Introduction
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death
worldwide, and the steady year-on-year increase in cancer incidence
and mortality cannot be ignored. According to data released by the
World Health Organization in 2019, malignant tumors are the first
or second leading cause of death in 112 of 183 countries (1). In 2022, there were 4.82 million new
cancer cases in China and 2.37 million new cancer cases in the
United States, and 3.21 million and 640,000 cancer deaths (2). Despite continuous progress in
radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgery (3), due to the lack of effective diagnostic
markers and detection methods in the early stage, a number of
patients receive a late diagnosis, and thus have a poor prognosis
and a low 5-year survival rate (4).
Therefore, it is important to formulate a cancer treatment
strategy, to understand the occurrence and development of cancer,
and to identify markers of early diagnosis and treatment.
Cancer is related to endogenous factors, such as
gene mutations, epigenetic damage, chromosomal deletions and
abnormal amplification, as well as exogenous factors, such as
living habits and environmental pollution (5,6). It
has previously been reported that oncogene activation leads to
abnormal tumor cell proliferation (7). In addition, recent studies reported
that non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are expressed in a variety of
malignant tumors. and affect the occurrence, development and
sensitivity of malignant tumors to molecular targeted therapy
(2,4). ncRNAs are an emerging class of
genomically encoded transcripts (5,8). In
recent years, with the innovation of sequencing technologies,
several ncRNAs have been detected in eukaryotic genomes, and are
estimated to account for >80% of the genome (8,9).
Approximately 50,000 ncRNAs have been identified in the last 10
years; however, most of them have not been reported on in depth
(10). ncRNAs include microRNAs
(miRNAs/miRs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), small interfering
RNAs and circular RNAs (circRNAs) (9). Currently, miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs
are research hotspots in the field of biomedical science, as they
mediate a variety of cellular processes, including chromatin
remodeling, gene transcription, epigenetic regulation,
post-transcriptional modification, cell cycle regulation, cell
differentiation and signal transduction (8,11,12).
In terms of epigenetic changes, dysregulation of circRNAs, lncRNAs
and miRNAs has been shown to affect the development and progression
of cervical and thyroid cancer (13,14).
In addition, ncRNAs can act as oncogenic molecules and tumor
suppressors in cancer, including thyroid cancer (15,16),
prostate cancer (PCa) (17),
melanoma (18) and osteosarcoma
(19), by interacting with coding
proteins. Notably, lncRNAs and circRNAs can regulate cancer
development by acting as miRNA sponges involved in the
transcription of proteins. In the present review, PubMed
(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) and
Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com) were used to search the
keywords ‘miR-10a’, ‘miR-10b’, ‘cancer’ or ‘tumor’ and ‘circRNA’ or
‘lncRNA’. The present review aimed to describe the specific
regulatory mechanisms of lncRNA and circRNA in cancer through the
miR-10 family.
ncRNAs
lncRNAs
lncRNAs are long non-coding transcription factors
that are >200 nucleotides in length (20). lncRNAs do not encode proteins due to
the lack of an open reading frame (ORF); however, they can serve as
important regulatory RNAs (21).
The vast majority of lncRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II,
form 5′ cap structures and undergo polyadenylation at the 3′ region
(21,22). They are classified into the
following four groups based on their relative position to the
protein-coding genes: i) intergenic lncRNAs; ii) intronic lncRNAs;
iii) overlapping lncRNAs; and iv) antisense lncRNAs (23). Most of these lncRNAs can interact
with RNA or DNA molecules through base pairing, forming functional
networks that consist of DNA, protein and RNA, and that are
involved in the inheritance and transcription of genes (20,21,23).
Furthermore, there is growing evidence that lncRNAs act as
oncogenic factors in malignant tumors, inhibiting or promoting cell
proliferation, apoptosis, metastatic differentiation and cell
invasion in cancer cells (14–18),
as well as regulating the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells
(22).
circRNAs
circRNAs are a specific class of RNA widely found in
mammalian cells that were initially hypothesized to be a ‘junk’
byproduct of RNA transcription, and thus did not receive much
attention from researchers (24).
circRNAs are linear precursor mRNAs reverse spliced in the nucleus
to form closed RNA loops without 5′-3′ polar or polyadenine tails,
and range in length from 100s to 1,000s of bases (25,26).
Due to their specific structure, circRNAs are protected from
degradation by nucleic acid exonucleases, and have a longer
half-life and stability than their parental mRNAs (27). Based on this conserved property,
circRNAs may serve as promising biomarkers for the identification
of malignancies (28). Unlike
lncRNAs, circRNAs have an ORF in their sequence, thus circRNAs can
be translated into proteins via internal ribosome entry site-driven
or N6-adenylation-mediated initiation sites (29). In addition, circRNAs can bind to
mRNAs to act as miRNA sponges or interact with RNA-binding proteins
to directly regulate transcription (30).
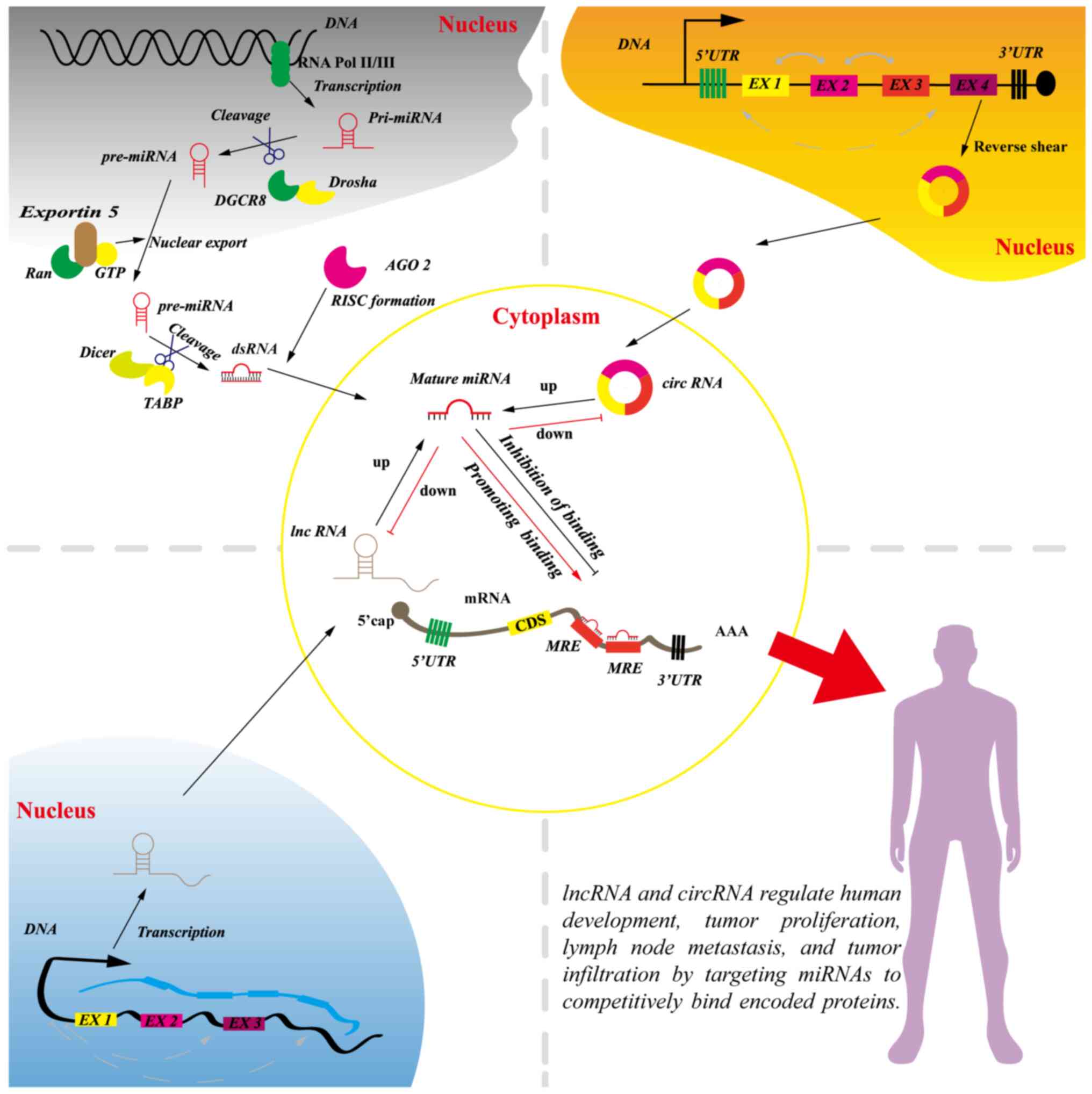
miRNAs
miRNAs are small, single-stranded, conserved ncRNAs
that are 18–25 nucleotides in length (31). miRNAs are transcribed into early
miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) in cells, and pri-miRNAs are cleaved into
precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) in the nucleus, transported out of
the nucleus, and then cleaved into small mature double-stranded
RNAs in the cytoplasm, eventually forming the RNA-induced silencing
complex (32–34). The majority of miRNAs direct mRNA
inhibition or activation through degradation or translational
repression. Thus, miRNAs can act as oncogenic factors or tumor
suppressors (Fig. 1) (33,35).
miRNAs regulate the expression of >1/3 of the encoded proteins
in vivo, and are closely associated with cell proliferation,
apoptosis and differentiation (33,35,36).
