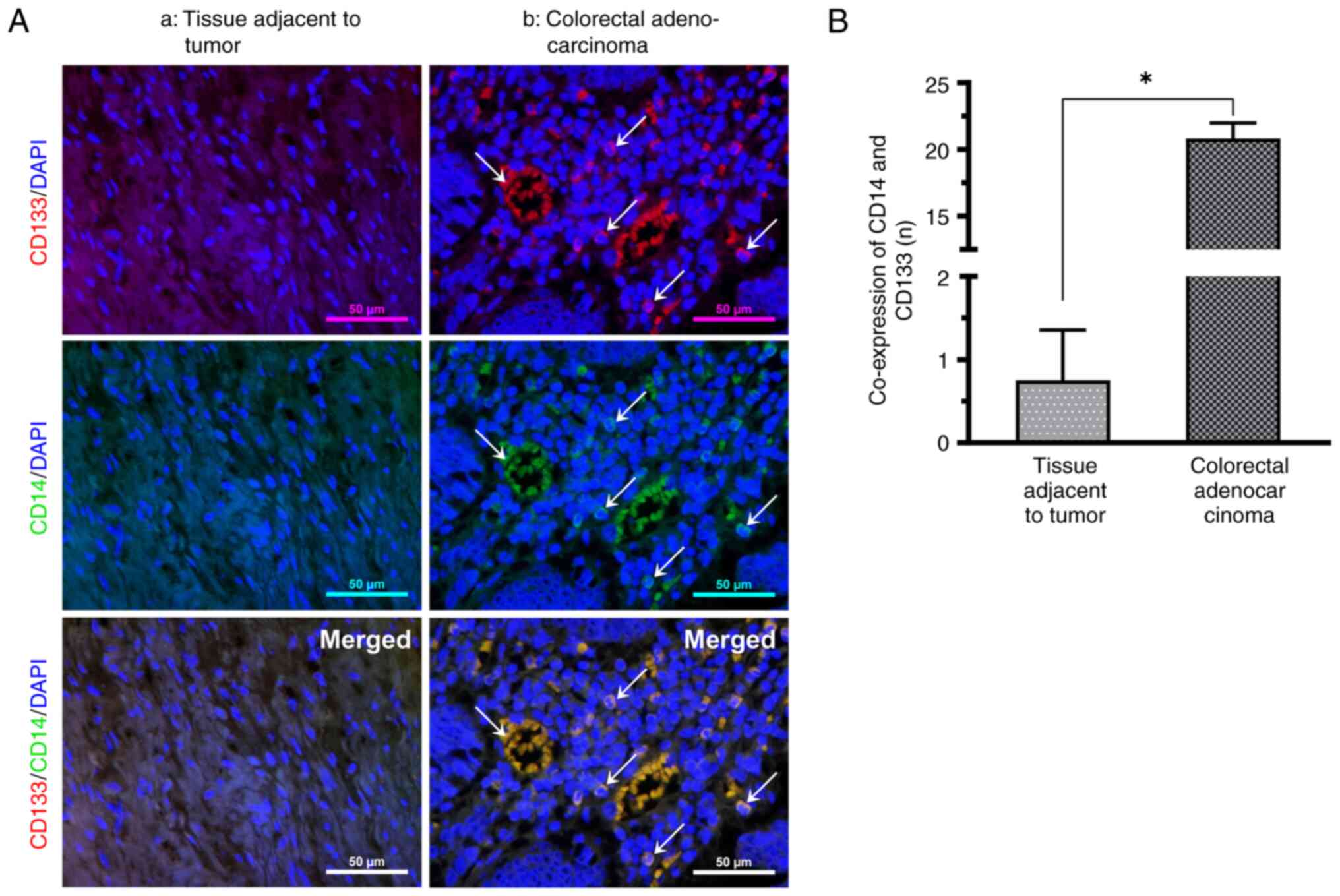
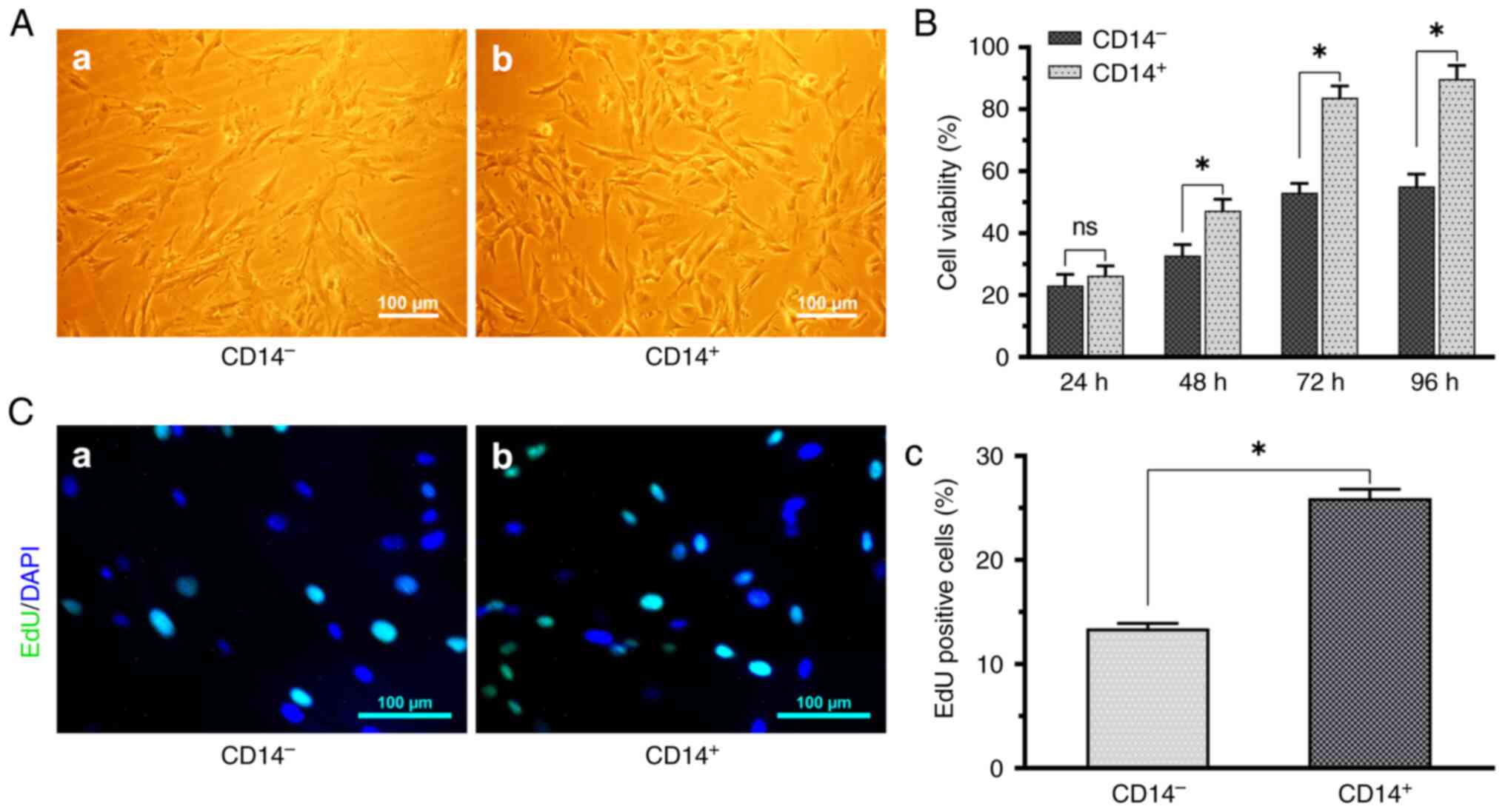
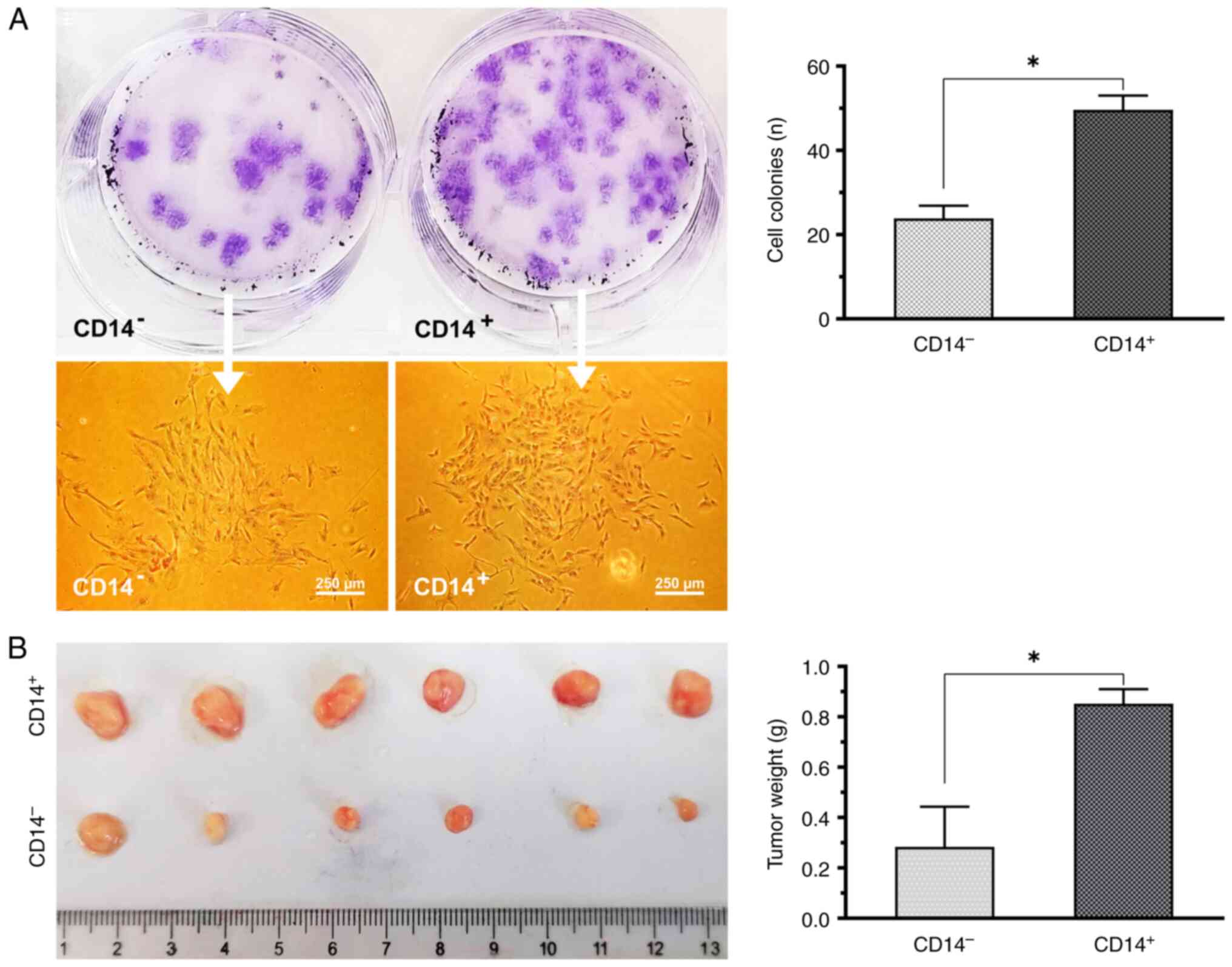
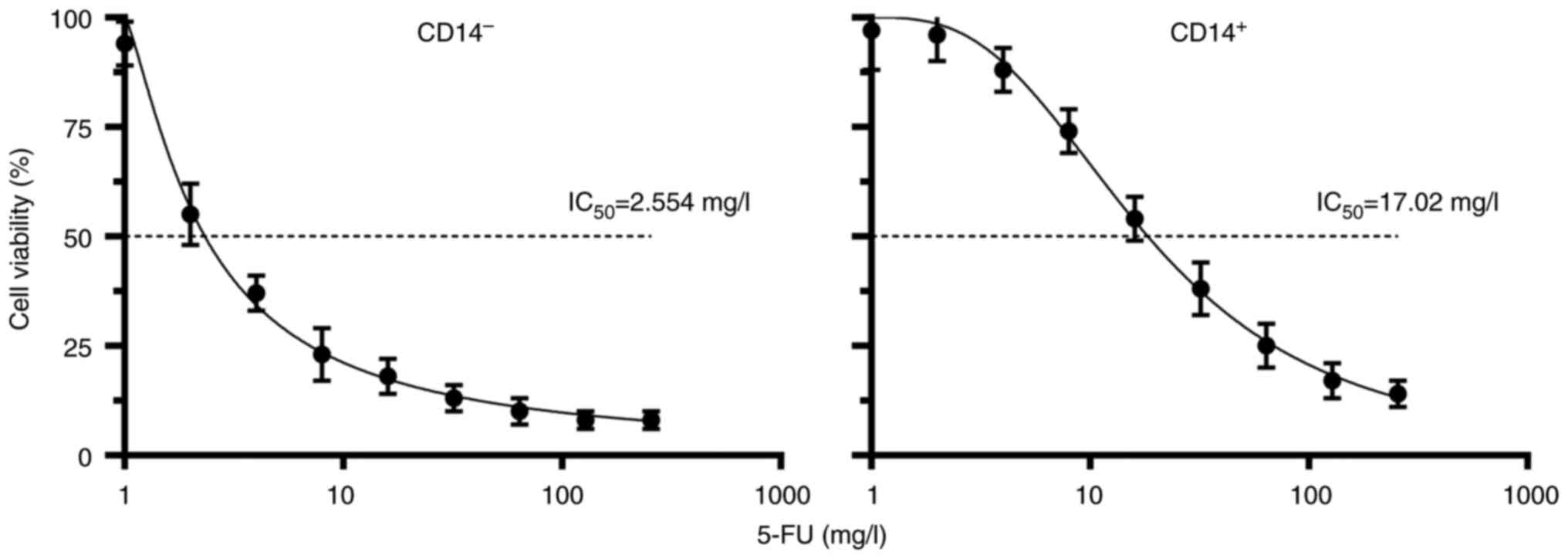
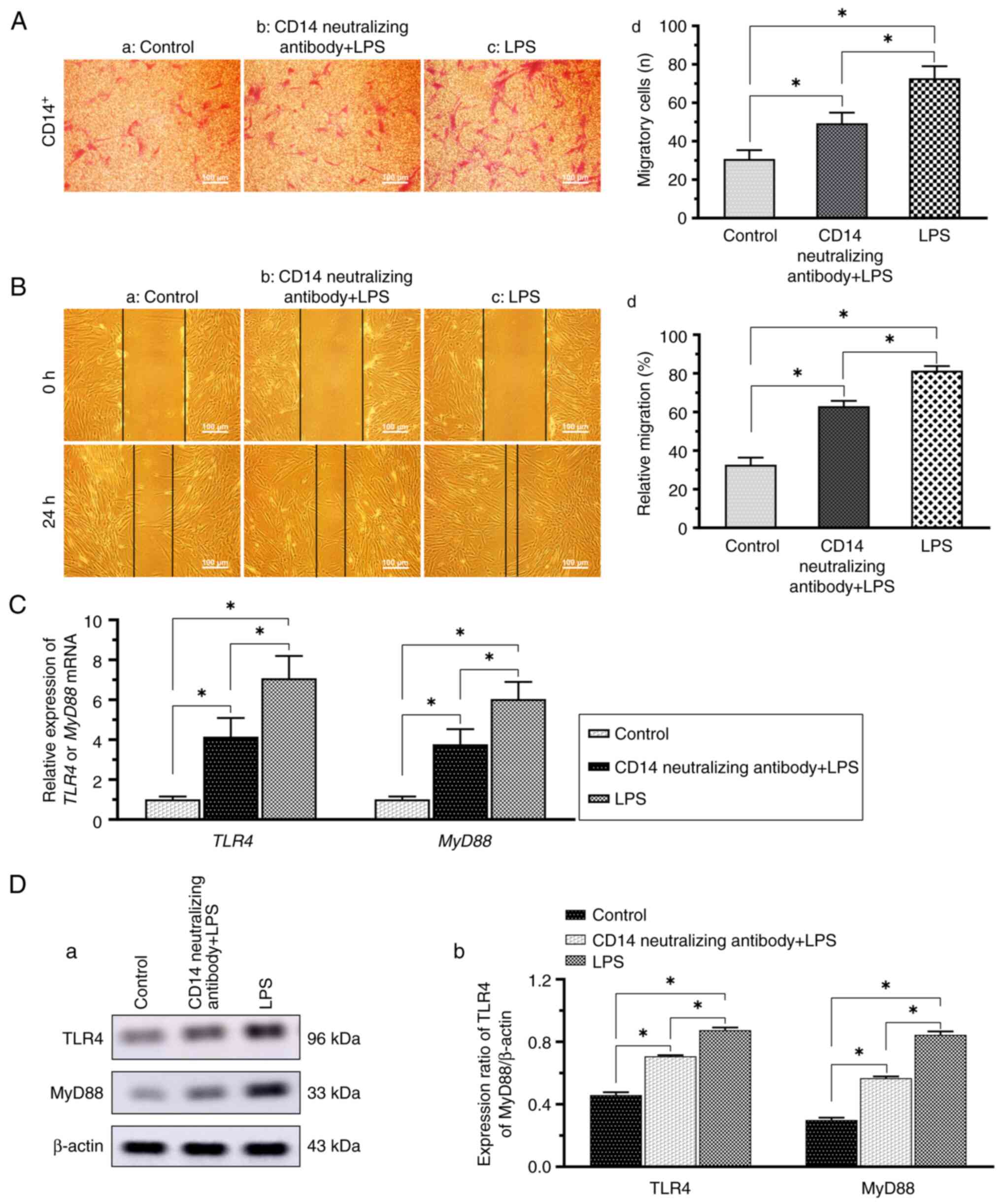
|
1
|
Ahmad R, Singh JK, Wunnava A, Al-Obeed O,
Abdulla M and Srivastava SK: Emerging trends in colorectal cancer:
Dysregulated signaling pathways (Review). Int J Mol Med. 47:142021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lewandowska A, Rudzki G, Lewandowski T,
Stryjkowska-Góra A and Rudzki S: Title: risk factors for the
diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Control.
29:107327482110566922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Salibasic M, Pusina S, Bicakcic E, Pasic
A, Gavric I, Kulovic E, Rovcanin A and Beslija S: Colorectal cancer
surgical treatment, our experience. Med Arch. 73:412–414. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li Y, Wu M, Xu S, Huang H, Yan L and Gu Y:
Colorectal cancer stem cell-derived exosomal long intergenic
noncoding RNA 01315 (LINC01315) promotes proliferation, migration,
and stemness of colorectal cancer cells. Bioengineered.
13:10827–10842. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Batlle E and Clevers H: Cancer stem cells
revisited. Nat Med. 23:1124–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hervieu C, Christou N, Battu S and
Mathonnet M: The role of cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer:
From the basics to novel clinical trials. Cancers (Basel).
