|
1
|
Block TM, Mehta AS, Fimmel CJ and Jordan
R: Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
33:5093–5107. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and El-Serag HB:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 73 (Suppl
1):S4–S13. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
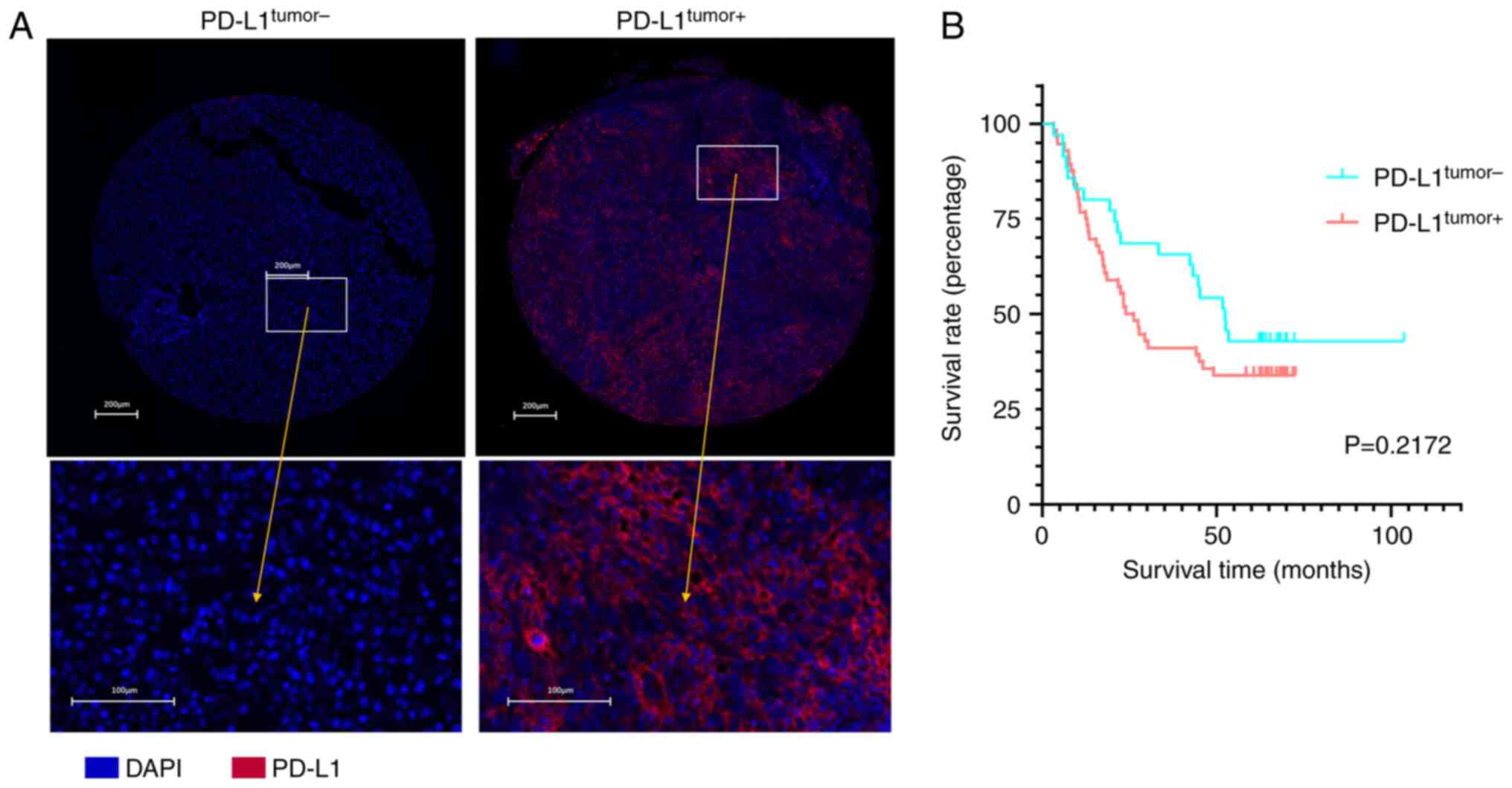
Han Z, Yang F, Zhang Y, Wang J, Ni Q, Zhu
H, Zhou X, Gao H and Lu J: Prognostic efficacy and prognostic
factors of TACE plus TKI with ICIs for the treatment of
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study. Front
Oncol. 12:10299512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chew V, Lai L, Pan L, Lim CJ, Li J, Ong R,
Chua C, Leong JY, Lim KH, Toh HC, et al: Delineation of an
immunosuppressive gradient in hepatocellular carcinoma using
high-dimensional proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 114:E5900–E5909. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu P and Fu YX: Tumor-infiltrating T
lymphocytes: Friends or foes? Lab Invest. 86:231–245. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Djenidi F, Adam J, Goubar A, Durgeau A,
Meurice G, de Montpréville V, Validire P, Besse B and Mami-Chouaib
F: CD8+CD103+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are tumor-specific
tissue-resident memory T cells and a prognostic factor for survival
in lung cancer patients. J Immunol. 194:3475–3486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Anraku M, Cunningham KS, Yun Z, Tsao MS,
Zhang L, Keshavjee S, Johnston MR and de Perrot M: Impact of
tumor-infiltrating T cells on survival in patients with malignant
pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 135:823–829. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mahmoud SM, Paish EC, Powe DG, Macmillan
RD, Grainge MJ, Lee AH, Ellis IO and Green AR: Tumor-infiltrating
CD8+ lymphocytes predict clinical outcome in breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 29:1949–1955. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang Y, Li Y and Zhu B: T-cell exhaustion
in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17922015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Antonioli L, Pacher P, Vizi ES and Haskó
G: CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol Med.
