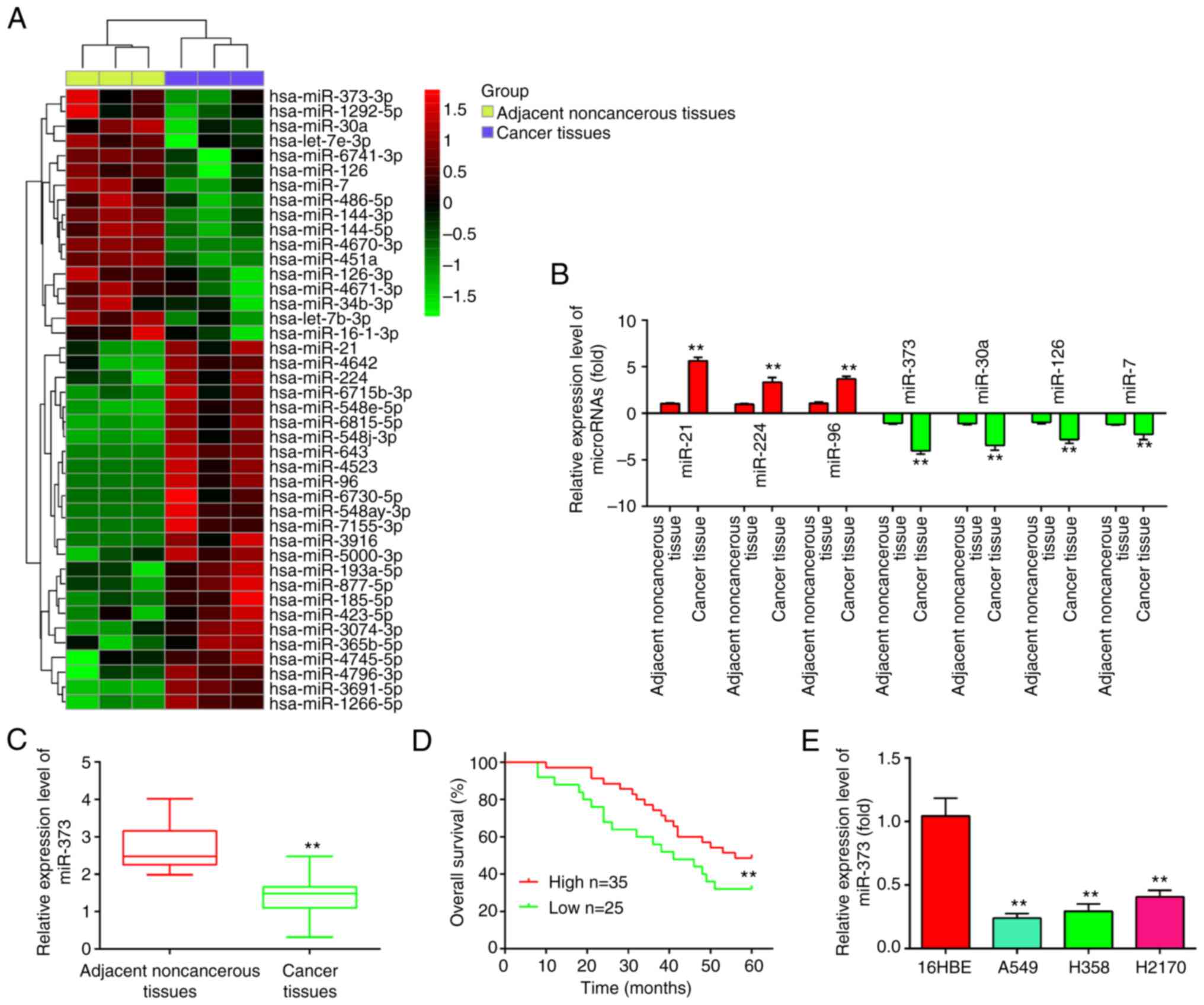
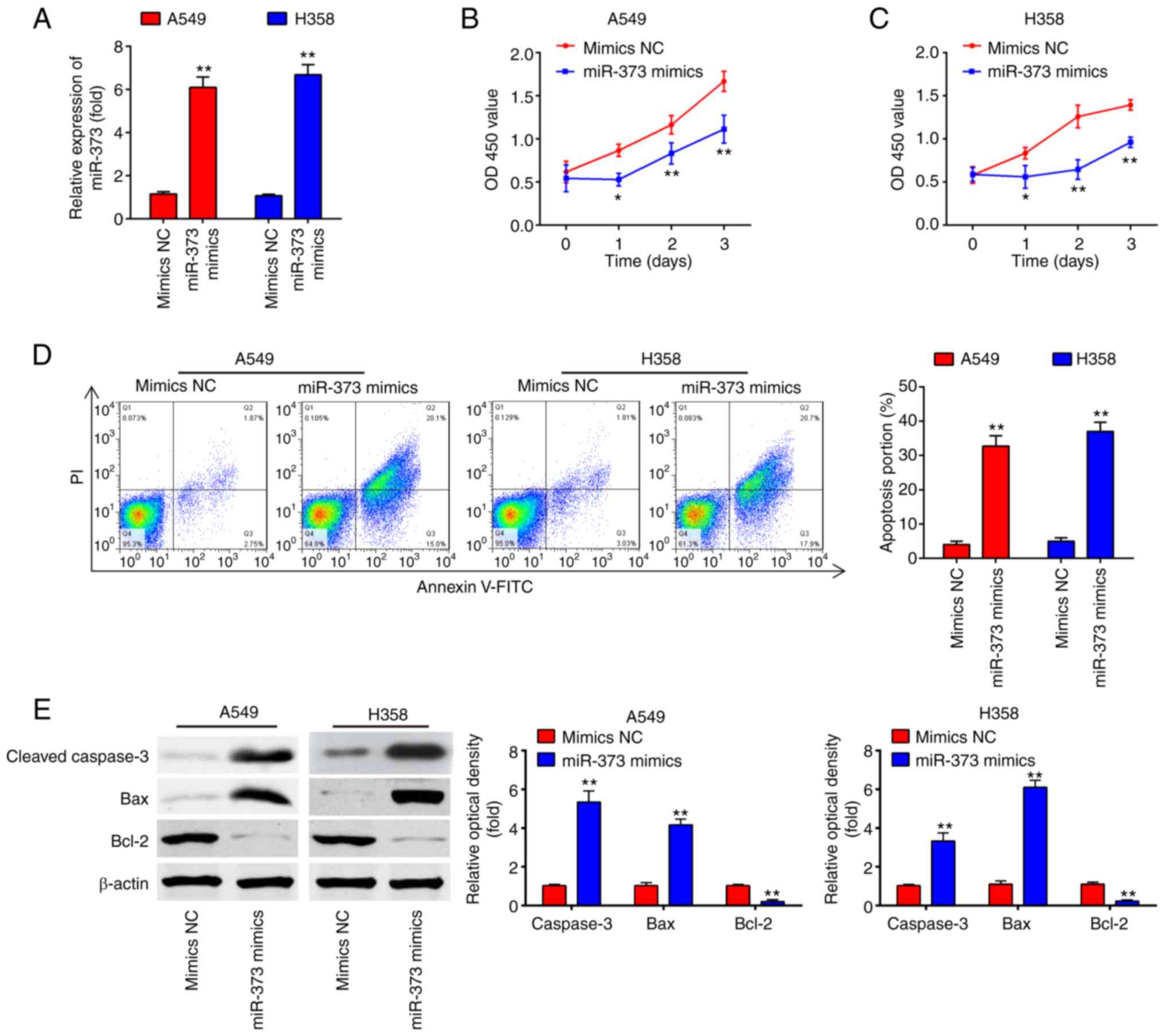
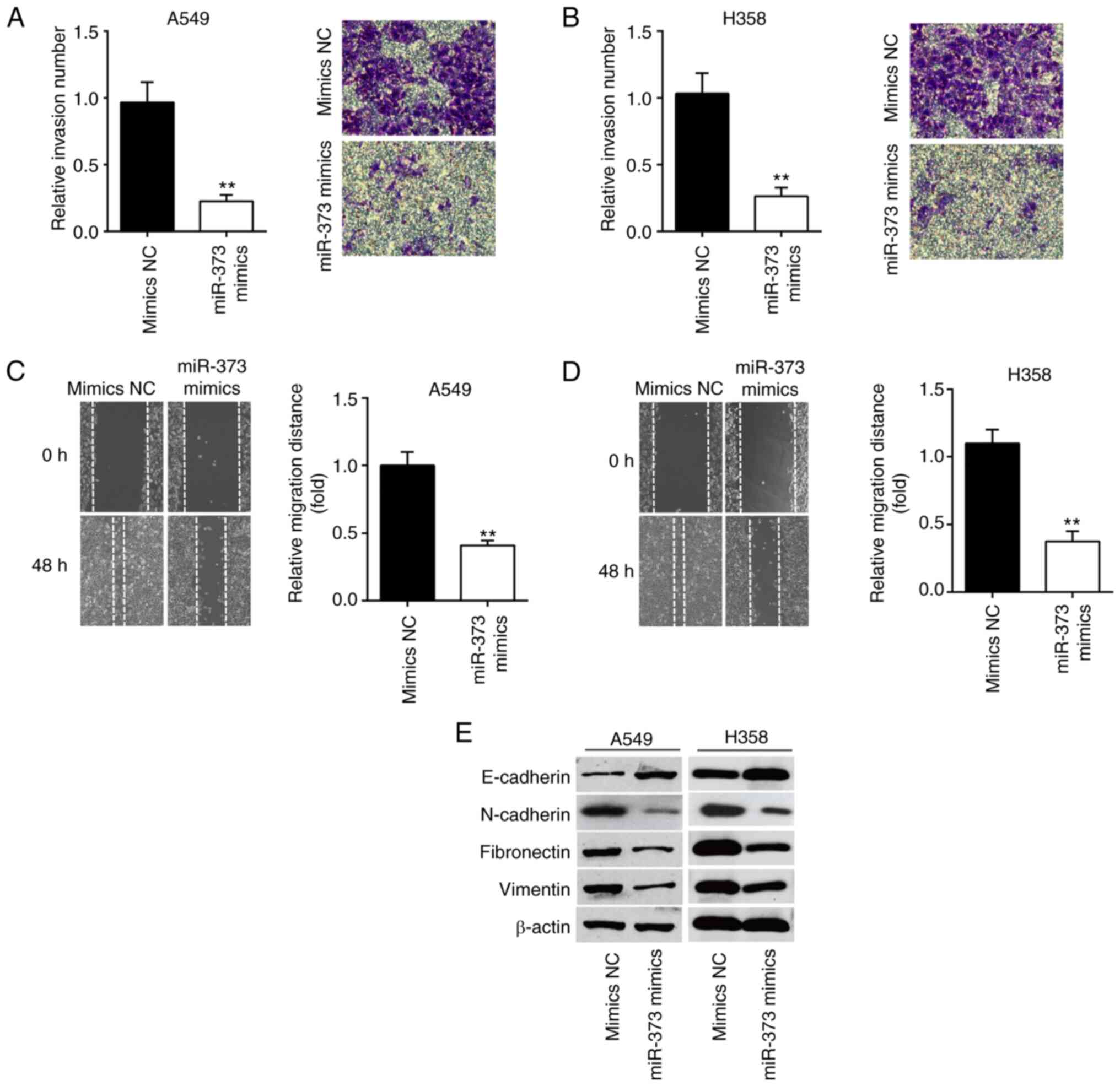
