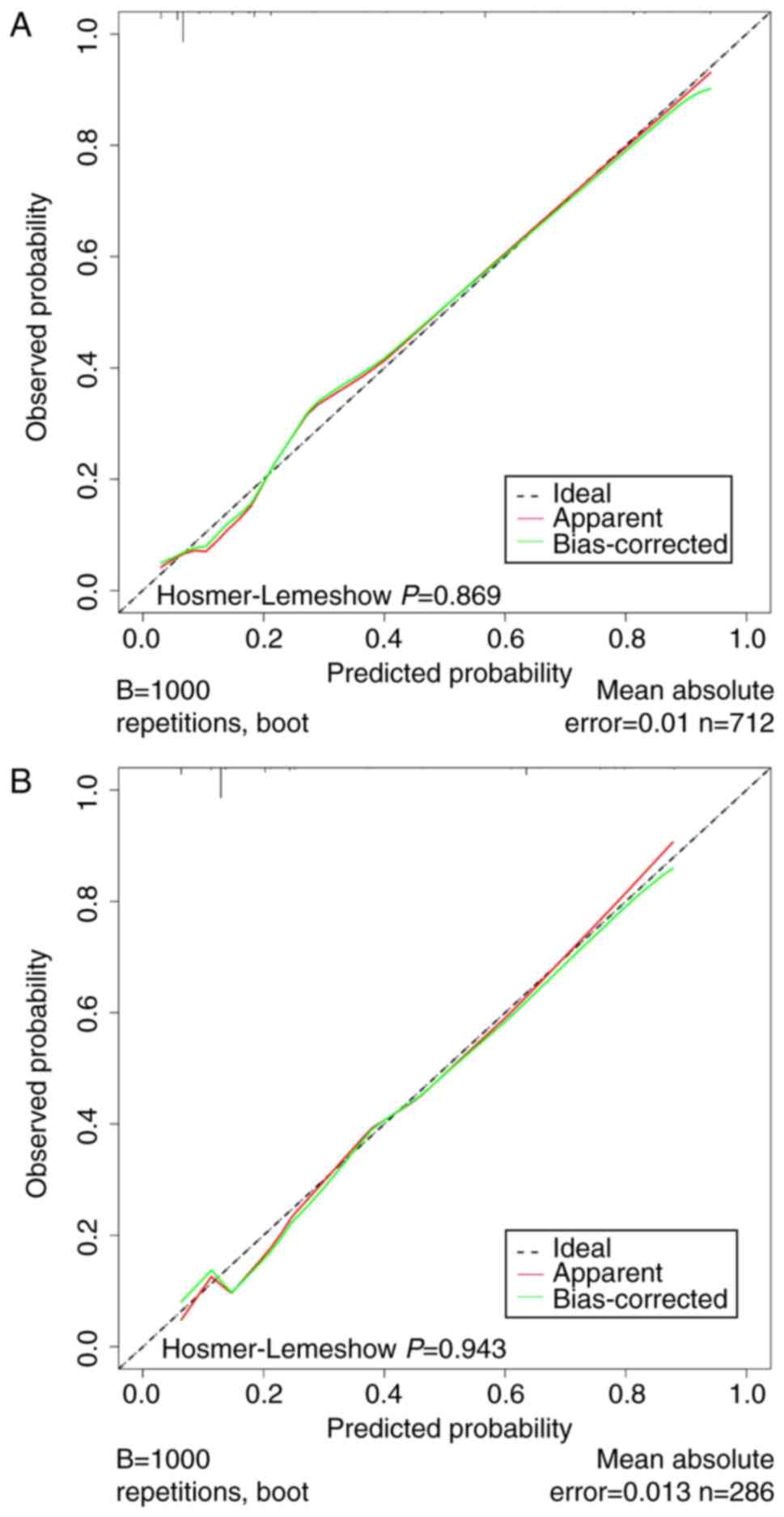
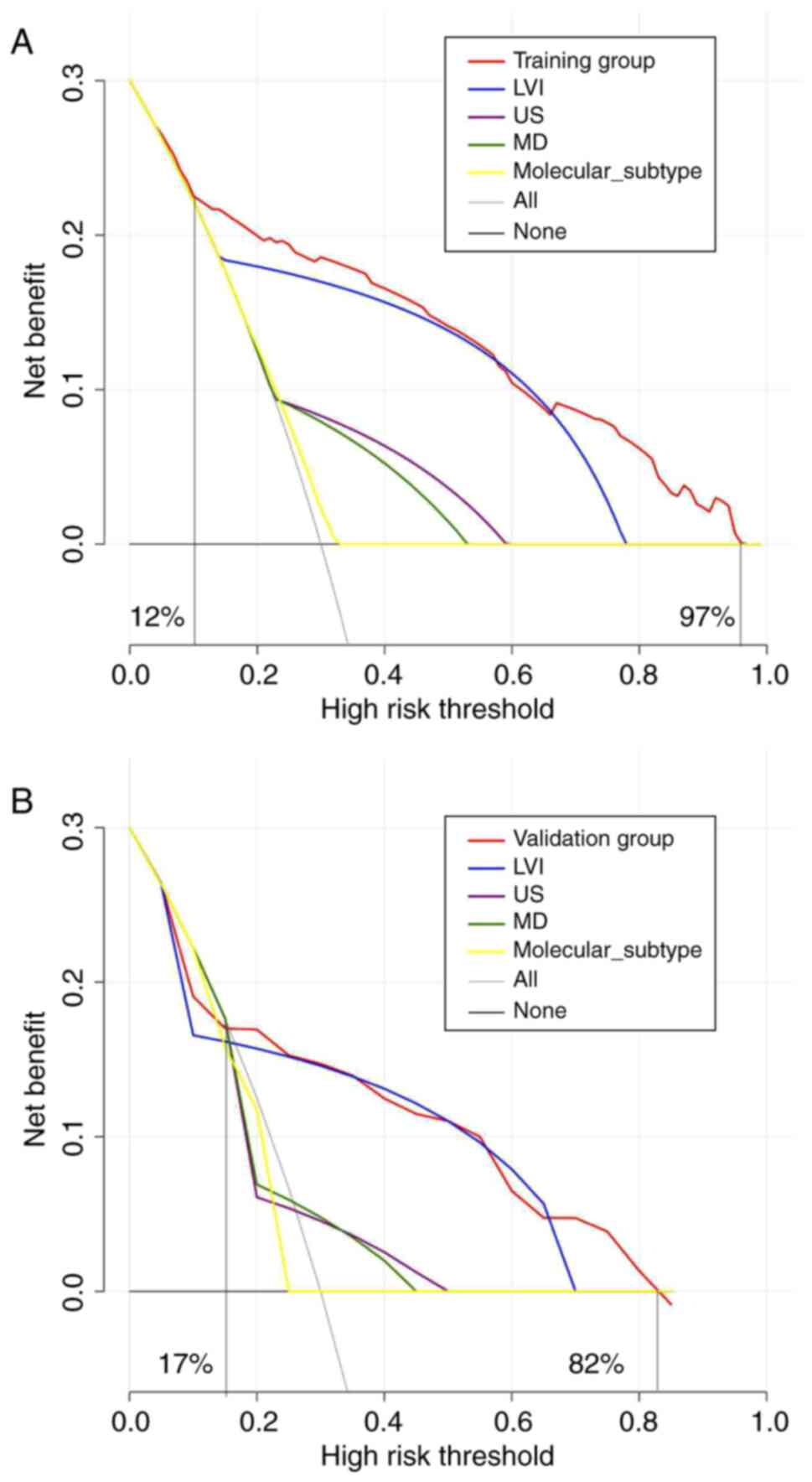
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM and Jemal A:
Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends-an update.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malter W, Hellmich M, Badian M, Kirn V,
Mallmann P and Kraemer S: Factors predictive of sentinel lymph node
involvement in primary breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 38:3657–3662.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM,
Harlow SP, Costantino JP, Ashikaga T, Weaver DL, Mamounas EP,
Jalovec LM, et al: Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with
conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically
node-negative patients with breast cancer: Overall survival
findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 11:927–933. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reimer T, Engel J, Schmidt M, Offersen BV,
Smidt ML and Gentilini OD: Is axillary sentinel lymph node biopsy
required in patients who undergo primary breast surgery? Breast
Care (Basel). 13:324–330. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Langer I, Guller U, Berclaz G, Koechli OR,
Schaer G, Fehr MK, Hess T, Oertli D, Bronz L, Schnarwyler B, et al:
Morbidity of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLN) alone versus SLN and
completion axillary lymph node dissection after breast cancer
surgery: A prospective Swiss multicenter study on 659 patients. Ann
Surg. 245:452–461. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McLaughlin S: A longitudinal comparison of
arm morbidity in stage I–II breast cancer patients treated with
sentinel lymph node biopsy, sentinel lymph node biopsy followed by
