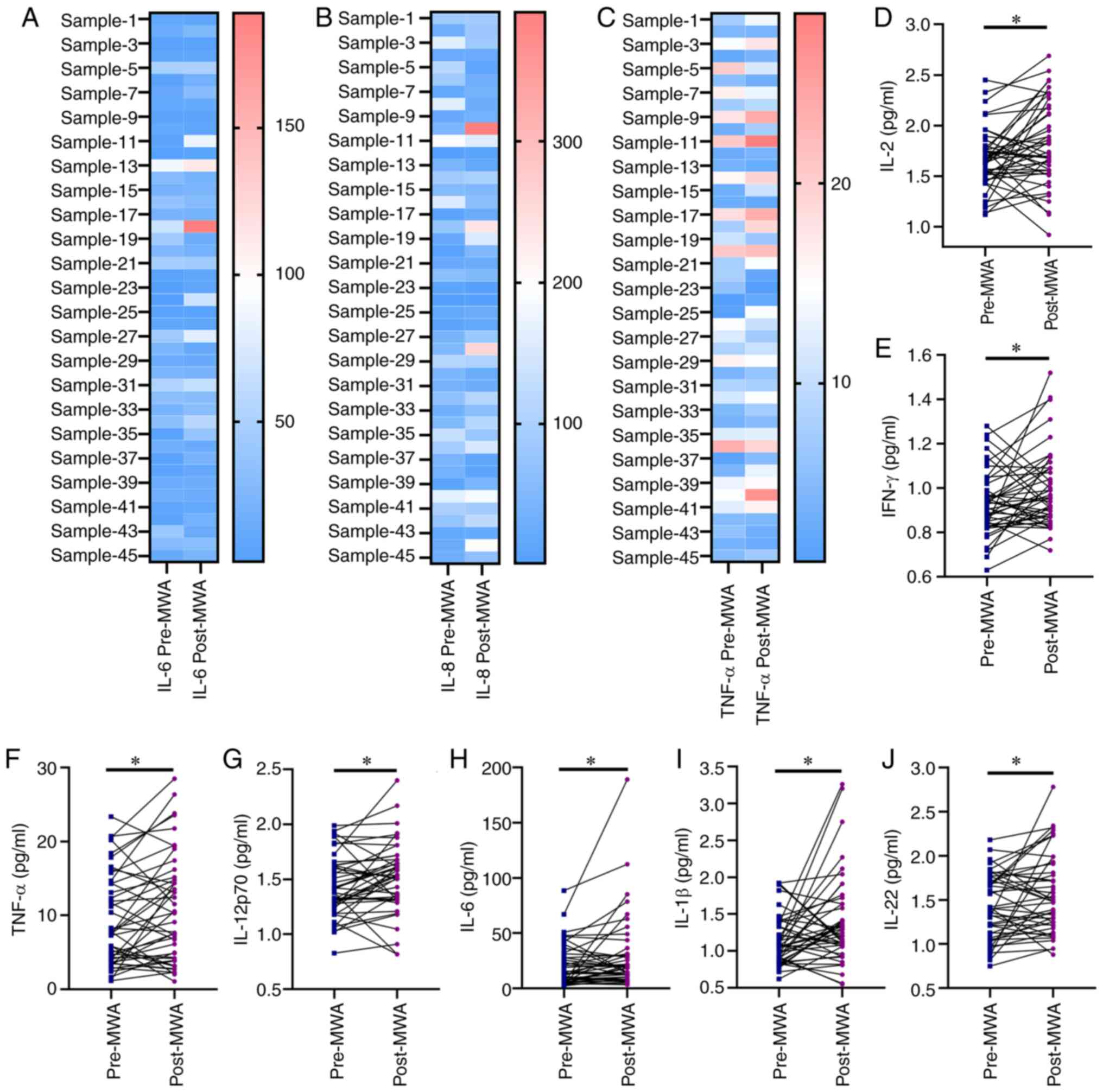
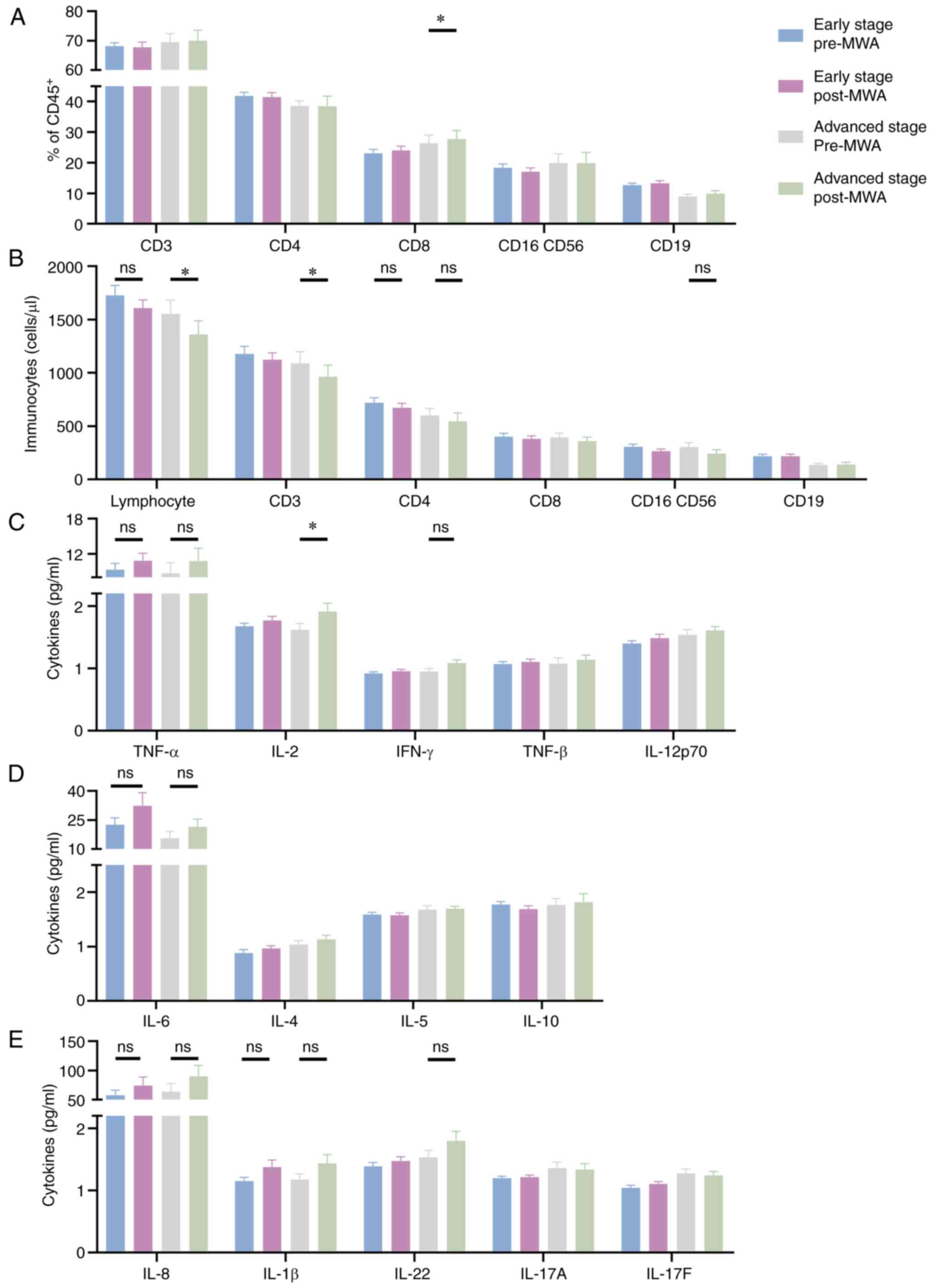
|
1
|
Wu F, Wang L and Zhou C: Lung cancer in
China: Current and prospect. Curr Opin Oncol. 33:40–46. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao S, Li N, Wang S, Zhang F, Wei W, Li N,
Bi N, Wang Z and He J: Lung cancer in People's Republic of China. J
Thorac Oncol. 15:1567–1576. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brody H: Lung cancer. Nature. 587:S72020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aokage K, Yoshida J, Hishida T, Tsuboi M,
Saji H, Okada M, Suzuki K, Watanabe S and Asamura H: Limited
resection for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer as
function-preserving radical surgery: A review. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
47:7–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ni Y, Xu H and Ye X: Image-guided
percutaneous microwave ablation of early-stage non-small cell lung
cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 16:320–325. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ryan MJ, Willatt J, Majdalany BS, Kielar
AZ, Chong S, Ruma JA and Pandya A: Ablation techniques for primary
and metastatic liver tumors. World J Hepatol. 8:191–199. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vogl TJ, Nour-Eldin NA, Albrecht MH,
Kaltenbach B, Hohenforst-Schmidt W, Lin H, Panahi B, Eichler K,
Gruber-Rouh T and Roman A: Thermal ablation of lung tumors: Focus
on microwave ablation. Rofo. 189:828–843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chan MV, Huo YR, Cao C and Ridley L:
Survival outcomes for surgical resection versus CT-guided
percutaneous ablation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol.
