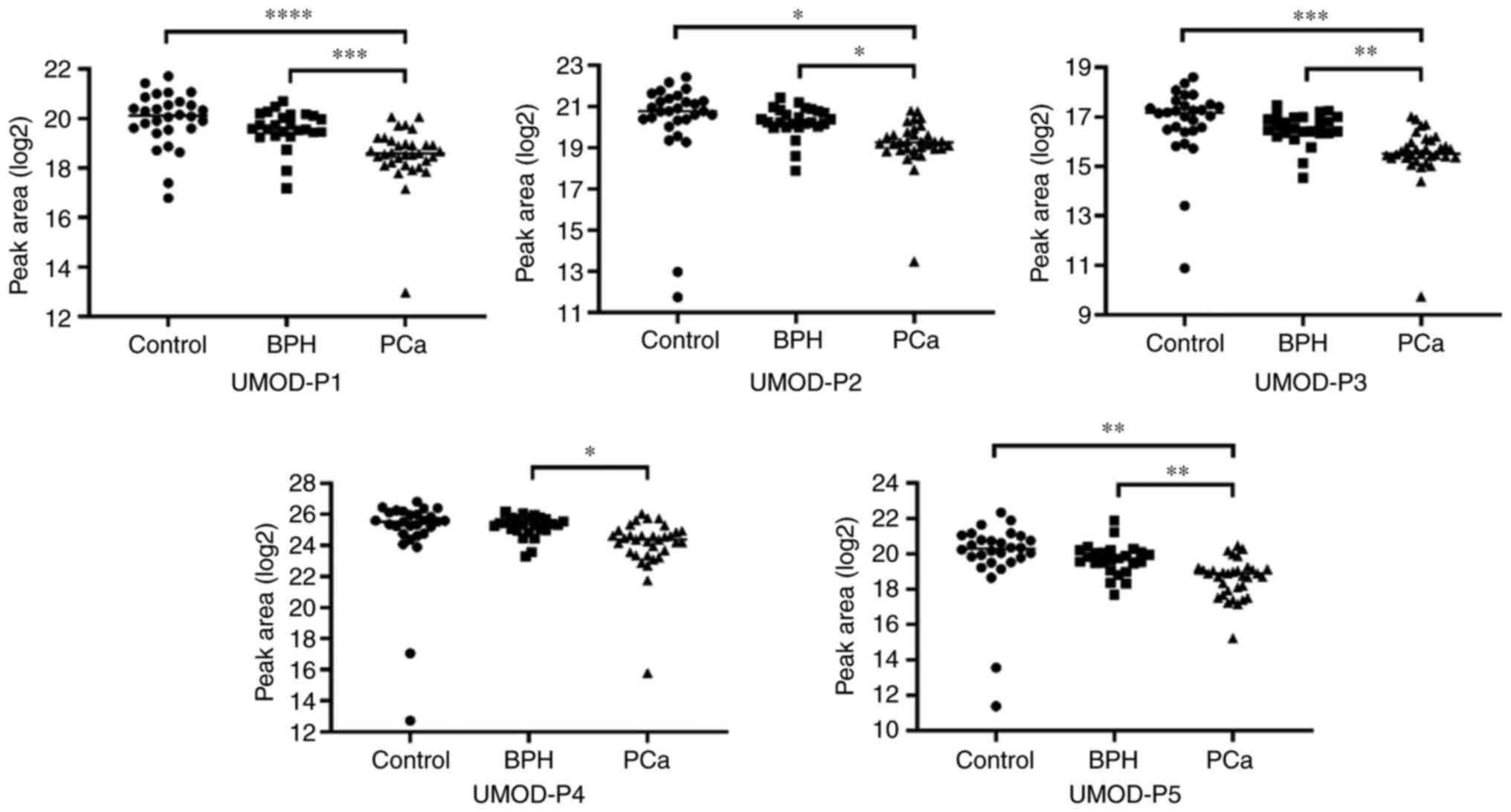
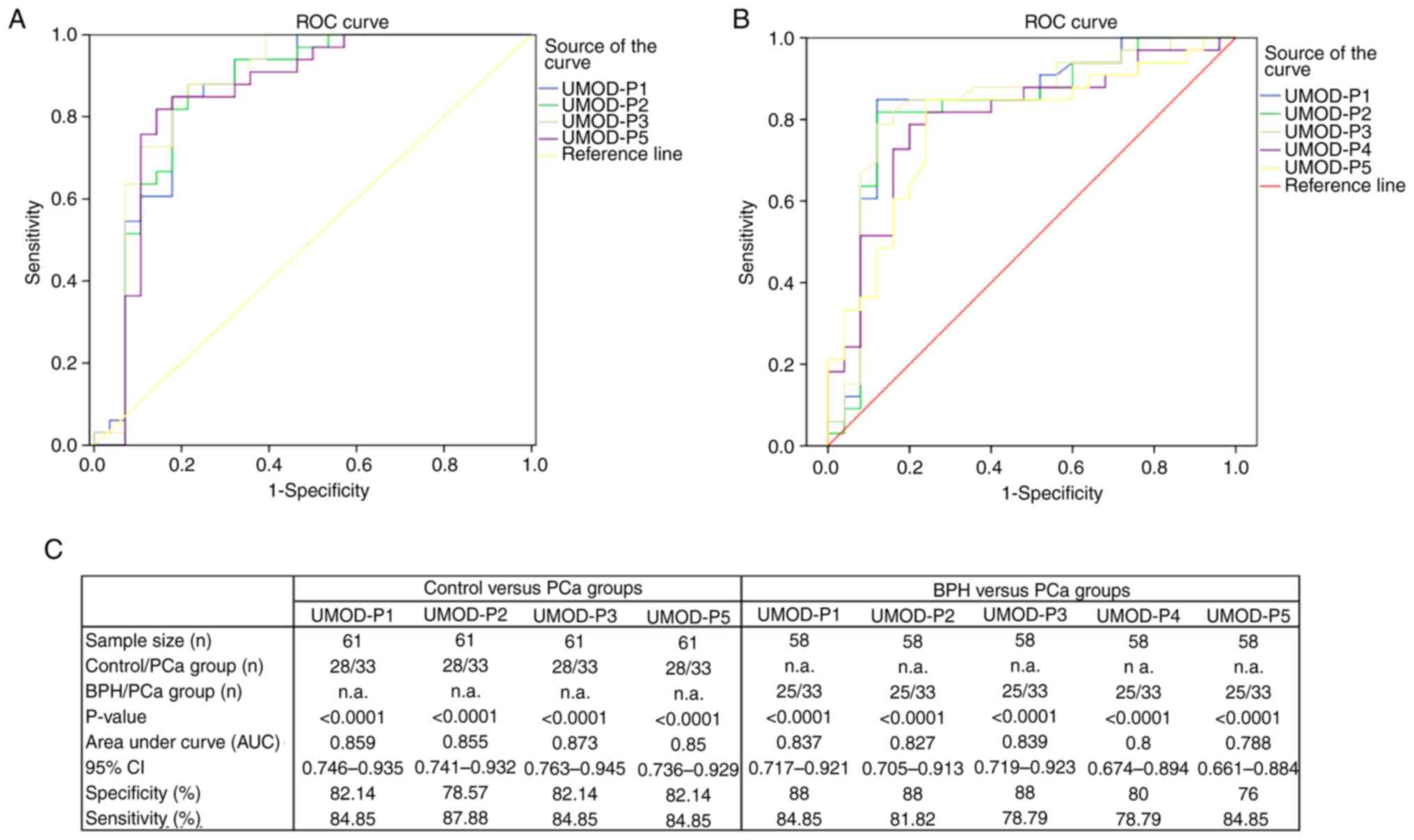
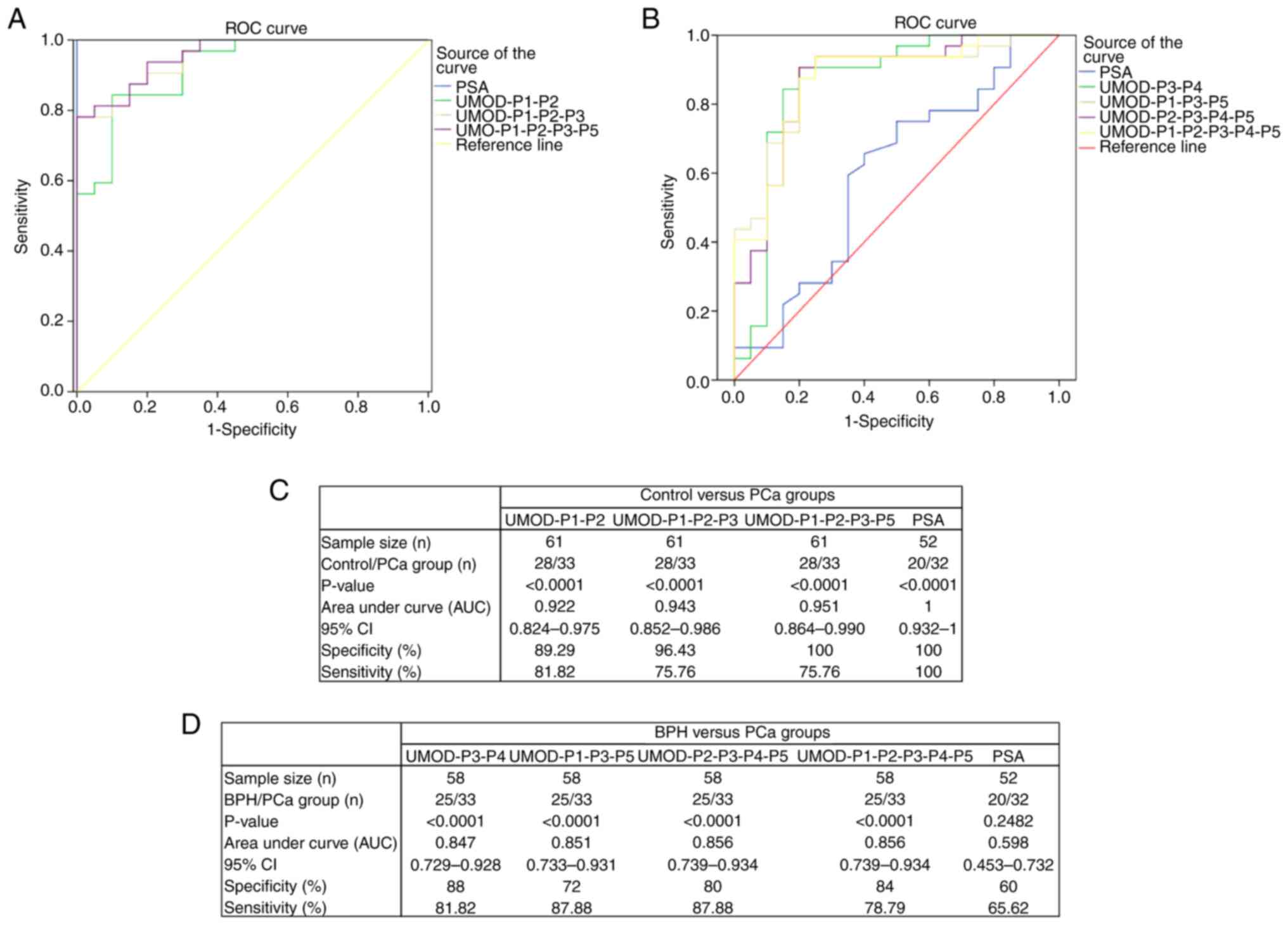
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36
Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Heidenreich A, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau
S, Mason M, Matveev V, Mottet N, Schmid HP, Van Der Kwast T, Wiegel
T, et al: EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: Screening,
diagnosis, and treatment of clinically localised disease. Eur Urol.
59:61–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gretzer MB and Partin AW: PSA levels and
the probability of prostate cancer on biopsy. Eur Urol. (Suppl
1):21–27. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Thompson IM, Pauler DK, Goodman PJ, Tangen
CM, Lucia MS, Parnes HL, Minasian LM, Ford LG, Lippman SM, Crawford
ED, et al: Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a
prostate-specific antigen level < or =4.0 ng per milliliter. N
Engl J Med. 350:2239–2246. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oshi M, Murthy V, Takahashi H, Huyser M,
Okano M, Tokumaru Y, Rashid OM, Matsuyama R, Endo I and Takabe K:
Urine as a source of liquid biopsy for cancer. Cancers (Basel).