completion lymph node dissection, or axillary lymph node
dissection. Breast Diseases. 22:68–70. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Liu D, Lan Y, Zhang L, Wu T, Cui H, Li Z,
Sun P, Tian P, Tian J and Li X: Nomograms for predicting axillary
lymph node status reconciled with preoperative breast ultrasound
images. Front Oncol. 11:5676482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gentilini OD, Botteri E, Sangalli C,
Galimberti V, Porpiglia M, Agresti R, Luini A, Viale G, Cassano E,
Peradze N, et al: Sentinel lymph node biopsy vs no axillary surgery
in patients with small breast cancer and negative results on
ultrasonography of axillary lymph nodes: The SOUND randomized
clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 9:1557–1564. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jung JG, Ahn SH, Lee S, Kim EK, Ryu JM,
Park S, Lim W, Jung YS, Chung IY, Jeong J, et al: No axillary
surgical treatment for lymph node-negative patients after
ultra-sonography [NAUTILUS]: Protocol of a prospective randomized
clinical trial. BMC Cancer. 22:1892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cools-Lartigue J and Meterissian S:
Accuracy of axillary ultrasound in the diagnosis of nodal
metastasis in invasive breast cancer: A review. World J Surg.
36:46–54. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ibrahim-Zada I, Grant CS, Glazebrook KN
and Boughey JC: Preoperative axillary ultrasound in breast cancer:
Safely avoiding frozen section of sentinel lymph nodes in
breast-conserving surgery. J Am Coll Surg. 217:7–15; discussion
15–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang H, Sui X, Zhou S, Hu L and Huang X:
