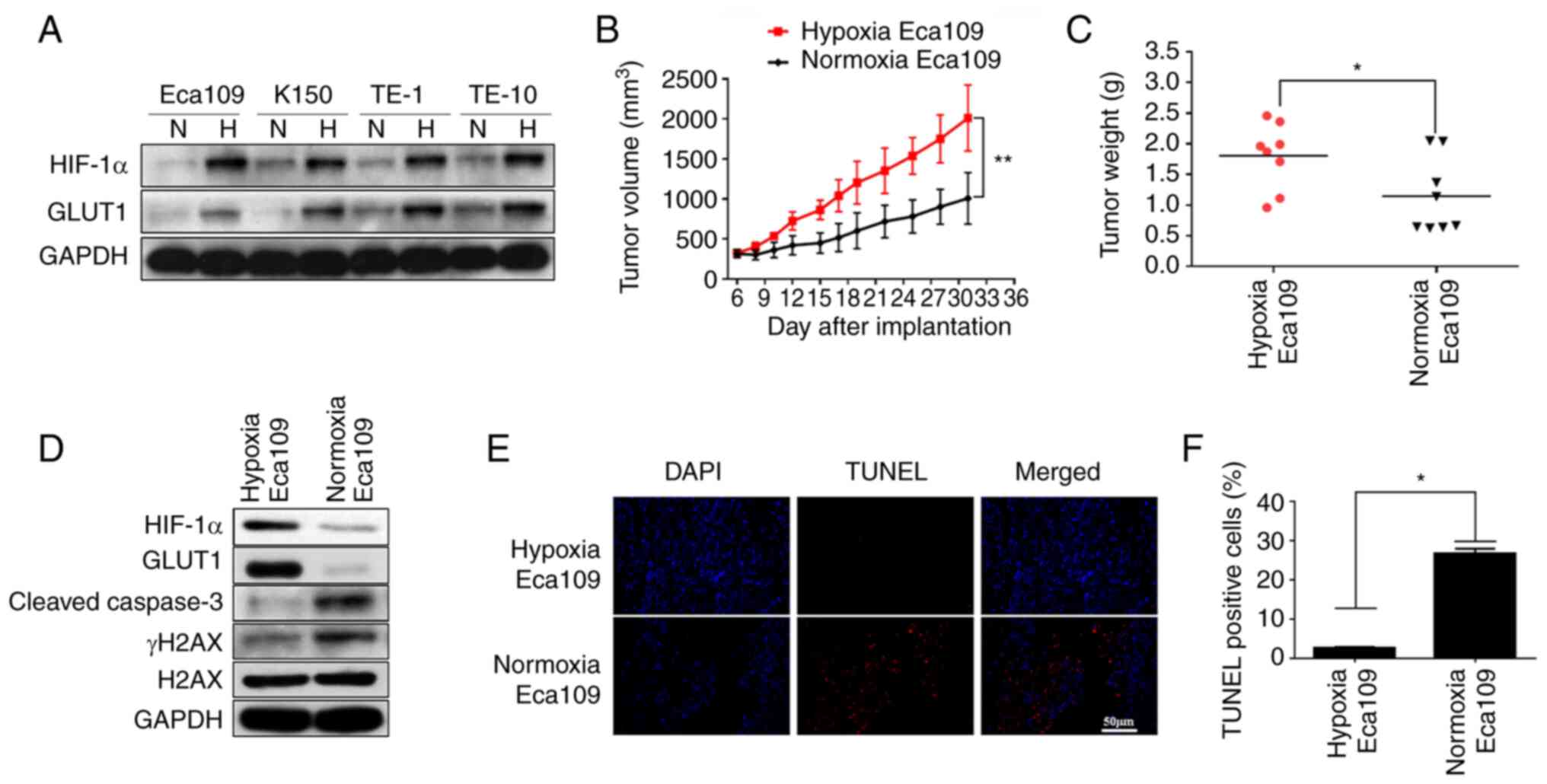
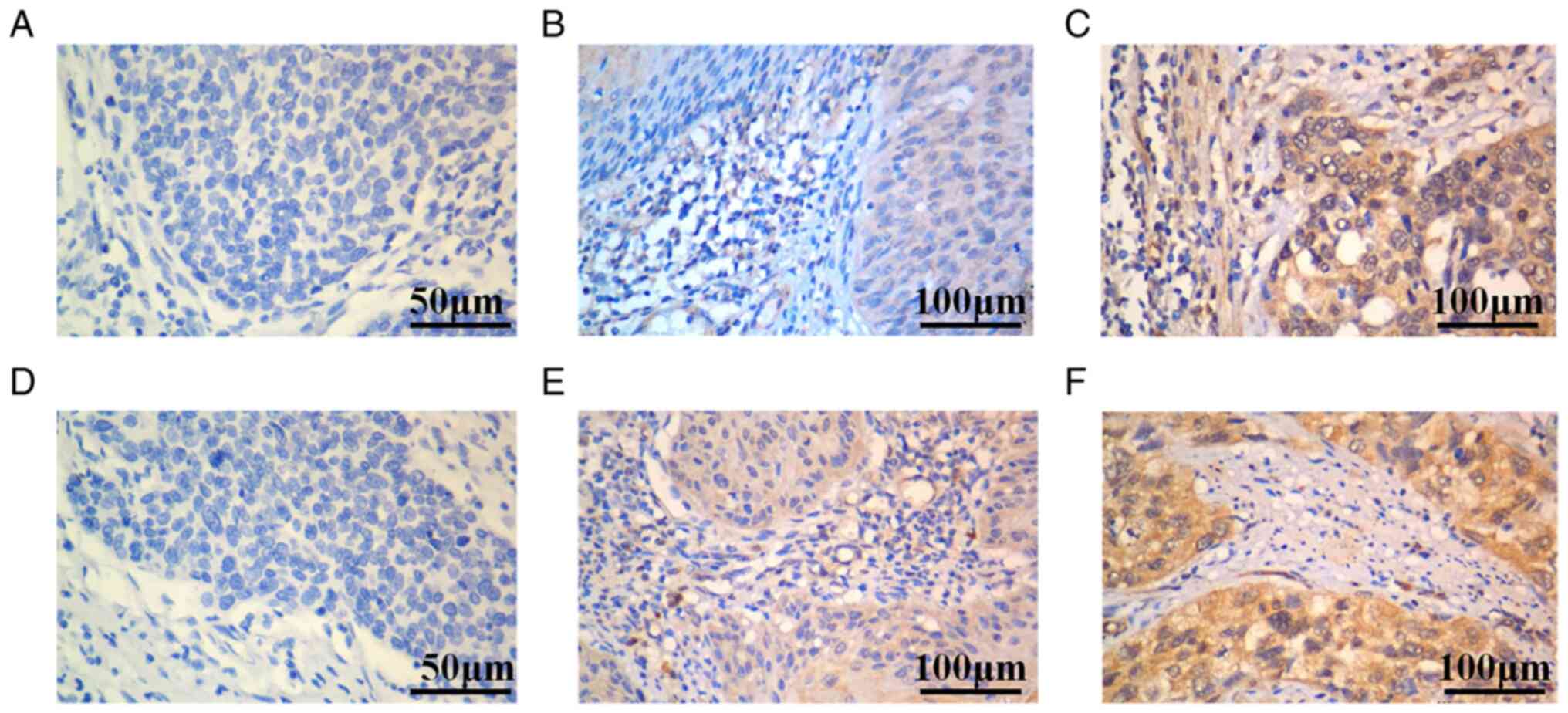
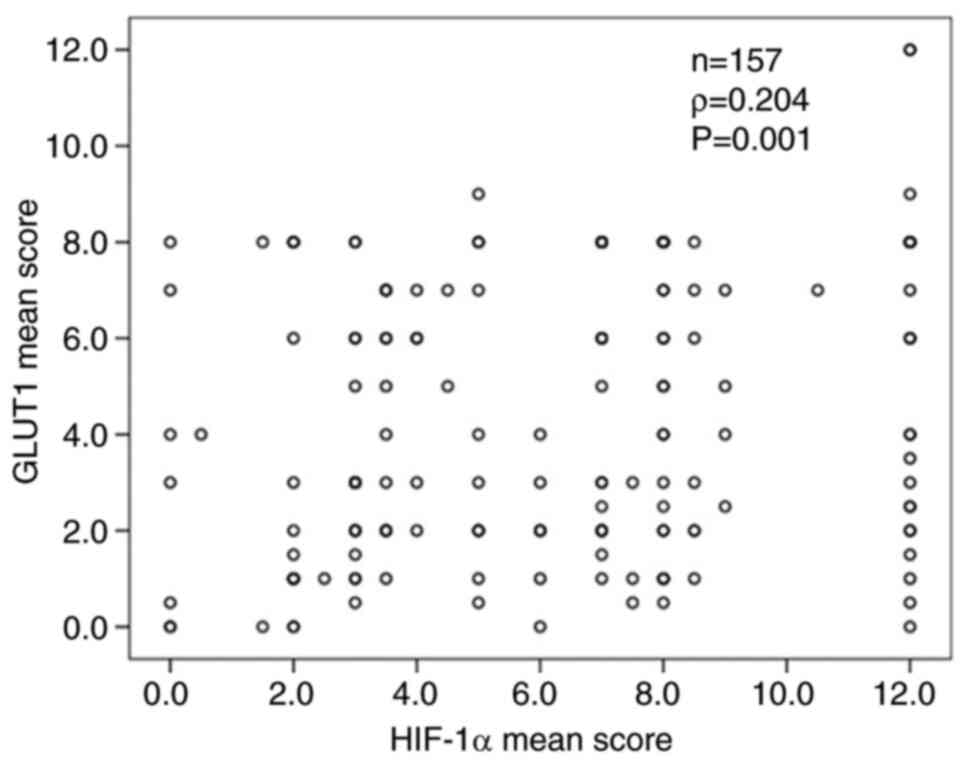
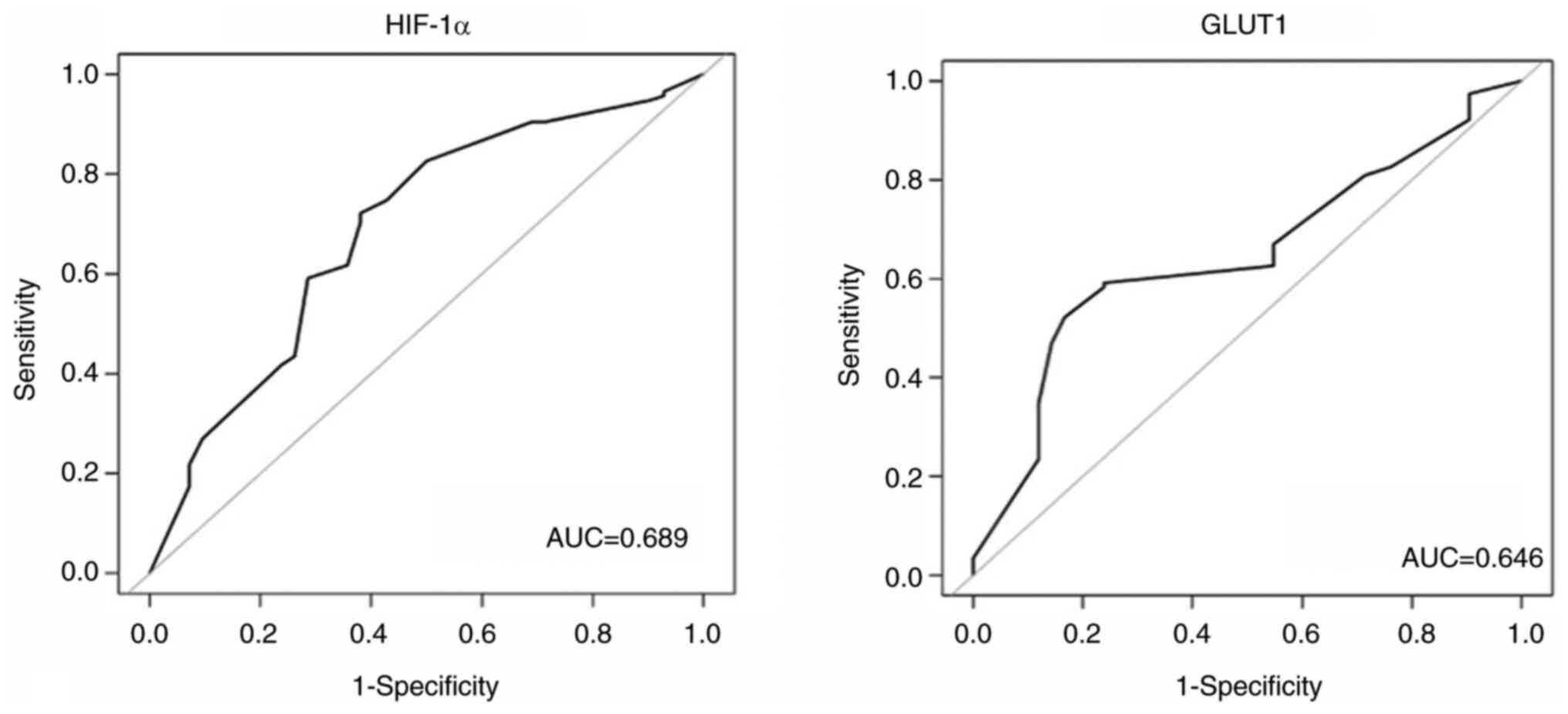