31:5421–5433. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Dong Y, Kong L, Shi F, Zhu H and Yu
J: Abscopal effect of radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint
inhibitors. J Hematol Oncol. 11:1042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chu KF and Dupuy DE: Thermal ablation of
tumours: Biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:199–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van den Bijgaart RJE, Eikelenboom DC,
Hoogenboom M, Fütterer JJ, den Brok MH and Adema G J: Thermal and
mechanical high-intensity focused ultrasound: Perspectives on tumor
ablation, immune effects and combination strategies. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 66:247–258. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vilinovszki O, Andratschke N, Huellner M,
Curioni-Fontecedro A and Kroeze SGC: True abscopal effect in a
patient with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol.
16:1942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pierini S, Mishra A, Perales-Linares R,
Uribe-Herranz M, Beghi S, Giglio A, Pustylnikov S, Costabile F,
Rafail S, Amici A, et al: Combination of vasculature targeting,
hypofractionated radiotherapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitor
elicits potent antitumor immune response and blocks tumor
progression. J Immunother Cancer. 9:e0016362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shao C, Yang M, Pan Y, Xie D, Chen B, Ren
S and Zhou C: Case report: Abscopal effect of microwave ablation in
a patient with advanced squamous NSCLC and resistance to
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 12:6967492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu H, Sun W, Kong Y, Huang Y, Wei Z, Zhang
L, Liang J and Ye X: Immune abscopal effect of microwave ablation
for lung metastases of endometrial carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther.
16:1718–1721. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu L, Xie H, Wang L, Cheng M, Liu J, Xu J,
Wei Z, Ye X, Xie Q and Liang J: Microwave ablation induces abscopal
effect via enhanced systemic antitumor immunity in colorectal
cancer. Front Oncol. 13:11747132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song X, Li N, Liu Y, Wang Z, Wang T, Tan
S, Li C, Qiu C, Gao L, Asano K, et al: CD169-positive macrophages
enhance abscopal effect of radiofrequency ablation therapy in liver
cancer. Transl Oncol. 15:1013062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khan SY, Melkus MW, Rasha F, Castro M, Chu
V, Brandi L, Khan H, Gill HS, Pruitt K and Layeequr Rahman R:
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) as a biomarker of abscopal
effect of cryoablation in breast cancer: A pilot study. Ann Surg
Oncol. 29:2914–2925. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He C, Huang X, Zhang Y, Lin X and Li S:
T-cell activation and immune memory enhancement induced by
irreversible electroporation in pancreatic cancer. Clin Transl Med.
