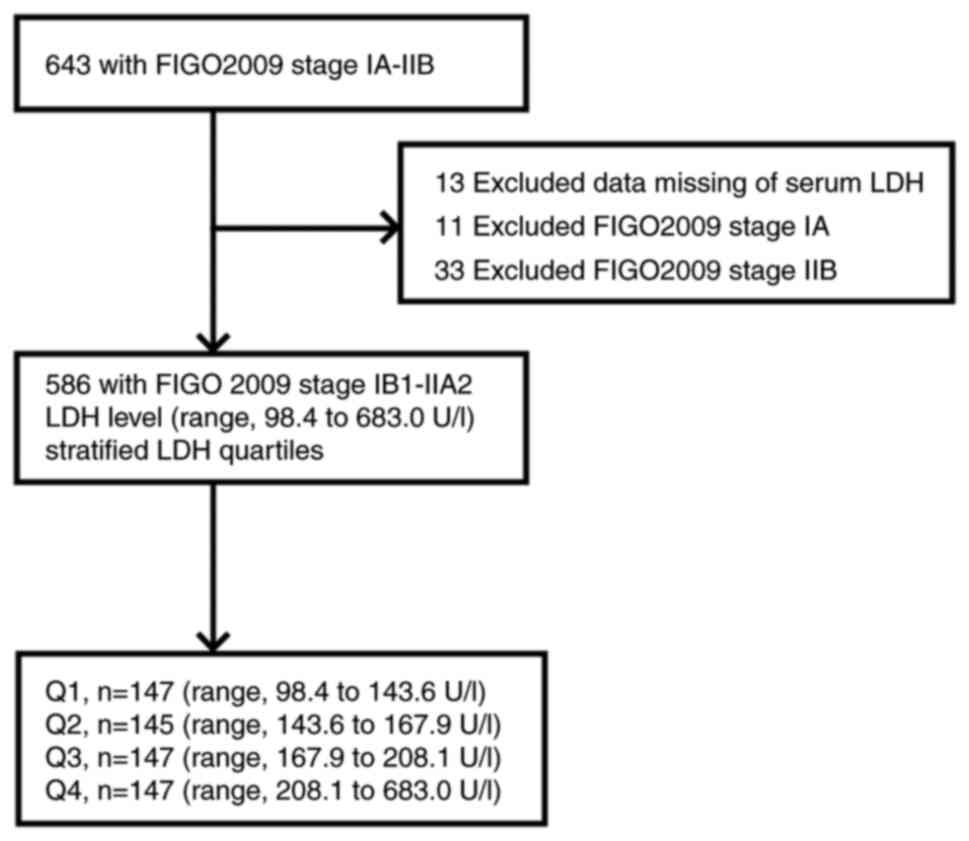
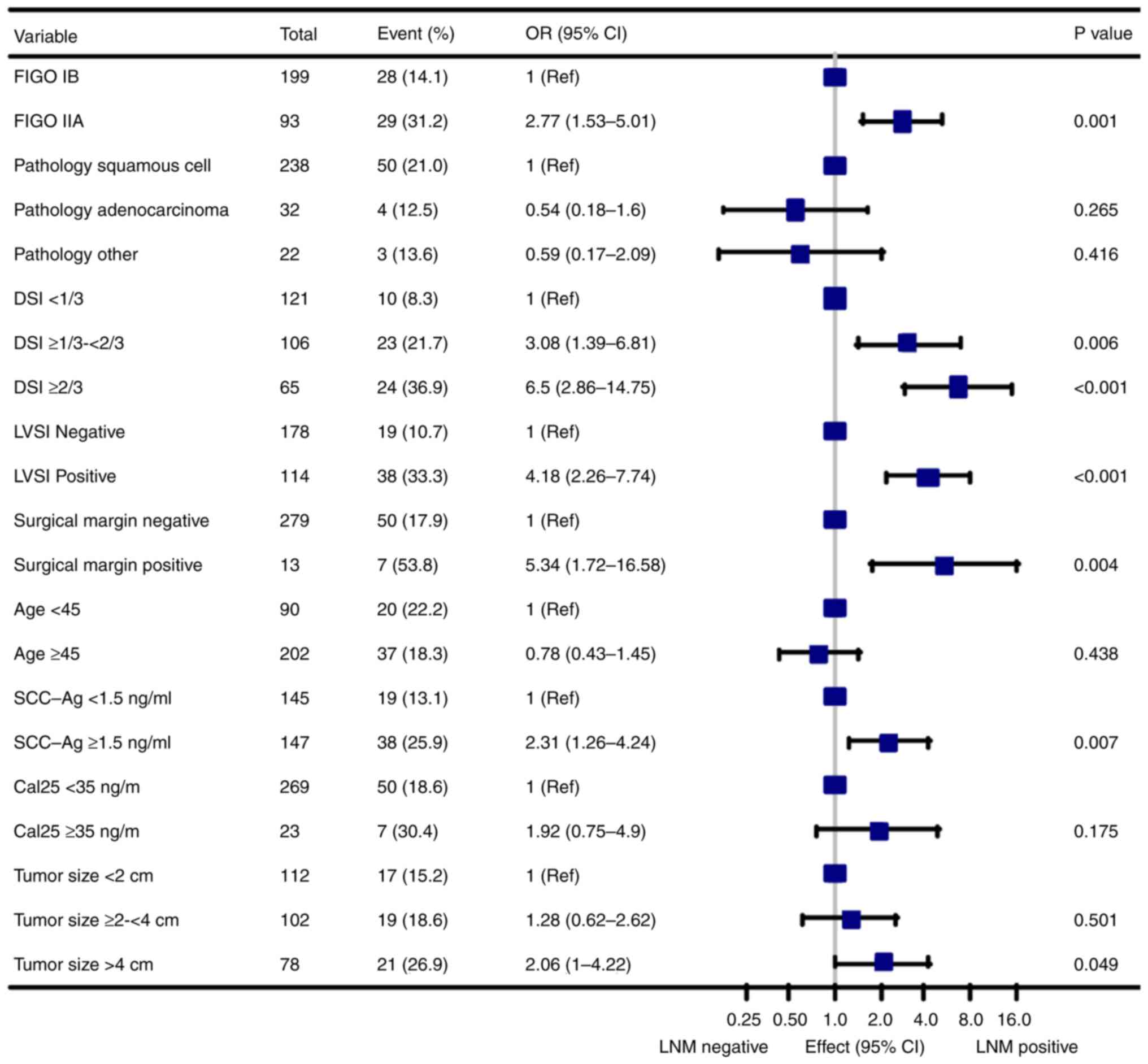
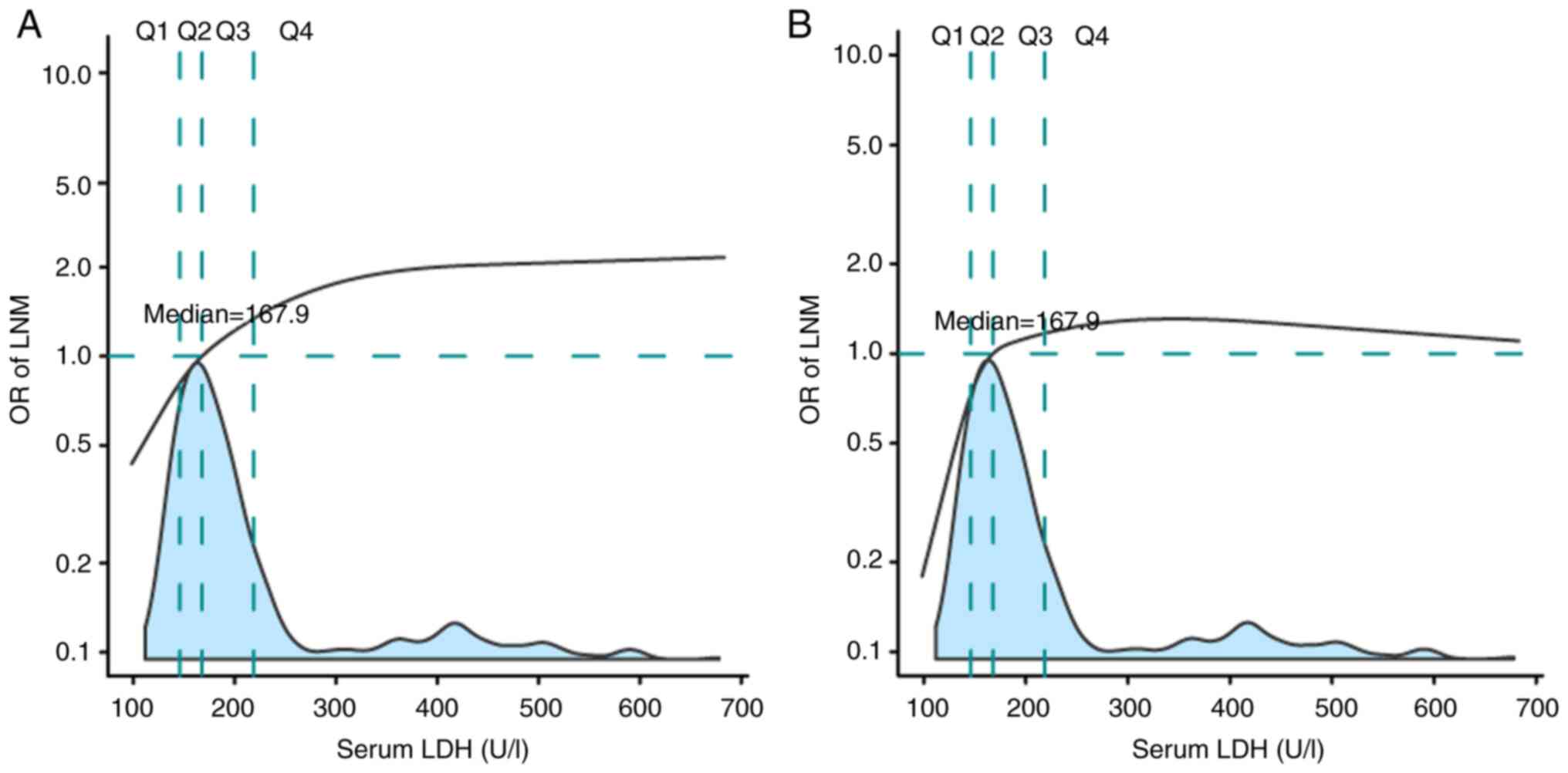
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koh W, Abu-Rustum N, Bean S, Bradley K,
Campos SM, Cho KR, Chon HS, Chu C, Clark R, Cohn D, et al: Cervical
cancer, version 3.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in
oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 17:64–84. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sedlis A, Bundy BN, Rotman MZ, Lentz SS,
Muderspach LI and Zaino RJ: A randomized trial of pelvic radiation
therapy versus no further therapy in selected patients with stage
IB carcinoma of the cervix after radical hysterectomy and pelvic
lymphadenectomy: A gynecologic oncology group study. Gynecol Oncol.
73:177–183. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chao B, Ju X, Zhang L, Xu X and Zhao Y: A
novel prognostic marker systemic inflammation response index (SIRI)
for operable cervical cancer patients. Front Oncol. 10:7662020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Deng Q, Long Q, Liu Y, Yang Z, Du Y and
Chen X: Prognostic value of preoperative peripheral blood mean
platelet volume/platelet count ratio (MPV/PC) in patients with
resectable cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. 21:12822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang P, Kong W, Gong C, Chen Y, Li F, Xu
L, Yang Y, Gou S and Hu Z: Predicting the recurrence of operable
cervical cancer patients based on hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte,
and platelet (HALP) score and classical clinicopathological
parameters. J Inflamm Res. 15:5265–5281. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Markert C: Lactate dehydrogenase isozymes:
Dissociation and recombination of subunits. Science. 140:1329–1330.