13:26522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wood SL, Knowles MA, Thompson D, Selby PJ
and Banks RE: Proteomic studies of urinary biomarkers for prostate,
bladder and kidney cancers. Nat Rev Urol. 10:206–218. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jedinak A, Loughlin KR and Moses MA:
Approaches to the discovery of non-invasive urinary biomarkers of
prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 9:32534–32550. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koo KM, Mainwaring PN, Tomlins SA and Trau
M: Merging new-age biomarkers and nanodiagnostics for precision
prostate cancer management. Nat Rev Urol. 16:302–317. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tonry C, Finn S, Armstrong J and
Pennington SR: Clinical proteomics for prostate cancer:
Understanding prostate cancer pathology and protein biomarkers for
improved disease management. Clin Proteomics. 17:412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parker BL, Burchfield JG, Clayton D,
Geddes TA, Payne RJ, Kiens B, Wojtaszewski JFP, Richter EA and
James DE: Multiplexed temporal quantification of the
exercise-regulated plasma peptidome. Mol Cell Proteomics.
16:2055–2068. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Perez-Riverol Y, Bai J, Bandla C,
García-Seisdedos D, Hewapathirana S, Kamatchinathan S, Kundu DJ,
Prakash A, Frericks-Zipper A, Eisenacher M, et al: The PRIDE
database resources in 2022: A Hub for mass spectrometry-based
proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 50((D1)): D543–D552. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schilling B, Rardin MJ, MacLean BX,
Zawadzka AM, Frewen BE, Cusack MP, Sorensen DJ, Bereman MS, Jing E,
Wu CC, et al: Platform-independent and label-free quantitation of
proteomic data using MS1 extracted ion chromatograms in skyline:
Application to protein acetylation and phosphorylation. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 11:202–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Willforss J, Chawade A and Levander F:
NormalyzerDE: Online tool for improved normalization of omics
expression data and high-sensitivity differential expression
analysis. J Proteome Res. 18:732–740. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Klein J, Eales J, Zürbig P, Vlahou A,
Mischak H and Stevens R: Proteasix: A tool for automated and
large-scale prediction of proteases involved in naturally occurring
peptide generation. Proteomics. 13:1077–1082. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Loeb S and Partin AW: Review of the
Literature: PCA3 for prostate cancer risk assessment and
prognostication. Rev Urol. 13:e191–e195. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fujita K and Nonomura N: Urinary
biomarkers of prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 25:770–779. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng B, Zhang P, Wang H, Wang J, Liu ZH
and Zhang DH: Advances in research on bladder cancer targeting
peptides: A review. Cell Biochem Biophys. 79:711–718. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mavrogeorgis E, Mischak H, Latosinska A,
Siwy J, Jankowski V and Jankowski J: Reproducibility evaluation of
urinary peptide detection using CE-MS. Molecules. 26:72602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Van JAD, Clotet-Freixas S, Zhou J, Batruch
I, Sun C, Glogauer M, Rampoldi L, Elia Y, Mahmud FH, Sochett E, et
al: Peptidomic analysis of urine from youths with early type 1
diabetes reveals novel bioactivity of uromodulin peptides in vitro.
Mol Cell Proteomics. 19:501–517. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nkuipou-Kenfack E, Bhat A, Klein J,
Jankowski V, Mullen W, Vlahou A, Dakna M, Koeck T, Schanstra JP,
Zürbig P, et al: Identification of ageing-associated naturally
occurring peptides in human urine. Oncotarget. 6:34106–34117. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Good DM, Zürbig P, Argilés À, Bauer HW,
Behrens G, Coon JJ, Dakna M, Decramer S, Delles C, Dominiczak AF,
et al: Naturally occurring human urinary peptides for use in
diagnosis of chronic kidney disease. Mol Cell Proteomics.
9:2424–2437. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Principe S, Kim Y, Fontana S, Ignatchenko
V, Nyalwidhe JO, Lance RS, Troyer DA, Alessandro R, Semmes OJ,
Kislinger T, et al: Identification of prostate-enriched proteins by
in-depth proteomic analyses of expressed prostatic secretions in
urine. J Proteome Res. 11:2386–2396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Haffner MC, Zwart W, Roudier MP, True LD,
Nelson WG, Epstein JI, De Marzo AM, Nelson PS and Yegnasubramanian
S: Genomic and phenotypic heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nat Rev
Urol. 18:79–92. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiao K, Guo J, Zhang X, Feng X, Zhang H,
Cheng Z, Johnson H, Persson JL and Chen L: Use of two gene panels
for prostate cancer diagnosis and patient risk stratification.