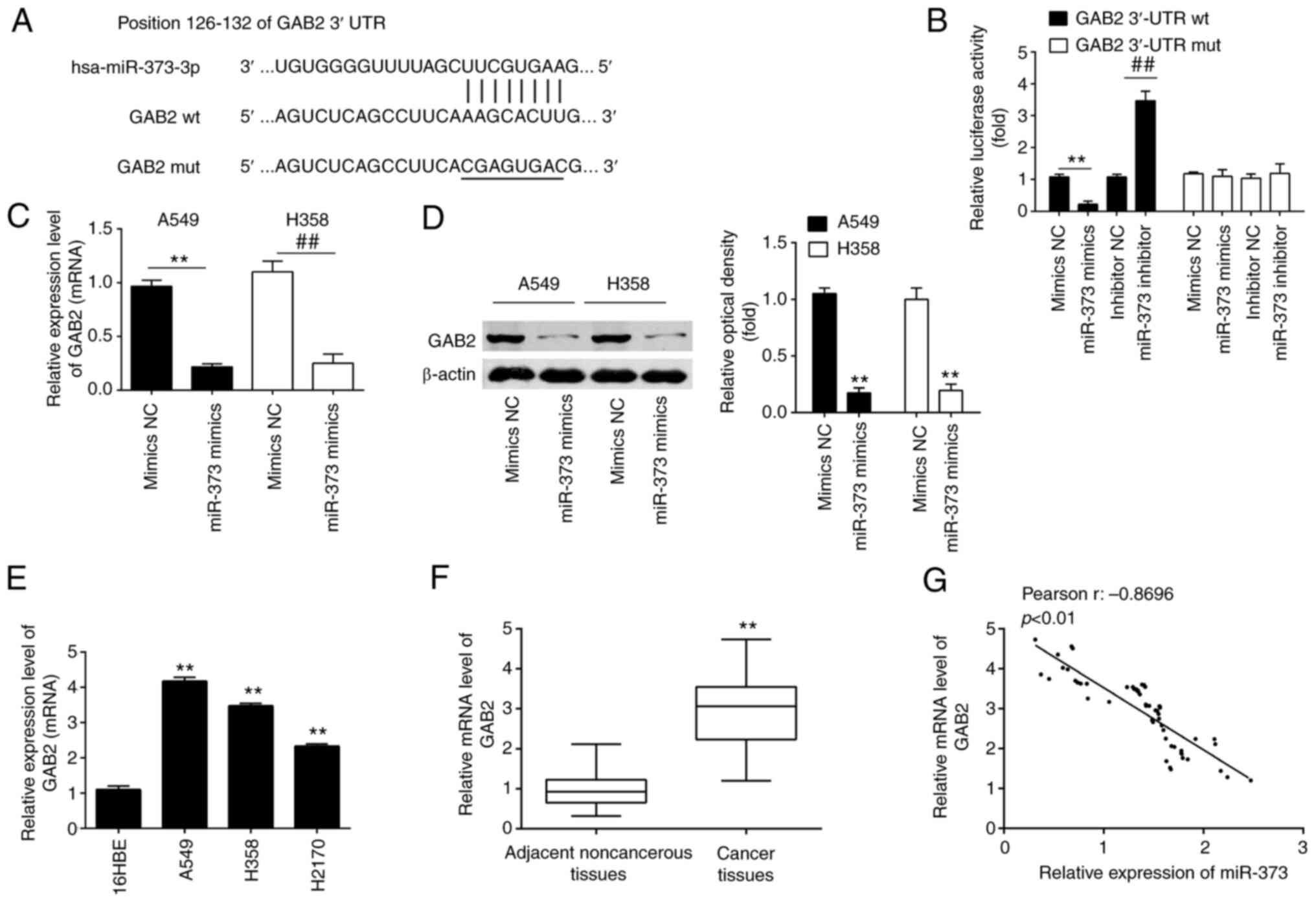
|
1
|
Chen P, Li Y, Liu R, Xie Y, Jin Y, Wang M,
Yu Z, Wang W and Luo X: Non-small cell lung cancer-derived exosomes
promote proliferation, phagocytosis, and secretion of microglia via
exosomal microRNA in the metastatic microenvironment. Transl Oncol.