In addition, miRNAs are involved in soft tissue construction,
embryonic and organ development, and malignant transformation of
disease in humans (36), with
miR-10a and miR-10b being the most widely studied. For example,
Yang et al (37) found that
miR-10a and miR-10b can act as oncogenic factors in gastric cancer,
and are also novel genetic markers for the diagnosis and treatment
of gastric cancer.
Association between lncRNAs/circRNAs
and miRNAs
The classical biological theory of miRNAs is that
they bind to target 3′-UTRs in their target mRNAs by complementary
base-pairing as negative regulators (38). miRNA response elements (MREs) are
present in the majority of lncRNAs and circRNAs; MREs can compete
with mRNAs to bind miRNAs to promote tumor malignancy, lymph node
metastasis, tumor proliferation and tumor metastasis (Fig. 1) (39–41).
This theory was developed in 2011 by Salmena et al (42) and is now supported by a large body
of experimental data (43–48). Furthermore, this mode of regulation
underlies the theory that networks of endogenous RNA molecules
compete with each other.
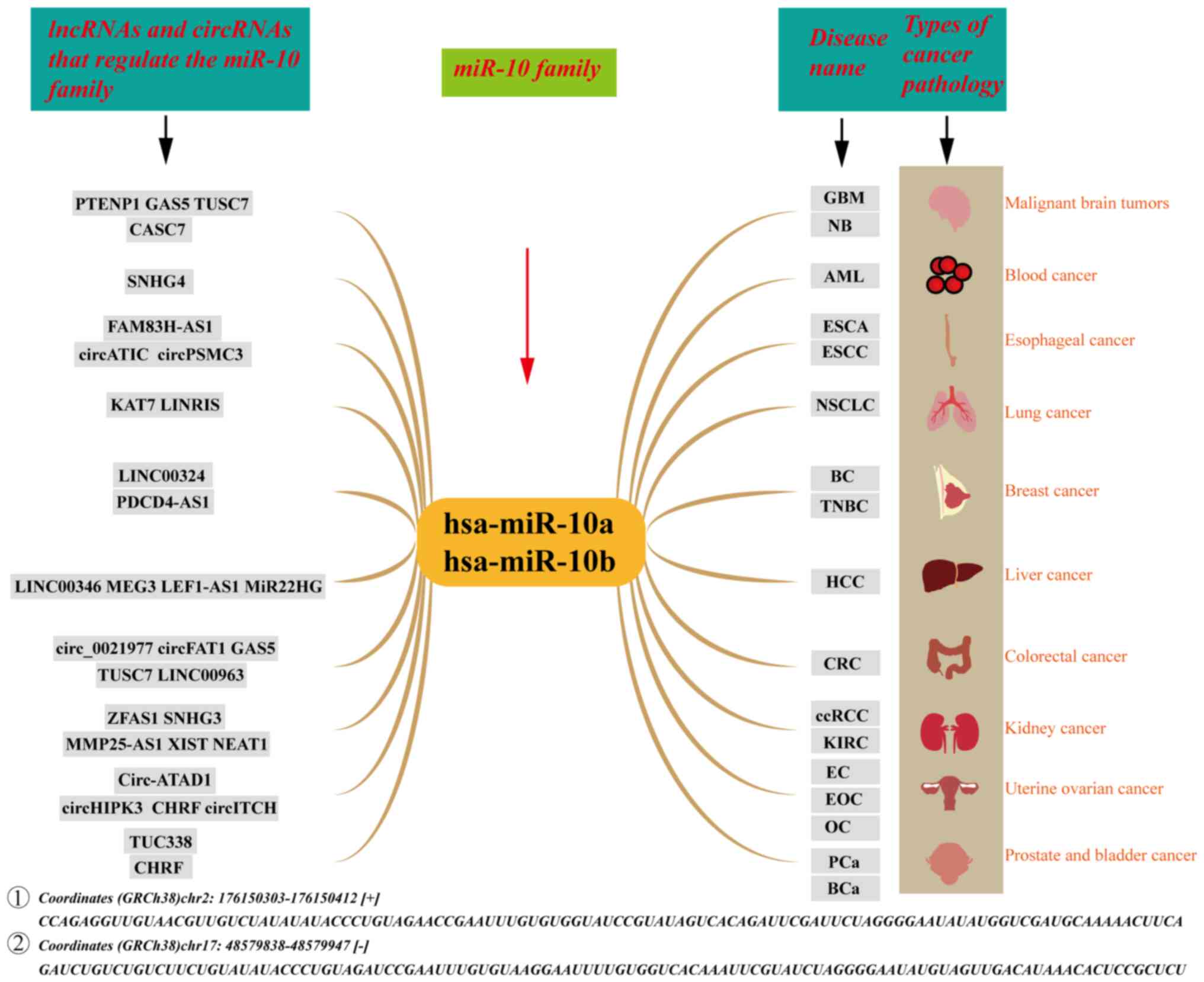
miR-10 family
The miR-10 gene family is involved in the regulation
of a number of malignant diseases (49). The miR-10 family has two primary
members: miR-10a and miR-10b. miR-10a is located on human
chromosome 17 and miR-10b is located on human chromosome 2. The
nucleotide sequences of the two miRNAs are highly consistent,
indicating that their biological functions may be similar (50). Members of the miR-10 family are
involved in tumor proliferation (51), lymph node metastasis (52), direct tumor invasion (53), tumor cell apoptosis (25) and other malignant behaviors in
cancer. In addition, the miR-10 family can serve as early
diagnostic and prognostic markers for bladder cancer (BCa)
(37), PCa (17), acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
(54) and intraductal papillary
mucinous neoplasm (55). The
lncRNAs and circRNAs that target the miR-10 family in cancer are
shown in Fig. 2. miR-10
family-related lncRNAs and circRNAs are involved in numerous cancer
processes including epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), the
tumor immune response, drug resistance and sensitivity to
radiotherapy (Table I). It can be
hypothesized that the miR-10 family-associated lncRNAs and circRNAs
may be novel molecular targets for the diagnosis, prognosis and
treatment of oncological diseases.
 | Table I.Functions of lncRNAs/circRNAs
targeting the miR-10 family in cancer. |
Table I.
Functions of lncRNAs/circRNAs
targeting the miR-10 family in cancer.
| A, miR-10a |
|---|
|
|---|
| First author,
year | Upstream
lncRNA/circRNA | Downstream
mRNA | Tumor type | Function | Mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Liu, 2021 | circFAT1 | - | CRC | Proliferation
Invasion, Migration | Overexpression of
circFAT1 or knockdown of miR-10a inhibited cell proliferation,
migration and invasion | (112) |
| Ren et al,
2017 | TUSC7 | - | CRC | Proliferation,
Invasion | Overexpression of
lncRNA TUSC7 inhibited cell proliferation and invasion of CRC
cells, and overexpression of miR-10a reversed this effect | (73) |
| Zhu et al,
2022 | LINRIS | - | NSCLC | Proliferation | Silencing of lncRNA
LINRIS significantly inhibited cell viability | (58) |
| Zhou et al,
2020 | CASC7 | PTEN | NB | Proliferation | Abnormal increase
in lncRNA CASC7 led to decreased cell proliferation via the
miR-10a/PTEN axis | (99) |
| Yuan et al,
2020 | SNHG4 | PTEN | AML | Proliferation | lncRNA SNHG4 and
miR-10a competitively bound to PTEN, inhibiting cell viability | (106) |
| Gao et al,
2021 | KAT7 | - | NSCLC | Proliferation | Overexpression of
lncRNA KAT7 inhibited the effect of miR-10a on proliferation of
NSCLC | (59) |
| Shang et al,
2018 | TUSC7 | - | GBM | Drug
resistance | lncRNA TUSC7
overexpression in GBM cells inhibited TMZ resistance | (104) |
| Yang et al,
2021 | Circ-ATAD1 | - | EC | Invasion,
Migration | Circ-ATAD1
attenuated miR-10a methylation to inhibit EC cell invasion and
migration | (117) |
| Luo et al,
2018 | circ-ITCH | - | EOC | Proliferation,
Apoptosis | Transfection of
circ-ITCH inhibited SKOV3 cell proliferation and enhanced
apoptosis | (113) |
| Dong et al,
2019 | ZFAS1 | SKA1 | ccRCC | Proliferation,
Migration | Knockdown of lncRNA
ZFAS1 or mRNA SKA1 effectively attenuated the ability of ccRCC
cells to proliferate, migrate and invade | (78) |
|
| B,
miR-10a-5p |
|
| First author,
year | Upstream
lncRNA/circRNA | Downstream
mRNA | Tumor
type |
Function |
Mechanism | (Refs.) |
|
| Wu et al,
2019 | miR-22HG | NCOR2 | HCC | Proliferation
Migration, Invasion | lncRNA MIR22HG
regulated the proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC cells by
competitively binding to the coding protein NCOR2 and
miR-10a-5p | (68) |
| Hao et al,
2019 | PTENP1 | PTEN | GBM | Proliferation
Apoptosis | Co-culture of
hUC-MSC-derived exosome lncRNA PTENP1 and U87 inhibited the
proliferation of U87 cells and promoted cell apoptosis | (102) |
| Zhang et al,
2019 | MEG3 | PTEN | HCC | Proliferation
Apoptosis Migration Invasion | Overexpression of
lncRNA MEG3 inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of
HCC cells, and promoted apoptosis | (67) |
| Feng et al,
2020 | FAM83H-AS1 | CCDC88A | ESCC | EMT | Downregulation of
lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 promoted TGF-β-induced EMT activation in
esophageal cancer | (63) |
| Liu et al,
2022 | NEAT1 | SERPINE1 | KIRC | Tumor immunity
Proliferation Migration | lncRNA NEAT1
promoted cell proliferation and migration by activating SERPINE1
through miR-10a-5p. SERPINE1 expression was positively correlated
with immune infiltration | (82) |
| Teng et al,
2019 | circHIPK3 | - | EOC | Proliferation,
Migration, Invasion | Knockdown of
circHIPK3 promoted cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and
inhibited cell apoptosis | (114) |
| Tan et al,
2021 | MMP-25-AS1 | SERPINE1 | KIRC | Tumor immunity | The lncRNA
MMP25-AS1/hsa-miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1 axis was involved in tumor
immunity | (83) |
| Liu et al,
2021 | XIST | SERPINE1 | KIRC | Tumor immunity | lncRNA XIST
regulated SERPINE1 targeting of miR-10a-5p and regulated the levels
of immune-related cells | (81) |
| Li et al,
2019 | LINC00346 | CDK1 | HCC | - | The
LINC00346-miR-10a-5p-CDK1/CCNE1 axis may be associated with the
relapse-free survival time of HCC | (66) |
| Gao et al,
2021 | LEF1-AS1 | MSI1 | HCC | Proliferation,
Apoptosis Drug resistance | Knockout of lncRNA
LEF1-AS1 inhibited proliferation of cisplatin-resistant cells,
promoted apoptosis and increased sensitivity | (69) |
| Zhu et al,
2021 | circPSMC3 | PTEN | ESCA | Proliferation
Apoptosis | Overexpression of
circPSMC3 or knockdown of miR-10a-5p reduced the cell survival rate
of GR cells and induced cell apoptosis | (70) |
|
| C,
miR-10b |
|
| First author,
year | Upstream
lncRNA/circRNA | Downstream
mRNA | Tumor
type |
Function |
Mechanism | (Refs.) |
|
| Liu et al,
2019 | CHRF | GSK3β | PCa | Proliferation
EMT | lncRNA CHRF
promoted GSK3β through miR-10b. lncRNA CHRF overexpression enhanced
TGF-β1-induced EMT in PC3 cells | (95) |
| Yang et al,
2022 | GAS5 | - | CRC | Proliferation
Migration | lncRNA GAS5
overexpression inhibited tumor growth rate and tumor weight in
mice | (74) |
| Wu et al,
2021 | LINC00963 | FGF13 | CRC | Migration Invasion