1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Passardi A, Scarpi E, Tamberi S, Cavanna
L, Tassinari D, Fontana A, Pini S, Bernardini I, Accettura C, Ulivi
P, et al: Impact of pre-treatment lactate dehydrogenase levels on
prognosis and bevacizumab efficacy in patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01347322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Valvona CJ, Fillmore HL, Nunn PB and
Pilkington GJ: The regulation and function of lactate dehydrogenase
A: Therapeutic potential in brain tumor. Brain Pathol. 26:3–17.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koch A, Fohlin H and Sörenson S:
Prognostic significance of C-reactive protein and smoking in
patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with
first-line palliative chemotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. 4:326–332.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim CH, Oh HG, Lee SY, Lim JK, Lee YH, Seo
H, Yoo SS, Lee SY, Cha SI, Park JY and Lee J: Differential
diagnosis between lymphoma-associated malignant pleural effusion
and tuberculous pleural effusion. Ann Transl Med. 7:3732019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Wu MF, Lu HW, Chen Q, Lin ZQ and
Wang LJ: Pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase is an independent
prognostic factor for patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy
for locally advanced cervical cancer. Cancer Med. 5:1863–1872.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Wang MS, Zhou YH, Shi JP and Wang
WJ: Prognostic values of LDH and CRP in cervical cancer. Onco
Targets Ther. 13:1255–1263. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ye Y, Chen M, Chen X, Xiao J, Liao L and
Lin F: Clinical significance and prognostic value of lactate
dehydrogenase expression in cervical cancer. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 26:107–117. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tholen DW, Musiolkroll EM, Kroll M, Astles
JR, Caffo AL, Happe TM and Lasky F: Evaluation of the linearity of
quantitative measurement procedures: A statistical approach;
approved guideline. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;
2003
|
|
16
|
Tholen DW, Linnet K, Kondratovich M,
Armbruster DA, Garrett PE, Jones RL, Kroll MH, Lequin RM, Pankratz
TJ, Scassellati GA, et al: Protocols for determination of limits of
detection and limits of quantitation; approved guidelines. Clinical
and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2004
|
|
17
|
White IR, Royston P and Wood AM: Multiple
imputation using chained equations: Issues and guidance for
practice. Stat Med. 30:377–399. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Meira-Machado L, Cadarso-Suárez C, Gude F
and Araújo A: smoothHR: An R package for pointwise nonparametric
estimation of hazard ratio curves of continuous predictors. Comput
Math Methods Med. 2013:7457422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Y, Cao JZ, Lan SM, Wu JX, Wu T, Zhu
SY, Qian LT, Hou XR, Zhang FQ, Zhang YJ, et al: Association of
improved locoregional control with prolonged survival in
early-stage extranodal nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma.
JAMA Oncol. 3:83–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koukourakis M, Kontomanolis E,
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E and Liberis V: Serum and tissue LDH
levels in patients with breast/gynaecological cancer and benign
diseases. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 67:162–168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Burgner JW II and Ray WJ Jr: On the origin
of the lactate dehydrogenase induced rate effect. Biochemistry.
23:3636–3648. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Harris A: Hypoxia-a key regulator factor
in tumor growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu S, Zhou HY, Deng SC, Deng SJ, He C, Li
X, Chen JY, Jin Y, Hu ZL, Wang F, et al: ASIC1 and ASIC3 contribute
to acidity-induced EMT of pancreatic cancer through activating
Ca2+/RhoA pathway. Cell Death Dis. 8:e28062017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Gatter K,
Turley H, Harris A, Koukourakis M and Tumour; Angiogenesis Research
Group, : Lactate dehydrogenase 5 (LDH-5) expression in endometrial
cancer relates to the activated VEGF/VEGFR2(KDR) pathway and
prognosis. Gynecol Oncol. 103:912–918. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Scartozzi M, Giampieri R, Maccaroni E, Del
Prete M, Faloppi L, Bianconi M, Galizia E, Loretelli C, Belvederesi
L, Bittoni A and Cascinu S: Pre-treatment lactate dehydrogenase
levels as predictor of efficacy of first-line bevacizumab-based
therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
106:799–804. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tewari KS, Sill MW, Long HJ III, Penson
RT, Huang H, Ramondetta LM, Landrum LM, Oaknin A, Reid TJ, Leitao
MM, et al: Improved survival with bevacizumab in advanced cervical
cancer. N Engl J Med. 370:734–743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Liao X and Ma L: ERCC1 is a
potential biomarker for predicting prognosis, immunotherapy,
chemotherapy efficacy, and expression validation in HER2
over-expressing breast cancer. Front Oncol. 12:9557192022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Doherty JR and Cleveland JL: Targeting
lactate metabolism for cancer therapeutics. J Clin Invest.
123:3685–3692. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hummitzsch L, Zitta K, Rusch R, Cremer J,
Steinfath M, Gross J, Fandrich F, Berndt R and Albrecht M:
Characterization of the angiogenic potential of human regulatory
macrophages (Mreg) after ischemia/reperfusion injury in vitro. Stem
Cells Int. 2019:37258632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Yao YH, Li BG, Yang Q, Zhang PY
and Wang HT: Prognostic value of pretreatment serum lactate
dehydrogenase level in patients with solid tumors: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5:98002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|