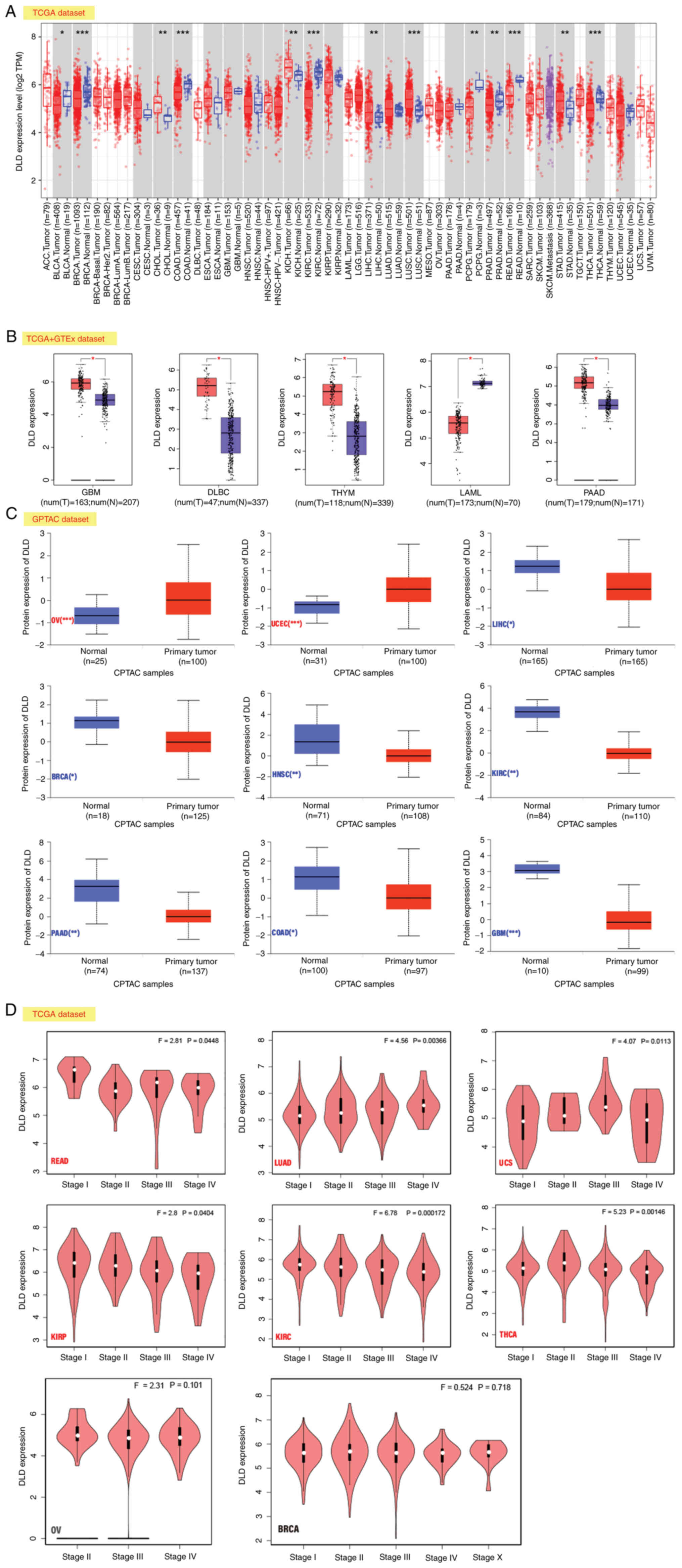
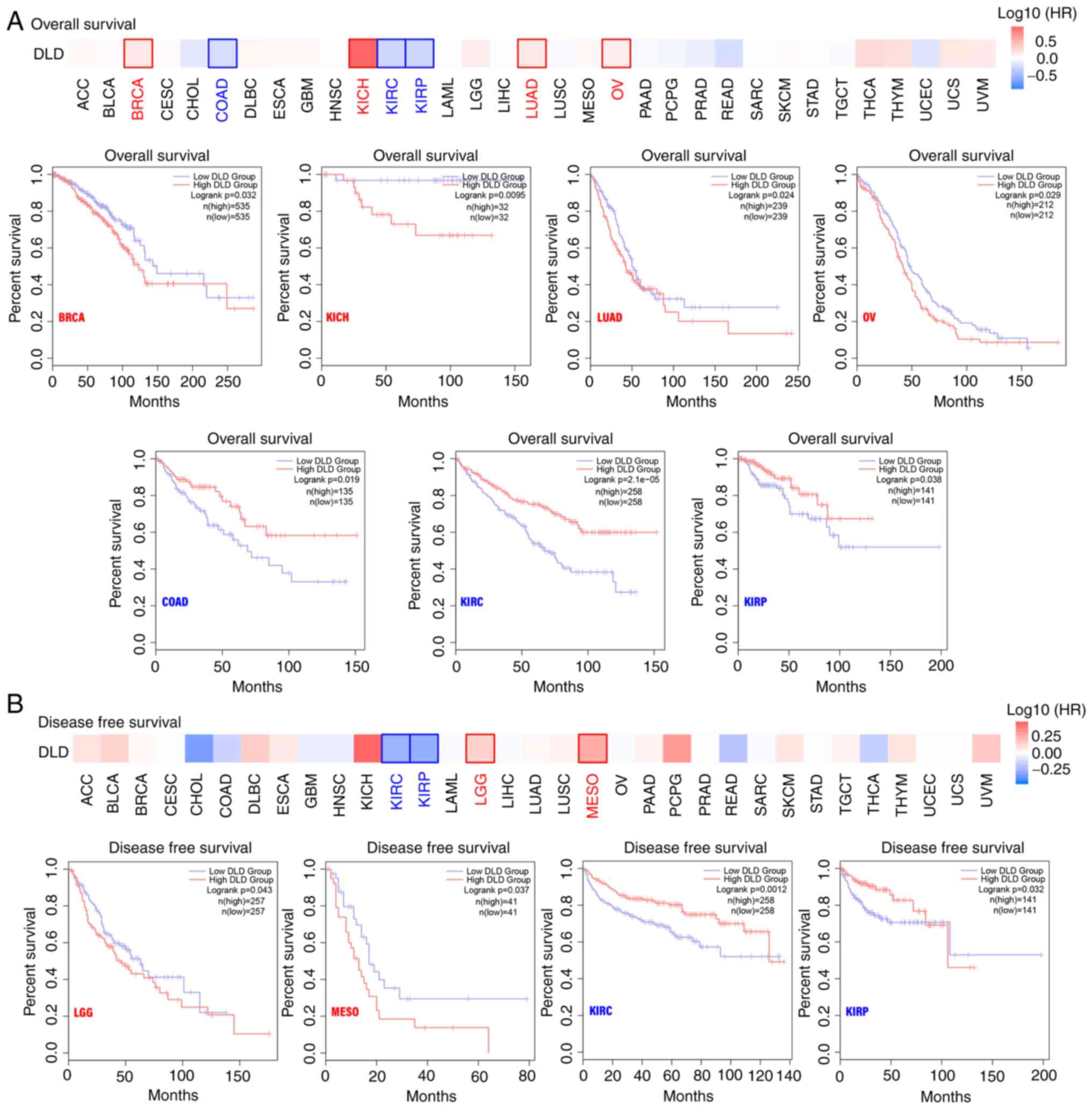
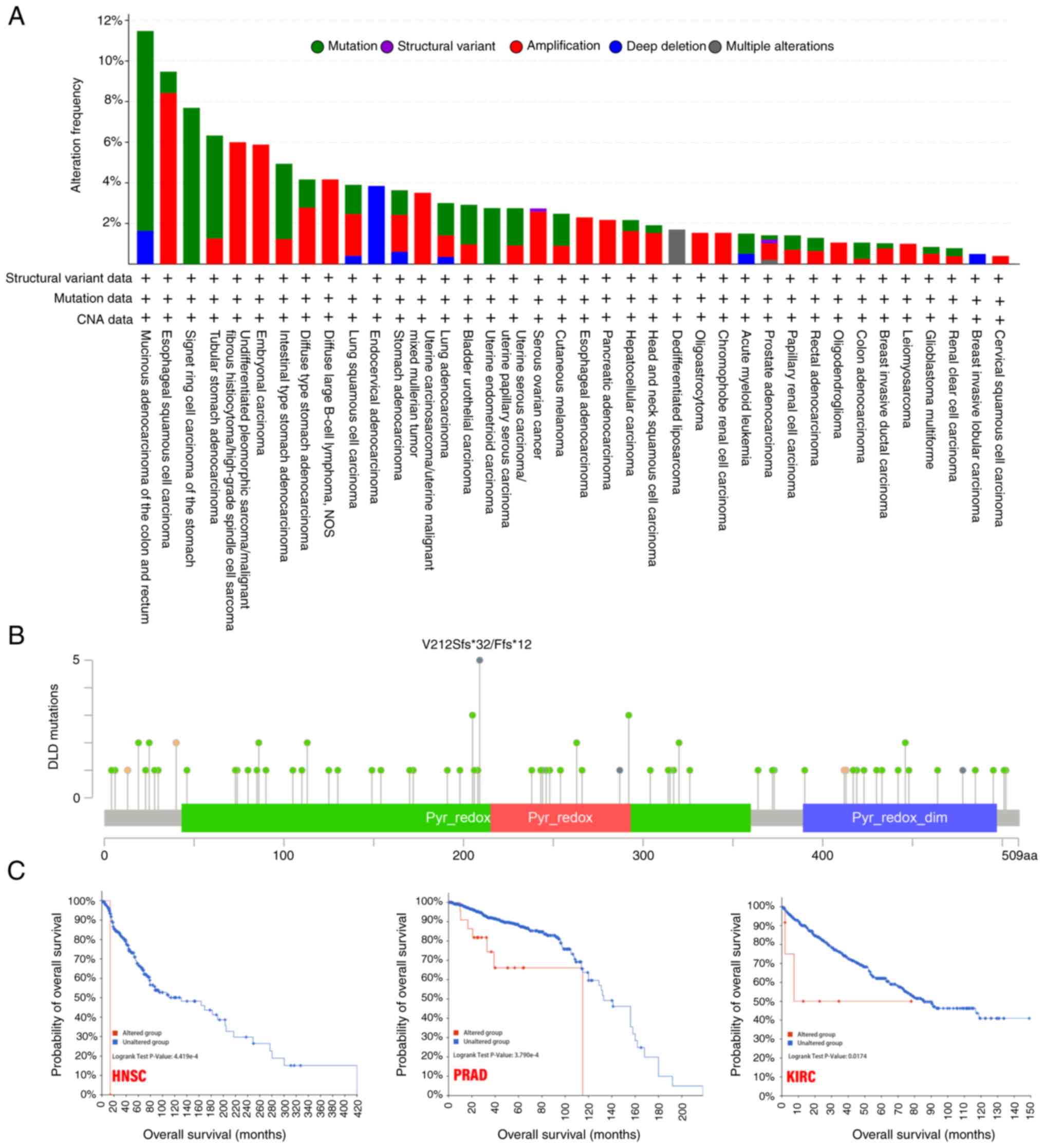
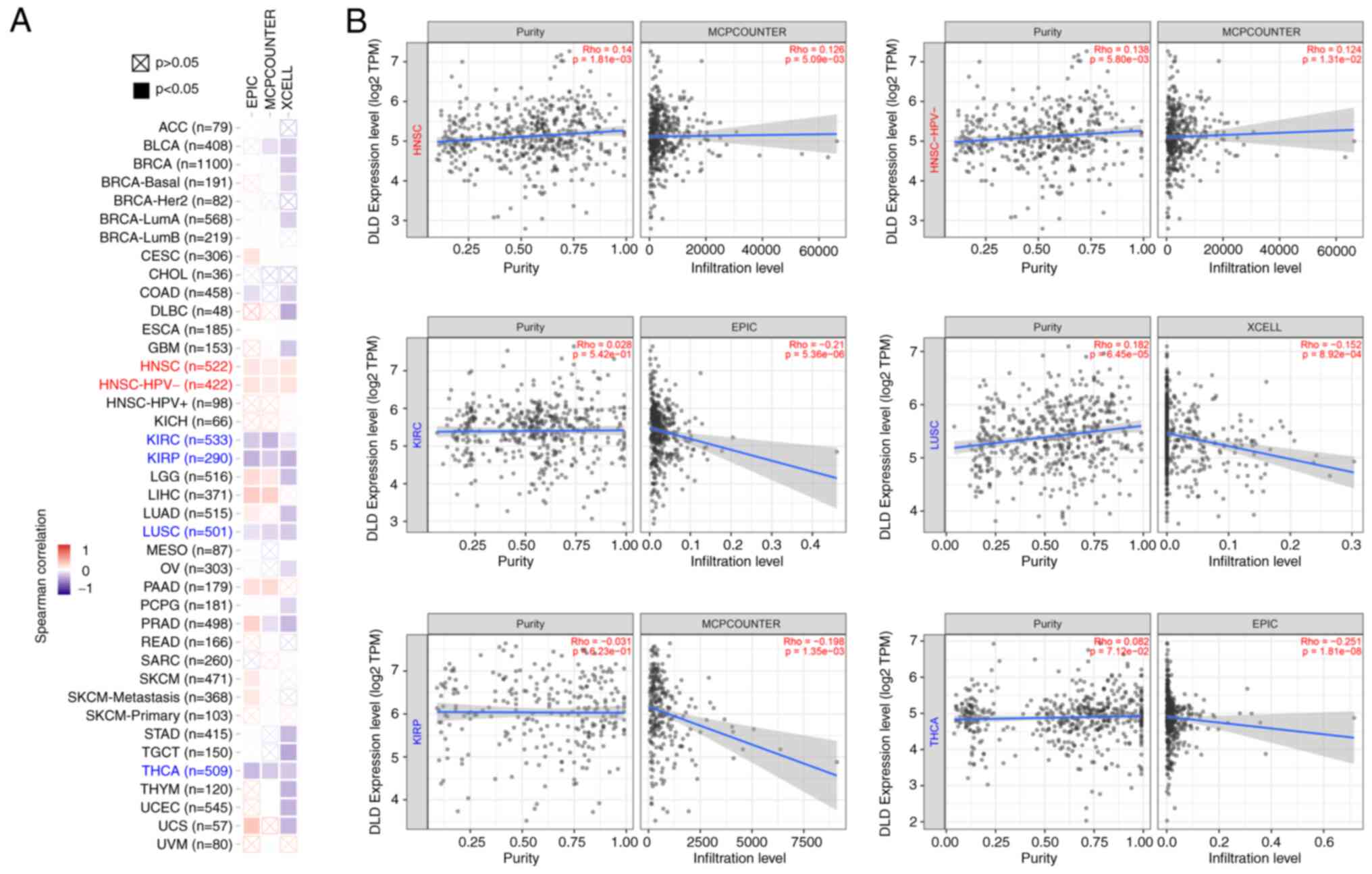
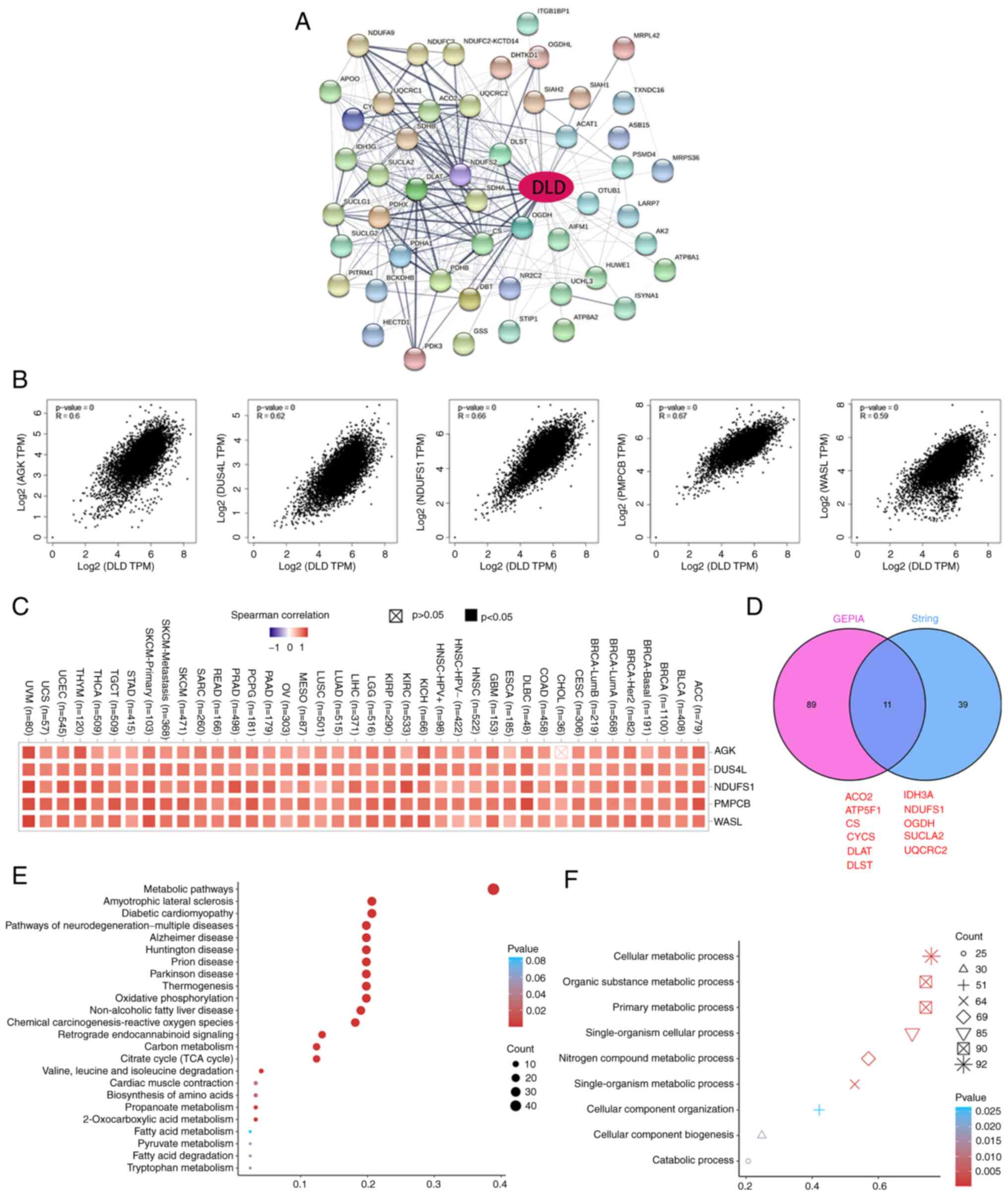
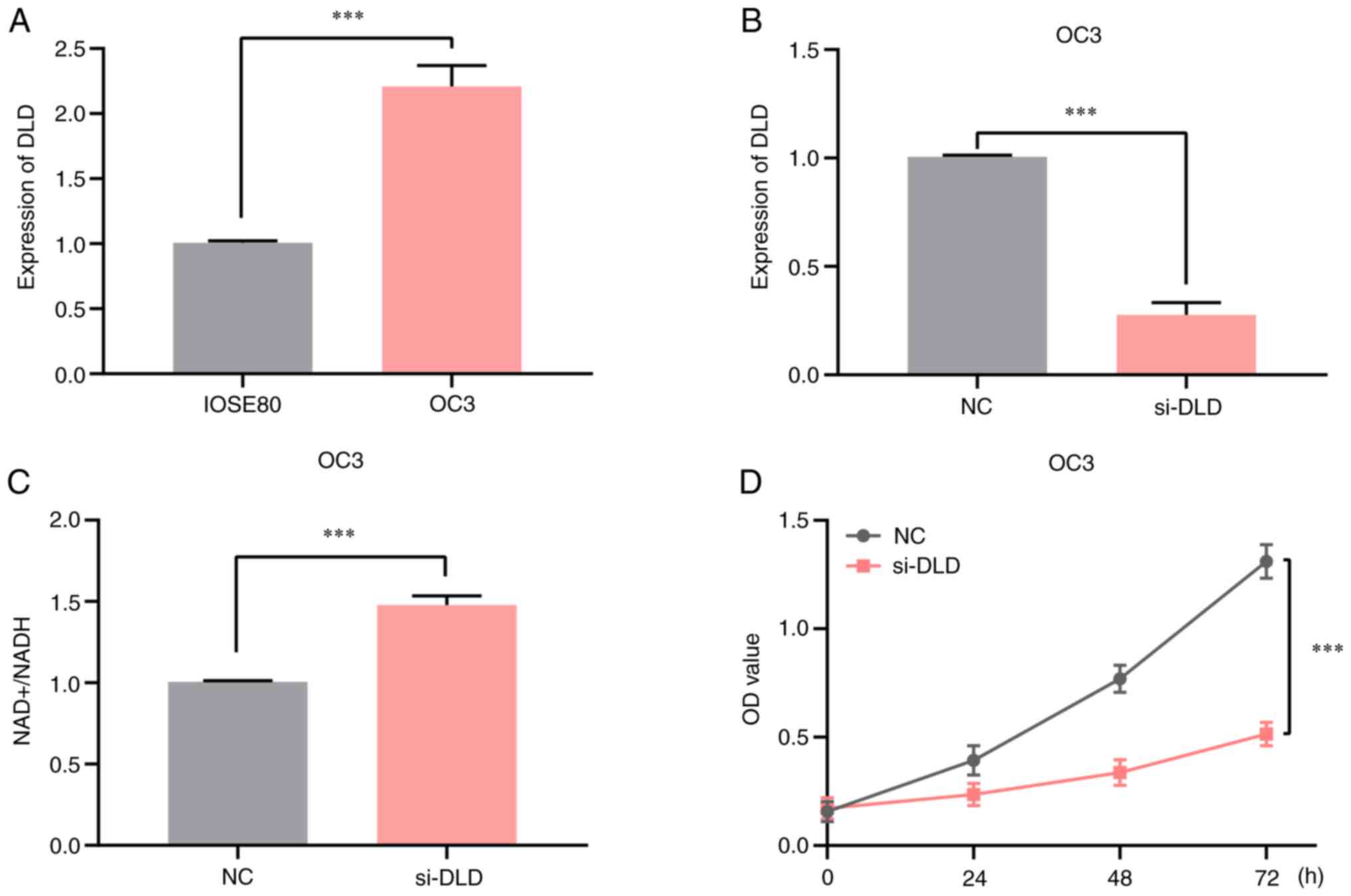
|
1
|
Cobine PA and Brady DC: Cuproptosis:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying copper-induced cell