EMT | LINC00963 can act
as a sponge of miR-10b to inhibit the activation of FGFR13 Knockout
of LINC00963 inhibited the EMT process | (75) |
| Ding et al,
2020 | GAS5 | Sirt1 | GBM | Proliferation
Apoptosis Migration Invasion | lncRNA GAS5 acted
synergistically with miR-10b to downregulate Sirt1 expression,
inhibit cell growth, migration and invasion, and promote
apoptosis | (103) |
| Li et al,
2019 | TUC338 | - | BCa | Migration
Invasion | Overexpression of
lncRNA TUC338 significantly promoted cell invasion and
migration | (97) |
| Tan et al,
2020 | CHRF | STAT3 | OC | Proliferation | Downregulation of
lncRNA CHRF significantly reduced the growth of transplanted tumors
in mice | (92) |
|
| D,
miR-10b-3p |
|
| First author,
year | Upstream
lncRNA/circRNA | Downstream
mRNA | Tumor
type |
Function |
Mechanism | (Refs.) |
|
| Zhang et al,
2022 | circATIC | RHCG | ESCA | Proliferation
Migration Invasion | Overexpression of
circATIC or RHCG inhibited the proliferation, migration and
invasion of ESCA cells | (110) |
|
| E,
miR-10b-5p |
|
| First author,
year | Upstream
lncRNA/circRNA | Downstream
mRNA | Tumor
type |
Function |
Mechanism | (Refs.) |
|
| Xu et al,
2021 | SNHG3 | BIRC5 | ccRCC | Proliferation
Migration Invasion | lncRNA SNHG3
activated the expression of BIRC5 by binding to miR-10b-5p, and
promoted the proliferation, invasion and migration of ccRCC
cells | (79) |
| Wang et al,
2020 | LINC00324 | E-cadherin | BC | Proliferation
Migration Apoptosis EMT | LINC00324 inhibited
EMT markers through miR-10b-5p, inhibited cell viability and
migration, and promoted apoptosis | (89) |
| Lu et al,
2020 | circ_0021977 | P21/P53 | CRC | Proliferation
Migration Invasion | circ_0021977
competitively bound to miR-10b-5p to regulate p21 and p53, and
inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC
cells | (111) |
| Wang et al,
2021 | PDCD4-AS1 | IQGAP2 | TNBC | Proliferation
Migration Invasion | Overexpression of
lncRNA PDCD4-AS1 decreased cell proliferation, migration and
invasion of breast cancer cells, and increased the cell apoptotic
rate | (90) |
lncRNAs and cancer
Lung cancer
The global mortality rate from lung cancer has
remained high in recent years, with 2.2 million new cases worldwide
in 2020, of which, ~1.79 million are predicted to die from the
cancer (56). Early screening and
surgery for lung cancer greatly improve post-operative cure and
survival rates for patients (56,57).
In addition, it has been shown that lncRNAs can act as ceRNAs
targeting the miR-10 family members involved in lung cancer. For
example, Zhu et al (58)
detected high expression of the lncRNA LINRIS in non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) samples and cell lines, and patients with high
LINRIS expression had significantly lower 5-year survival rates.
Silencing lncRNA LINRIS significantly inhibited the viability of
NSCLC cells, whereas overexpression of miR-10a reversed this
phenomenon. Another study (59)
found that lncRNA KAT7 expression was decreased in NSCLC tissues
and tumor cells. The low expression of lncRNA KAT7 was associated
with the survival of patients. Functionally, lncRNA KAT7 promoted
the methylation of miR-10a. Furthermore, in vitro
experiments showed that overexpression of miR-10a increased the
proliferation of NSCLC cells. Conversely, overexpression of lncRNA
KAT7 inhibited the effect of miR-10a on NSCLC proliferation
(59). These findings suggested
that lncRNAs targeting the miR-10 family may act as key genes in
the progression of NSCLC.
Esophageal cancer (ESCA)
It is estimated that 17,650 individuals were
diagnosed with ESCA in the United States in 2019, and ~16,080 of
them died from the disease (60).
Although early screening and prevention efforts have helped to
improve the survival of patients with ESCA, the 5-year overall
survival (OS) rate of patients with advanced ESCA remains <20%
(60,61). The high mortality and low survival
rates of ESCA are currently a major challenge for clinical
practitioners and exploring novel biomarkers for prognostic
analysis is an important topic in ESCA research (62). Feng et al (63) detected a trend toward decreased
expression of the lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 in ESCC tissues and cells.
lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 was negatively associated with TNM stage, lymph
node metastasis and pathological stage. Mechanistically, lncRNA
FAM83H-AS1 acted as a sponge for miR-10a-5p to activateCCDC88A.
Functionally, the knockdown of lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 significantly
inhibited the ability of Kyse150 and TE1 ESCA cells to proliferate,
migrate and invade. By contrast, miR-10a-5p inhibitors partially
rescued the inhibitory effects of lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 knockdown on
cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Downregulated lncRNA
FAM83H-AS1 promoted E-cadherin expression in tumor growth
factor-β-induced Eca109 ESCA cells, and inhibited N-cadherin,
vimentin, Snail and Twist1 expression at the transcriptional level,
whereas overexpression of lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 had the opposite effect
(63). These results suggested that
lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 can mediate EMT, and serve as a novel diagnostic
marker and therapeutic target for ESCA.
Liver cancer
Liver cancer continues to be a significant burden
worldwide, with incidence rates increasing globally. It is
estimated that one million individuals will develop liver cancer in
2025 (64). Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) accounts for 90% of all primary liver cancer cases
(65). Patients with HCC often do
not show early signs of clinical presentation, as such, patients
are often diagnosed in the first instance with advanced-stage liver
cancer, and thus have a greater risk of tumor recurrence and
metastasis (64,66). lncRNA MEG3 expression has been
revealed to be downregulated in HCC tissues and cells, whereas
miR-10a-5p levels were shown to be upregulated. Overexpression of
lncRNA MEG3 directly inhibited Hep2 HCC cell proliferation,
migration and invasion, and increased cell cycle progression and
apoptosis of Hep2 cells through inhibition of miR-10a-5p,
activating PTEN via the AKT signaling pathway. In addition, it has
been shown that PTEN is a miR-10a-5p target gene (67). Low expression of lncRNA miR-22HG was
detected in HCC tissues and cells. lncRNA miR-22HG regulates the
proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC cells by competitively
binding to the protein NCOR2 and miR-10a-5p. In addition, lncRNA
miR-22HG was significantly associated with patient OS and
disease-free survival (68). Gao
et al (69) detected
abnormally elevated expression levels of lncRNA LEF1-AS1 in HCC
clinical samples and HCC cancer cell lines. Mechanistically,
overexpressed lncRNA LEF1-AS1 regulated activation of the AKT
signaling pathway by MSI1 through miR-10a-5p. Functionally,
knockdown of lncRNA LEF1-AS1 and MSI1 or overexpression of
miR-10a-5p inhibited the proliferation of cisplatin (DDP)-resistant
Huh7 HCC cells, promoted apoptosis and enhanced chemosensitivity of
Huh7 cells to DDP (69). This may
provide a novel direction for research on HCC drug resistance. In
addition, to screen for lncRNAs that can serve as early markers of
HCC, Li et al (66)
constructed a ceRNA regulatory network using bioinformatics tools.