13:10922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kopenhaver J, Crutcher M, Waldman SA and
Snook AE: The shifting paradigm of colorectal cancer treatment: A
look into emerging cancer stem cell-directed therapeutics to lead
the charge toward complete remission. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
21:1335–1345. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gupta R, Bhatt LK, Johnston TP and
Prabhavalkar KS: Colon cancer stem cells: Potential target for the
treatment of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 20:1068–1082.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Munro MJ, Wickremesekera SK, Peng L, Tan
ST and Itinteang T: Cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer: A
review. J Clin Pathol. 71:110–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu X, Lin Y, Yan X, Tian Q, Li L and Lin
EH: CD133, stem cells, and cancer stem cells: Myth or Reality? Curr
Colorectal Cancer Rep. 7:253–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Janova H, Böttcher C, Holtman IR, Regen T,
van Rossum D, Götz A, Ernst AS, Fritsche C, Gertig U, Saiepour N,
et al: CD14 is a key organizer of microglial responses to CNS
infection and injury. Glia. 64:635–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ciesielska A, Matyjek M and Kwiatkowska K:
TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced
pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:1233–1261. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hsu RY, Chan CH, Spicer JD, Rousseau MC,
Giannias B, Rousseau S and Ferri LE: LPS-induced TLR4 signaling in
human colorectal cancer cells increases beta1 integrin-mediated
cell adhesion and liver metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:1989–1998. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Santaolalla R, Sussman DA, Ruiz JR, Davies
JM, Pastorini C, España CL, Sotolongo J, Burlingame O, Bejarano PA,
Philip S, et al: TLR4 activates the β-catenin pathway to cause
intestinal neoplasia. PLoS One. 8:e632982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song W, Tiruthani K, Wang Y, Shen L, Hu M,
Dorosheva O, Qiu K, Kinghorn KA, Liu R and Huang L: Trapping of
lipopolysaccharide to promote immunotherapy against colorectal
cancer and attenuate liver metastasis. Adv Mater. 30:e18050072018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao D, Sun T, Zhang X, Guo Y, Yu D, Yang
M, Tan W, Wang G and Lin D: Role of CD14 promoter polymorphisms in
Helicobacter pylori infection-related gastric carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:2362–2368. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arihara F, Mizukoshi E, Kitahara M, Takata
Y, Arai K, Yamashita T, Nakamoto Y and Kaneko S: Increase in
CD14+HLA-DR-/low myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma patients and its impact on prognosis. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 62:1421–1430. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang A, Zhang B, Wang B, Zhang F, Fan KX
and Guo YJ: Increased CD14(+)HLA-DR (−/low) myeloid-derived
suppressor cells correlate with extrathoracic metastasis and poor
response to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 62:1439–1451. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin Y, Dong J, Yu W, Li Y, Liu Z, Liu J,
Wang C, Qin J, Zhu L and Liang J: CD14, a novel surface marker of
esophageal cancer stem cells. Oncol Rep. 49:132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zalewski A, Snook AE and Waldman SA: Stem
cells as therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer. Per Med.
18:171–183. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui G, Xu G, Zhu L, Pang Z, Zheng W, Li Z
and Yuan A: Temporal and spatial changes of cells positive for
stem-like markers in different compartments and stages of human
colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Oncotarget. 8:45311–45322.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Akbarzadeh M, Maroufi NF, Tazehkand AP,
Akbarzadeh M, Bastani S, Safdari R, Farzane A, Fattahi A, Nejabati
HR, Nouri M and Samadi N: Current approaches in identification and
isolation of cancer stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 234:14759–14772.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han GD, Sun Y, Hui HX, Tao MY, Liu YQ and
Zhu J: MiR-1224 acts as a prognostic biomarker and inhibits the
progression of gastric cancer by targeting SATB1. Front Oncol.
11:7488962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vargo-Gogola T and Rosen JM: Modelling
breast cancer: One size does not fit all. Nat Rev Cancer.
7:659–672. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsai RY: Balancing self-renewal against
genome preservation in stem cells: How do they manage to have the
cake and eat it too? Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:1803–1823. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chiodi I, Belgiovine C, Donà F, Scovassi
AI and Mondello C: Drug treatment of cancer cell lines: A way to
select for cancer stem cells? Cancers (Basel). 3:1111–1128. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang Y, Yan C, Zhao Q, Zhao B, Liao Y,
Chen Y, Wang D and Tang D: The association between gut microbiota,
toll-like receptors, and colorectal cancer. Clin Med Insights.