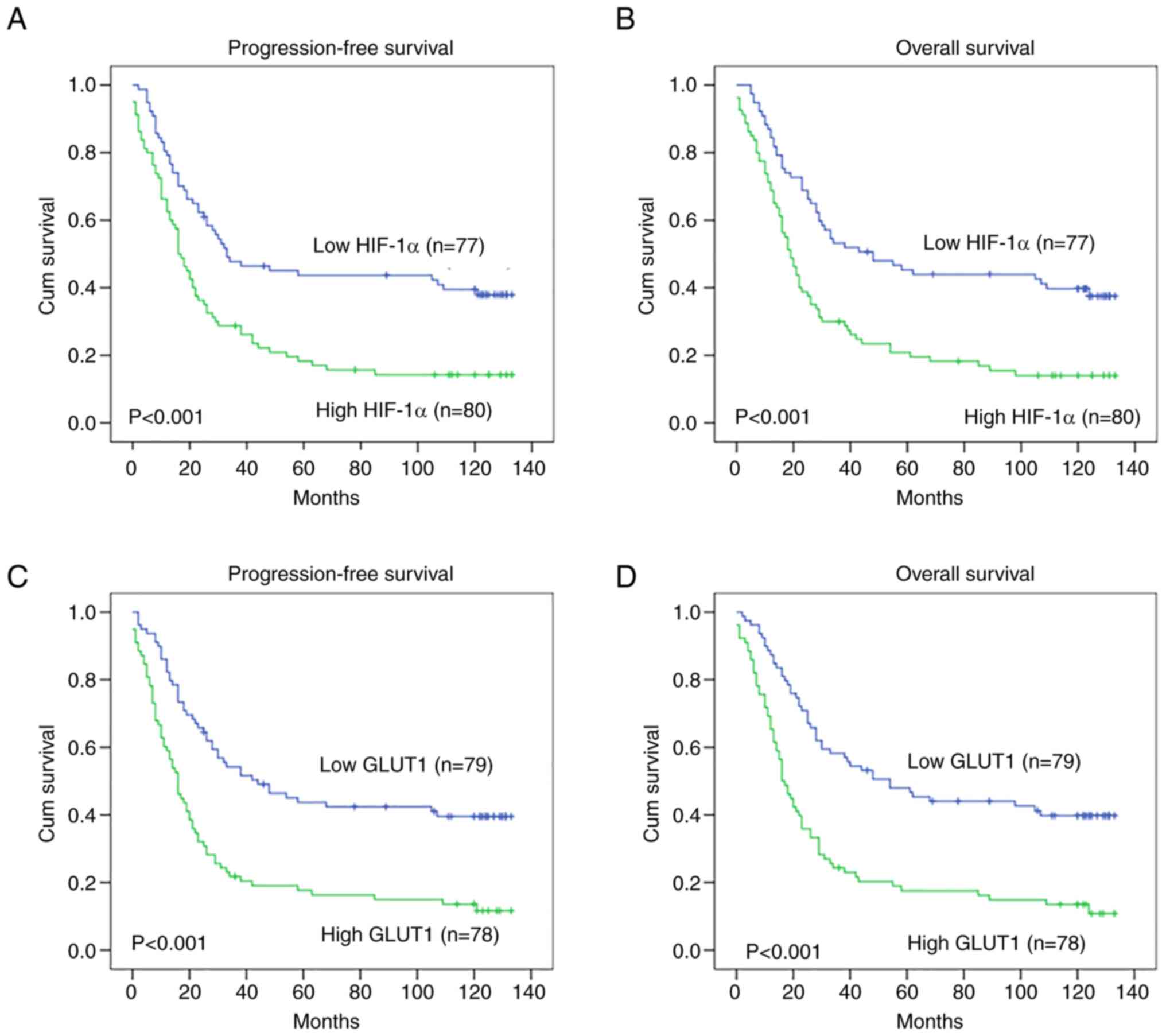
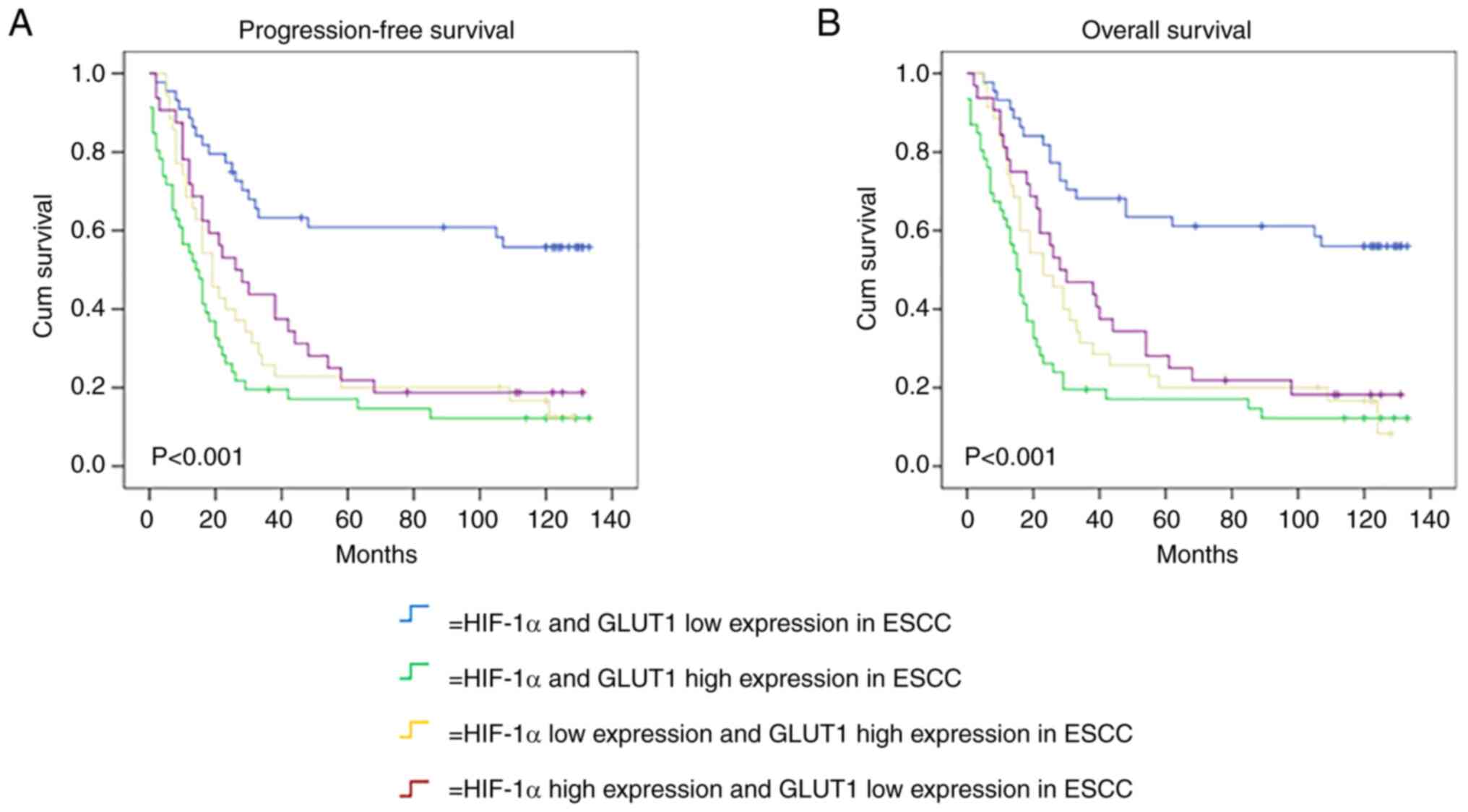
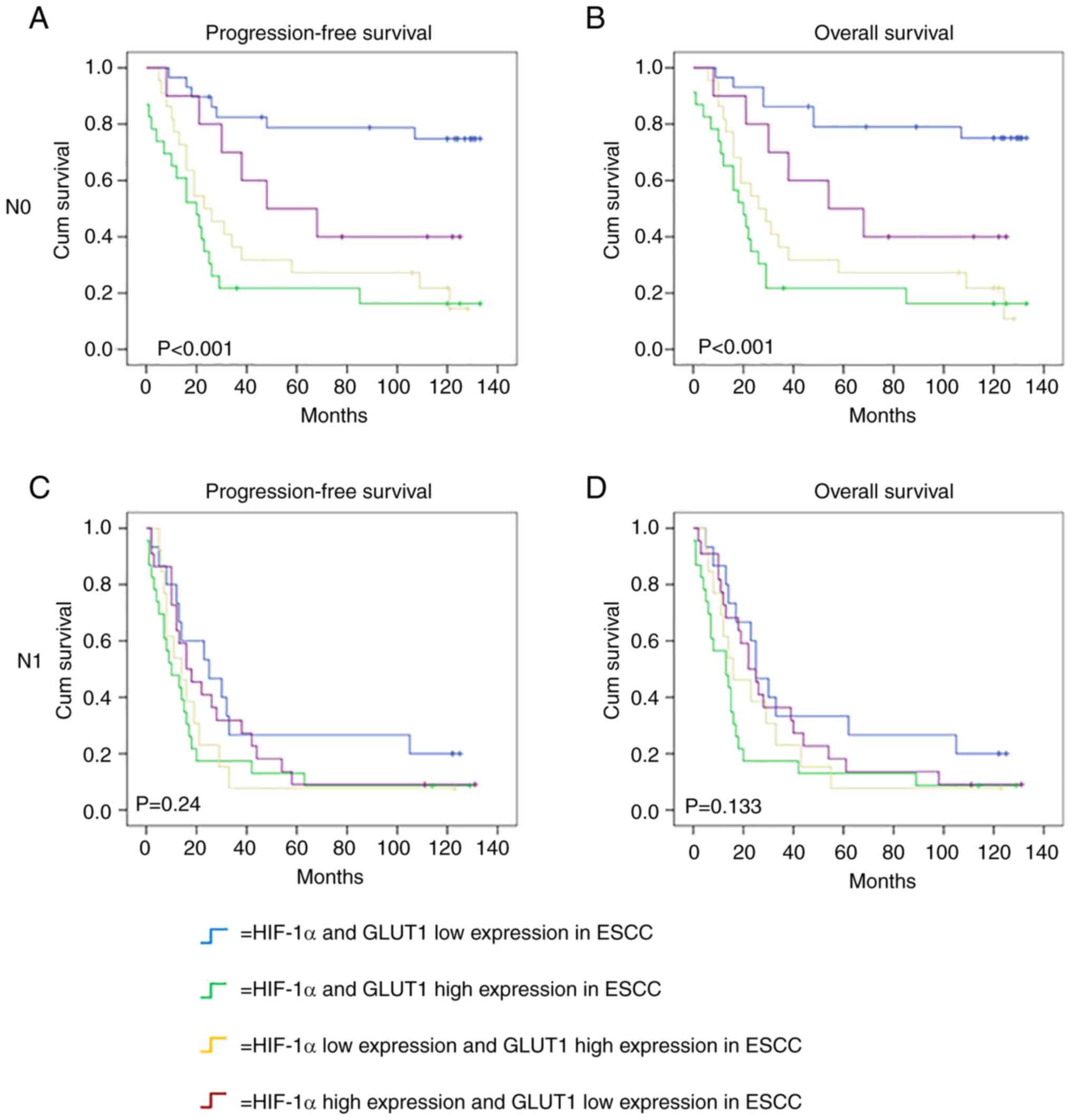
|
1
|
Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Sun KX, Chen R, Wang
SM, Li L, Zeng HM, Wei WW and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2016. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 45:212–220. 2023.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J and Pouyssegur
J: Hypoxia and cancer. J Mol Med (Berl). 85:1301–1307. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH and Kim
KW: Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: Its protein stability
and biological functions. Exp Mol Med. 36:1–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen C, Pore N, Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F
and Maity A: Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible
factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J Biol Chem.