Bioinformatics analysis identified the
LINC00346/miR-10a-5p/CDK1/CCNE1 axis as having a possible
association with HCC. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that CDK1 and
CCNE1 were associated with relapse-free survival time in HCC. Thus,
lncRNAs targeting the miR-10 family may have significant potential
as diagnostic/prognostic markers and therapeutic targets for the
management of HCC.
Colorectal cancer (CRC)
CRC is a global health problem, accounting for 10%
of all cancer diagnoses and deaths each year (70). The number of CRC cases worldwide is
expected to increase to 2.5 million by 2035 (71). Early tumor screening has reduced the
morbidity and postoperative mortality rates of patients with CRC,
but ~25% of patients with CRC are diagnosed with advanced-stage
cancer in the first instance, and 25–50% of patients develop early
metastases (72). A commitment to
the development of diagnostic and prognostic markers for CRC is
essential. Ren et al (73)
found that lncRNA TUSC7 expression was suppressed in CRC cells and
clinical cancer samples, and that low expression of lncRNA TUSC7
was associated with patient OS. In addition, lncRNA TUSC7
expression was lower in specimens classified as stage C/D than in
those classified as stage A/B according to the Duke's
classification system for colon cancer. Functionally,
overexpression of lncRNA TUSC7 inhibited cell proliferation and
invasion of SW480 and HT29 CRC cells, whereas overexpression of
miR-10a reversed the effects of overexpression of lncRNA TUSC7 on
CRC cells. In another study, significant downregulation of lncRNA
GAS5 was detected in CRC samples and cells. Mechanistically,
overexpression of lncRNA GAS5 inhibited the migration and
proliferation of CRC cells through direct interaction with miR-10b.
Animal model experiments showed that overexpression of lncRNA GAS5
resulted in significantly lower tumor-forming growth rates and
tumor weights in vivo, in contrast to miR-10b
overexpression, which restored tumor growth rates and increased
tumor weight (74). Wu et al
(75) found that LINC00963
expression was upregulated in CRC samples and CRC cells, and that
it could inhibit CRC cell viability, colony formation, migration
and invasion through a LINC00963/miR-10b/FGF13 axis. Knockdown of
LINC00963 resulted in the downregulation of waveform protein and
N-cadherin expression levels, and increased expression of
E-cadherin. These findings suggested that LINC00963 may be involved
in EMT in colon cancer (75). Thus,
miR-10 family-related lncRNAs may serve as key factors in the
progression of CRC.
Kidney cancer
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common and
deadly urological malignancy, accounting for 2.2% of all diagnosed
cancers worldwide, of which 70–80% are clear cell RCC (ccRCC)
(76,77). A study of ccRCC found that lncRNA
ZFAS1 expression was upregulated in ccRCC samples and cell lines,
and was strongly associated with tumor size, lymph node metastasis
and patient OS. Knockdown of lncRNA ZFAS1 or mRNA SKA1 has been
shown to effectively attenuate the ability of ACHN and Caki-1 ccRCC
cells to proliferate, migrate and invade, whereas transfection with
miR-10a inhibitors attenuated the effect of knockdown of lncRNA
ZFAS1 or SKA1 on ccRCC cells (78).
Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis showed that lncRNA SNHG3 was
associated with a poorer prognosis in patients with ccRCC. lncRNA
SNHG3 promoted the proliferation, invasion and migration of ccRCC
cells by activating BIRC5 expression through binding to miR-10b-5p
(79). In addition, it has been
shown that lncRNAs are involved in the immune process of the tumor
microenvironment (TME) (80). For
example, Liu et al (81)
showed that a lncRNA XIST/miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1 axis mediated the TME
of ccRCC. Immune cell infiltration analysis revealed that the
lncRNA XIST can regulate the levels of CD4+ T cells,
CD8+ T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils
and other immune-related cells through the regulation of miR-10a-5p
targeting SERPINE1 expression (81). Another study showed that lncRNA
NEAT1 similarly promoted the proliferation and migration of 786-O
and ACHN kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) cells by acting
as a sponge of miR-10a-5p, thus indirectly activating SERPINE1. The
area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic
curve analysis indicated that SERPINE1 (AUC=0.789) and miR-10a-5p
(AUC=0.892) had good prognostic performance. Furthermore, SERPINE1
expression was positively associated with the levels of immune
infiltration of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells,
macrophages, dendritic cells and neutrophils (82). In another study, a ceRNA regulatory
network consisting of the lncRNA MMP25-AS1/hsa-miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1
axis was identified. lncRNA MMP25-AS1 expression was significantly
associated with sex, pathological stage, T-stage and M-stage.
Immune infiltration analysis showed that the lncRNA
MMP25-AS1/hsa-miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1 axis could affect the chemokines
CCL4, CCL5, CXCL13 and XCL2. High SERPINE1 expression was also
shown to be associated with tumor immune evasion in KIRC (83). Thus, the miR-10 family may be a core
miRNA in the immune-related processes of kidney cancer, and the
associated lncRNAs may serve as biomarkers/prognostic factors in
kidney cancer, and could also participate in the regulation of the
TME.
Breast cancer (BC)
BC is one of the most common malignancies among
women worldwide (84). More than
268,000 cases are expected to be diagnosed each year in the United
States, accounting for approximately one-third of all new cancer
cases in women and 15% of all cancer-related deaths (85). Despite the progress made in the
study of BC, it remains a major global health problem (86). Under normal conditions, EMT plays a
key role in embryonic development, wound repair and tissue
remodeling; however, aberrant EMT leads to lymph node metastasis
and infiltration of cancerous tissue in BC (87,88).
Low expression of LINC00324 in BC cells has been reported to be
associated with a poorer patient prognosis and reduced OS.
Functionally, LINC00324 inhibited cell viability, suppressed cell
migration and promoted apoptosis in MCF-7 BC cells by directly
interacting with miR-10b-5p through inhibition of the EMT marker
E-cadherin. In addition, animal models have shown that LINC00324
overexpression limits the size of xenograft tumors (89). lncRNA PDCD4-AS1 expression was shown
to be lower in clinical triple-negative BC (TNBC) samples and
cells. Overexpression of the lncRNA PDCD4-AS1 attenuated the
proliferation, migration and invasion of TNBC cells, and increased
apoptosis. Coincidentally, IQGAP2 overexpression had the same
effect as overexpression of lncRNA PDCD4-AS1, whereas miR-10b-5p
downregulation reversed this result (90). These results suggested that miR-10
family-related lncRNAs may regulate cancer metastasis in BC by
participating in the EMT process, and could also serve as novel
therapeutic targets or diagnostic markers for BC.
Ovarian cancer (OC)
OC accounts for 4% of new cancer cases and 5% of
cancer deaths in women in the United States (91). DDP is the chemotherapy of choice for
OC, and the primary reason for the ineffectiveness of chemotherapy
is the development of resistance of tumor cells to DDP (91,92).
lncRNA CHRF was found to be upregulated in DDP-resistant ES2 cells
and in OC samples. In addition, lncRNA CHRF expression was
significantly higher in patients with OC and liver metastases
compared with samples from OC patients without liver metastases.
Mechanistically, lncRNA CHRF regulated miR-10b and significantly
increased the resistance of DDP-resistant cells to DDP via the EMT
and STAT3 signaling pathways. Functionally, xenograft experiments
showed that inoculation of DDP-resistant cells with lower levels of
lncRNA CHRF expression resulted in a significant reduction in
transplanted tumor growth in mice in vivo, an effect that
could be attenuated by ectopic expression of miR-10b in xenograft
tumors (92). These findings
suggested that lncRNA CHRF and miR-10b may be molecular targets for
reducing DDP resistance in OC.
PCa
PCa is the second most common type of cancer
affecting men worldwide and the sixth leading cause of
cancer-associated death in men (93). PCa is a heterogeneous disease that
progresses slowly in the early stages of development, but is highly
aggressive in the later stages (94). Therefore, it is particularly
important to explore its pathogenesis. Studies have found that
lncRNA CHRF participates in the proliferation of PCa cells by
promoting activation of the GSK3β/AKT and NF-κB signaling cascades
through miR-10b. In addition, overexpression of lncRNA CHRF can
enhance TGF-β1-induced changes in the expression of EMT-related
proteins in PC3 cells, whereas miR-10b overexpression reversed
these changes (95). These findings
suggested that CHRF targeting of miR-10b may affect tumor
progression by regulating EMT in PCa.
