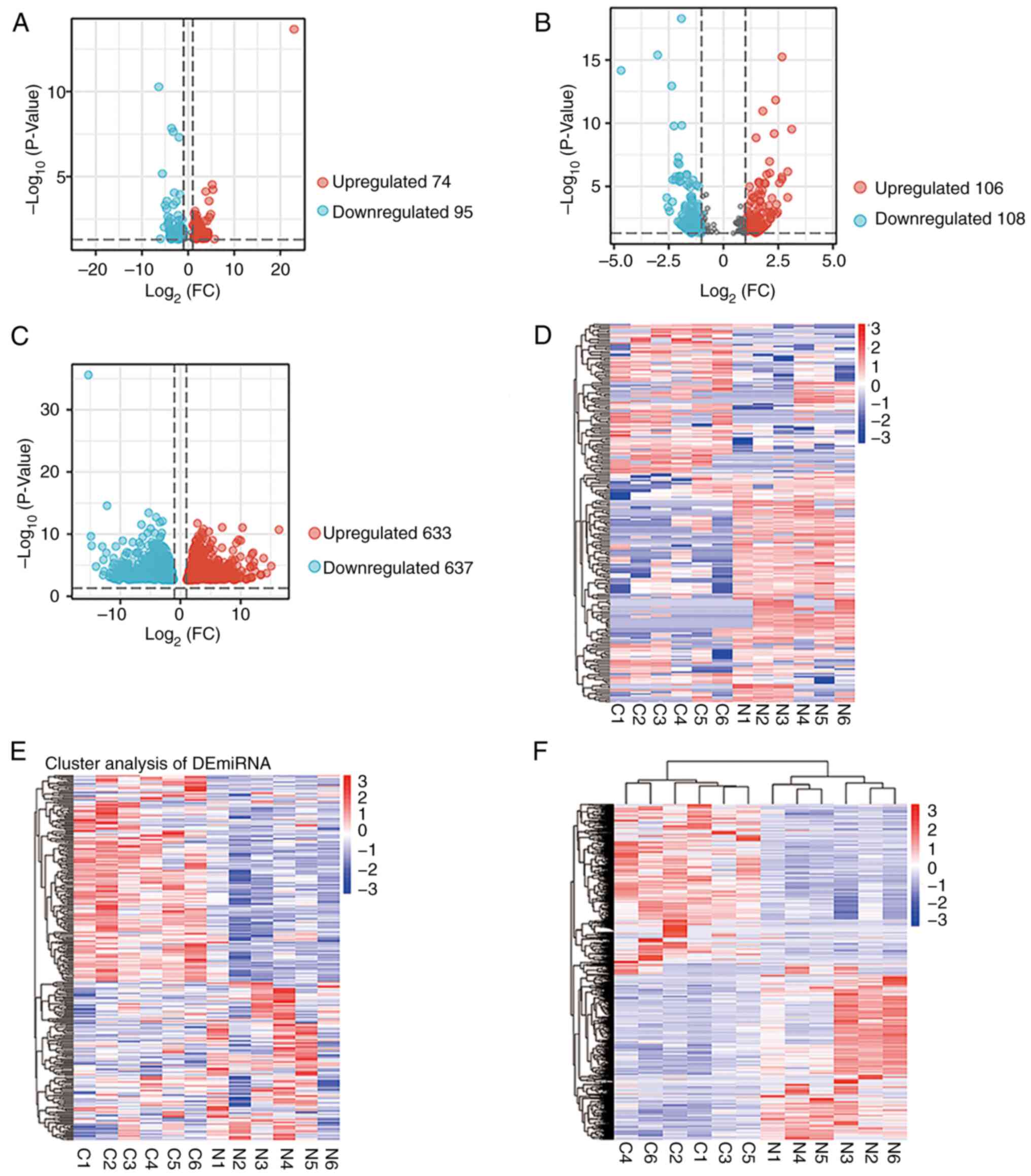
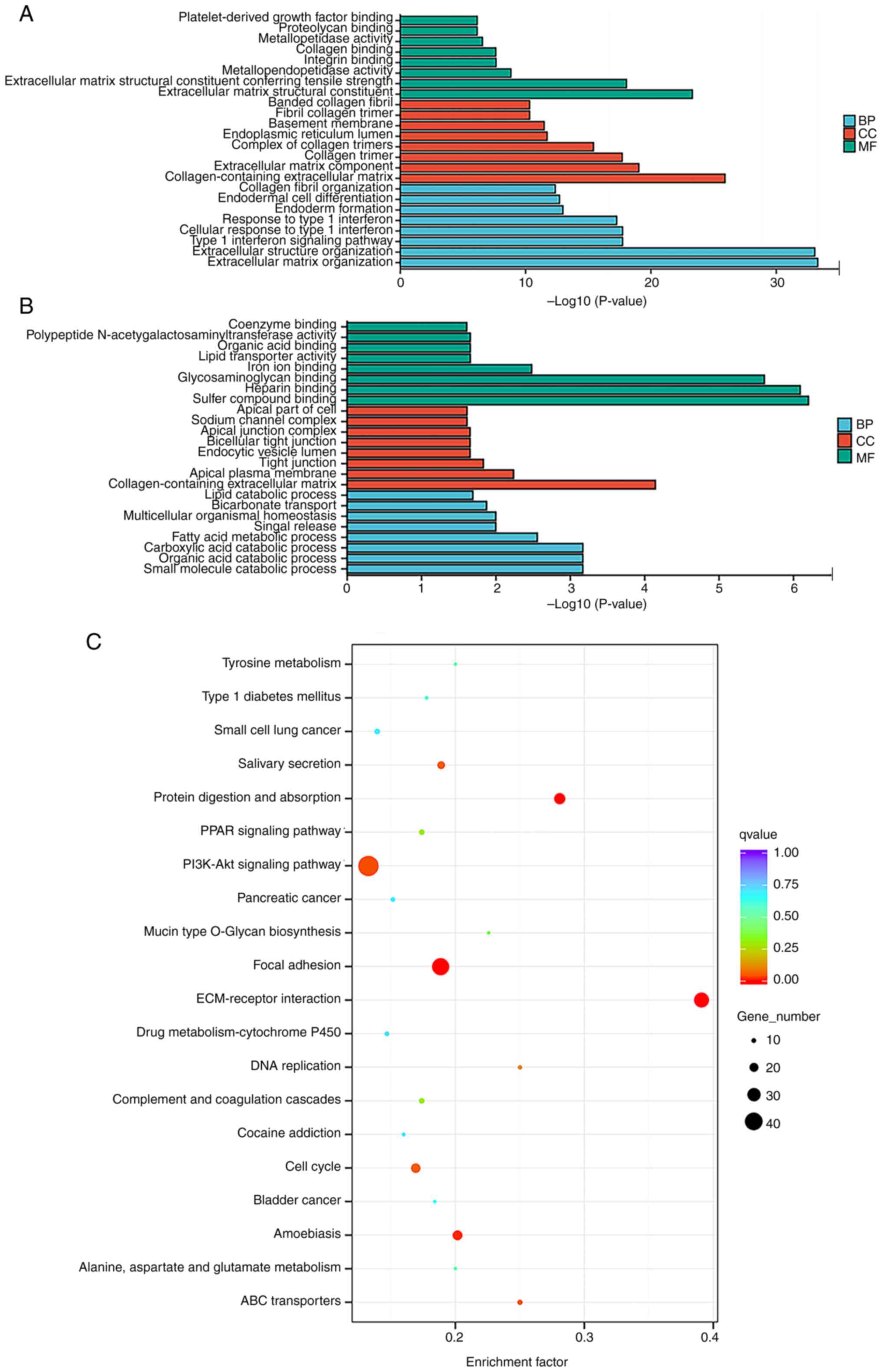
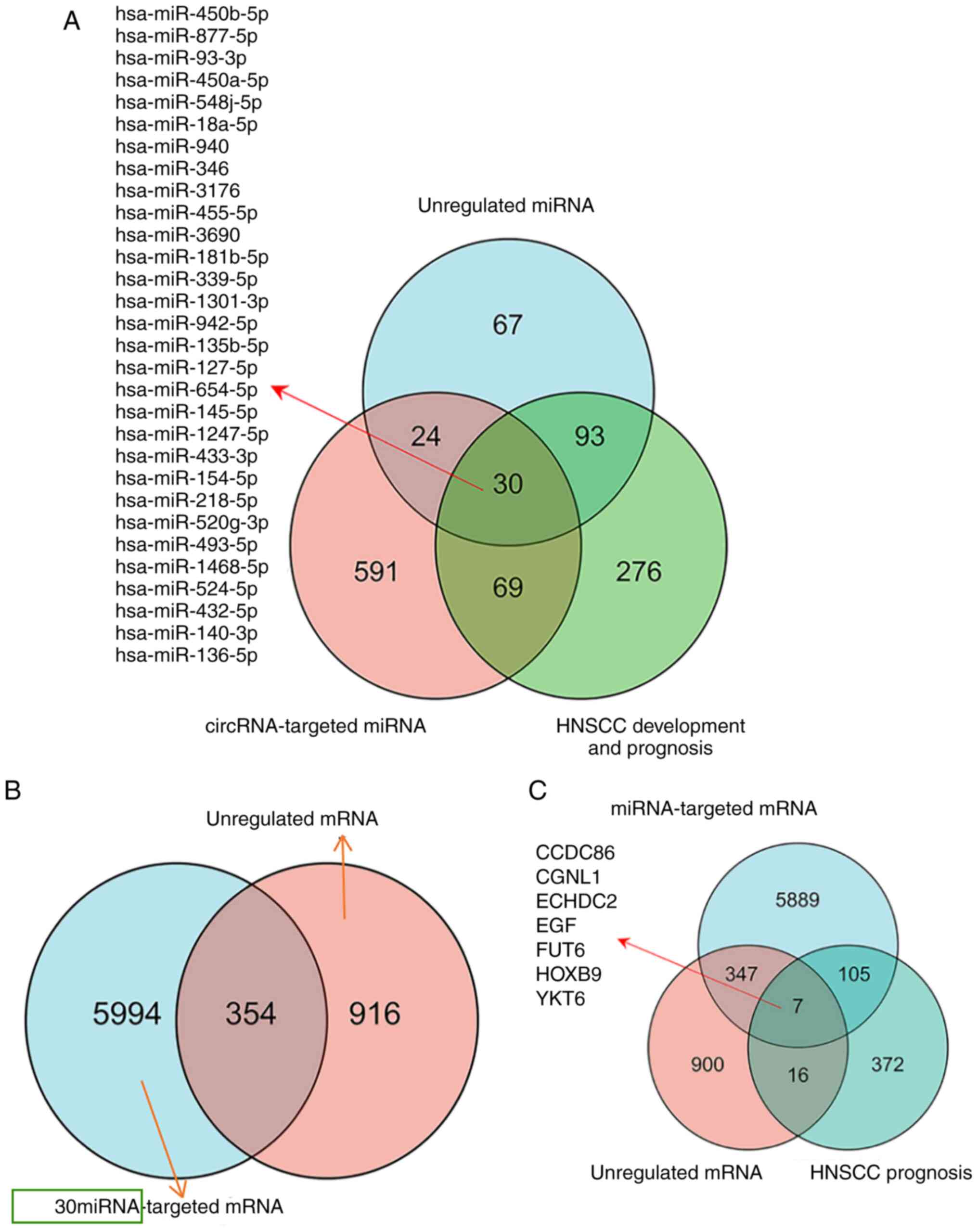
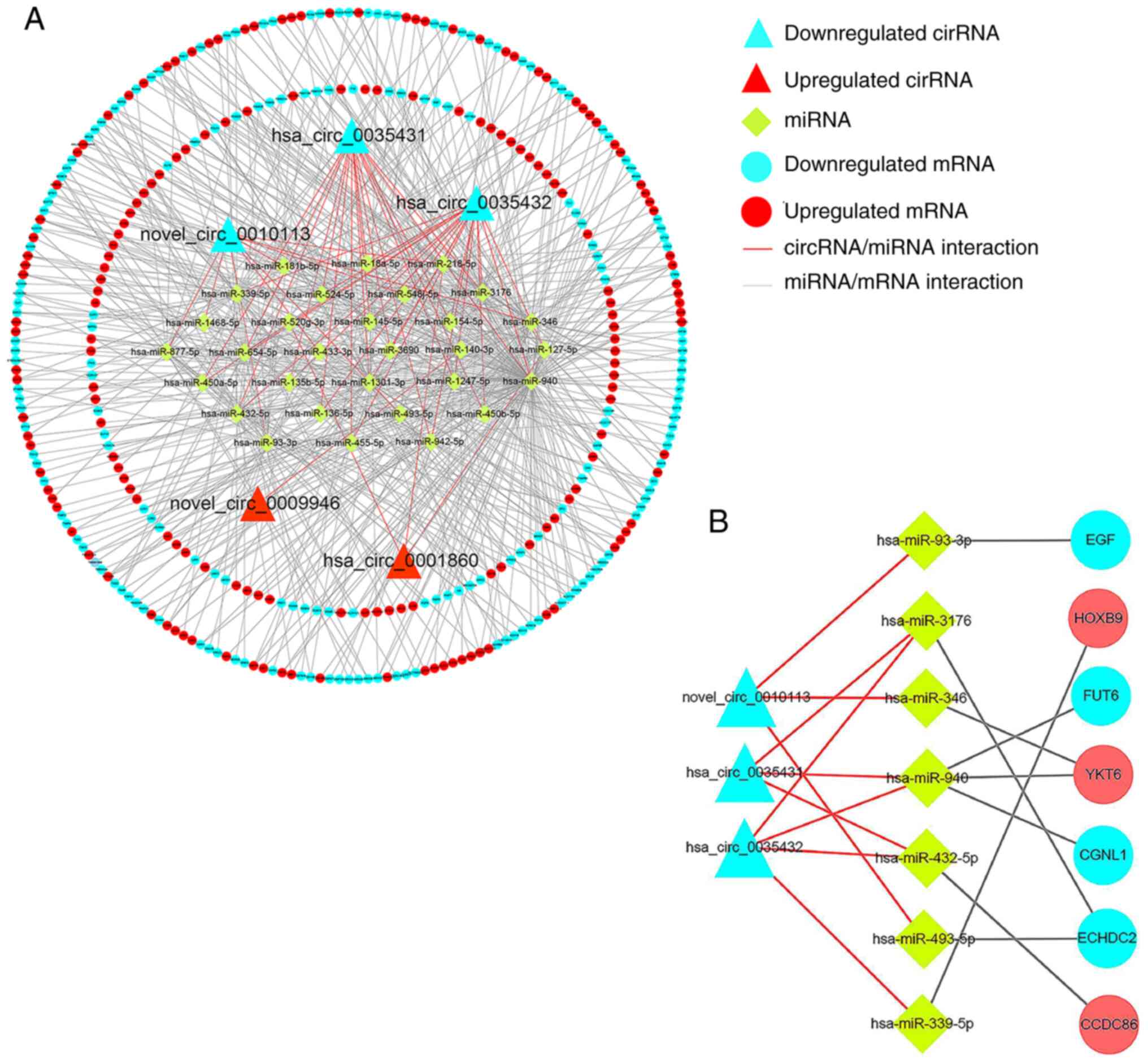
|
1
|
Chow L: Head and neck cancer. N Engl J
Med. 382:60–72. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang J, Chen X, Tian Y, Zhu G, Qin Y, Chen
X, Pi L, Wei M, Liu G, Li Z, et al: Six-gene signature for
predicting survival in patients with head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 12:767–783. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garbo S, Maione R, Tripodi M and
Battistelli C: Next RNA therapeutics: The mine of Non-coding. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:74712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang X, Ren H, Guo M, Qian J, Yang Y and
Gu C: Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in
cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 19:910–928. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qiu S, Li B, Xia Y, Xuan Z, Li Z, Xie L,
Gu C, Lv J, Lu C, Jiang T, et al: CircTHBS1 drives gastric cancer
progression by increasing INHBA mRNA expression and stability in a
ceRNA- and RBP-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 13:2662022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang J, Qi M, Fei X, Wang X and Wang K:
Hsa_circRNA_0088036 acts as a ceRNA to promote bladder cancer
progression by sponging miR-140-3p. Cell Death Dis. 13:3222022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mo M, Liu B, Luo Y, Tan J, Zeng X, Zeng X,
Huang D, Li C, Liu S and Qiu X: Construction and comprehensive
analysis of a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network to reveal the
pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci.
