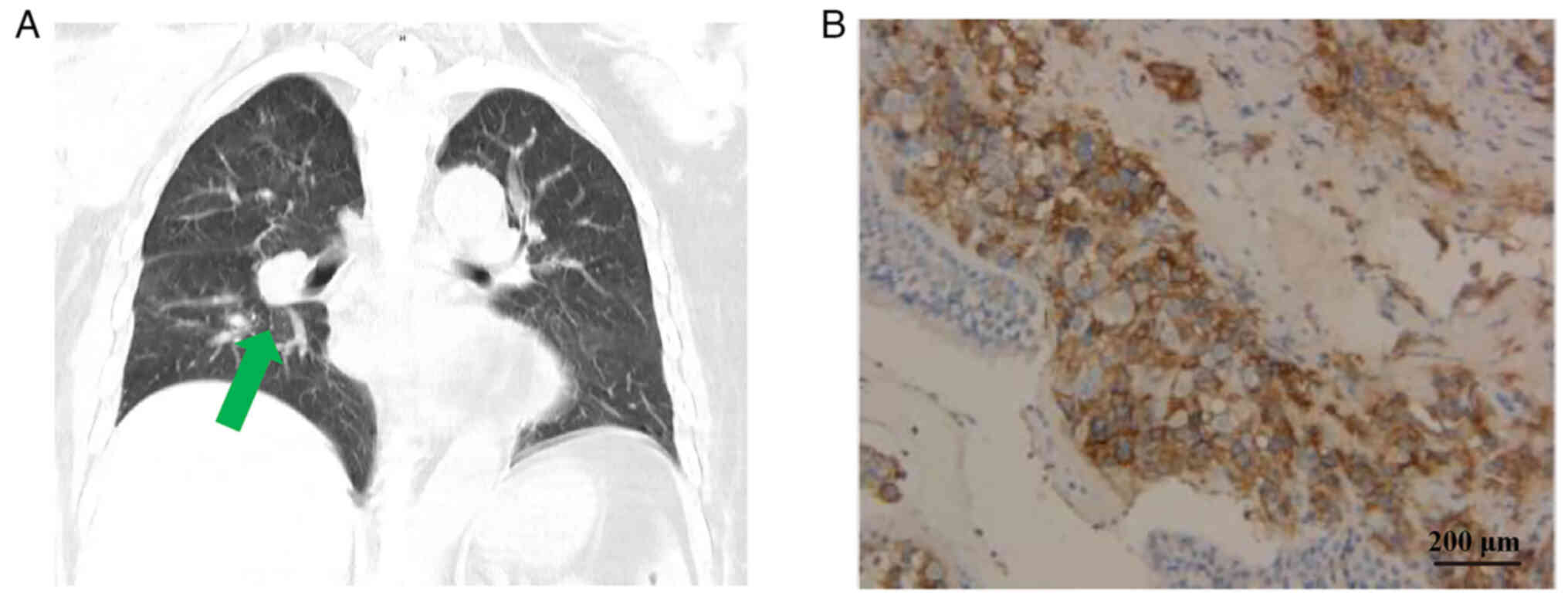
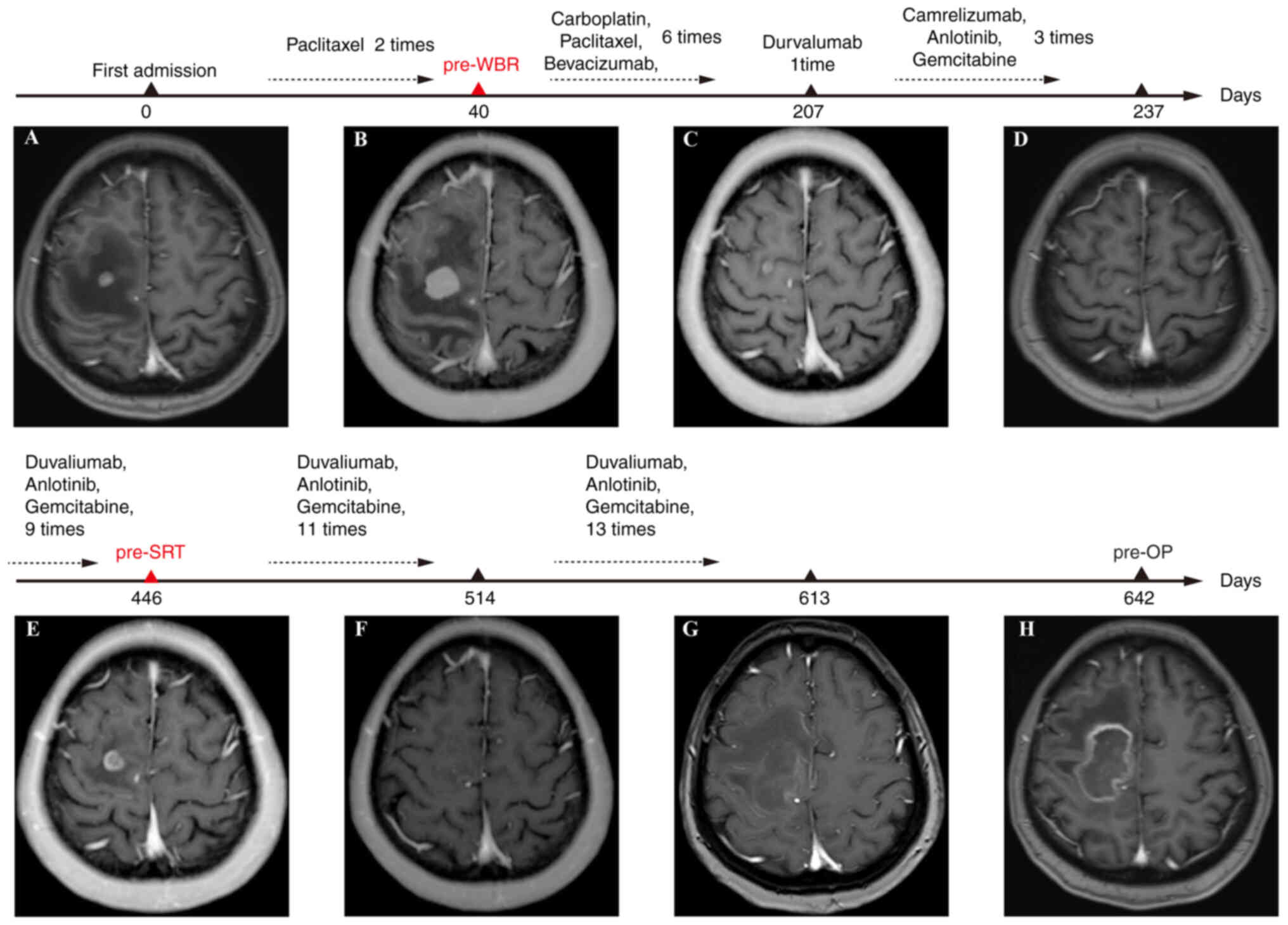
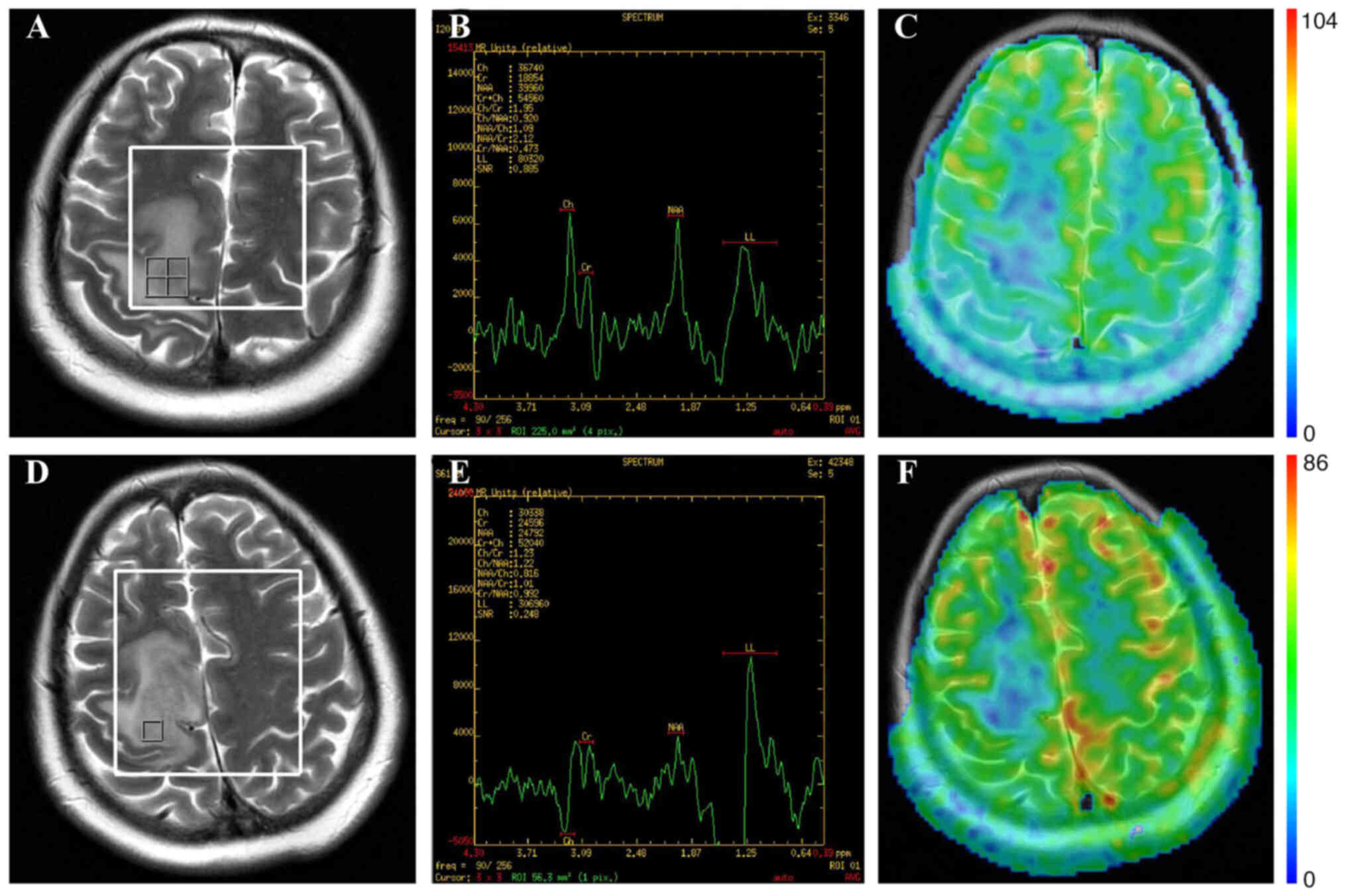
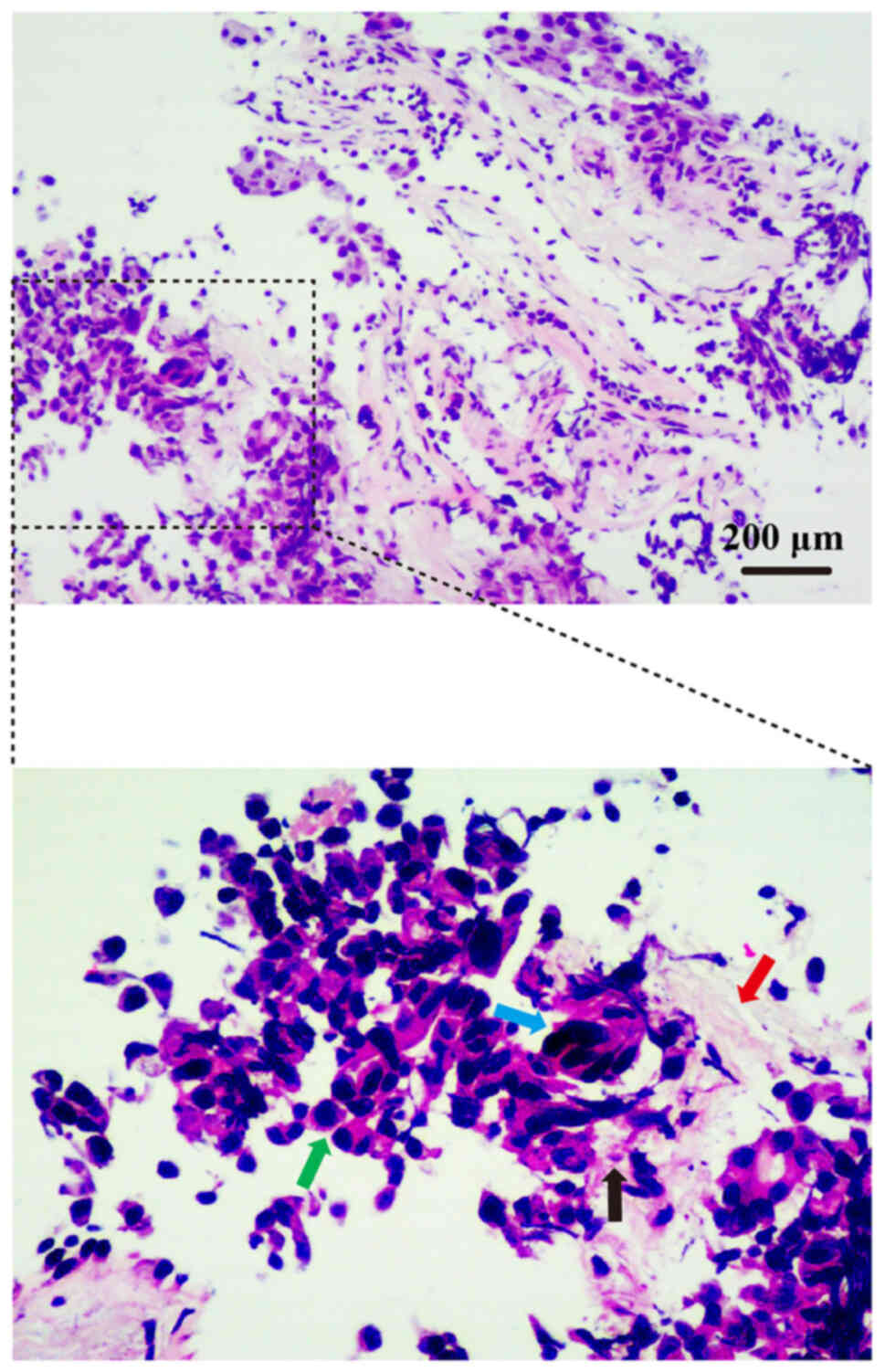
|
1
|
Achrol AS, Rennert RC, Anders C, Soffietti
R, Ahluwalia MS, Nayak L, Peters S, Arvold ND, Harsh GR, Steeg PS
and Chang SD: Brain metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5:52019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rybarczyk-Kasiuchnicz A, Ramlau R and
Stencel K: Treatment of brain metastases of non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 22:5932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang X, Zeng Y, Tan Q, Huang Z, Jia J and
Jiang G: Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors versus chemotherapy in
lung cancer with brain metastases: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Immunol Res. 2022:45188982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Horn L, Mansfield AS, Szczęsna A, Havel L,