Correlation of conventional ultrasound characteristics of breast
tumors with axillary lymph node metastasis and Ki-67 expression in
patients with breast cancer. J Ultrasound Med. 38:1833–1840. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marino MA, Avendano D, Zapata P, Riedl CC
and Pinker K: Lymph node imaging in patients with primary breast
cancer: Concurrent diagnostic tools. Oncologist. 25:e231–e242.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diepstraten SC, Sever AR, Buckens CF,
Veldhuis WB, van Dalen T, van den Bosch MA, Mali WP and Verkooijen
HM: Value of preoperative ultrasound-guided axillary lymph node
biopsy for preventing completion axillary lymph node dissection in
breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg
Oncol. 21:51–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koehler KE and Ohlinger R: Sensitivity and
specificity of preoperative ultrasonography for diagnosing nodal
metastases in patients with breast cancer. Ultraschall Med.
32:393–399. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vohra LM, Gulzar R and Saleem O: Intra
operative frozen examination of sentinel lymph node in breast
cancer. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 27:40–44. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Andersson Y, Bergkvist L, Frisell J and de
Boniface J: Long-term breast cancer survival in relation to the
metastatic tumor burden in axillary lymph nodes. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 171:359–369. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feu J, Tresserra F, Fábregas R, Navarro B,
Grases PJ, Suris JC, Fernández-Cíd A and Alegret X: Metastatic
breast carcinoma in axillary lymph nodes: In vitro US detection.