9:8014782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nath M, Roy D and Choudhury Y: Circular
RNAs are potential prognostic markers of head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma: Findings of a Meta-analysis study. Front Oncol.
12:7824392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Dai F, Lu Y, Dai
L, Niu M, Guo H, Li W, Xue X, et al: Circular RNA circCORO1C
promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by
modulating the let-7c-5p/PBX3 axis. Mol Cancer. 19:992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Robinson MD, Mccarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK and
Oshlack A: Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for
selection bias. Genome Biol. 11:R142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ke MJ, Ji LD and Li YX: Explore prognostic
marker of colorectal cancer based on ceRNA network. J Cell Biochem.
120:19358–19370. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kruger J and Rehmsmeier M: RNAhybrid:
microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids
Res. 34:W451–W454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Knapek KJ, Georges HM, Van Campen H,
Bishop JV, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Smirnova NP and Hansen TR: Fetal
lymphoid organ immune responses to transient and persistent
infection with bovine viral diarrhea virus. Viruses. 12:8162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garcia-Hidalgo MC, Gonzalez J, Benitez ID,
Carmona P, Santisteve S, Perez-Pons M, Moncusi-Moix A,
Gort-Paniello C, Rodriguez-Jara F, Molinero M, et al:
Identification of circulating microRNA profiles associated with
pulmonary function and radiologic features in survivors of
SARS-CoV-2-induced ARDS. Emerg Microbes Infect. 11:1537–1549. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A,
Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F,
et al: Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature.
489:101–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Diao L and Han L: Small
non-coding RNAs in human cancer: Function, clinical utility, and
characterization. Oncogene. 40:1570–1577. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yousefi H, Maheronnaghsh M, Molaei F,
Mashouri L, Reza AA, Momeny M and Alahari SK: Long noncoding RNAs
and exosomal lncRNAs: Classification, and mechanisms in breast
cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Oncogene. 39:953–974. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo L, Jia L, Luo L, Xu X, Xiang Y, Ren Y,
Ren D, Shen L and Liang T: Critical roles of circular RNA in tumor
metastasis via acting as a sponge of miRNA/isomiR. Int J Mol Sci.
23:70242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Prats AC, David F, Diallo LH, Roussel E,
Tatin F, Garmy-Susini B and Lacazette E: Circular RNA, the key for
translation. Int J Mol Sci. 21:85912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou R, Wu Y, Wang W, Su W, Liu Y, Wang Y,
Fan C, Li X, Li G, Li Y, et al: CircularRNAs (circRNAs) incancer.
Cancer Lett. 425:134–142. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Derks KW, Misovic B, van den Hout MC,
Kockx CE, Gomez CP, Brouwer RW, Vrieling H, Hoeijmakers JH, van
Ijcken WF and Pothof J: Deciphering the RNA landscape by RNAome
sequencing. RNA Biol. 12:30–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Szabo L and Salzman J: Detecting circular
RNAs: Bioinformatic and experimental challenges. Nat Rev Genet.
17:679–692. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng R, Zhang K, Tan S, Gao F, Zhang Y,
Xu W, Wang H, Gu D, Zhu L, Li S, et al: Exosomal circLPAR1
functions in colorectal cancer diagnosis and tumorigenesis through
suppressing BRD4 via METTL3-eIF3h interaction. Mol Cancer.
21:492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Z, Sun A, Yan A, Yao J, Huang H, Gao
Z, Han T, Gu J, Li N, Wu H and Li K: Circular RNA MTCL1 promotes
advanced laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by
inhibiting C1QBP ubiquitin degradation and mediating beta-catenin
activation. Mol Cancer. 21:922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao F, Han J, Wang Y, Jia L, Luo W and
Zeng Y: Circ_0109291 promotes cisplatin resistance of oral squamous
cell carcinoma by sponging miR-188-3p to increase ABCB1 expression.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 37:233–245. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qi X, Zhang DH, Wu N, Xiao JH, Wang X and
Ma W: ceRNA in cancer: Possible functions and clinical
implications. J Med Genet. 52:710–718. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thomson DW and Dinger ME: Endogenous
microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet.
