|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schopper D and de Wolf C: How effective
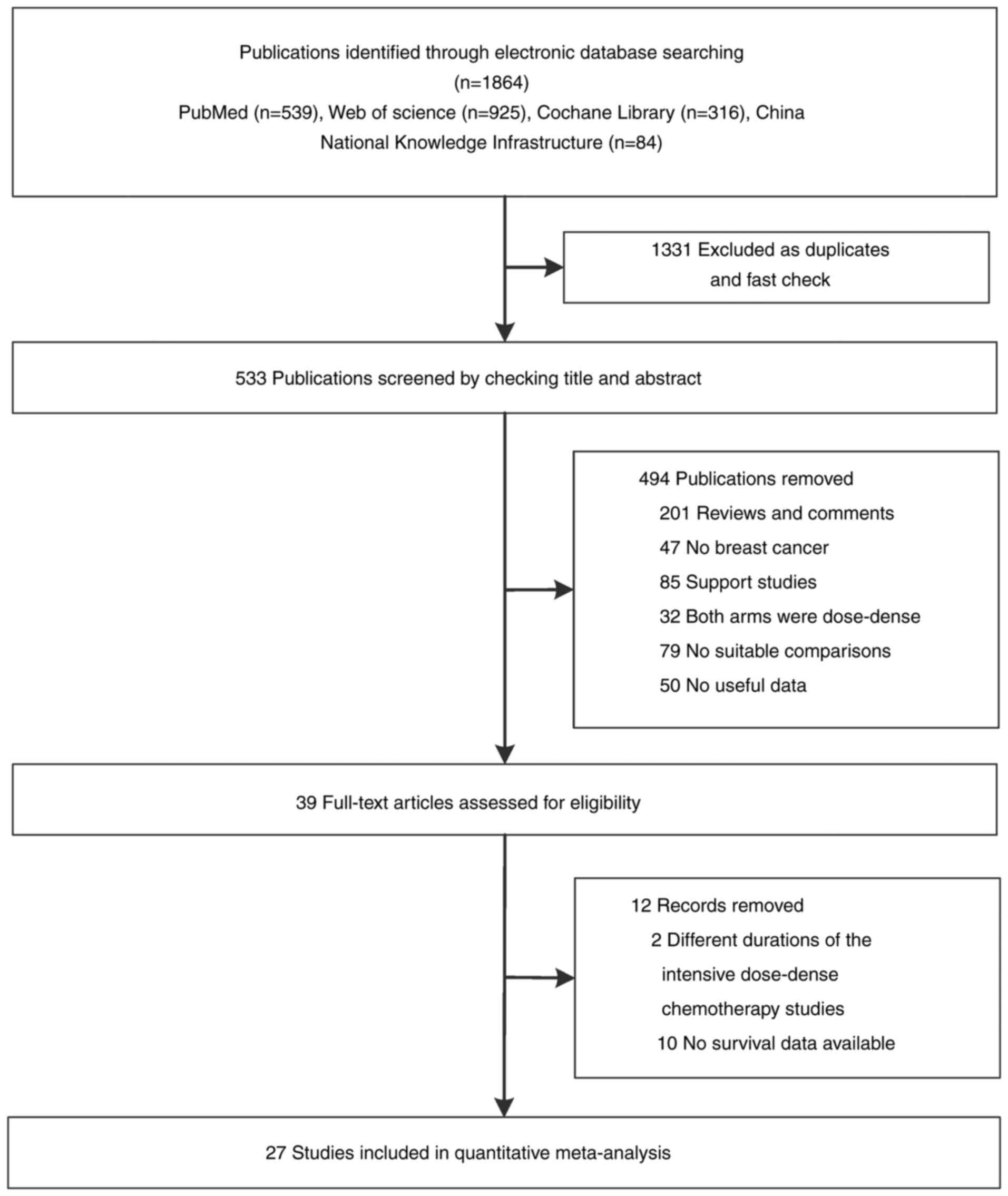
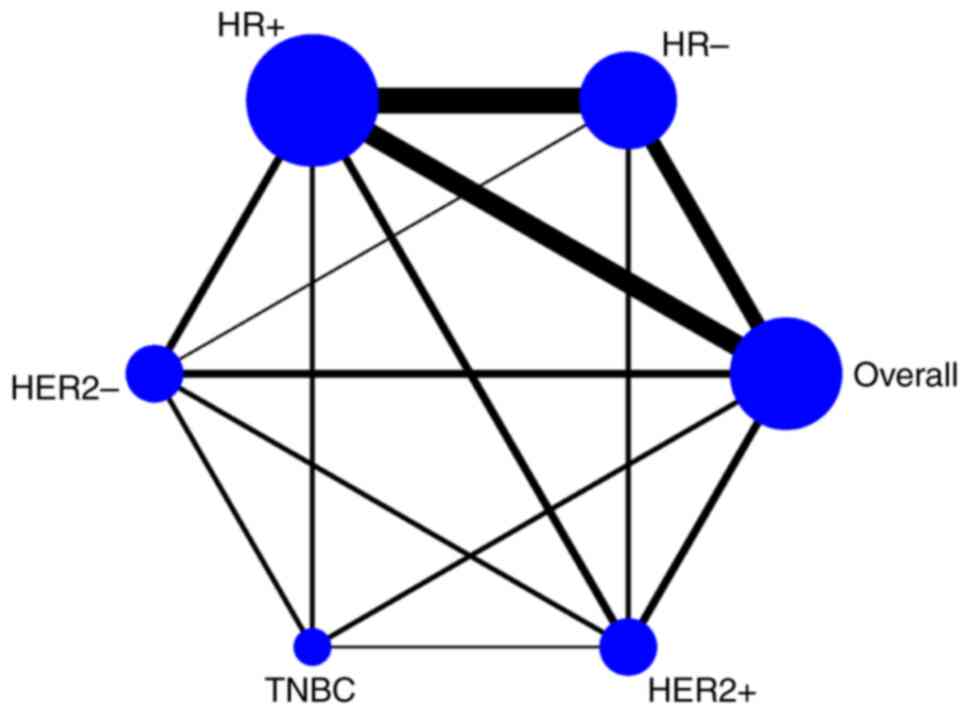
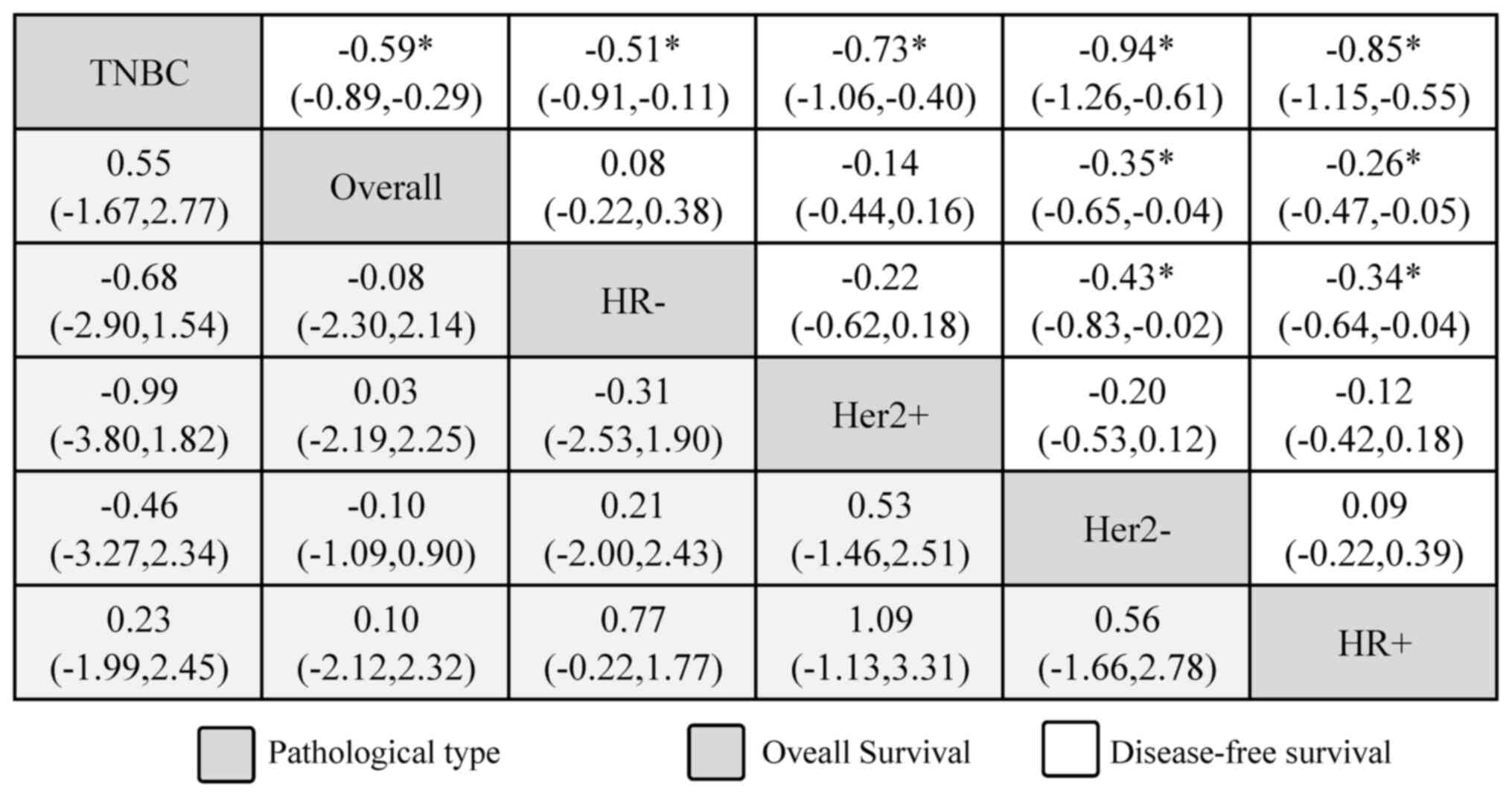
are breast cancer screening programmes by mammography? Review of
the current evidence. Eur J Cancer. 45:1916–1923. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tian Z, Tang J, Liao X, Yang Q, Wu Y and
Wu G: An immune-related prognostic signature for predicting breast
cancer recurrence. Cancer Med. 9:7672–7685. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li BX, Chen XJ, Ding TJ, Liu YH, Ma TT,
Zhang GL and Wang XM: Potentially overestimated efficacy of
nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with solvent-based
paclitaxel in breast cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis. J
Cancer. 12:5164–5172. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu T, Xu F, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Yang C,
Cheng M, Chen F and Wang K: Measurement of molecular biomarkers
that predict the tumor response in estrogen receptor-positive
breast cancers after dose-dense (biweekly) paclitaxel/carboplatin
neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 8:101087–101094. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lambertini M, Poggio F, Bruzzone M, Conte
B, Bighin C, de Azambuja E, Giuliano M, De Laurentiis M, Cognetti