10:e392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao Y, Zhang T, Wang Y, Lu D, Du J, Feng
X, Zhou H, Liu N, Zhu H, Qin S, et al: ICAM-1 orchestrates the
abscopal effect of tumor radiotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118:e20103331182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang YS, Zhang YH, Li XJ, Hu TC, Chen WZ,
Pan X, Chai HY and Ye YC: Bystander effect and abscopal effect in
recurrent thymic carcinoma treated with carbon-ion radiation
therapy: A case report. World J Clin Cases. 9:6538–6543. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leuchte K, Staib E, Thelen M, Gödel P,
Lechner A, Zentis P, Garcia-Marquez M, Waldschmidt D, Datta RR,
Wahba R, et al: Microwave ablation enhances tumor-specific immune
response in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 70:893–907. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou W, Yu M, Mao X, Pan H, Tang X, Wang
J, Che N, Xie H, Ling L, Zhao Y, et al: Landscape of the peripheral
immune response induced by local microwave ablation in patients
with breast cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). 9:e22000332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang L, Zhang M, Wang J, Li Y, Wang T,
Xia J, Feng B and Shen J: Immunogenic change after percutaneous
microwave ablation in pulmonary malignancies: Variation in immune
cell subsets and cytokines in peripheral blood. Front Immunol.
13:10691922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu H, Tan X, Kong Y, Huang Y, Wei Z and Ye
X: Microwave ablation of non-small cell lung cancer tumors changes
plasma levels of cytokines IL-2 and IFN-γ. J Cancer Res Ther.
18:532–544. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Puri S, Shafique M and Gray JE: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors in early-stage and locally advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 19:392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye X, Fan W, Wang H, Wang J, Wang Z, Gu S,
Feng W, Zhuang Y, Liu B, Li X, et al: Expert consensus workshop
report: Guidelines for thermal ablation of primary and metastatic
lung tumors (2018 edition). J Cancer Res Ther. 14:730–744. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Palussière J, Cazayus M, Cousin S, Cabart
M, Chomy F, Catena V and Buy X: Is there a role for percutaneous
ablation for early stage lung cancer? What Is the evidence? Curr
Oncol Rep. 23:812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Xu J, Yu J and Liang P: Review of
clinical tumor ablation advance in Asia. Int J Hyperthermia.
38:1639–1649. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Flynn MJ, Sayed AA, Sharma R, Siddique A
and Pinato DJ: Challenges and opportunities in the clinical
development of immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 69:2258–2270. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rangamuwa K, Leong T, Weeden C,
Asselin-Labat ML, Bozinovski S, Christie M, John T, Antippa P,
Irving L and Steinfort D: Thermal ablation in non-small cell lung
cancer: A review of treatment modalities and the evidence for
combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Transl Lung Cancer
Res. 10:2842–2857. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
den Brok MH, Sutmuller RP, van der Voort
R, Bennink EJ, Figdor CG, Ruers TJ and Adema GJ: In situ tumor
ablation creates an antigen source for the generation of antitumor
immunity. Cancer Res. 64:4024–4029. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang K, Wang C, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Lin W,
Mo J and Jin C: Combination of ablation and immunotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma: Where we are and where to go. Front
Immunol. 12:7927812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Keisari Y: Tumor abolition and antitumor
immunostimulation by physico-chemical tumor ablation. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 22:310–347. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wei Z, Zhan X, Fan L, Ye X, Yang X, Huang
G, Li W, Wang J, Han X, Meng M, et al: Programmed death-ligand 1
expression and CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer treated with microwave ablation and
chemotherapy. Int J Hyperthermia. 35:591–598. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu T, Sui GQ, Teng DK, Luo Q, Wang H and
Lin YQ: Study on changes in immune function after microwave
ablation of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Cancer Manag Res.
14:2861–2868. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li L, Wang W, Pan H, Ma G, Shi X, Xie H,
Liu X, Ding Q, Zhou W and Wang S: Microwave ablation combined with
OK-432 induces Th1-type response and specific antitumor immunity in
a murine model of breast cancer. J Transl Med. 15:232017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Hou X, Cai H and Zhuang X:
Effects of microwave ablation on T-cell subsets and cytokines of
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Minim Invasive Ther Allied
Technol. 26:207–211. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Volkó J, Kenesei Á, Zhang M, Várnai P,
Mocsár G, Petrus MN, Jambrovics K, Balajthy Z, Müller G, Bodnár A,
et al: IL-2 receptors preassemble and signal in the ER/Golgi
causing resistance to antiproliferative anti-IL-2Rα therapies. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:21120–21130. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nguyen KG, Vrabel MR, Mantooth SM, Hopkins
JJ, Wagner ES, Gabaldon TA and Zaharoff DA: Localized
interleukin-12 for cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol.