BCa
Approximately 440,000 new cases of BCa are diagnosed
each year, resulting in >130,000 deaths worldwide. The primary
reasons for the low survival rates in patients with early and
advanced BCa following surgery are the lack of early specific
diagnostic markers and the limited availability of treatments for
late-stage BCa (96). It has been
shown that lncRNAs can be used to distinguish between patients with
early-stage BCa malignancy and healthy patients. For example, Li
et al (97) found that
lncRNA TUC338 was abnormally elevated in the plasma of patients
with early-stage BCa. Plasma lncRNA TUC338 levels were
significantly downregulated after surgical resection, with an AUC
value of 0.9239, indicating that lncRNA TUC338 was specific and
sensitive for the diagnosis of BCa. Functional overexpression of
lncRNA TUC338 and miR-10b have both been shown to significantly
promote cell invasion and cell migration in HT-1197 and HT-1376 BCa
cells. Thus, TUC338 targeting of miR-10b may be a novel molecular
diagnostic marker for the detection of early-stage BCa.
Neuroblastoma (NB)
NB is an embryonic malignant extracranial solid
tumor that is relatively common in children and often has a poor
prognosis (98). lncRNAs targeting
miR-10a are involved in the progression of NB. For example, Zhou
et al (99) detected
abnormally reduced levels of lncRNA CASC7 epitopes by fluorescent
quantitative (q)PCR in NB tissues and cells. lncRNA CASC7 resulted
in reduced proliferation of NB cells, whereas overexpression of
miR-10a activated PTEN to promote NB cell proliferation.
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)
GBM is the most common primary malignant glioma,
accounting for 48% of all malignant central nervous malignancies
worldwide (100). Molecularly
targeted therapy, radiotherapy, primary resection and postoperative
supportive care can be used to treat GBM to some extent, but the
postoperative and prognostic outcomes for patients remain limited
(100,101). Therefore, there is an urgent need
to investigate the pathogenesis of GBM and to explore potential
therapeutic targets. In GBM, Hao et al (102) showed that lncRNA PTENP1 was
reduced in tumor samples and miR-10a-5p expression was
significantly increased. The expression of lncRNA PTENP1 was
increased in U87 cells treated with human umbilical
cord-mesenchymal stem cell (hUC-MSC)-derived exosomes. In addition,
hUC-MSC-derived exosomes and U87 co-culture inhibited the
proliferation of U87 cells and promoted cell apoptosis.
Overexpression of lncRNA PTENP1 or inhibition of miR-10a-p reduced
cell proliferation and promoted cell death in U87 cells not treated
with hUC-MSCs. Luciferase experiments showed that when U87 cells
were co-transfected with miR-10a-5p mimics and lncRNA PTENP1-WT or
PTEN-WT plasmids, the luciferase activity was decreased. Thus, a
lncRNA PTENP1/miR-10a-5p/PTEN axis may have potential clinical
application in the management of glioma. Ding et al
(103) found that overexpression
or knockdown of lncRNA GAS5 in glioma cells altered the
proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells.
It was suggested that lncRNA GAS5 acts synergistically with miR-10b
to downregulate Sirt1 expression, inhibit PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK
signaling pathways, and to suppress the proliferation, migration
and invasion, and promote the apoptosis of U251 and A172 GBM cells.
In addition, it has been shown that miR-10a-related lncRNAs can
increase chemosensitivity in GBM. For example, low expression
levels of lncRNA TUSC7 were detected in GBM cells and temozolomide
(TMZ)-resistant tissues. Furthermore, expression of lncRNA TUSC7
was lower in samples from TMZ-insensitive patients compared with
that in TMZ-sensitive patients. Notably, overexpression of lncRNA
TUSC7 suppressed TMZ resistance and expression of multidrug
resistance protein 1 (MDR1) in U87TR GBM cells (104). Conversely, overexpression of
miR-10a increased the expression of MDR1, increased the
half-inhibitory concentration of TMZ and inhibited TMZ-induced
cytotoxicity in U87TR cells (104). These data suggested that lncRNA
TUSC7 may inhibit the chemosensitivity of U87TR cells to TMZ by
targeting MDR1 through interaction with miR-10a (104).
AML
AML is a malignant cancer of the blood and bone
marrow. Its incidence increases with age, and the 5-year OS rate in
younger patients with de novo AML is 40–50% worldwide
(105,106). Yuan and Wang (106) found reduced levels of lncRNA SNHG4
expression in The Cancer Genome Atlas AML dataset and AML tissues.
Overexpression of lncRNA SNHG4 partially abolished the enhancing
effect of upregulated miR-10a on AML cell proliferation, the same
way overexpression of PTEN similarly attenuated the effect of
miR-10a on the proliferation rate of AML cells (106). Taken together, lncRNA SNHG4 may
serve as an oncogenic factor in AML.
circRNAs and tumors
Previous studies have demonstrated the role and
regulatory mechanisms of miR-10 family-related lncRNAs in numerous
types of cancer. These studies suggested that miR-10-related
lncRNAs may be used as early and specific diagnostic and prognostic
markers for cancer. In addition, they can be used as novel
therapeutic targets for the management of cancer and for modulation
of sensitivity to chemotherapy. Notably, in addition to
miR-10-related lncRNAs, miR-10-related circRNAs are also important
in cancer development and progression.
ESCA
Gefitinib (GR) is the most common and effective
chemotherapeutic agent for the management of ESCA (107). It is estimated that 60–80% of
patients with advanced ESCA have elevated EGFR expression levels in
the cancerous tissue (107–109),
and GR can inhibit EGFR expression and thus improve the prognosis
of patients with ESCA. However, GR resistance in patients with
advanced ESCA has become a major limiting factor affecting
long-term patient prognosis, and the mechanisms of resistance are
currently unclear. Therefore, exploring the molecular mechanisms of
resistance to GR in ESCA is of significant importance for the
clinical management of patients with ESCA (107,109). One study found that circPSMC3 was
downregulated in ESCC tissues and gefitinib-resistant (GR) cells,
while miR-10a-5p was upregulated. Overexpression of circPSMC3 or
knockdown of miR-10a-p decreased the survival rate of GR ESCC cells
(TE1/GR and KYSE450/GR) and induced apoptosis, while downregulation
of PTEN reversed this effect (70).
Luciferase assays were used to confirm that circPSMC3-WT activity
could be inhibited by miR-10a-5p mimics, whereas circPSMC3-MUT was
unaffected. Thus, circPSMC3 could overcome the chemosensitivity
resistance to GR by sponging miR-10a-5p to promote downstream PTEN
activation (70). miR-10-related
circRNAs can regulate ESCA development and modulate radiotherapy
sensitivity, in addition to increasing ESCA chemosensitivity to GR.
For example, Zhang et al (110) detected reduced circATIC expression
in ESCA tissues. circATIC expression was reduced in high TNM stage
cancer and in patients with positive lymph node metastasis compared
with that in low TNM stage cancer and in patients without lymph
node metastasis group. Functionally, overexpression of circATIC or
RHCG inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of EC109 and
KYSE150 ESCA cells, and promoted apoptosis of EC109 and KYSE150
cells under radiation exposure, whereas this was reversed by
upregulation of miR-10b-3p. Furthermore, in vivo animal
studies showed that circATIC overexpression promoted the inhibitory
effect of radiation on tumor volume and weight. Taken together,
targeting the miR-10 family of circRNAs may improve radiotherapy
sensitivity in ESCA.
CRC
The value of lncRNA research in CRC has been
demonstrated in previous studies. In addition, circRNAs in the
serum can be used as a diagnostic marker for CRC. For example,
circ_002197 expression has been reported to be reduced in clinical
samples and cell lines from patients with colon cancer. Most
notably, its expression was significantly lower in the preoperative
blood of patients with CRC and lymph node metastases compared with
that in patients without lymph node metastases. The AUC of
circ_0021977 between plasma from patients with CRC and normal
plasma was 0.873, the sensitivity was 85.71%, and the specificity
was 77.78%. These findings suggested that the circ_0021977
diagnostic model had high specificity. In addition, low expression
of circ_0021977 was significantly associated with a poor prognosis.
In vitro and in vivo experiments showed that
circ_0021977 competitively bound to miR-10b-5p to regulate p21 and
p53 to inhibit proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells
(111). This highlights its value
for early diagnosis and treatment of patients with CRC. Similarly,
Liu (112) found that circFAT1
expression was low in CRC tissues and cells, and its expression was
negatively associated with miR-10a. Functional studies have shown
that circFAT1 overexpression or miR-10a knockdown can inhibit the
proliferation, invasion and migration of CRC cells. Thus, circRNAs
targeting the miR-10 family may serve as novel diagnostic markers
and therapeutic targets for the management of CRC.
OC
Luo et al (113) detected low expression levels of
circ-ITCH in human OC epithelial cell lines. It was revealed that
transfection of SKOV3 cells with circ-ITCH mimics inhibited
proliferation and enhanced apoptosis, whereas knockdown of
circ-ITCH promoted cell proliferation and inhibited apoptosis.
Reverse transcription-qPCR detected a decrease in miR-10a
expression levels following overexpression of circ-ITCH. In
addition, rescue assays showed that overexpression of circ-ITCH
could rescue SKOV3 cell proliferation and apoptosis caused by the
overexpression of miR-10a (113).