27:1015942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mercier O, Fadel E, de Perrot M, Mussot S,
Stella F, Chapelier A and Dartevelle P: Surgical treatment of
solitary adrenal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 130:136–140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL,
Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL and Paz-Ares L: Lung cancer: Current
therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 389:299–311. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giovannetti E, Toffalorio F, De Pas T and
Peters GJ: Pharmacogenetics of conventional chemotherapy in
non-small-cell lung cancer: A changing landscape? Pharmacogenomics.
13:1073–1086. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi L, Zhu W, Huang Y, Zhuo L, Wang S,
Chen S, Zhang B and Ke B: Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived
exosomal microRNA-20a suppresses the PTEN/PI3K-AKT pathway to
promote the progression and chemoresistance of non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Transl Med. 12:e9892022. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han B, Molins L, He Y, Viñolas N,
Sánchez-Lorente D, Boada M, Guirao A, Díaz T, Martinez D, Ramirez
J, et al: Characterization of the MicroRNA Cargo of Extracellular
Vesicles Isolated from a Pulmonary Tumor-Draining Vein Identifies
miR-203a-3p as a relapse biomarker for resected non-small cell lung
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 23:71382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yan X, Wang T and Wang J: Circ_0016760
Acts as a Sponge of MicroRNA-4295 to Enhance E2F transcription
factor 3 expression and facilitates cell proliferation and
glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 37:147–158. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gong J, Shen Y, Jiang F, Wang Y, Chu L,
Sun J, Shen P and Chen M: MicroRNA-20a promotes non-small cell lung
cancer proliferation by upregulating PD-L1 by targeting PTEN. Oncol
Lett. 23:1482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
MicroRNA-211 promotes non-small-cell lung
cancer proliferation and invasion by targeting MxA [Retraction].
Onco Targets Ther. 15:1387–1388. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei J, Meng G, Wu J, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Dong
T, Bao J, Wang C and Zhang J: MicroRNA-326 impairs chemotherapy
resistance in non small cell lung cancer by suppressing histone
deacetylase SIRT1-mediated HIF1α and elevating VEGFA.
Bioengineered. 13:5685–5699. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fang X, Shi H and Sun F: The
microRNA-520a-3p inhibits invasion and metastasis by targeting
NF-kappaB signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Transl Oncol. 24:1569–1579. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu C, Shan Z, Hong J and Yang L:
MicroRNA-92a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
activation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell
lung cancer metastasis. Int J Oncol. 51:235–244. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ye Y, Zhuang J, Wang G, He S, Ni J, Xia W
and Wang J: microRNA-605 promotes cell proliferation, migration and
invasion in non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting LATS2.
Exp Ther Med. 24:4882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eyking A, Reis H, Frank M, Gerken G,
Schmid KW and Cario E: MiR-205 and MiR-373 are associated with
aggressive human mucinous colorectal cancer. PLoS One.
11:e01568712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Zhao FJ, Chen LL, Wang LQ, Nephew
KP, Wu YL and Zhang S: MiR-373 targeting of the Rab22a oncogene
suppresses tumor invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer.
Oncotarget. 5:12291–12303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seol HS, Akiyama Y, Shimada S, Lee HJ, Kim
TI, Chun SM, Singh SR and Jang SJ: Epigenetic silencing of
microRNA-373 to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell
lung cancer through IRAK2 and LAMP1 axes. Cancer Lett. 353:232–241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Xu J, Yan X, Jin K, Li W and Zhang
R: MicroRNA-485 plays tumour-suppressive roles in colorectal cancer
by directly targeting GAB2. Oncol Rep. 40:554–564. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei J, Gao W, Zhu CJ, Liu YQ, Mei Z, Cheng
T and Shu YQ: Identification of plasma microRNA-21 as a biomarker
for early detection and chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung
cancer. Chin J Cancer. 30:407–414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui R, Meng W, Sun HL, Kim T, Ye Z, Fassan
M, Jeon YJ, Li B, Vicentini C, Peng Y, et al: MicroRNA-224 promotes
tumor progression in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:E4288–E4297. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma L, Huang Y, Zhu W, Zhou S, Zhou J, Zeng
F, Liu X, Zhang Y and Yu J: An integrated analysis of miRNA and
mRNA expressions in non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS One.