11:5755972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao J, Li Q, Muktiali M, Ren B, Hu Y, Li
D, Li Z, Li D, Xie Y, Tao M and Liang R: Effect of microwave
ablation treatment of hepatic malignancies on serum cytokine
levels. BMC Cancer. 20:8122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou W, Yu M, Pan H, Qiu W, Wang H, Qian
M, Che N, Zhang K, Mao X, Li L, et al: Microwave ablation induces
Th1-type immune response with activation of ICOS pathway in
early-stage breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 9:e0023432021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bent EH, Millán-Barea LR, Zhuang I, Goulet
DR, Fröse J and Hemann MT: Microenvironmental IL-6 inhibits
anti-cancer immune responses generated by cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Nat Commun. 12:62182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu Y, Min J, Ge C, Shu J, Tian D, Yuan Y
and Zhou D: Interleukin 22 in liver injury, inflammation and
cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 16:2405–2413. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun R, Gao DS, Shoush J and Lu B: The IL-1
family in tumorigenesis and antitumor immunity. Semin Cancer Biol.
86:280–295. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bent R, Moll L, Grabbe S and Bros M:
Interleukin-1 beta-A friend or foe in malignancies? Int J Mol Sci.
19:21552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fisher DT, Appenheimer MM and Evans SS:
The two faces of IL-6 in the tumor microenvironment. Semin Immunol.
26:38–47. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hossein-Khannazer N, Zian Z, Bakkach J,
Kamali AN, Hosseinzadeh R, Anka AU, Yazdani R and Azizi G: Features
and roles of T helper 22 cells in immunological diseases and
malignancies. Scand J Immunol. 93:e130302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Perez LG, Kempski J, McGee HM, Pelzcar P,
Agalioti T, Giannou A, Konczalla L, Brockmann L, Wahib R, Xu H, et
al: TGF-β signaling in Th17 cells promotes IL-22 production and
colitis-associated colon cancer. Nat Commun. 11:26082020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rodriguez AE, Ducker GS, Billingham LK,
Martinez CA, Mainolfi N, Suri V, Friedman A, Manfredi MG, Weinberg
SE, Rabinowitz JD and Chandel NS: Serine metabolism supports
macrophage IL-1β production. Cell Metab. 29:1003–1011.e4. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hirani D, Alvira CM, Danopoulos S, Milla
C, Donato M, Tian L, Mohr J, Dinger K, Vohlen C, Selle J, et al:
Macrophage-derived IL-6 trans-signalling as a novel target in the
pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur Respir J.
59:20022482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hou Y, Zhu L, Tian H, Sun HX, Wang R,
Zhang L and Zhao Y: IL-23-induced macrophage polarization and its
pathological roles in mice with imiquimod-induced psoriasis.
Protein Cell. 9:1027–1038. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nishiga Y, Drainas AP, Baron M,
Bhattacharya D, Barkal AA, Ahrari Y, Mancusi R, Ross JB, Takahashi
N, Thomas A, et al: Radiotherapy in combination with CD47 blockade
elicits a macrophage-mediated abscopal effect. Nat Cancer.
3:1351–1366. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Teijeira A, Garasa S, Ochoa MDC, Cirella
A, Olivera I, Glez-Vaz J, Andueza MP, Migueliz I, Alvarez M,
Rodriguez-Ruiz ME, et al: Differential Interleukin-8 thresholds for
chemotaxis and netosis in human neutrophils. Eur J Immunol.
51:2274–2280. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yasuda K, Takeuchi Y and Hirota K: The
pathogenicity of Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Semin
Immunopathol. 41:283–297. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu T, Li S, Ying S, Tang S, Ding Y, Li Y,
Qiao J and Fang H: The IL-23/IL-17 pathway in inflammatory skin
diseases: From bench to bedside. Front Immunol. 11:5947352020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou Y, Xu X, Ding J, Jing X, Wang F, Wang
Y and Wang P: Dynamic changes of T-cell subsets and their relation
with tumor recurrence after microwave ablation in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 14:40–45. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Takaoka Y, Abe Y, Haraguchi R and Kito K:
Lymphotoxin (TNF-beta). Nihon Rinsho. 68 (Suppl 7):S93–S95.