Krzakowski M, Hochmair MJ, Huemer F, Losonczy G, Johnson ML, Nishio
M, et al: First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
379:2220–2229. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takamori S, Toyokawa G, Takada K, Shoji F,
Okamoto T and Maehara Y: Combination therapy of radiotherapy and
anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer: A
mini-review. Clin Lung Cancer. 19:12–16. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vellayappan B, Tan CL, Yong C, Khor LK,
Koh WY, Yeo TT, Detsky J, Lo S and Sahgal A: Diagnosis and
management of radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases.
Front Oncol. 8:3952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barajas RF, Chang JS, Sneed PK, Segal MR,
McDermott MW and Cha S: Distinguishing recurrent intra-axial
metastatic tumor from radiation necrosis following gamma knife
radiosurgery using dynamic susceptibility-weighted
contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
30:367–372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Forsyth PA, Kelly PJ, Cascino TL,
Scheithauer BW, Shaw EG, Dinapoli RP and Atkinson EJ: Radiation
necrosis or glioma recurrence: Is computer-assisted stereotactic
biopsy useful? J Neurosurg. 82:436–344. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Budimir N, Thomas GD, Dolina JS and
Salek-Ardakani S: Reversing T-cell exhaustion in cancer: Lessons
learned from PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Immunol
Res. 10:146–153. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gong X, Li X, Jiang T, Xie H, Zhu Z, Zhou
F and Zhou C: Combined radiotherapy and anti-PD-L1 antibody
synergistically enhances antitumor effect in non-small cell lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 12:1085–1097. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gupta A, Probst HC, Vuong V, Landshammer
A, Muth S, Yagita H, Schwendener R, Pruschy M, Knuth A and van den
Broek M: Radiotherapy promotes tumor-specific effector CD8+ T cells
via dendritic cell activation. J Immunol. 189:558–566. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hong JH, Chiang CS, Campbell IL, Sun JR,
Withers HR and McBride WH: Induction of acute phase gene expression
by brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 33:619–626.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hong JH, Chiang CS, Tsao CY, Lin PY,
McBride WH and Wu CJ: Rapid induction of cytokine gene expression
in the lung after single and fractionated doses of radiation. Int J
Radiat Biol. 75:1421–1427. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dovedi SJ, Adlard AL, Lipowska-Bhalla G,
McKenna C, Jones S, Cheadle EJ, Stratford IJ, Poon E, Morrow M,
Stewart R, et al: Acquired resistance to fractionated radiotherapy
can be overcome by concurrent PD-L1 blockade. Cancer Res.