16:117955492211305492022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu WT, Jing YY, Yan F, Han ZP, Lai FB,
Zeng JX, Yu GF, Fan QM, Li R, Zhao QD, et al: LPS-induced
CXCR4-dependent migratory properties and a mesenchymal-like
phenotype of colorectal cancer cells. Cell Adh Migr. 11:13–23.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeong JW, Park C, Cha HJ, Hong SH, Park
SH, Kim GY, Kim WJ, Kim CH, Song KS and Choi YH: Cordycepin
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cell migration and invasion in
human colorectal carcinoma HCT-116 cells through down-regulation of
prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4. BMB Rep. 51:532–537. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu G, Cheng Z, Lin C, Hoffman RM, Huang
Y, Singh SR, Zheng W, Yang S and Ye J: MyD88 Regulates LPS-induced
NF-ĸB/MAPK cytokines and promotes inflammation and malignancy in
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 16:409–419.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
d'Hennezel E, Abubucker S, Murphy LO and
Cullen TW: Total Lipopolysaccharide from the human gut microbiome
silences toll-like receptor signaling. mSystems. 2:e00046–17.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang M, Edmundson P, Araujo-Perez F, McCoy
AN, Galanko J and Keku TO: Association of plasma endotoxin,
inflammatory cytokines and risk of colorectal adenomas. BMC Cancer.
13:912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu G, Huang Q, Huang Y, Zheng W, Hua J,
Yang S, Zhuang J, Wang J and Ye J: Lipopolysaccharide increases the
release of VEGF-C that enhances cell motility and promotes
lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis through the TLR4-
NF-κB/JNK pathways in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:73711–73724.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
de Waal GM, de Villiers WJS, Forgan T,
Roberts T and Pretorius E: Colorectal cancer is associated with
increased circulating lipopolysaccharide, inflammation and
hypercoagulability. Sci Rep. 10:87772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou W, Chen X, Hu Q, Chen X, Chen Y and
Huang L: Galectin-3 activates TLR4/NF-κB signaling to promote lung
adenocarcinoma cell proliferation through activating lncRNA-NEAT1
expression. BMC Cancer. 18:5802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang W and Wang J: Toll-Like Receptor 4
(TLR4)/Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) regulates prostate cancer cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion by NF-κB activation. Med Sci
Monit. 24:5588–5597. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rakoff-Nahoum S and Medzhitov R:
Regulation of spontaneous intestinal tumorigenesis through the
adaptor protein MyD88. Science. 317:124–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang HY, Zhang ZJ, Cao CB, Wang N, Liu
FF, Peng JQ, Ren XJ and Qian J: The TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
mediates the growth of colon cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:3834–3843. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fukata M, Chen A, Vamadevan AS, Cohen J,
Breglio K, Krishnareddy S, Hsu D, Xu R, Harpaz N, Dannenberg AJ, et
al: Toll-like receptor-4 promotes the development of
colitis-associated colorectal tumors. Gastroenterology.
133:1869–1881. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fukata M, Chen A, Klepper A, Krishnareddy
S, Vamadevan AS, Thomas LS, Xu R, Inoue H, Arditi M, Dannenberg AJ
and Abreu MT: Cox-2 is regulated by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4)
signaling: Role in proliferation and apoptosis in the intestine.
Gastroenterology. 131:862–877. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fukata M, Shang L, Santaolalla R,
Sotolongo J, Pastorini C, España C, Ungaro R, Harpaz N, Cooper HS,
Elson G, et al: Constitutive activation of epithelial TLR4 augments
inflammatory responses to mucosal injury and drives
colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:1464–1473.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheah MT, Chen JY, Sahoo D,
Contreras-Trujillo H, Volkmer AK, Scheeren FA, Volkmer JP and
Weissman IL: CD14-expressing cancer cells establish the
inflammatory and proliferative tumor microenvironment in bladder
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:4725–4730. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|