
76:359–370. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yarchoan M, Hopkins A and Jaffee EM: Tumor
mutational burden and response rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N Engl J
Med. 377:2500–2501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pitt JM, Vetizou M, Daillere R, Roberti
MP, Yamazaki T, Routy B, Lepage P, Boneca IG, Chamaillard M,
Kroemer G and Zitvogel L: Resistance mechanisms to
immune-checkpoint blockade in cancer: Tumor-intrinsic and
-extrinsic factors. Immunity. 44:1255–1269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K,
Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne
MC, et al: Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a
novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang T, Ren C, Lu C, Qiao P, Han X, Wang
L, Wang D, Lv S, Sun Y and Yu Z: Phosphorylation of HSF1 by PIM2
Induces PD-L1 expression and promotes tumor growth in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 79:5233–5244. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim W, Chu TH, Nienhuser H, Jiang Z, Del
Portillo A, Remotti HE, White RA, Hayakawa Y, Tomita H, Fox JG, et
al: PD-1 Signaling promotes tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived
suppressor cells and gastric tumorigenesis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 160:781–796. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao H, Zhang J and Ren X: PD-L1 regulates
tumorigenesis and autophagy of ovarian cancer by activating mTORC
signaling. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201910412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mu L, Wang Y, Su H, Lin Y, Sui W, Yu X and
Lv Z: HIF1A-AS2 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of
gastric cancer cells through miR-429/PD-L1 Axis. Dig Dis Sci.
66:4314–4325. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zak KM, Kitel R, Przetocka S, Golik P,
Guzik K, Musielak B, Dömling A, Dubin G and Holak TA: Structure of
the complex of human programmed death 1, PD-1, and Its Ligand
PD-L1. Structure. 23:2341–2348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gato-Canas M, Zuazo M, Arasanz H,
Ibañez-Vea M, Lorenzo L, Fernandez-Hinojal G, Vera R, Smerdou C,
Martisova E, Arozarena I, et al: PDL1 signals through conserved
sequence motifs to overcome interferon-mediated cytotoxicity. Cell
Rep. 20:1818–1829. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin DY, Tanaka Y, Iwasaki M, Gittis AG, Su
HP, Mikami B, Okazaki T, Honjo T, Minato N and Garboczi DN: The
PD-1/PD-L1 complex resembles the antigen-binding Fv domains of
antibodies and T cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:3011–3016. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Jiang CC, Jin L and Zhang XD:
Regulation of PD-L1: A novel role of pro-survival signalling in
cancer. Ann Oncol. 27:409–416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Azuma T, Yao S, Zhu G, Flies AS, Flies SJ
and Chen L: B7-H1 is a ubiquitous antiapoptotic receptor on cancer
cells. Blood. 111:3635–3643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang RSP, Decker B, Murugesan K, Hiemenz
M, Mata DA, Li G, Creeden J, Ramkissoon SH and Ross JS: Pan-cancer
analysis of CD274 (PD-L1) mutations in 314,631 patient samples and
subset correlation with PD-L1 protein expression. J Immunother
Cancer. 9:e0025582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brody R, Zhang Y, Ballas M, Siddiqui MK,
Gupta P, Barker C, Midha A and Walker J: PD-L1 expression in
advanced NSCLC: Insights into risk stratification and treatment
selection from a systematic literature review. Lung Cancer.
112:200–215. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yagi T, Baba Y, Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M,
Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N, Watanabe M and Baba H: PD-L1 expression,
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and clinical outcome in patients
with surgically resected esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 269:471–478.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hassen G, Kasar A, Jain N, Berry S, Dave
J, Zouetr M, Priyanka Ganapathiraju VLN, Kurapati T, Oshai S, Saad
M, et al: Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) positivity and factors
associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer: An
umbrella meta-analysis. Cureus. 14:e238452022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wan X, Hu T, Wu H, Cheng X and Xu S:
Predictive values of PDL1 expression for survival outcomes in
patients with cervical cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ginekol Pol. Aug 19–2022.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iacovelli R, Nole F, Verri E, Renne G,
Paglino C, Santoni M, Cossu Rocca M, Giglione P, Aurilio G, Cullurà
D, et al: Prognostic Role of PD-L1 expression in renal cell
carcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Target Oncol.
11:143–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang W, Ran R, Shao B and Li H:
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of PD-L1 expression in
primary breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
178:17–33. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Xue R and Pan C: Prognostic and
clinicopathological value of PD-L1 in colorectal cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther.
12:3671–3682. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang J, Dong M, Shui Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Z,
Mi Y, Zuo X, Jiang L, Liu K, Liu Z, et al: A pooled analysis of the
prognostic value of PD-L1 in melanoma: Evidence from 1062 patients.