74:5458–5468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luke JJ, Lemons JM, Karrison TG, Pitroda
SP, Melotek JM, Zha Y, Al-Hallaq HA, Arina A, Khodarev NN, Janisch
L, et al: Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab and
multisite stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with advanced
solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 36:1611–1618. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Theelen WSME, Peulen HMU, Lalezari F, van
der Noort V, de Vries JF, Aerts JGJV, Dumoulin DW, Bahce I,
Niemeijer AN, de Langen AJ, et al: Effect of pembrolizumab after
stereotactic body radiotherapy vs pembrolizumab alone on tumor
response in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer:
Results of the PEMBRO-RT phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA
Oncol. 5:1276–1282. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su Z, Zhou L, Xue J and Lu Y: Integration
of stereotactic radiosurgery or whole brain radiation therapy with
immunotherapy for treatment of brain metastases. Chin J Cancer Res.
32:448–466. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wen L, Tong F, Zhang R, Chen L, Huang Y
and Dong X: The research progress of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors
enhancing radiotherapy efficacy. Front Oncol. 11:7999572021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Trommer M, Adams A, Celik E, Fan J, Funken
D, Herter JM, Linde P, Morgenthaler J, Wegen S, Mauch C, et al:
Oncologic outcome and immune responses of radiotherapy with
anti-PD-1 treatment for brain metastases regarding timing and
benefiting subgroups. Cancers (Basel). 14:12402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente
D, Murakami S, Hui R, Yokoi T, Chiappori A, Lee KH, de Wit M, et
al: Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 377:1919–1929. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ahn JS, Ahn YC, Kim JH, Lee CG, Cho EK,
Lee KC, Chen M, Kim DW, Kim HK, Min YJ, et al: Multinational
randomized phase III trial with or without consolidation
chemotherapy using docetaxel and cisplatin after concurrent
chemoradiation in inoperable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer:
KCSG-LU05-04. J Clin Oncol. 33:2660–2666. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wozniak AJ, Moon J, Thomas CR Jr, Kelly K,
Mack PC, Gaspar LE, Raben D, Fitzgerald TJ, Pandya KJ and Gandara
DR: A pilot trial of cisplatin/etoposide/radiotherapy followed by
consolidation docetaxel and the combination of bevacizumab
(NSC-704865) in patients with inoperable locally advanced stage III
non-small-cell lung cancer: SWOG S0533. Clin Lung Cancer.
16:340–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mowery YM, Patel K, Chowdhary M, Rushing
CN, Roy Choudhury K, Lowe JR, Olson AC, Wisdom AJ, Salama JK, Hanks
BA, et al: Retrospective analysis of safety and efficacy of
anti-PD-1 therapy and radiation therapy in advanced melanoma: A
bi-institutional study. Radiother Oncol. 138:114–120. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhuang H, Shi S, Yuan Z and Chang JY:
Bevacizumab treatment for radiation brain necrosis: Mechanism,
efficacy and issues. Mol Cancer. 18:212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gonzalez J, Kumar AJ, Conrad CA and Levin
VA: Effect of bevacizumab on radiation necrosis of the brain. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 67:323–326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dashti SR, Kadner RJ, Folley BS, Sheehan
JP, Han DY, Kryscio RJ, Carter MB, Shields LBE, Plato BM, La Rocca
RV, et al: Single low-dose targeted bevacizumab infusion in adult
patients with steroid-refractory radiation necrosis of the brain: A
phase II open-label prospective clinical trial. J Neurosurg.