6:e265022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumarswamy R, Mudduluru G, Ceppi P,
Muppala S, Kozlowski M, Niklinski J, Papotti M and Allgayer H:
MicroRNA-30a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by
targeting Snai1 and is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Cancer. 130:2044–2053. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K, Yu L,
Hunter MG, Otterson GA, Nuovo G, Marsh CB and Nana-Sinkam SP:
MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma
cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 373:607–612. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiong S, Zheng Y, Jiang P, Liu R, Liu X
and Chu Y: MicroRNA-7 inhibits the growth of human non-small cell
lung cancer A549 cells through targeting BCL-2. Int J Biol Sci.
7:805–814. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adams SJ, Aydin IT and Celebi JT: GAB2-a
scaffolding protein in cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1265–1270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ding CB, Yu WN, Feng JH and Luo JM:
Structure and function of Gab2 and its role in cancer (Review). Mol
Med Rep. 12:4007–4014. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gu DH, Mao JH, Pan XD, Zhu H, Chen X,
Zheng B and Shan Y: microRNA-302c-3p inhibits renal cell carcinoma
cell proliferation by targeting Grb2-associated binding 2 (Gab2).
Oncotarget. 8:26334–26343. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mu L, Guan B, Tian J, Li X, Long Q, Wang
M, Wang W, She J, Li X, Wu D and Du Y: MicroRNA218 inhibits tumor
angiogenesis of human renal cell carcinoma by targeting GAB2. Oncol
Rep. 44:1961–1970. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu S, Geng S and Hu Y: miR-486-5p inhibits
cell proliferation and invasion through repressing GAB2 in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 16:3525–3530.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu H, Tou FF, Mao WM, Xu YL, Jin H, Kuang
YK, Han CB and Guo CY: microRNA-1321 and microRNA-7515 contribute
to the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting
CDC20. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 38:425–436. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ye J, Luo W, Luo L, Zhai L and Huang P:
MicroRNA-671-5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion
in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting MFAP3L. Mol Med Rep.
25:302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shang Y, Zang A, Li J, Jia Y, Li X, Zhang
L, Huo R, Yang J, Feng J, Ge K, et al: MicroRNA-383 is a tumor
suppressor and potential prognostic biomarker in human non-small
cell lung caner. Biomed Pharmacother. 83:1175–1181. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zeng Y, Zhu J, Shen D, Qin H, Lei Z, Li W,
Liu Z and Huang JA: MicroRNA-205 targets SMAD4 in non-small cell
lung cancer and promotes lung cancer cell growth in vitro and in
vivo. Oncotarget. 8:30817–30829. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qin Q, Wei F, Zhang J and Li B: miR-134
suppresses the migration and invasion of nonsmall cell lung cancer
by targeting ITGB1. Oncol Rep. 37:823–830. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang JX, Zhai JF, Yang XT and Wang J:
MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in
human non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:3793–3801. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang W, He Y, Shi Y, Guo Z, Yang S, Wei
K, Pan C, Xia Y and Chen Y: MicroRNA-1204 promotes cell
proliferation by regulating PITX1 in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cell Biol Int. 43:253–264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu HM, Yi WW, Ma YS, Wu W, Yu F, Fan HW,
Lv ZW, Yang HQ, Chang ZY, Zhang C, et al: Prognostic implications
of decreased microRNA-101-3p expression in patients with non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 16:7048–7056. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pang J, Dai L, Zhang C and Zhang Q:
MiR-373 Inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostatic
cancer via targeting runt-related transcription factor 2. J Healthc
Eng. 2021:69742252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu N, Liu X, Xu X, Fan X, Liu M, Li X,
Zhong Q and Tang H: MicroRNA-373, a new regulator of protein
phosphatase 6, functions as an oncogene in hepatocellular
carcinoma. FEBS J. 278:2044–2054. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis
AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A,
et al: A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as
oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Adv Exp Med Biol.