F, Fabi A, et al: Dose-dense adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive
early breast cancer patients before and after the introduction of
trastuzumab: Exploratory analysis of the GIM2 trial. Int J Cancer.
147:160–169. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tomasello G, Valeri N, Ghidini M, Smyth
EC, Liguigli W, Toppo L, Mattioli R, Curti A, Hahne JC, Negri FM,
et al: First-line dose-dense chemotherapy with docetaxel,
cisplatin, folinic acid and 5-fluorouracil (DCF) plus panitumumab
in patients with locally advanced or metastatic cancer of the
stomach or gastroesophageal junction: Final results and biomarker
analysis from an Italian oncology group for clinical research
(GOIRC) phase II study. Oncotarget. 8:111795–111806. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou W, Chen S, Xu F and Zeng X: Survival
benefit of pure dose-dense chemotherapy in breast cancer: A
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Surg Oncol.
16:1442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goldvaser H, Majeed H, Ribnikar D, Šeruga
B, Ocaña A, Cescon DW and Amir E: Influence of control group
therapy on the benefit from dose-dense chemotherapy in early breast
cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 169:413–425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Petrelli F, Coinu A, Lonati V, Cabiddu M,
Ghilardi M, Borgonovo K and Barni S: Neoadjuvant dose-dense
chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer: A meta-analysis of
published studies. Anticancer Drugs. 27:702–708. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372:n712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Tulder M, Furlan A, Bombardier C and
Bouter L; Editorial Board of the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review
Group, : Updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the
cochrane collaboration back review group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
28:1290–1299. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jinatongthai P, Kongwatcharapong J, Foo
CY, Phrommintikul A, Nathisuwan S, Thakkinstian A, Reid CM and
Chaiyakunapruk N: Comparative efficacy and safety of reperfusion
therapy with fibrinolytic agents in patients with ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction: A systematic review and network
meta-analysis. Lancet. 390:747–759. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG,
Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng HY, Corbett MS, Eldridge
SM, et al: RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 366:l48982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wells G: The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS)
for assessing the quality of non-randomised studies in
meta-analyses. Symposium on Systematic Reviews: Beyond the Basics.