137:1676–1686. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Levin VA, Bidaut L, Hou P, Kumar AJ, Wefel
JS, Bekele BN, Grewal J, Prabhu S, Loghin M, Gilbert MR and Jackson
EF: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of bevacizumab
therapy for radiation necrosis of the central nervous system. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:1487–1495. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jeyaretna DS, Curry WT Jr, Batchelor TT,
Stemmer-Rachamimov A and Plotkin SR: Exacerbation of cerebral
radiation necrosis by bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol. 29:e159–e162.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fang P, Jiang W, Allen P, Glitza I, Guha
N, Hwu P, Ghia A, Phan J, Mahajan A, Tawbi H and Li J: Radiation
necrosis with stereotactic radiosurgery combined with CTLA-4
blockade and PD-1 inhibition for treatment of intracranial disease
in metastatic melanoma. J Neurooncol. 133:595–602. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pires da Silva I, Glitza IC, Haydu LE,
Johnpulle R, Banks PD, Grass GD, Goldinger SMA, Smith JL, Everett
AS, Koelblinger P, et al: Incidence, features and management of
radionecrosis in melanoma patients treated with cerebral
radiotherapy and anti-PD-1 antibodies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
32:553–563. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim JM, Miller JA, Kotecha R, Xiao R,
Juloori A, Ward MC, Ahluwalia MS, Mohammadi AM, Peereboom DM,
Murphy ES, et al: The risk of radiation necrosis following
stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent systemic therapies. J
Neurooncol. 133:357–368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Colaco RJ, Martin P, Kluger HM, Yu JB and
Chiang VL: Does immunotherapy increase the rate of radiation
necrosis after radiosurgical treatment of brain metastases? J
Neurosurg. 125:17–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Martin AM, Cagney DN, Catalano PJ,
Alexander BM, Redig AJ, Schoenfeld JD and Aizer AA: Immunotherapy
and symptomatic radiation necrosis in patients with brain
metastases treated with stereotactic radiation. JAMA Oncol.
4:1123–1124. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Weingarten N, Kruser TJ and Bloch O:
Symptomatic radiation necrosis in brain metastasis patients treated
with stereotactic radiosurgery and immunotherapy. Clin Neurol
Neurosurg. 179:14–18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Andring L, Squires B, Seymour Z, Fahim D,
Jacob J, Ye H, Marvin K and Grills I: Radionecrosis (RN) in
patients with brain metastases treated with stereotactic
radiosurgery (SRS) and immunotherapy. Int J Neurosci. 133:186–193.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R,
Kline R, Loeffler J and Farnan N: Single dose radiosurgical
treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors
and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90–05. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:291–298. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vaios EJ, Winter SF, Shih HA, Dietrich J,
Peters KB, Floyd SR, Kirkpatrick JP and Reitman ZJ: Novel
mechanisms and future opportunities for the management of radiation
necrosis in patients treated for brain metastases in the era of
immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 15:24322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yaman E, Buyukberber S, Benekli M, Oner Y,
Coskun U, Akmansu M, Ozturk B, Kaya AO, Uncu D and Yildiz R:
Radiation induced early necrosis in patients with malignant gliomas
receiving temozolomide. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 112:662–667. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Leeman JE, Clump DA, Flickinger JC, Mintz
AH, Burton SA and Heron DE: Extent of perilesional edema
differentiates radionecrosis from tumor recurrence following
stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Neuro Oncol.