Radiology. 205:831–835. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang WT, Chang J and Metreweli C: Patients
with breast cancer: differences in color Doppler flow and
gray-scale US features of benign and malignant axillary lymph
nodes. Radiology. 215:568–573. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bedi DG, Krishnamurthy R, Krishnamurthy S,
Edeiken BS, Le-Petross H, Fornage BD, Bassett RL Jr and Hunt KK:
Cortical morphologic features of axillary lymph nodes as a
predictor of metastasis in breast cancer: In vitro sonographic
study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 191:646–652. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Elmore LC, Appleton CM, Zhou G and
Margenthaler JA: Axillary ultrasound in patients with clinically
node-negative breast cancer: which features are predictive of
disease? J Surg Res. 184:234–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Q, Xing P, Dong H, Zhao T and Jin F:
Preoperative assessment of axillary lymph node status in breast
cancer patients by ultrasonography combined with mammography: A
STROBE compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e114412018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Allison KH, Hammond MEH, Dowsett M,
McKernin SE, Carey LA, Fitzgibbons PL, Hayes DF, Lakhani SR,
Chavez-MacGregor M, Perlmutter J, et al: Estrogen and progesterone
receptor testing in breast cancer: American society of clinical
oncology/College of American pathologists guideline update. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 144:545–563. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M,
McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M,
Fitzgibbons P, et al: Recommendations for human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American society of
clinical oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical
practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 31:3997–4013. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, Harvey
BE, McShane LM and Dowsett M: HER2 testing in breast cancer:
American society of clinical oncology/College of American
pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update summary. J
Oncol Pract. 14:437–441. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ; Panel members, :
Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer:
Highlights of the St Gallen International expert consensus on the
primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol.
24:2206–2223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kerr KF, Brown MD, Zhu K and Janes H:
Assessing the clinical impact of risk prediction models with
decision curves: Guidance for correct interpretation and
appropriate use. J Clin Oncol. 34:2534–2540. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schisterman EF, Perkins NJ, Liu A and
Bondell H: Optimal cut-point and its corresponding Youden Index to
discriminate individuals using pooled blood samples. Epidemiology.
16:73–81. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lan A, Chen J, Li C, Jin Y, Wu Y, Dai Y,
Jiang L, Li H, Peng Y and Liu S: Development and assessment of a
novel core biopsy-based prediction model for pathological complete
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in women with breast cancer.
Int J Environ Res Public Health. 20:16172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Franken R, den Hartog AW, de Waard V,
Engele L, Radonic T, Lutter R, Timmermans J, Scholte AJ, van den
Berg MP, Zwinderman AH, et al: Circulating transforming growth
factor-beta as a prognostic biomarker in Marfan syndrome. Int J
Cardiol. 168:2441–2446. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Canavese G, Bruzzi P, Catturich A, Tomei
D, Carli F, Garrone E, Spinaci S, Lacopo F, Tinterri C and Dozin B:
Sentinel lymph node biopsy versus axillary dissection in
node-negative early-stage breast cancer: 15-year follow-up update
of a randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 23:2494–2500. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Uematsu T, Sano M and Homma K: In vitro
high-resolution helical CT of small axillary lymph nodes in
patients with breast cancer: Correlation of CT and histology. AJR
Am J Roentgenol. 176:1069–1074. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
García Vicente AM, Soriano Castrejón Á,
León Martín A, Relea Calatayud F, Muñoz Sánchez Mdel M, Cruz Mora
MA, Jiménez Londoño GA and Espinosa Aunión R: Early and delayed
prediction of axillary lymph node neoadjuvant response by (18)F-FDG
PET/CT in patients with locally advanced breast cancer. Eur J Nucl
Med Mol Imaging. 41:1309–1318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Memarsadeghi M, Riedl CC, Kaneider A,
Galid A, Rudas M, Matzek W and Helbich TH: Axillary lymph node
metastases in patients with breast carcinomas: Assessment with
nonenhanced versus uspio-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology.
241:367–377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fong W, Tan L, Tan C, Wang H, Liu F, Tian
H, Shen S, Gu R, Hu Y, Jiang X, et al: Predicting the risk of
axillary lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer patients
based on ultrasonographic-clinicopathologic features and the use of
nomograms: A prospective single-center observational study. Eur
Radiol. 32:8200–8212. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Q, Li B, Liu Z, Shang H, Jing H, Shao
H, Chen K, Liang X and Cheng W: Prediction model of axillary lymph
node status using automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) and ki-67
status in early-stage breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 22:9292022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiong J, Zuo W, Wu Y, Wang X, Li W, Wang
Q, Zhou H, Xie M and Qin X: Ultrasonography and clinicopathological
features of breast cancer in predicting axillary lymph node
metastases. BMC Cancer. 22:11552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fujii T, Yajima R, Hirakata T, Miyamoto T,
Fujisawa T, Tsutsumi S, Ynagita Y, Iijima M and Kuwano H: Impact of
the prognostic value of vascular invasion, but not lymphatic
invasion, of the primary tumor in patients with breast cancer.