Cancer Cell Int. 20:962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fife BT, Pauken KE, Eagar TN, Obu T, Wu J,
Tang Q, Azuma M, Krummel MF and Bluestone JA: Interactions between
PD-1 and PD-L1 promote tolerance by blocking the TCR-induced stop
signal. Nat Immunol. 10:1185–1192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li J, Chen L, Xiong Y, Zheng X, Xie Q,
Zhou Q, Shi L, Wu C, Jiang J and Wang H: Knockdown of PD-L1 in
human gastric cancer cells inhibits tumor progression and improves
the cytotoxic sensitivity to CIK therapy. Cell Physiol Biochem.
41:907–920. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lotfinejad P, Kazemi T, Safaei S, Amini M,
Roshani Asl E, Baghbani E, Sandoghchian Shotorbani S, Jadidi
Niaragh F, Derakhshani A, Abdoli Shadbad M, et al: PD-L1 silencing
inhibits triple-negative breast cancer development and upregulates
T-cell-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biomed Pharmacother.
138:1114362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang CH, Qiu J, O'Sullivan D, Buck MD,
Noguchi T, Curtis JD, Chen Q, Gindin M, Gubin MM, van der Windt GJ,
et al: Metabolic competition in the tumor microenvironment is a
driver of cancer progression. Cell. 162:1229–1241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Clark CA, Gupta HB, Sareddy G, Pandeswara
S, Lao S, Yuan B, Drerup JM, Padron A, Conejo-Garcia J, Murthy K,
et al: Tumor-Intrinsic PD-L1 signals regulate cell growth,
pathogenesis, and autophagy in ovarian cancer and melanoma. Cancer
Res. 76:6964–6974. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fan Y, Che X, Hou K, Zhang M, Wen T, Qu X
and Liu Y: MiR-940 promotes the proliferation and migration of
gastric cancer cells through up-regulation of programmed death
ligand-1 expression. Exp Cell Res. 373:180–187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kong T, Ahn R, Yang K, Zhu X, Fu Z, Morin
G, Bramley R, Cliffe NC, Xue Y, Kuasne H, et al: CD44 Promotes
PD-L1 expression and its tumor-intrinsic function in breast and
lung cancers. Cancer Res. 80:444–457. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu J, Qin B, Moyer AM, Nowsheen S, Tu X,
Dong H, Boughey JC, Goetz MP, Weinshilboum R, Lou Z and Wang L:
Regulation of sister chromatid cohesion by nuclear PD-L1. Cell Res.
30:590–601. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang N, Zeng Y, Du W, Zhu J, Shen D, Liu
Z and Huang JA: The EGFR pathway is involved in the regulation of
PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in
EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 49:1360–1368.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ghebeh H, Lehe C, Barhoush E, Al-Romaih K,
Tulbah A, Al-Alwan M, Hendrayani SF, Manogaran P, Alaiya A,
Al-Tweigeri T, et al: Doxorubicin downregulates cell surface B7-H1
expression and upregulates its nuclear expression in breast cancer
cells: Role of B7-H1 as an anti-apoptotic molecule. Breast Cancer
Res. 12:R482010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liao Y, Chen L, Feng Y, Shen J, Gao Y,
Cote G, Choy E, Harmon D, Mankin H, Hornicek F and Duan Z:
Targeting programmed cell death ligand 1 by CRISPR/Cas9 in
osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget. 8:30276–30287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shen B, Huang D, Ramsey AJ, Ig-Izevbekhai
K, Zhang K, Lajud SA, O'Malley BW and Li D: PD-L1 and MRN synergy
in platinum-based chemoresistance of head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 122:640–647. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang P, Liu J, Li W, Li S and Han X:
Lactoferricin B reverses cisplatin resistance in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma cells through targeting PD-L1. Cancer Med.
7:3178–3187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang H, Fu C, Du J, Wang H, He R, Yin X,
Li H, Li X, Wang H, Li K, et al: Enhanced histone H3 acetylation of
the PD-L1 promoter via the COP1/c-Jun/HDAC3 axis is required for
PD-L1 expression in drug-resistant cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 39:292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao Q, Xiang SD, Wilson K, Madondo M,
Stephens AN and Plebanski M: Sperm Protein 17 expression by murine
epithelial ovarian cancer cells and its impact on tumor
progression. Cancers (Basel). 10:2762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu F, Niu R and Shao X and Shao X:
FGD5AS1 promotes cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma
cell via the miR1425p/PDL1 axis. Int J Mol Med. 47:523–532. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li D, Wang X, Yang M, Kan Q and Duan Z:
MiR3609 sensitizes breast cancer cells to adriamycin by blocking
the programmed death-ligand 1 immune checkpoint. Exp Cell Res.