death. Mol Cell. 82:1786–1787. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li X, Wang L, Li Y, Fu J, Zhen L, Yang Q,
Li S and Zhang Y: Tyrosine phosphorylation of dihydrolipoamide
dehydrogenase as a potential cadmium target and its inhibitory role
in regulating mouse sperm motility. Toxicology. 357–358. 52–64.
2016.
|
|
3
|
Mayr JA, Feichtinger RG, Tort F, Ribes A
and Sperl W: Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis.
37:553–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon
M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, Rossen J, Joesch-Cohen L, Humeidi R,
Spangler RD, et al: Copper induces cell death by targeting
lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 375:1254–1261. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jiang Y, Huo Z, Qi X, Zuo T and Wu Z:
Copper-induced tumor cell death mechanisms and antitumor
theragnostic applications of copper complexes. Nanomedicine (Lond).
17:303–324. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang C, Zeng Y, Guo X, Shen H, Zhang J,
Wang K, Ji M and Huang S: Pan-cancer analyses confirmed the
cuproptosis-related gene FDX1 as an immunotherapy predictor and
prognostic biomarker. Front Genet. 13:9237372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bardou P, Mariette J, Escudié F, Djemiel C
and Klopp C: jvenn: An interactive venn diagram viewer. BMC
Bioinformatics. 15:2932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ito K and Murphy D: Application of ggplot2
to pharmacometric graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol.
