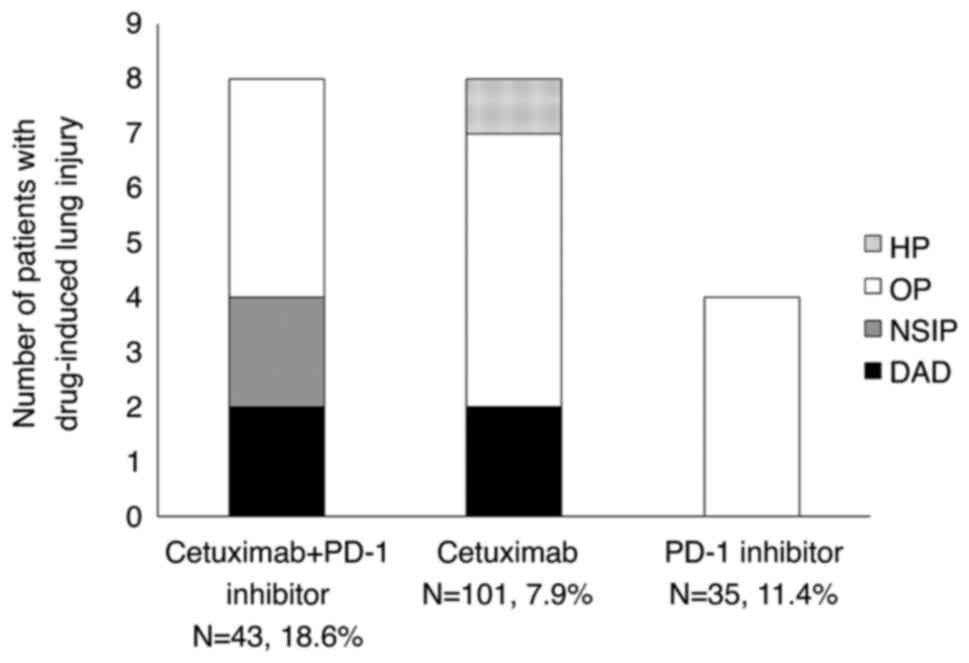
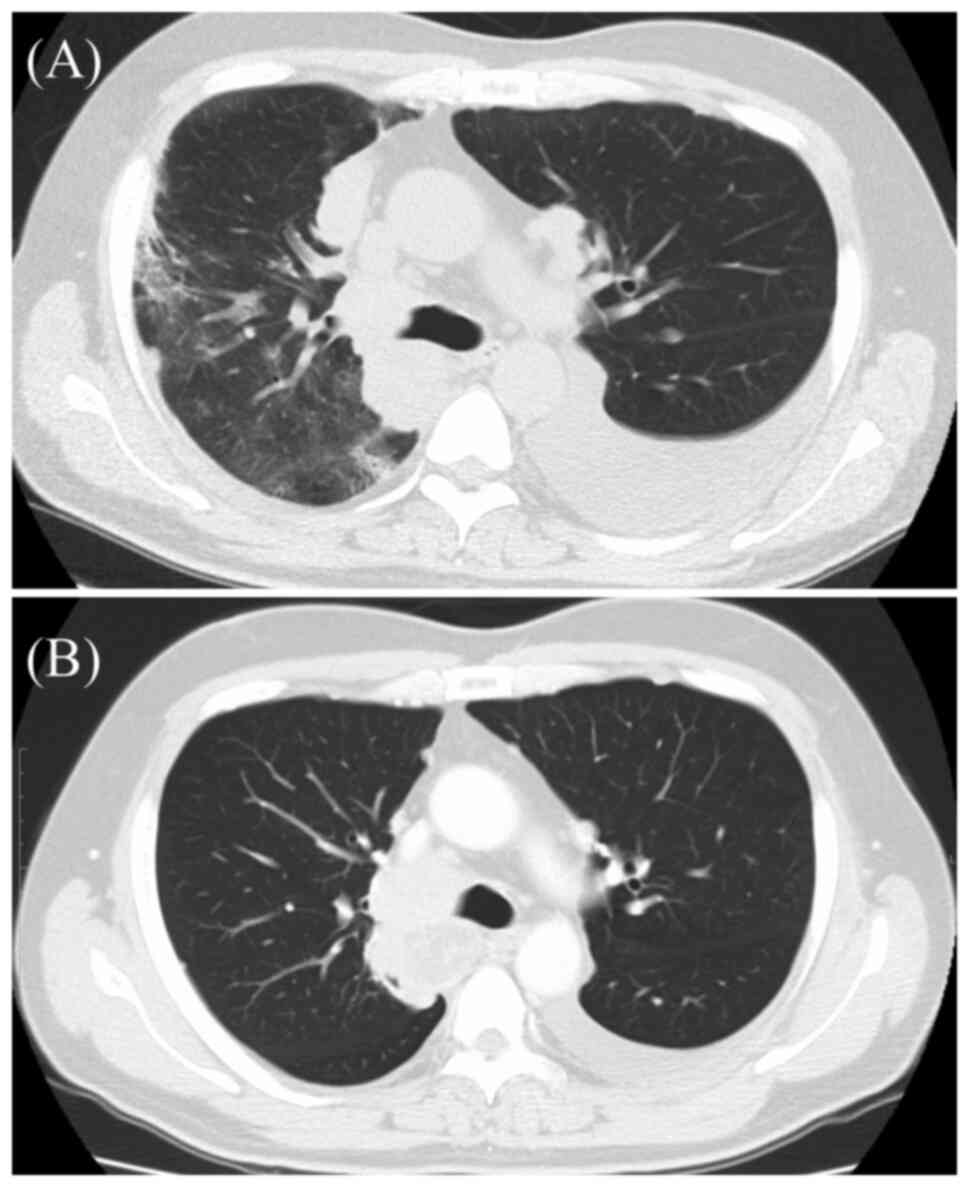
|
1
|
Kubo K, Azuma A, Kanazawa M, Kameda H,
Kusumoto M, Genma A, Saijo Y, Sakai F, Sugiyama Y, Tatsumi K, et
al: Consensus statement for the diagnosis and treatment of
drug-induced lung injuries. Respir Investig. 51:260–277. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oxnard GR, Yang JC, Yu H, Kim SW, Saka H,
Horn L, Goto K, Ohe Y, Mann H, Thress KS, et al: TATTON: A
multi-arm, phase Ib trial of osimertinib combined with selumetinib,
savolitinib, or durvalumab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Ann Oncol.
31:507–516. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Petrelli F, Signorelli D, Ghidini M,
Ghidini A, Pizzutilo EG, Ruggieri L, Cabiddu M, Borgonovo K,
Dognini G, Brighenti M, et al: Association of steroids use with
survival in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). 12:5462020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bradley B, Branley HM, Egan JJ, Greaves
MS, Hansell DM, Harrison NK, Hirani N, Hubbard R, Lake F, Millar
AB, et al: Interstitial lung disease guideline: The British
thoracic society in collaboration with the thoracic society of
Australia and New Zealand and the Irish thoracic society. Thorax.
63 (Suppl 5):v1–v58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N,
Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, et al:
Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head
and neck. N Engl J Med. 354:567–578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Licitra L, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenár É,
Hitt R, Erfán J, Rottey S, Kawecki A, Zabolotnyy D, Benasso M, et
al: Evaluation of EGFR gene copy number as a predictive biomarker
for the efficacy of cetuximab in combination with chemotherapy in
the first-line treatment of recurrent and/or metastatic squamous
cell carcinoma of the head and neck: EXTREME study. Ann Oncol.
22:1078–1087. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harrington KJ, Ferris RL, Blumenschein G
Jr, Colevas AD, Fayette J, Licitra L, Kasper S, Even C, Vokes EE,
Worden F, et al: Nivolumab versus standard, single-agent therapy of
investigator's choice in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck (CheckMate 141): Health-related
quality-of-life results from a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 18:1104–1115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R,
Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr, Psyrri A, Basté N, Neupane
P, Bratland Å, et al: Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy
versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 394:1915–1928. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nishino M, Giobbie-Hurder A, Hatabu H,
Ramaiya NH and Hodi FS: Incidence of programmed cell death 1
inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with advanced cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2:1607–1616. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Khunger M, Rakshit S, Pasupuleti V,
Hernandez AV, Mazzone P, Stevenson J, Pennell NA and Velcheti V:
Incidence of pneumonitis with use of programmed death 1 and
programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of trials. Chest.