2010.(In Japanese).
|
|
59
|
Chen Z, Huang Y, Hu Z, Zhao M, Li M, Bi G,
Zheng Y, Liang J, Lu T, Jiang W, et al: Landscape and dynamics of
single tumor and immune cells in early and advanced-stage lung
adenocarcinoma. Clin Transl Med. 11:e3502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gabrielson A, Wu Y, Wang H, Jiang J,
Kallakury B, Gatalica Z, Reddy S, Kleiner D, Fishbein T, Johnson L,
et al: Intratumoral CD3 and CD8 T-cell densities associated with
relapse-free survival in HCC. Cancer Immunol Res. 4:419–430. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Huff WX, Kwon JH, Henriquez M, Fetcko K
and Dey M: The evolving role of CD8+CD28−
immunosenescent T cells in cancer immunology. Int J Mol Sci.
20:28102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ren Z, Zhang A, Sun Z, Liang Y, Ye J, Qiao
J, Li B and Fu YX: Selective delivery of low-affinity IL-2 to PD-1+
T cells rejuvenates antitumor immunity with reduced toxicity. J
Clin Invest. 132:e1536042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tison A, Garaud S, Chiche L, Cornec D and
Kostine M: Immune-checkpoint inhibitor use in patients with cancer
and pre-existing autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
18:641–656. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jiang R and Sun B: IL-22 signaling in the
tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1290:81–88. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rallis KS, Corrigan AE, Dadah H,
Stanislovas J, Zamani P, Makker S, Szabados B and Sideris M: IL-10
in cancer: An essential thermostatic regulator between homeostatic
immunity and inflammation-a comprehensive review. Future Oncol.
18:3349–3365. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Qiao J, Liu Z, Dong C, Luan Y, Zhang A,
Moore C, Fu K, Peng J, Wang Y, Ren Z, et al: Targeting tumors with
IL-10 prevents dendritic cell-mediated CD8+ T cell
apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 35:901–915.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dromi SA, Walsh MP, Herby S, Traughber B,
Xie J, Sharma KV, Sekhar KP, Luk A, Liewehr DJ, Dreher MR, et al:
Radiofrequency ablation induces antigen-presenting cell
infiltration and amplification of weak tumor-induced immunity.
Radiology. 251:58–66. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Faraoni EY, O'Brien BJ, Strickland LN,
Osborn BK, Mota V, Chaney J, Atkins CL, Cen P, Rowe J, Cardenas J,
et al: Radiofrequency ablation remodels the tumor microenvironment
and promotes neutrophil-mediated abscopal immunomodulation in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 11:4–12. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kanegasaki S and Tsuchiya T: Alarmins
released during local antitumor treatments play an essential role
in enhancing tumor growth inhibition at treated and non-treated
sites via a derivative of CCL3. Oncoimmunology. 3:e9589562014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yin J, Dong J, Gao W and Wang Y: A case
report of remarkable response to association of radiofrequency
ablation with subsequent Atezolizumab in stage IV nonsmall cell
lung cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e131122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yu W, Sun J, Wang T and Du Y: The effect
of microwave ablation combined with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody
on T cell subsets and long-term prognosis in patients suffering
from non-small-cell lung cancer. Comput Math Methods Med.
2022:70954232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Huang G, Li W, Meng M, Ni Y, Han X, Wang
J, Zou Z, Zhang T, Dai J, Wei Z, et al: Synchronous microwave
ablation combined with cisplatin intratumoral chemotherapy for
large non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 12:9555452022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Feng K and Lu Y: Clinical analysis of
systemic chemotherapy combined with microwave ablation in the
treatment of lung cancer. Asian J Surg. 45:1107–1112. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Shi L, Wang J, Ding N, Zhang Y, Zhu Y,
Dong S, Wang X, Peng C, Zhou C, Zhou L, et al: Inflammation induced
by incomplete radiofrequency ablation accelerates tumor progression
and hinders PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 10:54212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kutob L and Schneider F: Lung cancer
staging. Surg Pathol Clin. 13:57–71. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|