2:e792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu D, Xu X, Zhang M and Wang T: TPX2
regulated by miR-29c-3p induces cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
via the AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 23:1432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anderson KA, Madsen AS, Olsen CA and
Hirschey MD: Metabolic control by sirtuins and other enzymes that
sense NAD(+), NADH, or their ratio. Biochimica Biophysica Acta
Bioenerg. 1858:991–998. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li H, Han D, Hou Y, Chen H and Chen Z:
Statistical inference methods for two crossing survival curves: A
comparison of methods. PloS One. 10:e01167742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Domingues P, González-Tablas M, Otero Á,
Pascual D, Miranda D, Ruiz L, Sousa P, Ciudad J, Gonçalves JM,
Lopes MC, et al: Tumor infiltrating immune cells in gliomas and
meningiomas. Brain Behav Immun. 53:1–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Erdogan B and Webb DJ: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts modulate growth factor signaling and extracellular
matrix remodeling to regulate tumor metastasis. Biochem Soc Trans.
45:229–236. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duarte IF, Caio J, Moedas MF, Rodrigues
LA, Leandro AP, Rivera IA and Silva MFB: Dihydrolipoamide
dehydrogenase, pyruvate oxidation, and acetylation-dependent
mechanisms intersecting drug iatrogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
78:7451–7468. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li R, Luo X, Wu J, Thangthaeng N, Jung ME,
Jing S, Li L, Ellis DZ, Liu L, Ding Z, et al: Mitochondrial
dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase is upregulated in response to
intermittent hypoxic preconditioning. Int J Med Sci. 12:432–440.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carrozzo R, Torraco A, Fiermonte G,
Martinelli D, Di Nottia M, Rizza T, Vozza A, Verrigni D, Diodato D,
Parisi G, et al: Riboflavin responsive mitochondrial myopathy is a
new phenotype of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency. The
chaperon-like effect of vitamin B2. Mitochondrion. 18:49–57. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dayan A, Yeheskel A, Lamed R, Fleminger G
and Ashur-Fabian O: Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase moonlighting
activity as a DNA chelating agent. Proteins. 2020.Online ahead of
print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin D, Lee J, You JH, Kim D and Roh JL:
Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase regulates cystine
deprivation-induced ferroptosis in head and neck cancer. Redox
Biol. 30:1014182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yumnam S, Kang MC, Oh SH, Kwon HC, Kim JC,
Jung ES, Lee CH, Lee AY, Hwang JI and Kim SY: Downregulation of
dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase by UVA suppresses melanoma progression
via triggering oxidative stress and altering energy metabolism.
Free Radic Biol Med. 162:77–87. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu WJ, Zhou JJ, Xie Y, Wang WL, Zhao Y,
Chen X and Li Y: Association between the expression and methylation
of energy-related genes with helicobacter pylori infection in
gastric cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 92:366–370. 2012.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoneyama K, Kojima S, Kodani Y, Yamaguchi
N, Igarashi A, Kurose K, Kawase R, Takeshita T, Hattori S and
Nagata K: Proteomic identification of autoantibodies in sera from
patients with ovarian cancer as possible diagnostic biomarkers.
Anticancer Res. 35:881–889. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Starostik P: Clinical mutation assay of
tumors: New developments. Anticancer Drugs. 28:1–10. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sokratous G, Polyzoidis S and Ashkan K:
Immune infiltration of tumor microenvironment following
immunotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
13:2575–2582. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Amjad S, Nisar S, Bhat AA, Shah AR,
Frenneaux MP, Fakhro K, Haris M, Reddy R, Patay Z, Baur J, et al:
Role of NAD(+) in regulating cellular and metabolic signaling
pathways. Mol Metab. 49:1011952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ippolito L, Morandi A, Taddei ML, Parri M,
Comito G, Iscaro A, Raspollini MR, Magherini F, Rapizzi E,
Masquelier J, et al: Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote prostate
cancer malignancy via metabolic rewiring and mitochondrial
transfer. Oncogene. 38:5339–5355. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|