2014.
|
|
16
|
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R,
Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P and Schünemann HJ; GRADE Working
Group, : GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence
and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 336:924–926. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang C, Xu C, Li X and Zhang Y, Zhang S,
Zhang T and Zhang Y: Could camrelizumab plus chemotherapy improve
clinical outcomes in advanced malignancy? A systematic review and
network meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 11:7001652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feng F, Jiang Q, Jia H, Sun H, Chai Y, Li
X, Rong G, Zhang Y and Li Z: Which is the best combination of TACE
and Sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treatment? A
systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res.
135:89–101. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Higgins JPT, Jackson D, Barrett JK, Lu G,
Ades AE and White IR: Consistency and inconsistency in network
meta-analysis: Concepts and models for multi-arm studies. Res Synth
Methods. 3:98–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
König J, Krahn U and Binder H: Visualizing
the flow of evidence in network meta-analysis and characterizing
mixed treatment comparisons. Stat Med. 32:5414–5429. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schneeweiss A, Michel LL, Möbus V, Tesch
H, Klare P, Hahnen E, Denkert C, Kast K, Pohl-Rescigno E, Hanusch
C, et al: Survival analysis of the randomised phase III GeparOcto
trial comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy of intense dose-dense
epirubicin, paclitaxel, cyclophosphamide versus weekly paclitaxel,
liposomal doxorubicin (plus carboplatin in triple-negative breast
cancer) for patients with high-risk early breast cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 160:100–111. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y: Efficacy and long-term survival
outcomes of dose-dense carboplatin plus paclitaxel as neoadjuvant
chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer. PhD Thesis. Chin
Acad Med Sci. 2021.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Blondeaux E, Lambertini M, Michelotti A,
Conte B, Benasso M, Dellepiane C, Bighin C, Pastorino S, Levaggi A,
Alonzo A, et al: Dose-dense adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast
cancer patients: 15-Year results of the phase 3 Mammella
InterGruppo (MIG)-1 study. Br J Cancer. 122:1611–1617. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He J: Application of Dose-dense
Chemotherapy in Neoadjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer. PhD Thesis.
Hebei Med Univ. 2020.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Schneeweiss A, Möbus V, Tesch H, Hanusch
C, Denkert C, Lübbe K, Huober J, Klare P, Kümmel S, Untch M, et al:
Intense dose-dense epirubicin, paclitaxel, cyclophosphamide versus
weekly paclitaxel, liposomal doxorubicin (plus carboplatin in
triple-negative breast cancer) for neoadjuvant treatment of
high-risk early breast cancer (GeparOcto-GBG 84): A randomised
phase III trial. Eur J Cancer. 106:181–192. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Möbus V, Jackisch C, Lück HJ, du Bois A,
Thomssen C, Kuhn W, Nitz U, Schneeweiss A, Huober J, Harbeck N, et
al: Ten-year results of intense dose-dense chemotherapy show
superior survival compared with a conventional schedule in
high-risk primary breast cancer: Final results of AGO phase III
iddEPC trial. Ann Oncol. 29:178–185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van Rossum AGJ, Kok M, van Werkhoven E,
Opdam M, Mandjes IAM, van Leeuwen-Stok AE, van Tinteren H, Imholz
ALT, Portielje JEA, Bos MMEM, et al: Adjuvant dose-dense
doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide versus
docetaxel-doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide for high-risk breast cancer:
First results of the randomised MATADOR trial (BOOG 2004–04). Eur J
Cancer. 102:40–48. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cameron D, Morden JP, Canney P, Velikova
G, Coleman R, Bartlett J, Agrawal R, Banerji J, Bertelli G,
Bloomfield D, et al: Accelerated versus standard epirubicin
followed by cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil or
capecitabine as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer in the
randomised UK TACT2 trial (CRUK/05/19): A multicentre, phase 3,