Another study identified the presence of a circHIPK3/miR-10a-5p
axis using bioinformatics tools. In vitro experiments
revealed that the knockdown of circHIPK3 promoted proliferation,
migration and invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells and
inhibited apoptosis of A2780 and SKOV3 OC cells (114). These results suggested that
circRNAs targeting miR-10a may have a tumor-suppressive role in
OC.
Endometrial cancer (EC)
EC is the second most common female malignancy after
BC worldwide, and is the most common type of cancer in developing
countries (115). In the United
States and Europe, EC is the sixth and eighth leading cause of
cancer-associated death in women, respectively (116). There is increasing evidence that
circRNAs may be oncogenic factors in EC. Yang et al
(117) showed that circ-ATAD1
expression was downregulated in EC, whereas miR-10a expression was
upregulated in EC. Mechanistically, circ-ATAD1 attenuated miR-10a
methylation, which resulted in the inhibition of EC cell invasion
and migration.
Conclusion and future prospects
In the context of cancer, lncRNAs and circRNAs
primarily function by sponging miRNAs. We found that lncRNAs and
circRNAs regulate the malignant progression of diseases, including
lung cancer, ESCA, liver cancer, CRC, kidney cancer, PCa, BCa, BC,
OC, GBM, NB, AML and EC by activating or inhibiting miR-10a or
miR-10b. The present review described the relevant mechanisms by
which lncRNAs and circRNAs target the miR-10 family to regulate
cancer. It was revealed that the expression levels of
lncRNAs/circRNAs targeting the miR-10 family members are related to
tumor size, local invasion, tumor metastasis and TME. They are also
related to clinical factors, such as TNM stage, lymph node
metastasis and pathological type. For example, the lncRNAs CHRF,
FAM83H-AS1, LINC00963 and LINC00324 also participate in EMT in
cancer by acting as a sponge of the miR-10 family members and
affecting the metastatic ability of cancer cells. Additionally,
lncRNAs and circRNAs regulate cancer progression through the
modulation of various signaling pathways. For example, the lncRNAs
MEG3, CHRF and GAS5 are involved in the regulation of PIK/AKT,
MEK/ERK, GSK3β/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways by targeting the
miR-10 family. In addition, by evaluating the expression levels of
miR-10a and miR-10b-related lncRNAs/circRNAs, it has been shown
that lncRNAs and circRNAs can be used as diagnostic markers for
several types of cancer. For example, circ_002197 and lncRNA TUC338
targeting miR-10 family members could be used to distinguish
patients with malignant cancer from healthy individuals based on
their expression in plasma, and could also be used to predict the
prognosis of patients with cancer.
The present review highlights the role of
miR-10-related lncRNAs/circRNAs in the early diagnosis and
prognosis of cancer. For the treatment of malignant tumors, a
combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy is the standard mode
of treatment for advanced malignancies (110,111); however, its effectiveness is
limited due to intrinsic and acquired resistance (118). In addition, sensitivity to
radiotherapy is key to the efficacy of treatment of malignant
tumors, and as some tumors are not sensitive to radiotherapy, a
proportion of patients will exhibit a poor prognosis, recurrence,
tumor metastasis and/or resistance (119). circPSMC3, circATIC, lncRNAs TUSC7
and LEF1-AS1 can act as ceRNAs to regulate the miR-10 family
members to reduce resistance to chemotherapy or improve sensitivity
to radiotherapy in malignant tumors. Immunotherapy may be a
treatment of last resort for advanced malignancies that are
resistant to radiotherapy. In contrast to radiotherapy,
immunotherapy kills tumor cells by facilitating the innate immune
response through modulation of the TME (120,121). Coincidentally, the present study
found that the lncRNAs XIST, NEAT1 and MMP25-AS1 are involved in
regulating tumor immunity and escape in renal cancer by targeting
the miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1 axis.
Although the roles of miR-10 family-related lncRNAs
in cancer have been extensively studied, to the best of our
knowledge, the mechanisms of miR-10 family-related lncRNAs in
cancer, such as thyroid cancer, oral cancer, pancreatic cancer,
bone tumors and vaginal cancer, have not been reported. In
addition, only a few miR-10-related circRNAs have been reported so
far in malignant tumors, due to a lack of studies targeting miR-10
family circRNAs. In addition, although researchers have found,
through bioinformatics, that the lncRNA-targeted miR-10 family may
be involved in renal tumor immunity, the specific regulatory
mechanisms are not yet fully understood (70–72),
and prediction by bioinformatics analysis alone is not rigorous;
therefore, the regulatory mechanisms should be elaborated through
cellular experiments or animal models. In conclusion, future
research should continue to expand the lncRNAs and circRNAs
targeting the miR-10 family and explore the mechanisms of their
action in malignancies. Of note, targeted drugs and biomarkers
based on miR-10 family-related lncRNAs and circRNAs may be the next
direction in the translation of this field of research from the
bench to bedside. In summary, targeting the miR-10 family of
lncRNAs and circRNAs may be a new strategy for treating cancer.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
SG and WW contributed to the literature search and
selected the studies for inclusion. SG, SL and WW drafted the
manuscript and revised it critically for important intellectual
content. FM and YQ conceived the topic of the present review and
revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final
version of the manuscript. Data authentication is not
applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Deo SVS, Sharma J and Kumar S: GLOBOCAN
2020 report on global cancer burden: Challenges and opportunities
for surgical oncologists. Ann Surg Oncol. 29:6497–6500. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S,
Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Li N and Chen W: Cancer statistics in China
and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin
Med J (Engl). 135:584–590. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei C, Zhao L, Liang H, Zhen Y and Han L:
Recent advances in unraveling the molecular mechanisms and
functions of HOXA11-AS in human cancers and other diseases
(review). Oncol Rep. 43:1737–1754. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mao M, Zhang J, Xiang Y, Gong M, Deng Y
and Ye D: Role of exosomal competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) in
diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors. Bioengineered.
13:12156–12168. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and Cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ye J, Li J and Zhao P: Roles of ncRNAs as
ceRNAs in gastric cancer. Genes (Basel). 12:10362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee YR and Pandolfi PP: PTEN mouse models
of cancer initiation and progression. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Med. 10:a0372832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Zhu S, Meng N, He Y, Lu R and Yan
GR: ncRNA-encoded peptides or proteins and cancer. Mol Ther.
27:1718–1725. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu C, Wu Y and Ma J: Interaction of
non-coding RNAs and Hippo signaling: Implications for
tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 493:207–216. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Slack FJ and Chinnaiyan AM: The role of
non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell. 179:1033–1055. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS and Slack FJ:
Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:5–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Li K, Zheng H and Zhu Y: Research
progress review on long non-coding RNA in colorectal cancer.
Neoplasma. 68:240–252. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Basera A, Hull R, Demetriou D, Bates DO,
Kaufmann AM, Dlamini Z and Marima R: Competing endogenous RNA
(ceRNA) networks and splicing switches in cervical cancer: HPV
oncogenesis, clinical significance and therapeutic opportunities.
Microorganisms. 10:18522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Khan S, Li L, Ten Hagen TLM and
Falahati M: Molecular mechanisms of thyroid cancer: A competing
endogenous RNA (ceRNA) point of view. Biomed Pharmacother.
146:1122512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu H, Deng H, Zhao Y, Li C and Liang Y:
LncRNA XIST/miR-34a axis modulates the cell proliferation and tumor
growth of thyroid cancer through MET-PI3K-AKT signaling. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 37:2792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lima CR, Geraldo MV, Fuziwara CS, Kimura
ET and Santos MF: MiRNA-146b-5p upregulates migration and invasion
of different Papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer.
16:1082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Worst TS, Previti C, Nitschke K, Diessl N,
Gross JC, Hoffmann L, Frey L, Thomas V, Kahlert C, Bieback K, et
al: miR-10a-5p and miR-29b-3p as extracellular vesicle-associated
prostate cancer detection markers. Cancers (Basel). 12:432019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang J, Wang B, Chen LQ, Yang J, Gong ZQ,
Zhao XL, Zhang CQ and Du KL: miR-10b promotes invasion by targeting
KLF4 in osteosarcoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:947–953. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu H, Kang M and Bai X: TCF21 regulates
miR-10a-5p/LIN28B signaling to block the proliferation and invasion
of melanoma cells. PLoS One. 16:e02559712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Cho KB, Li Y, Tao G, Xie Z and Guo
B: Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competing endogenous RNA
networks provide novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets
for colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:57582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xing C, Sun SG, Yue ZQ and Bai F: Role of
lncRNA LUCAT1 in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 134:1111582021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan YT, Lin JF, Li T, Li JJ, Xu RH and Ju
HQ: LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and
reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond).
41:109–120. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Peng WX, Koirala P and Mo YY:
LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene.
36:5661–5667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang X, Ren H, Guo M, Qian J, Yang Y and
Gu C: Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in
cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 19:910–928. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen L, Wang C, Sun H, Wang J, Liang Y,
Wang Y and Wong G: The bioinformatics toolbox for circRNA discovery
and analysis. Brief Bioinform. 22:1706–1728. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu P, Mo Y, Peng M, Tang T, Zhong Y, Deng
X, Xiong F, Guo C, Wu X, Li Y, et al: Emerging role of
tumor-related functional peptides encoded by lncRNA and circRNA.