380:20–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Liu T, Du W, Zhu J, Liu Z
and Huang JA: The canonical TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway is
involved in PD-L1-induced primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in
EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Respir Res. 20:1642019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang TY, Chang TC, Chin YT, Pan YS, Chang
WJ, Liu FC, Hastuti ED, Chiu SJ, Wang SH, Changou CA, et al: NDAT
Targets PI3K-Mediated PD-L1 upregulation to reduce proliferation in
gefitinib-resistant colorectal cancer. Cells. 9:18302020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li D, Sun FF, Wang D, Wang T, Peng JJ,
Feng JQ, Li H, Wang C, Zhou DJ, Luo H, et al: Programmed death
ligand-1 (PD-L1) Regulated by NRF-2/MicroRNA-1 regulatory axis
enhances drug resistance and promotes tumorigenic properties in
sorafenib-resistant hepatoma cells. Oncol Res. 28:467–481. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen L, Xiong Y, Li J, Zheng X, Zhou Q,
Turner A, Wu C, Lu B and Jiang J: PD-L1 expression promotes
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human esophageal cancer.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:2267–2280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cao Y, Zhang L, Kamimura Y, Ritprajak P,
Hashiguchi M, Hirose S and Azuma M: B7-H1 overexpression regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and accelerates carcinogenesis in
skin. Cancer Res. 71:1235–1243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim S, Koh J, Kim MY, Kwon D, Go H, Kim
YA, Jeon YK and Chung DH: PD-L1 expression is associated with
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Hum Pathol. 58:7–14. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Inaguma S, Lasota J, Wang Z,
Felisiak-Golabek A, Ikeda H and Miettinen M: Clinicopathologic
profile, immunophenotype, and genotype of CD274 (PD-L1)-positive
colorectal carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 30:278–285. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tieche CC, Gao Y, Buhrer ED, Hobi N,
Berezowska SA, Wyler K, Froment L, Weis S, Peng RW, Bruggmann R, et
al: Tumor initiation capacity and therapy resistance are
differential features of EMT-Related subpopulations in the NSCLC
cell line A549. Neoplasia. 21:185–196. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhi Y, Mou Z, Chen J, He Y, Dong H, Fu X
and Wu Y: B7H1 expression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
phenotypes on colorectal cancer stem-like cells. PLoS One.
10:e01355282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ock CY, Kim S, Keam B, Kim M, Kim TM, Kim
JH, Jeon YK, Lee JS, Kwon SK, Hah JH, et al: PD-L1 expression is
associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:15901–15914. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Alsuliman A, Colak D, Al-Harazi O, Fitwi
H, Tulbah A, Al-Tweigeri T, Al-Alwan M and Ghebeh H: Bidirectional
crosstalk between PD-L1 expression and epithelial to mesenchymal
transition: Significance in claudin-low breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer. 14:1492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang Y, Wang H, Zhao Q, Xia Y, Hu X and
Guo J: PD-L1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via
activating SREBP-1c in renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 32:2122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
David JM, Dominguez C, McCampbell KK,
Gulley JL, Schlom J and Palena C: A novel bifunctional
anti-PD-L1/TGF-β Trap fusion protein (M7824) efficiently reverts
mesenchymalization of human lung cancer cells. Oncoimmunology.
6:e13495892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Almozyan S, Colak D, Mansour F, Alaiya A,
Al-Harazi O, Qattan A, Al-Mohanna F, Al-Alwan M and Ghebeh H: PD-L1
promotes OCT4 and Nanog expression in breast cancer stem cells by
sustaining PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Int J Cancer.
141:1402–1412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fang X, Chen C, Xia F, Yu Z, Zhang Y,
Zhang F, Gu H, Wan J, Zhang X, Weng W, et al: CD274 promotes cell
cycle entry of leukemia-initiating cells through JNK/Cyclin D2
signaling. J Hematol Oncol. 9:1242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wei F, Zhang T, Deng SC, Wei JC, Yang P,
Wang Q, Chen ZP, Li WL, Chen HC, Hu H and Cao J: PD-L1 promotes
colorectal cancer stem cell expansion by activating HMGA1-dependent
signaling pathways. Cancer Lett. 450:1–13. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhao L, Liu Y, Zhang J, Liu Y and Qi Q:
LncRNA SNHG14/miR-5590-3p/ZEB1 positive feedback loop promoted
diffuse large B cell lymphoma progression and immune evasion
through regulating PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint. Cell Death Dis.
10:7312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen L, Gibbons DL, Goswami S, Cortez MA,
Ahn YH, Byers LA, Zhang X, Yi X, Dwyer D, Lin W, et al: Metastasis
is regulated via microRNA-200/ZEB1 axis control of tumour cell
PD-L1 expression and intratumoral immunosuppression. Nat Commun.