open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:929–945.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lambertini M, Ceppi M, Cognetti F,
Cavazzini G, De Laurentiis M, De Placido S, Michelotti A, Bisagni
G, Durando A, Valle E, et al: Dose-dense adjuvant chemotherapy in
premenopausal breast cancer patients: A pooled analysis of the MIG1
and GIM2 phase III studies. Eur J Cancer. 71:34–42. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bao Z, Chen Y, Ren H, Jiang Y, Yang J and
Li S: Clinical observation of dose-dense chemotherapy in the
postoperative treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. J Mod
Oncol. 24:2221–2224. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Foukakis T, von Minckwitz G, Bengtsson NO,
Brandberg Y, Wallberg B, Fornander T, Mlineritsch B, Schmatloch S,
Singer CF, Steger G, et al: Effect of tailored dose-dense
chemotherapy vs standard 3-weekly adjuvant chemotherapy on
recurrence-free survival among women with high-risk early breast
cancer: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 316:1888–1896. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Del Mastro L, De Placido S, Bruzzi P, De
Laurentiis M, Boni C, Cavazzini G, Durando A, Turletti A, Nisticò
C, Valle E, et al: Fluorouracil and dose-dense chemotherapy in
adjuvant treatment of patients with early-stage breast cancer: An
open-label, 2 × 2 factorial, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet.
385:1863–1872. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou Y: Clinical study of postoperative
intensive chemotherapy with pirarubicin for triple negative breast
cancer. J Clin Med. 2:6059–6062. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Swain SM, Tang G, Geyer CE Jr, Rastogi P,
Atkins JN, Donnellan PP, Fehrenbacher L, Azar CA, Robidoux A,
Polikoff JA, et al: Definitive results of a phase III adjuvant
trial comparing three chemotherapy regimens in women with operable,
node-positive breast cancer: The NSABP B-38 trial. J Clin Oncol.
31:3197–3204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu X, Qin Q, Wei C, Zhu F, Mo G and Lian
B: Clinical effect analysis of intensive chemotherapy and
conventional adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced breast
cancer. Pract Geriatr. 27:157–173. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Gogas H, Dafni U, Karina M, Papadimitriou
C, Batistatou A, Bobos M, Kalofonos HP, Eleftheraki AG, Timotheadou
E, Bafaloukos D, et al: Postoperative dose-dense sequential versus
concomitant administration of epirubicin and paclitaxel in patients
with node-positive breast cancer: 5-Year results of the Hellenic
cooperative oncology group HE 10/00 phase III trial. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 132:609–619. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jin C, Zhang Y, Ma L, Zhou Y, Wei Y and Li
H and Li H: Clinical analysis of intensive chemotherapy with
perarubicin after high risk breast cancer surgery. Guide China Med.
10:558–559. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
38
|
Arun BK, Dhinghra K, Valero V, Kau SW,
Broglio K, Booser D, Guerra L, Yin G, Walters R, Sahin A, et al:
Phase III randomized trial of dose intensive neoadjuvant
chemotherapy with or without G-CSF in locally advanced breast
cancer: Long-term results. Oncologist. 16:1527–1534. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Untch M, Fasching PA, Konecny GE, von Koch
F, Conrad U, Fett W, Kurzeder C, Lück HJ, Stickeler E, Urbaczyk H,
et al: PREPARE trial: A randomized phase III trial comparing
preoperative, dose-dense, dose-intensified chemotherapy with
epirubicin, paclitaxel and CMF versus a standard-dosed
epirubicin/cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel ± darbepoetin
alfa in primary breast cancer-results at the time of surgery. Ann
Oncol. 22:1988–1998. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Untch M, von Minckwitz G, Konecny GE,
Conrad U, Fett W, Kurzeder C, Lück HJ, Stickeler E, Urbaczyk H,
Liedtke B, et al: PREPARE trial: A randomized phase III trial
comparing preoperative, dose-dense, dose-intensified chemotherapy
with epirubicin, paclitaxel, and CMF versus a standard-dosed
epirubicin-cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel with or without
darbepoetin alfa in primary breast cancer-outcome on prognosis. Ann
Oncol. 22:1999–2006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Burnell M, Levine MN, Chapman JA, Bramwell