Mol Cancer. 19:222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T
and Shu Y: CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: A review. J Hematol
Oncol. 12:902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kong S, Tao M, Shen X and Ju S:
Translatable circRNAs and lncRNAs: Driving mechanisms and functions
of their translation products. Cancer Lett. 483:59–65. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR,
Soleymani Fard S and Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs:
Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell
Physiol. 234:5451–5465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang S, Talukder A, Cha M, Li X and Hu H:
Computational annotation of miRNA transcription start sites. Brief
Bioinform. 22:380–392. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee
M and Song SJ: Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:17232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Catalanotto C, Cogoni C and Zardo G:
MicroRNA in control of gene expression: An overview of nuclear
functions. Int J Mol Sci. 17:17122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He B, Zhao Z, Cai Q, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Shi
S, Xie H, Peng X, Yin W, Tao Y and Wang X: miRNA-based biomarkers,
therapies, and resistance in Cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 16:2628–2647.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao Z, Sun W, Guo Z, Zhang J, Yu H and
Liu B: Mechanisms of lncRNA/microRNA interactions in angiogenesis.
Life Sci. 254:1169002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang L, Sun HF, Guo LQ and Cao HB:
MiR-10a-5p: A promising biomarker for early diagnosis and prognosis
evaluation of bladder cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 13:7841–7850. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han TS, Hur K, Cho HS and Ban HS:
Epigenetic associations between lncRNA/circRNA and miRNA in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 12:26222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qi X, Zhang DH, Wu N, Xiao JH, Wang X and
Ma W: ceRNA in cancer: Possible functions and clinical
implications. J Med Genet. 52:710–718. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu J, Zhang X, Gao W, Hu H, Wang X and
Hao D: lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Rep. 20:3160–3174.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheng Y, Su Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Jin L, Wan
Q, Liu Y, Li C, Sang X, Yang L, et al: Identification of
circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competitive endogenous RNA network as
novel prognostic markers for acute myeloid leukemia. Genes (Basel).
11:8682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Moreno-Garcia L, López-Royo T, Calvo AC,
Toivonen JM, de la Torre M, Moreno-Martínez L, Molina N, Aparicio
P, Zaragoza P, Manzano R and Osta R: Competing endogenous RNA
networks as biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:95822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhou T, Lin K, Nie J, Pan B, He B, Pan Y,
Sun H, Xu T and Wang S: LncRNA SPINT1-AS1 promotes breast cancer
proliferation and metastasis by sponging let-7 a/b/i-5p. Pathol Res
Pract. 217:1532682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tajima H, Kumazaki T, Gemma K, Iida E,
Kawamata H, Murakami R, Goto S and Aoyama T: Rotational digital
angiography of ulcer-like projection of pelvis. Radiat Med.
14:49–51. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li C, Mu J, Shi Y and Xin H: LncRNA CCDC26
interacts with CELF2 protein to enhance myeloid leukemia cell
proliferation and invasion via the circRNA_ANKIB1/miR-195-5p/PRR11
axis. Cell Transplant. 30:9636897209860802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zeng X, Xiao J, Bai X, Liu Y, Zhang M, Liu
J, Lin Z and Zhang Z: Research progress on the
circRNA/lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in gastric cancer. Pathol Res Pract.
238:1540302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cao J, Zhang M, Zhang L, Lou J, Zhou F and
Fang M: Non-coding RNA in thyroid cancer-functions and mechanisms.
Cancer Lett. 496:117–126. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tehler D, Hoyland-Kroghsbo NM and Lund AH:
The miR-10 microRNA precursor family. RNA Biol. 8:728–734. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu F, Shi Y, Liu Z, Li Z and Xu W: The
emerging role of miR-10 family in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle.
20:1468–1476. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Guo L, Li Y, Zhao C, Peng J, Song K, Chen
L, Zhang P, Ma H, Yuan C, Yan S, et al: RECQL4, negatively
regulated by miR-10a-5p, facilitates cell proliferation and
invasion via MAFB in ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. 10:5241282020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lu Y, Wei G, Liu L, Mo Y, Chen Q, Xu L,
Liao R, Zeng D and Zhang K: Direct targeting of MAPK8IP1 by
miR-10a-5p is a major mechanism for gastric cancer metastasis.
Oncol Lett. 13:1131–1136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu J, Du S, Zhang J, Huang G, Dong L, Ren
E and Liu D: microRNA-10a-5p from gastric cancer cell-derived
exosomes enhances viability and migration of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells by targeting zinc finger MYND-type containing 11.
Bioengineered. 13:496–507. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Vu TT, Stölzel F, Wang KW, Röllig C,
Tursky ML, Molloy TJ and Ma DD: miR-10a as a therapeutic target and
predictive biomarker for MDM2 inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 35:1933–1948. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kuratomi N, Takano S, Fukasawa M, Maekawa
S, Kadokura M, Shindo H, Takahashi E, Hirose S, Fukasawa Y,
Kawakami S, et al: MiR-10a in pancreatic juice as a biomarker for
invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm by miRNA
sequencing. Int J Mol Sci. 22:32212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF
and Heist RS: Lung cancer. Lancet. 398:535–554. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS: Lung cancer
2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med.
41:1–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhu Y, Ma K, Ye Y, Tang J and Zhu J: Long
non-coding RNA LINRIS is upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer
and its silencing inhibits cell proliferation by suppressing
microRNA-10a maturation. Bioengineered. 13:4340–4346. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gao Y, Zhao H and Mu L: LncRNA-KAT7
negatively regulates miR-10a through an epigenetic pathway to
participate in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 36:441–445. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Thrift AP: Global burden and epidemiology
of Barrett oesophagus and oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 18:432–443. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Iriarte F, Su S, Petrov RV, Bakhos CT and
Abbas AE: Surgical management of early esophageal cancer. Surg Clin
North Am. 101:427–441. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
He N, Xiang L, Chen L, Tong H, Wang K,
Zhao J, Song F, Yang H, Wei X and Jiao Z: The role of long
non-coding RNA FGD5-AS1 in cancer. Bioengineered. 13:11026–11041.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Feng B, Wang G, Liang X, Wu Z, Wang X,
Dong Z, Guo Y, Shen S, Liang J and Guo W: LncRNA FAM83H-AS1
promotes oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via
miR-10a-5p/Girdin axis. J Cell Mol Med. 24:8962–8976. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal
AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Lencioni R, Koike K, Zucman-Rossi J and
Finn RS: Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 7:62021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Anwanwan D, Singh SK, Singh S, Saikam V
and Singh R: Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment
approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1873:1883142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li H, Zhao X, Li C, Sheng C and Bai Z:
Integrated analysis of lncRNA-associated ceRNA network reveals
potential biomarkers for the prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 11:877–897. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang Y, Liu J, Lv Y, Zhang C and Guo S:
LncRNA meg3 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and vivo
studies. Am J Transl Res. 11:4089–4099. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wu Y, Zhou Y, Huan L, Xu L, Shen M, Huang
S and Liang L: LncRNA MIR22HG inhibits growth, migration and
invasion through regulating the miR-10a-5p/NCOR2 axis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 110:973–984. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gao J, Dai C, Yu X, Yin XB and Zhou F:
Long noncoding RNA LEF1-AS1 acts as a microRNA-10a-5p regulator to
enhance MSI1 expression and promote chemoresistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activating AKT signaling
pathway. J Cell Biochem. 122:86–99. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhu H, Du F and Cao C: Restoration of
circPSMC3 sensitizes gefitinib-resistant esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells to gefitinib by regulating miR-10a-5p/PTEN axis.
Cell Biol Int. 45:107–116. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM
and Wallace MB: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 394:1467–1480. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Fan A, Wang B, Wang X, Nie Y, Fan D, Zhao
X and Lu Y: Immunotherapy in colorectal cancer: Current
achievements and future perspective. Int J Biol Sci. 17:3837–3849.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ren W, Chen S, Liu G, Wang X, Ye H and Xi
Y: TUSC7 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Am J
Transl Res. 9:4026–4035. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yang RQ, Jin ZZ, Jiang SY and Jin YJ:
LncRNA GAS5 interacts with MicroRNA-10b to inhibit cell
proliferation and migration and induces apoptosis in colorectal
cancer. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022:49968702022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wu Y, Cong L, Chen W, Wang X and Qiu F:
lncRNA LINC00963 downregulation regulates colorectal cancer
tumorigenesis and progression via the miR-10b/FGF13 axis. Mol Med
Rep. 23:2112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li F, Aljahdali IAM, Zhang R, Nastiuk KL,
Krolewski JJ and Ling X: Kidney cancer biomarkers and targets for
therapeutics: Survivin (BIRC5), XIAP, MCL-1, HIF1α, HIF2α, NRF2,
MDM2, MDM4, p53, KRAS and AKT in renal cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 40:2542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yong C, Stewart GD and Frezza C:
Oncometabolites in renal cancer. Nat Rev Nephrol. 16:156–172. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Dong D, Mu Z, Wei N, Sun M, Wang W, Xin N,
Shao Y and Zhao C: Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 promotes proliferation
and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via targeting
miR-10a/SKA1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 111:917–925. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xu Z, Ye J, Bao P, Wu Q, Xie F and Li P:
Long non-coding RNA SNHG3 promotes the progression of clear cell
renal cell carcinoma via regulating BIRC5 expression. Transl Cancer
Res. 10:4502–4513. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Luo Y, Yang J, Yu J, Liu X, Yu C, Hu J,
Shi H and Ma X: Long non-coding RNAs: Emerging roles in the
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Front Oncol. 10:482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu RJ, Xu ZP, Li S, Yu JJ, Xu B and Chen
M: Identification a ceRNA (XIST/miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1) axis as a
prognostic biomarker in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Research
Square. 2021.
|
|
82
|
Liu RJ, Xu ZP, Li SY, Yu JJ, Feng NH, Xu B
and Chen M: BAP1-related ceRNA (NEAT1/miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1) promotes
proliferation and migration of kidney cancer cells. Front Oncol.