17:272–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ge P, Chen X, Liu J, Jing R, Zhang X and
Li H: Hsa_circ_0088036 promotes nonsmall cell lung cancer
progression by regulating miR-1343-3p/Bcl-3 axis through
TGFβ/Smad3/EMT signaling. Mol Carcinog. 62:1073–1085. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen Y, Zhang N, Chai J, Wang T, Ma C, Han
L and Yang M: CircPDIA4 induces gastric cancer progressionby
promoting ERK1/2 activation and enhancing biogenesisof oncogenic
circRNAs. Cancer Res. 83:538–552. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mo H, Shen J, Zhong Y, Chen Z, Wu T, Lv Y,
Xie Y and Hao Y: CircMAN1A2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through upregulating ERBB2 via
sponging miR-940. Oncol Res. 30:187–199. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dang Y, Ouyang X, Zhang F, Wang K, Lin Y,
Sun B, Wang Y, Wang L and Huang Q: Circular RNAs expression
profiles in human gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 7:90602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fan Y, Che X, Hou K, Zhang M, Wen T, Qu X
and Liu Y: MiR-940 promotes the proliferation and migration of
gastric cancer cells through up-regulation of programmed death
ligand-1 expression. Exp Cell Res. 373:180–187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu X, Ge X, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Chang J, Wu
Z, Tang W, Gan L, Sun M and Li J: MicroRNA-940 promotes tumor cell
invasion and metastasis by downregulating ZNF24 in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:25418–25428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Su K, Wang C, Zhang Y, Cai Y, Zhang Y and
Zhao Q: miR-940 upregulation contributes to human cervical cancer
progression through p27 and PTEN inhibition. Int J Oncol.
50:1211–1220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng L, Luo S, Jin C, Ma H, Zhou H and
Jia L: FUT family mediates the multidrug resistance of human
hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e9232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dai Y, Cheng Z, Pang Y, Jiao Y, Qian T,
Quan L, Cui L, Liu Y, Si C, Chen J, et al: Prognostic value of the
FUT family in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Gene Ther. 27:70–80.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mai Z, Chen H, Huang M, Zhao X and Cui L:
A robust metabolic enzyme-based prognostic signature for head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. 11:7702412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wei X, Luo T, Li J, Xue Z, Wang Y, Zhang
Y, Chen Y and Peng C: Development and validation of a prognostic
classifier based on lipid metabolism-related genes in gastric
cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 8:6911432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li N, Liu Y, Miao Y, Zhao L, Zhou H and
Jia L: MicroRNA-106b targets FUT6 to promote cell migration,
invasion, and proliferation in human breast cancer. IUBMB Life.
68:764–775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chrifi I, Hermkens D, Brandt MM, van Dijk
C, Burgisser PE, Haasdijk R, Pei J, van de Kamp E, Zhu C, Blonden
L, et al: Cgnl1, an endothelial junction complex protein, regulates
GTPase mediated angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 113:1776–1788. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lu X, Jing L, Liu S, Wang H and Chen B:
miR-149-3p is a potential prognosis biomarker and correlated with
immune infiltrates in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. Int J
Endocrinol. 2022:50061232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li W, Wang S, Qiu C, Liu Z, Zhou Q, Kong
D, Ma X and Jiang J: Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of
acquired progesterone resistance in endometrial cancer cell line. J
Transl Med. 17:582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jin Y and Qin X: Significance of TP53
mutation in treatment and prognosis in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Biomark Med. 15:15–28. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Song Y, Jin D, Ou N, Luo Z, Chen G, Chen
J, Yang Y and Liu X: Gene expression profiles identified novel
urine biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of high-grade bladder
urothelial carcinoma. Front Oncol. 10:3942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kutz LM, Abel J, Schweizer D, Tribius S,
Krull A, Petersen C and Loser A: Quality of life, HPV-status and
phase angle predict survival in head and neck cancer patients under
(chemo)radiotherapy undergoing nutritional intervention: Results
from the prospective randomized HEADNUT-trial. Radiother Oncol.
166:145–153. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|