604:17–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qu HW, Jin Y, Cui ZL and Jin XB:
MicroRNA-373-3p inhibits prostate cancer progression by targeting
AKT1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:6252–6259. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ye Y, Zhang L, Song Y, Zhuang J, Wang G,
Ni J, Zhang S and Xia W: MicroRNA373 exerts antitumor functions in
human liver cancer by targeting Rab22a. Mol Med Rep. 20:3874–3882.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu MM, Wang GJ, Wu KH, Xue SL, Ju LL, Li
QR, Xiong AW and Yin GP: MicroRNA-373-3p inhibits the growth of
cervical cancer by targeting AKT1 both in vitro and in vivo. Acta
Biochim Pol. 68:611–617. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang L, Qu J, Zhou L, Liao F and Wang J:
MicroRNA-373 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via targeting
BRF2 in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell line. Cancer Res
Treat. 50:936–949. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y, Xu Z and Wang X: miRNA-373
promotes urinary bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and
invasion through upregulating epidermal growth factor receptor. Exp
Ther Med. 17:1190–1195. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mu L, Guan B, Tian J, Li X, Long Q, Wang
M, Wang W, She J, Li X, Wu D and Du Y: [Corrigendum] MicroRNA-218
inhibits tumor angiogenesis of human renal cell carcinoma by
targeting GAB2. Oncol Rep. 48:1912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhuo Y, Li S, Hu W, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Zhang
F, Zhang J, Wang J, Liao M, Chen J, et al: Targeting SNORA38B
attenuates tumorigenesis and sensitizes immune checkpoint blockade
in non-small cell lung cancer by remodeling the tumor
microenvironment via regulation of GAB2/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0041132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Horst B, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Hopkins BD,
Bordone L, Yang Y, Chernoff KA, Uzoma I, Schwipper V, Liebau J,
Nowak NJ, et al: Gab2-mediated signaling promotes melanoma
metastasis. Am J Pathol. 174:1524–1533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bentires-Alj M, Gil SG, Chan R, Wang ZC,
Wang Y, Imanaka N, Harris LN, Richardson A, Neel BG and Gu H: A
role for the scaffolding adapter GAB2 in breast cancer. Nat Med.
12:114–121. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu LJ, Wang YC, Lan HW, Li J and Xia T:
Grb2-associated binder-2 gene promotes migration of non-small cell
lung cancer cells via Akt signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res.
8:1208–1217. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang YM, Zhang ZQ, Liu YY, Zhou X, Shi
XH, Jiang Q, Fan DL and Cao C: Requirement of Galphai1/3-Gab1
signaling complex for keratinocyte growth factor-induced
PI3K-AKT-mTORC1 activation. J Invest Dermatol. 135:181–191. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shioyama W, Nakaoka Y, Higuchi K, Minami
T, Taniyama Y, Nishida K, Kidoya H, Sonobe T, Naito H, Arita Y, et
al: Docking protein Gab1 is an essential component of postnatal
angiogenesis after ischemia via HGF/c-met signaling. Circ Res.
108:664–675. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X and
Peng J: Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: The framework of
malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep. 47:4587–4629. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Papadimitrakopoulou V: Development of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors and their application in
personalized therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 7:1315–1326. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Weng W, Liu C, Li G, Ruan Q, Li H, Lin N
and Chen G: Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 functions as a tumor
activator by sponging miR-3733p to regulate the TGF-β-R2/SMAD
pathway in prostate cancer. Mol Med Rep. 24:8432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang L and Wang L, Chang W, Li Y and Wang
L: MicroRNA-373 promotes the development of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma by targeting LATS2 and OXR1. Int J Biol Markers.
34:148–155. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|