12:8525152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tan P, Chen H, Huang Z, Huang M, Du Y, Li
T, Chen Z, Liu Y and Fu W: MMP25-AS1/hsa-miR-10a-5p/SERPINE1 axis
as a novel prognostic biomarker associated with immune cell
infiltration in KIRC. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 22:307–325. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liang Y, Zhang H, Song X and Yang Q:
Metastatic heterogeneity of breast cancer: Molecular mechanism and
potential therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer Biol. 60:14–27. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Coughlin SS: Epidemiology of breast cancer
in women. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1152:9–29. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Matamala N, Vargas MT, González-Cámpora R,
Miñambres R, Arias JI, Menéndez P, Andrés-León E, Gómez-López G,
Yanowsky K, Calvete-Candenas J, et al: Tumor microRNA expression
profiling identifies circulating microRNAs for early breast cancer
detection. Clin Chem. 61:1098–1106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lu Y, Ding Y, Wei J, He S, Liu X, Pan H,
Yuan B, Liu Q and Zhang J: Anticancer effects of traditional
Chinese medicine on epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in
breast cancer: Cellular and molecular targets. Eur J Pharmacol.
907:1742752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Liu Z, Huang L, Sun L, Nie H, Liang Y,
Huang J, Wu F and Hu X: Ecust004 suppresses breast cancer cell
growth, invasion, and migration via EMT regulation. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 15:3451–3461. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang B, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Lin F, Tan Q,
Qin Q, Bao W, Liu Y, Xie J and Zeng Q: Long intergenic non-protein
coding RNA 324 prevents breast cancer progression by modulating
miR-10b-5p. Aging (Albany NY). 12:6680–6699. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wang D, Wang Z, Zhang L and Sun S: LncRNA
PDCD4-AS1 alleviates triple negative breast cancer by increasing
expression of IQGAP2 via miR-10b-5p. Transl Oncol. 14:1009582021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Berek JS, Renz M, Kehoe S, Kumar L and
Friedlander M: Cancer of the ovary, fallopian tube, and peritoneum:
2021 Update. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 155 (Suppl 1):S61–S85. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Tan WX, Sun G, Shangguan MY, Gui Z, Bao Y,
Li YF and Jia ZH: Novel role of lncRNA CHRF in cisplatin resistance
of ovarian cancer is mediated by miR-10b induced EMT and STAT3
signaling. Sci Rep. 10:147682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhu Y, Mo M, Wei Y, Wu J, Pan J, Freedland
SJ, Zheng Y and Ye D: Epidemiology and genomics of prostate cancer
in Asian men. Nat Rev Urol. 18:282–301. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Adamaki M and Zoumpourlis V: Prostate
cancer biomarkers: From diagnosis to prognosis and precision-guided
therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 228:1079322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liu S, Wang L, Li Y, Cui Y, Wang Y and Liu
C: Long non-coding RNA CHRF promotes proliferation and mesenchymal
transition (EMT) in prostate cancer cell line PC3 requiring
up-regulating microRNA-10b. Biol Chem. Jul 9–2019.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
96
|
Li WJ, Li G, Liu ZW, Chen ZY and Pu R:
LncRNA LINC00355 promotes EMT and metastasis of bladder cancer
cells through the miR-424-5p/HMGA2 axis. Neoplasma. 68:1225–1235.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Li G, Zhang Y, Mao J, Hu P, Chen Q, Ding W
and Pu R: lncRNA TUC338 is a potential diagnostic biomarker for
bladder cancer. J Cell Biochem. 120:18014–18019. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ye M, Gao R, Chen S, Wei M, Wang J, Zhang
B, Wu S, Xu Y, Wu P, Chen X, et al: Downregulation of MEG3 and
upregulation of EZH2 cooperatively promote neuroblastoma
progression. J Cell Mol Med. 26:2377–2391. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhou X, Lu H, Li F, Han L, Zhang H, Jiang
Z, Dong Q and Chen X: LncRNA cancer susceptibility candidate
(CASC7) upregulates phosphatase and tensin homolog by
downregulating miR-10a to inhibit neuroblastoma cell proliferation.
Neuroreport. 31:381–386. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Tan AC, Ashley DM, López GY, Malinzak M,
Friedman HS and Khasraw M: Management of glioblastoma: State of the
art and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:299–312. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Uddin MS, Mamun AA, Alghamdi BS, Tewari D,
Jeandet P, Sarwar MS and Ashraf GM: Epigenetics of glioblastoma
multiforme: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic approaches.
Semin Cancer Biol. 83:100–120. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Hao SC, Ma H, Niu ZF, Sun SY, Zou YR and
Xia HC: hUC-MSCs secreted exosomes inhibit the glioma cell
progression through PTENP1/miR-10a-5p/PTEN pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:10013–10023. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Ding Y, Wang J, Zhang H and Li H: Long
noncoding RNA-GAS5 attenuates progression of glioma by eliminating
microRNA-10b and Sirtuin 1 in U251 and A172 cells. Biofactors.
46:487–496. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Shang C, Tang W, Pan C, Hu X and Hong Y:
Long non-coding RNA TUSC7 inhibits temozolomide resistance by
targeting miR-10a in glioblastoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
81:671–678. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Saleh K, Khalifeh-Saleh N and Kourie HR:
Acute myeloid leukemia transformed to a targetable disease. Future
Oncol. 16:961–972. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yuan Z and Wang W: LncRNA SNHG4 regulates
miR-10a/PTEN to inhibit the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia
cells. Hematology. 25:160–164. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Petty RD, Dahle-Smith A, Stevenson DAJ,
Osborne A, Massie D, Clark C, Murray GI, Dutton SJ, Roberts C,
Chong IY, et al: Gefitinib and EGFR gene copy number aberrations in
esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35:2279–2287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kang J, Guo Z, Zhang H, Guo R, Zhu X and
Guo X: Dual inhibition of EGFR and IGF-1R signaling leads to
enhanced antitumor efficacy against esophageal squamous cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 23:103822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Fu X, Cui G, Liu S and Zhao S: Linc01014
regulates gefitinib resistance in oesophagus cancer via
EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
24:1670–1675. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhang K, Fan R, Zhao D, Liu Z, Yang Z, Liu
J, Zhang S, Rao S, Wang Y and Wan L: CircATIC inhibits esophageal
carcinoma progression and promotes radiosensitivity by elevating
RHCG through sponging miR-10-3p. Thorac Cancer. 13:934–946. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Lu C, Jiang W, Hui B, Rong D, Fu K, Dong
C, Tang W and Cao H: The circ_0021977/miR-10b-5p/P21 and P53
regulatory axis suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion
in colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol. 235:2273–2285. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Liu M: CircFAT1 is overexpressed in
colorectal cancer and suppresses cancer cell proliferation,
invasion and migration by increasing the maturation of miR-10a.
Cancer Manag Res. 13:4309–4315. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Luo L, Gao YQ and Sun XF: Circular RNA
ITCH suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in human
epithelial ovarian cancer cells by sponging miR-10a-α. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:8119–8126. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Teng F, Xu J, Zhang M, Liu S, Gu Y, Zhang
M, Wang X, Ni J, Qian B, Shen R and Jia X: Comprehensive circular
RNA expression profiles and the tumor-suppressive function of
circHIPK3 in ovarian cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 112:8–17.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Raglan O, Kalliala I, Markozannes G,
Cividini S, Gunter MJ, Nautiyal J, Gabra H, Paraskevaidis E,
Martin-Hirsch P, Tsilidis KK and Kyrgiou M: Risk factors for
endometrial cancer: An umbrella review of the literature. Int J
Cancer. 145:1719–1730. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Urick ME and Bell DW: Clinical
actionability of molecular targets in endometrial cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 19:510–521. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Yang P, Yun K and Zhang R: CircRNA
circ-ATAD1 is downregulated in endometrial cancer and suppresses
cell invasion and migration by downregulating miR-10a through
methylation. Mamm Genome. 32:488–494. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Cui C, Yang J, Li X, Liu D, Fu L and Wang
X: Functions and mechanisms of circular RNAs in cancer radiotherapy
and chemotherapy resistance. Mol Cancer. 19:582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kim MK, Cho KJ, Kwon GY, Park SI, Kim YH,
Kim JH, Song HY, Shin JH, Jung HY, Lee GH, et al: ERCC1 predicting
chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in oesophageal cancer.
Eur J Cancer. 44:54–60. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Tan S, Li D and Zhu X: Cancer
immunotherapy: Pros, cons and beyond. Biomed Pharmacother.
124:1098212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
van den Bulk J, Verdegaal EM and de
Miranda NF: Cancer immunotherapy: Broadening the scope of
targetable tumours. Open Biol. 8:1800372018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|