5:52412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang QM, Lian GY, Song Y, Huang YF and
Gong Y: LncRNA MALAT1 promotes tumorigenesis and immune escape of
diffuse large B cell lymphoma by sponging miR-195. Life Sci.
231:1163352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rogers TJ, Christenson JL, Greene LI,
O'Neill KI, Williams MM, Gordon MA, Nemkov T, D'Alessandro A,
Degala GD, Shin J, et al: Reversal of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
EMT by miR-200c decreases tryptophan catabolism and a program of
immunosuppression. Mol Cancer Res. 17:30–41. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gao L, Guo Q, Li X, Yang X, Ni H, Wang T,
Zhao Q, Liu H, Xing Y, Xi T and Zheng L: MiR-873/PD-L1 axis
regulates the stemness of breast cancer cells. EBioMedicine.
41:395–407. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hong W, Xue M, Jiang J, Zhang Y and Gao X:
Circular RNA circ-CPA4/let-7 miRNA/PD-L1 axis regulates cell
growth, stemness, drug resistance and immune evasion in non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1492020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Takada K, Toyokawa G, Okamoto T, Baba S,
Kozuma Y, Matsubara T, Haratake N, Akamine T, Takamori S, Katsura
M, et al: Metabolic characteristics of programmed cell death-ligand
1-expressing lung cancer on (18) F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron
emission tomography/computed tomography. Cancer Med. 6:2552–2561.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang S, Li J, Xie J, Liu F, Duan Y, Wu Y,
Huang S, He X, Wang Z and Wu X: Programmed death ligand 1 promotes
lymph node metastasis and glucose metabolism in cervical cancer by
activating integrin β4/SNAI1/SIRT3 signaling pathway. Oncogene.
37:4164–4180. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cao D, Qi Z, Pang Y, Li H, Xie H, Wu J,
Huang Y, Zhu Y, Shen Y, Zhu Y, et al: Retinoic acid-related orphan
receptor C regulates proliferation, glycolysis, and chemoresistance
via the PD-L1/ITGB6/STAT3 signaling axis in bladder cancer. Cancer
Res. 79:2604–2618. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ma P, Xing M, Han L, Gan S, Ma J, Wu F,
Huang Y, Chen Y, Tian W, An C, et al: High PDL1 expression drives
glycolysis via an Akt/mTOR/HIF1α axis in acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncol Rep. 43:999–1009. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Feng J, Yang H, Zhang Y, Wei H, Zhu Z, Zhu
B, Yang M, Cao W, Wang L and Wu Z: Tumor cell-derived lactate
induces TAZ-dependent upregulation of PD-L1 through GPR81 in human
lung cancer cells. Oncogene. 36:5829–5839. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Cui Y, Li X, Du B, Diao Y and Li Y: PD-L1
in lung adenocarcinoma: Insights into the role of (18)F-FDG PET/CT.
Cancer Manag Res. 12:6385–6395. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Tu X, Qin B, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Kahila M,
Nowsheen S, Yin P, Yuan J, Pei H, Li H, et al: PD-L1 (B7-H1)
Competes with the RNA exosome to regulate the DNA damage response
and can be targeted to sensitize to radiation or chemotherapy. Mol
Cell. 74:1215–1226.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Du W, Zhu J, Zeng Y, Liu T, Zhang Y, Cai
T, Fu Y, Zhang W, Zhang R, Liu Z and Huang JA: KPNB1-mediated
nuclear translocation of PD-L1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer
cell proliferation via the Gas6/MERTK signaling pathway. Cell Death
Differ. 28:1284–1300. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen L, Deng H, Lu M, Xu B, Wang Q, Jiang
J and Wu C: B7-H1 expression associates with tumor invasion and
predicts patient's survival in human esophageal cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:6015–6023. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Satelli A, Batth IS, Brownlee Z, Rojas C,
Meng QH, Kopetz S and Li S: Potential role of nuclear PD-L1
expression in cell-surface vimentin positive circulating tumor
cells as a prognostic marker in cancer patients. Sci Rep.
6:289102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hou J, Zhao R, Xia W, Chang CW, You Y, Hsu
JM, Nie L, Chen Y, Wang YC, Liu C, et al: PD-L1-mediated gasdermin
C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and
facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 22:1264–1275. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Gao Y, Nihira NT, Bu X, Chu C, Zhang J,
Kolodziejczyk A, Fan Y, Chan NT, Ma L, Liu J, et al:
Acetylation-dependent regulation of PD-L1 nuclear translocation
dictates the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat Cell Biol.
22:1064–1075. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Bouillez A, Rajabi H, Jin C, Samur M,
Tagde A, Alam M, Hiraki M, Maeda T, Hu X, Adeegbe D, et al: MUC1-C
integrates PD-L1 induction with repression of immune effectors in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 36:4037–4046. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|