Anticancer Res. 34:1255–1259. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Karahallı Ö, Acar T, Atahan MK, Acar N,
Hacıyanlı M and Kamer KE: Clinical and pathological factors
affecting the sentinel lymph node metastasis in patients with
breast cancer. Indian J Surg. 79:418–422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yu FH, Wang JX, Ye XH, Deng J, Hang J and
Yang B: Ultrasound-based radiomics nomogram: A potential biomarker
to predict axillary lymph node metastasis in early-stage invasive
breast cancer. Eur J Radiol. 119:1086582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ding J, Jiang L and Wu W: Predictive value
of clinicopathological characteristics for sentinel lymph node
metastasis in early breast cancer. Med Sci Monit. 23:4102–4108.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Orsaria P, Caredda E, Genova F, Materazzo
M, Capuano I, Vanni G, Granai AV, DE Majo A, Portarena I, Sileri P,
et al: Additional nodal disease prediction in breast cancer with
sentinel lymph node metastasis based on clinicopathological
features. Anticancer Res. 38:2109–2117. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Houvenaeghel G, Lambaudie E, Classe JM,
Mazouni C, Giard S, Cohen M, Faure C, Charitansky H, Rouzier R,
Daraï E, et al: Lymph node positivity in different early breast
carcinoma phenotypes: A predictive model. BMC Cancer. 19:452019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lu X, Lu X, Wang ZC, Iglehart JD, Zhang X
and Richardson AL: Predicting features of breast cancer with gene
expression patterns. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 108:191–201. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gangi A, Mirocha J, Leong T and Giuliano
AE: Triple-negative breast cancer is not associated with increased
likelihood of nodal metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 21:4098–4103. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mattes MD, Bhatia JK, Metzger D, Ashamalla
H and Katsoulakis E: Breast cancer subtype as a predictor of lymph
node metastasis according to the SEER Registry. J Breast Cancer.
18:143–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhou W, He Z, Xue J, Wang M, Zha X, Ling
L, Chen L, Wang S and Liu X: Molecular subtype classification is a
determinant of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
patients with positive sentinel lymph nodes. PLoS One.
7:e358812012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Holm-Rasmussen EV, Jensen MB, Balslev E,
Kroman N and Tvedskov TF: Reduced risk of axillary lymphatic spread
in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
149:229–236. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Abdel-Razeq H, Iweir S, Abdel-Razeq R,
Rahman FA, Almasri H, Bater R, Taqash A and Abdelkhaleq H:
Differences in clinicopathological characteristics, treatment, and
survival outcomes between older and younger breast cancer patients.
Sci Rep. 11:143402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Andea AA, Bouwman D, Wallis T and Visscher
DW: Correlation of tumor volume and surface area with lymph node
status in patients with multifocal/multicentric breast carcinoma.
Cancer. 100:20–27. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu JL, Tseng HS, Yang LH, Wu HK, Kuo SJ,
Chen ST and Chen DR: Prediction of axillary lymph node metastases
in breast cancer patients based on pathologic information of the
primary tumor. Med Sci Monit. 20:577–581. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li J, Ma W, Jiang X, Cui C, Wang H, Chen
J, Nie R, Wu Y and Li L: Development and validation of nomograms
predictive of axillary nodal status to guide surgical
decision-making in early-stage breast cancer. J Cancer.
10:1263–1274. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Qiu SQ, Zeng HC, Zhang F, Chen C, Huang
WH, Pleijhuis RG, Wu JD, van Dam GM and Zhang GJ: A nomogram to
predict the probability of axillary lymph node metastasis in early
breast cancer patients with positive axillary ultrasound. Sci Rep.
6:211962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xie X, Tan W, Chen B, Huang X, Peng C, Yan
S, Yang L, Song C, Wang J, Zheng W, et al: Preoperative prediction
nomogram based on primary tumor miRNAs signature and
clinical-related features for axillary lymph node metastasis in
early-stage invasive breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 142:1901–1910.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|