152:271–281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saito Y, Sasaki S, Oikado K, Tominaga J,
Sata M, Sakai F, Kato T, Iwasawa T, Kenmotsu H, Kusumoto M, et al:
Radiographic features and poor prognostic factors of interstitial
lung disease with nivolumab for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer
Sci. 112:1495–1505. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rochester CL, Vogiatzis I, Holland AE,
Lareau SC, Marciniuk DD, Puhan MA, Spruit MA, Masefield S, Casaburi
R, Clini EM, et al: An official American thoracic society/European
respiratory society policy statement: Enhancing implementation,
use, and delivery of pulmonary rehabilitation. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 192:1373–1386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Conte P, Ascierto PA, Patelli G, Danesi R,
Vanzulli A, Sandomenico F, Tarsia P, Cattelan A, Comes A, De
Laurentiis M, et al: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease during
cancer therapies: Expert opinion on diagnosis and treatment. ESMO
Open. 7:1004042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ,
Atkins MB, Brassil KJ, Caterino JM, Chau I, Ernstoff MS, Gardner
JM, Ginex P, et al: Management of immune-related adverse events in
patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American
society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin
Oncol. 36:1714–1768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, Sporn TA
and Goodman PC: Pulmonary drug toxicity: Radiologic and pathologic
manifestations. Radiographics. 20:1245–1259. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ohnishi H, Yokoyama A, Yasuhara Y,
Watanabe A, Naka T, Hamada H, Abe M, Nishimura K, Higaki J, Ikezoe
J and Kohno N: Circulating KL-6 levels in patients with drug
induced pneumonitis. Thorax. 58:872–875. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Camus P, Fanton A, Bonniaud P, Camus C and
Foucher P: Interstitial lung disease induced by drugs and
radiation. Respiration. 71:301–326. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Balaji A, Hsu M, Lin CT, Feliciano J,
Marrone K, Brahmer JR, Forde PM, Hann C, Zheng L, Lee V, et al:
Steroid-refractory PD-(L)1 pneumonitis: Incidence, clinical
features, treatment, and outcomes. J Immunother Cancer.
9:e0017312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chuzi S, Tavora F, Cruz M, Costa R, Chae
YK, Carneiro BA and Giles FJ: Clinical features, diagnostic
challenges, and management strategies in checkpoint
inhibitor-related pneumonitis. Cancer Manag Res. 9:207–213. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Travis WD, Matsui K, Moss J and Ferrans
VJ: Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: Prognostic
significance of cellular and fibrosing patterns: Survival
comparison with usual interstitial pneumonia and desquamative
interstitial pneumonia. Am J Surg Pathol. 24:19–33. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kambouchner M, Levy P, Nicholson AG,
Schubel K, Magois E, Feuillet S, Valeyre D, Bernaudin JF and Nunes
H: Prognostic relevance of histological variants in nonspecific
interstitial pneumonia. Histopathology. 65:549–560. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsuo M, Yasumatsu R, Masuda M, Toh S,
Wakasaki T, Hashimoto K, Uchi R, Jiromaru R, Sato K, Manako T and
Nakagawa T: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease in recurrent
and/or metastatic head and neck cancer patients treated with
cetuximab and/or nivolumab. Oral Oncol. 113:1051292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McConnel FM and O'Connor A: Dysphagia
secondary to head and neck cancer surgery. Acta Otorhinolaryngol
Belg. 48:165–170. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Platteaux N, Dirix P, Dejaeger E and Nuyts
S: Dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients treated with
chemoradiotherapy. Dysphagia. 25:139–152. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Korpics MC, Turchan WT, Koshy M and
Spiotto MT: Decreased overall survival in patients with locally
advanced head and neck cancer receiving definitive radiotherapy and
concurrent cetuximab: National cancer database analysis. Head Neck.
44:1528–1544. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi
L, Ryerson CJ, Lederer DJ, Behr J, Cottin V, Danoff SK, Morell F,
et al: Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official
ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 198:e44–e68. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Skeoch S, Weatherley N, Swift AJ, Oldroyd
A, Johns C, Hayton C, Giollo A, Wild JM, Waterton JC, Buch M, et
al: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease: A systematic review. J
Clin Med. 7:3562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Spagnolo P, Bonniaud P, Rossi G,
Sverzellati N and Cottin V: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease.
Eur Respir J. 60:21027762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baumhäkel M, Kasel D, Rao-Schymanski RA,
Böcker R, Beckurts KT, Zaigler M, Barthold D and Fuhr U: Screening
for inhibitory effects of antineoplastic agents on CYP3A4 in human
liver microsomes. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 39:517–528. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gilbert CJ, Petros WP, Vredenburgh J,
Hussein A, Ross M, Rubin P, Fehdrau R, Cavanaugh C, Berry D,
McKinstry C and Peters WP: Pharmacokinetic interaction between
ondansetron and cyclophosphamide during high-dose chemotherapy for
breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 42:497–503. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|