15:1732–1738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Smith EJ, Naik A, Shaffer A, Goel M, Krist
DT, Liang E, Furey CG, Miller WK, Lawton MT, Barnett DH, et al:
Differentiating radiation necrosis from tumor recurrence: A
systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis comparing imaging
modalities. J Neurooncol. 162:15–23. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Le Fèvre C, Lhermitte B, Ahle G,
Chambrelant I, Cebula H, Antoni D, Keller A, Schott R, Thiery A,
Constans JM and Noël G: Pseudoprogression versus true progression
in glioblastoma patients: A multiapproach literature review: Part
1-molecular, morphological and clinical features. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 157:1031882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Lobato-Polo J, Zorro
O, Flickinger JC and Lunsford LD: T1/T2 matching to differentiate
tumor growth from radiation effects after stereotactic
radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 66:486–491. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kumar AJ, Leeds NE, Fuller GN, Van Tassel
P, Maor MH, Sawaya RE and Levin VA: Malignant gliomas: MR imaging
spectrum of radiation therapy- and chemotherapy-induced necrosis of
the brain after treatment. Radiology. 217:377–384. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Parvez K, Parvez A and Zadeh G: The
diagnosis and treatment of pseudoprogression, radiation necrosis
and brain tumor recurrence. Int J Mol Sci. 15:11832–11846. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zikou A, Sioka C, Alexiou GA, Fotopoulos
A, Voulgaris S and Argyropoulou MI: Radiation necrosis,
pseudoprogression, pseudoresponse, and tumor recurrence: Imaging
challenges for the evaluation of treated gliomas. Contrast Media
Mol Imaging. 2018:68283962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Metaweh NAK, Azab AO, El Basmy AAH,
Mashhour KN and El Mahdy WM: Contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging
to differentiate between recurrent/residual brain neoplasms and
radiation necrosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 19:941–948.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miyatake SI, Nonoguchi N, Furuse M,
Yoritsune E, Miyata T, Kawabata S and Kuroiwa T: Pathophysiology,
diagnosis, and treatment of radiation necrosis in the brain. Neurol
Med Chir (Tokyo). 55 (Suppl 1):S50–S59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mayo ZS, Halima A, Broughman JR, Smile TD,
Tom MC, Murphy ES, Suh JH, Lo SS, Barnett GH, Wu G, et al:
Radiation necrosis or tumor progression? A review of the
radiographic modalities used in the diagnosis of cerebral radiation
necrosis. J Neurooncol. 161:23–31. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zeng QS, Li CF, Liu H, Zhen JH and Feng
DC: Distinction between recurrent glioma and radiation injury using
magnetic resonance spectroscopy in combination with
diffusion-weighted imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
68:151–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rock JP, Scarpace L, Hearshen D, Gutierrez
J, Fisher JL, Rosenblum M and Mikkelsen T: Associations among
magnetic resonance spectroscopy, apparent diffusion coefficients,
and image-guided histopathology with special attention to radiation
necrosis. Neurosurgery. 54:1111–1119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kamada K, Houkin K, Abe H, Sawamura Y and
Kashiwaba T: Differentiation of cerebral radiation necrosis from
tumor recurrence by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurol
Med Chir (Tokyo). 37:250–256. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shah R, Vattoth S, Jacob R, Manzil FF,
O'Malley JP, Borghei P, Patel BN and Curé JK: Radiation necrosis in
the brain: Imaging features and differentiation from tumor
recurrence. Radiographics. 32:1343–1359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hattingen E, Bähr O, Rieger J, Blasel S,
Steinbach J and Pilatus U: Phospholipid metabolites in recurrent
glioblastoma: In vivo markers detect different tumor phenotypes
before and under antiangiogenic therapy. PLoS One. 8:e564392013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hattingen E, Jurcoane A, Bähr O, Rieger J,
Magerkurth J, Anti S, Steinbach JP and Pilatus U: Bevacizumab
impairs oxidative energy metabolism and shows antitumoral effects
in recurrent glioblastomas: A 31P/1H MRSI and quantitative magnetic
resonance imaging study. Neuro Oncol. 13:1349–1363. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Turnquist C, Harris BT and Harris CC:
Radiation-induced brain injury: Current concepts and therapeutic
strategies targeting neuroinflammation. Neurooncol Adv.
2:vdaa0572020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Katsura M, Sato J, Akahane M, Furuta T,
Mori H and Abe O: Recognizing radiation-induced changes in the
central nervous system: Where to look and what to look for.
Radiographics. 41:224–248. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nonoguchi N, Miyatake S, Fukumoto M,
Furuse M, Hiramatsu R, Kawabata S, Kuroiwa T, Tsuji M, Fukumoto M
and Ono K: The distribution of vascular endothelial growth
factor-producing cells in clinical radiation necrosis of the brain:
Pathological consideration of their potential roles. J Neurooncol.
105:423–431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yoshii Y: Pathological review of late
cerebral radionecrosis. Brain Tumor Pathol. 25:51–58. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|