V, Gelmon K, Walley B, Vandenberg T, Chalchal H, Albain KS, Perez
EA, et al: Cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and fluorouracil versus
dose-dense epirubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel
versus doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel in
node-positive or high-risk node-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 28:77–82. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moebus V, Jackisch C, Lueck HJ, du Bois A,
Thomssen C, Kurbacher C, Kuhn W, Nitz U, Schneeweiss A, Huober J,
et al: Intense dose-dense sequential chemotherapy with epirubicin,
paclitaxel, and cyclophosphamide compared with conventionally
scheduled chemotherapy in high-risk primary breast cancer: Mature
results of an AGO phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 28:2874–2880.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Untch M, Möbus V, Kuhn W, Muck BR,
Thomssen C, Bauerfeind I, Harbeck N, Werner C, Lebeau A,
Schneeweiss A, et al: Intensive dose-dense compared with
conventionally scheduled preoperative chemotherapy for high-risk
primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:2938–2945. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Venturini M, Del Mastro L, Aitini E,
Baldini E, Caroti C, Contu A, Testore F, Brema F, Pronzato P,
Cavazzini G, et al: Dose-dense adjuvant chemotherapy in early
breast cancer patients: Results from a randomized trial. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 97:1724–1733. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baldini E, Gardin G, Giannessi PG,
Evangelista G, Roncella M, Prochilo T, Collecchi P, Rosso R,
Lionetto R, Bruzzi P, et al: Accelerated versus standard
cyclophosphamide, epirubicin and 5-fluorouracil or
cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil: A randomized
phase III trial in locally advanced breast cancer. Ann Oncol.
14:227–232. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Citron ML, Berry DA, Cirrincione C, Hudis
C, Winer EP, Gradishar WJ, Davidson NE, Martino S, Livingston R,
Ingle JN, et al: Randomized trial of dose-dense versus
conventionally scheduled and sequential versus concurrent
combination chemotherapy as postoperative adjuvant treatment of
node-positive primary breast cancer: First report of intergroup
trial C9741/cancer and leukemia group B trial 9741. J Clin Oncol.
21:1431–1439. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Therasse P, Mauriac L, Welnicka-Jaskiewicz
M, Bruning P, Cufer T, Bonnefoi H, Tomiak E, Pritchard KI, Hamilton
A and Piccart MJ; EORTC: Final results of a randomized phase III
trial comparing cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and fluorouracil with
a dose-intensified epirubicin and cyclophosphamide + filgrastim as
neoadjuvant treatment in locally advanced breast cancer: An
EORTC-NCIC-SAKK multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 21:843–850. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Puglisi F, Gerratana L, Lambertini M,
Ceppi M, Boni L, Montemurro F, Russo S, Bighin C, De Laurentiis M,
Giuliano M, et al: Composite risk and benefit from adjuvant
dose-dense chemotherapy in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.
NPJ Breast Cancer. 7:822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Swain SM, Ewer MS, Viale G, Delaloge S,
Ferrero JM, Verrill M, Colomer R, Vieira C, Werner TL, Douthwaite
H, et al: Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and standard anthracycline- and
taxane-based chemotherapy for the neoadjuvant treatment of patients
with HER2-positive localized breast cancer (BERENICE): A phase II,
open-label, multicenter, multinational cardiac safety study. Ann
Oncol. 29:646–653. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chang CL, Hsu YT, Wu CC, Lai YZ, Wang C,
Yang YC, Wu TC and Hung CF: Dose-dense chemotherapy improves
mechanisms of antitumor immune response. Cancer Res. 73:119–127.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kumar A, Hoskins PJ and Tinker AV:
Dose-dense paclitaxel in advanced ovarian cancer. Clin Oncol (R
Coll Radiol). 27:40–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Crout CA, Koh LP, Gockerman JP, Moore JO,
Decastro C, Long GD, Diehl L, Gasparetto C, Niedzwiecki D, Edwards
J, et al: Overcoming drug resistance in mantle cell lymphoma using
a combination of dose-dense and intense therapy. Cancer Invest.
28:654–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|