276:9519–9525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Airley RE and Mobasheri A: Hypoxic
regulation of glucose transport, anaerobic metabolism and
angiogenesis in cancer: Novel pathways and targets for anticancer
therapeutics. Chemotherapy. 53:233–256. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Song K, Li M, Xu XJ, Xuan L, Huang GN,
Song XL and Liu QF: HIF-1α and GLUT1 gene expression is associated
with chemoresistance of acute myeloid leukemia. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:1823–1829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coleman CN: Modulating the radiation
response. Stem Cells. 14:10–15. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaira K, Murakami H, Endo M, Ohde Y, Naito
T, Kondo H, Nakajima T, Yamamoto N and Takahashi T: Biological
correlation of 18F-FDG uptake on PET in pulmonary
neuroendocrine tumors. Anticancer Res. 33:4219–4228.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen B, Tang H, Liu X, Liu P, Yang L, Xie
X, Ye F, Song C, Xie X and Wei W: miR-22 as a prognostic factor
targets glucose transporter protein type 1 in breast cancer. Cancer
Lett. 356:410–417. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim BW, Cho H, Chung JY, Conway C, Ylaya
K, Kim JH and Hewitt SM: Prognostic assessment of hypoxia and
metabolic markers in cervical cancer using automated digital image
analysis of immunohistochemistry. J Transl Med. 11:1852013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Osugi J, Yamaura T, Muto S, Okabe N,
Matsumura Y, Hoshino M, Higuchi M, Suzuki H and Gotoh M: Prognostic
impact of the combination of glucose transporter 1 and ATP citrate
lyase in node-negative patients with non-small lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 88:310–318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tohma T, Okazumi S, Makino H, Cho A,
Mochizuki R, Shuto K, Kudo H, Matsubara K, Gunji H, Matsubara H and
Ochiai T: Overexpression of glucose transporter 1 in esophageal
squamous cell carcinomas: A marker for poor prognosis. Dis
Esophagus. 18:185–189. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiba I, Ogawa K, Morioka T, Shimoji H,
Sunagawa N, Iraha S, Nishimaki T, Yoshimi N and Murayama S:
Clinical significance of GLUT-1 expression in patients with
esophageal cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Oncol
Lett. 2:21–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Waters JK and Reznik SI: Update on
management of squamous cell esophageal cancer. Curr Oncol Rep.
24:375–385. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He S, Xu J, Liu X and Zhen Y: Advances and
challenges in the treatment of esophageal cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B.
11:3379–3392. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ajduković J: HIF-1-a big chapter in the
cancer tale. Exp Oncol. 38:9–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang K, Toyozumi T, Murakami K, Sakata H,
Kano M, Endo S, Matsumoto Y, Suito H, Takahashi M, Sekino N, et al:
HIF-1α stimulates the progression of oesophageal squamous cell
carcinoma by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Br J
Cancer. 127:474–487. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dhani N, Fyles A, Hedley D and Milosevic
M: The clinical significance of hypoxia in human cancers. Semin
Nucl Med. 45:110–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu H, Zhang Z, Zhou S, Liu X, Li G, Song
B and Xu W: Claudin-1/4 as directly target gene of HIF-1α can
feedback regulating HIF-1α by PI3K-AKT-mTOR and impact the
proliferation of esophageal squamous cell though Rho GTPase and
p-JNK pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 29:665–682. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moreno-Acosta P, Vallard A, Carrillo S,
Gamboa O, Romero-Rojas A, Molano M, Acosta J, Mayorga D, Rancoule
C, Garcia MA, et al: Biomarkers of resistance to radiation therapy:
A prospective study in cervical carcinoma. Radiat Oncol.