Tumour Biol. 37:10115–10122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alarcón-Zendejas AP, Scavuzzo A,
Jiménez-Ríos MA, Álvarez-Gómez RM, Montiel-Manríquez R,
Castro-Hernández C, Jiménez-Dávila MA, Pérez-Montiel D,
González-Barrios R, Jiménez-Trejo F, et al: The promising role of
new molecular biomarkers in prostate cancer: From coding and
non-coding genes to artificial intelligence approaches. Prostate
Cancer Prostatic Dis. 5:431–443. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lone SN, Nisar S, Masoodi T, Singh M,
Rizwan A, Hashem S, El-Rifai W, Bedognetti D, Batra SK, Haris M, et
al: Liquid biopsy: A step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis
and future of cancer treatments. Mol Cancer. 21:792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hessels D and Schalken JA: Urinary
biomarkers for prostate cancer: A review. Asian J Androl.
15:333–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Padoan A, Basso D, Zambon CF,
Prayer-Galetti T, Arrigoni G, Bozzato D, Moz S, Zattoni F, Bellocco
R and Plebani M: MALDI-TOF peptidomic analysis of serum and
post-prostatic massage urine specimens to identify prostate cancer
biomarkers. Clin Proteomics. 15:232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Clarke RA, Schirra HJ, Catto JW, Lavin MF
and Gardiner RA: Markers for detection of prostate cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 2:1125–1154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Good DM, Thongboonkerd V, Novak J,
Bascands JL, Schanstra JP, Coon JJ, Dominiczak A and Mischak H:
Body fluid proteomics for biomarker discovery: Lessons from the
past hold the key to success in the future. J Proteome Res.
6:4549–4555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schönemeier B, Metzger J, Klein J, Husi H,
Bremer B, Armbrecht N, Dakna M, Schanstra JP, Rosendahl J, Wiegand
J, et al: Urinary peptide analysis differentiates pancreatic cancer
from chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 45:1018–1026. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Theodorescu D, Fliser D, Wittke S, Mischak
H, Krebs R, Walden M, Ross M, Eltze E, Bettendorf O, Wulfing C and
Semjonow A: Pilot study of capillary electrophoresis coupled to
mass spectrometry as a tool to define potential prostate cancer
biomarkers in urine. Electrophoresis. 26:2797–2808. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Okamoto A, Yamamoto H, Imai A, Hatakeyama
S, Iwabuchi I, Yoneyama T, Hashimoto Y, Koie T, Kamimura N, Mori K,
et al: Protein profiling of post-prostatic massage urine specimens
by surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass
spectrometry to discriminate between prostate cancer and benign
lesions. Oncol Rep. 21:73–79. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
M'Koma AE, Blum DL, Norris JL, Koyama T,
Billheimer D, Motley S, Ghiassi M, Ferdowsi N, Bhowmick I, Chang
SS, et al: Detection of pre-neoplastic and neoplastic prostate
disease by MALDI profiling of urine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
353:829–834. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Serafini-Cessi F, Malagolini N and
Cavallone D: Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein: Biology and clinical
relevance. Am J Kidney Dis. 42:658–676. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fuhrman-Luck RA, Loessner D and Clements
JA: Kallikrein-Related peptidases in prostate cancer: From
molecular function to clinical application. EJIFCC.
25:2692014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hong SK: Kallikreins as biomarkers for
prostate cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:5263412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Riddick ACP, Shukla CJ, Pennington CJ,
Bass R, Nuttall RK, Hogan A, Sethia KK, Ellis V, Collins AT,
Maitland NJ, et al: Identification of degradome components
associated with prostate cancer progression by expression analysis
of human prostatic tissues. Br J Cancer. 92:2171–2180. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shimoda M and Khokha R: Metalloproteinases
in extracellular vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1864((11 Pt A)): 1989–2000. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mary S, Small HY, Siwy J, Mullen W, Giri A
and Delles C: Polymerization-incompetent uromodulin in the pregnant
stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertens. 69:910–918.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu Y, Sikorski P, Smith M, Bowman-Gholston
C, Cacciabeve N, Nelson KE and Pieper R: Comprehensive
metaproteomic analyses of urine in the presence and absence of
neutrophil-associated inflammation in the urinary tract.
Theranostics. 7:238–252. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wei P, Hao L, Ma F, Yu Q, Buchberger AR,
Lee S, Bushman W and Li L: Urinary metabolomic and proteomic
analyses in a mouse model of prostatic inflammation. Urine (Amst).
1:17–23. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|