12:1202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen SW, Shen WC, Lin YC, Chen RY, Hsieh
TC, Yen KY and Kao CH: Correlation of pretreatment
18F-FDG PET tumor textural features with gene expression
in pharyngeal cancer and implications for radiotherapy-based
treatment outcomes. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 44:567–580. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Batchelor TT, Sorensen AG, di Tomaso E,
Zhang WT, Duda DG, Cohen KS, Kozak KR, Cahill DP, Chen PJ, Zhu M,
et al: AZD2171, a pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma
patients. Cancer Cell. 11:83–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu M, Yongzhi H, Chen S, Luo X, Lin Y,
Zhou Y, Jin H, Hou B, Deng Y, Tu L and Jian Z: The prognostic value
of GLUT1 in cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Oncotarget. 8:43356–43367. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carvalho KC, Cunha IW, Rocha RM, Ayala FR,
Cajaíba MM, Begnami MD, Vilela RS, Paiva GR, Andrade RG and Soares
FA: GLUT1 expression in malignant tumors and its use as an
immunodiagnostic marker. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 66:965–972. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brown RS and Wahl RL: Overexpression of
Glut-1 glucose transporter in human breast cancer. An
immunohistochemical study. Cancer. 72:2979–2985. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Ye C, Chen C, Xiong H, Xie B, Zhou
J, Chen Y, Zheng S and Wang L: Glucose transporter GLUT1 expression
and clinical outcome in solid tumors: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 8:16875–16886. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ping W, Sun W, Zu Y, Chen W and Fu X:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:
A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:4401–4409. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jun YJ, Jang SM, Han HL, Lee KH, Jang KS
and Paik SS: Clinicopathologic significance of GLUT1 expression and
its correlation with Apaf-1 in colorectal adenocarcinomas. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:1866–1873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun G, Hu W, Lu Y and Wang Y: A
meta-analysis of HIF-1α and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
(ESCC) risk. Pathol Oncol Res. 19:685–693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Esteban MA, Tran MG, Harten SK, Hill P,
Castellanos MC, Chandra A, Raval R, O'brien TS and Maxwell PH:
Regulation of E-cadherin expression by VHL and hypoxia-inducible
factor. Cancer Res. 66:3567–3575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fillies T, Werkmeister R, van Diest PJ,
Brandt B, Joos U and Buerger H: HIF1-alpha overexpression indicates
a good prognosis in early stage squamous cell carcinomas of the
oral floor. BMC Cancer. 5:842005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shao N, Han Y, Song L and Song W: Clinical
significance of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, and its correlation
with p53 and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in
resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther.
16:269–275. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zimna A and Kurpisz M: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 in physiological and pathophysiological angiogenesis:
Applications and therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2015:5494122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang L, Ye SB, Li ZL, Ma G, Chen SP, He
J, Liu WL, Xie D, Zeng YX and Li J: Increased HIF-1alpha expression
in tumor cells and lymphocytes of tumor microenvironments predicts
unfavorable survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3887–3897. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheng J, Yang HL, Gu CJ, Liu YK, Shao J,
Zhu R, He YY, Zhu XY and Li MQ: Melatonin restricts the viability
and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells by suppressing
HIF-1α/ROS/VEGF. Int J Mol Med. 43:945–955. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie L, Wang Y, Li Q, Ji X, Tu Y, Du S, Lou
H, Zeng X, Zhu L, Zhang J and Zhu M: The
HIF-1α/p53/miRNA-34a/Klotho axis in retinal pigment epithelial
cells promotes subretinal fibrosis and exacerbates choroidal
neovascularization. J Cell Mol Med. 25:1700–1711. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|