19:355–367. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
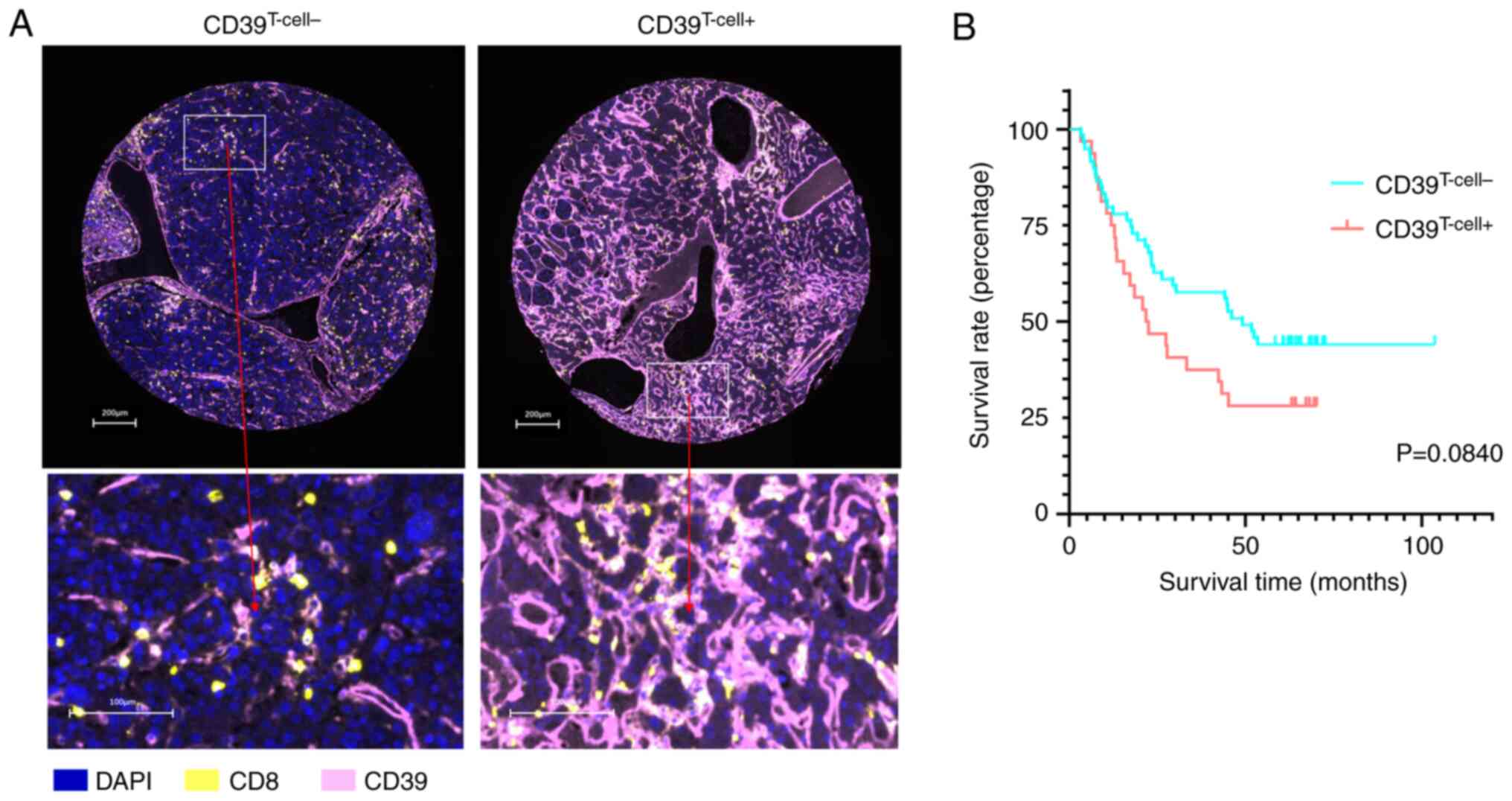
Canale FP, Ramello MC, Núñez N, Araujo
Furlan CL, Bossio SN, Gorosito Serrán M, Tosello Boari J, Del
Castillo A, Ledesma M, Sedlik C, et al: CD39 Expression defines
cell exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells.
Cancer Res. 78:115–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Simoni Y, Becht E, Fehlings M, Loh CY, Koo
SL, Teng KWW, Yeong JPS, Nahar R, Zhang T, Kared H, et al:
Bystander CD8+ T cells are abundant and phenotypically
distinct in human tumour infiltrates. Nature. 557:575–579. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Latchman YE, Liang SC, Wu Y, Chernova T,
Sobel RA, Klemm M, Kuchroo VK, Freeman GJ and Sharpe AH:
PD-L1-deficient mice show that PD-L1 on T cells, antigen-presenting
cells, and host tissues negatively regulates T cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:10691–10696. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-H1,
a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation
and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 5:1365–1369. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang Y, Chen M, Nie H and Yuan Y: PD-1
and PD-L1 in cancer immunotherapy: Clinical implications and future
considerations. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 15:1111–1122. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dolina JS, Van Braeckel-Budimir N, Thomas
GD and Salek-Ardakani S: CD8+ T cell exhaustion in
cancer. Front Immunol. 12:7152342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jung HI, Jeong D, Ji S, Ahn TS, Bae SH,
Chin S, Chung JC, Kim HC, Lee MS and Baek MJ: Overexpression of
PD-L1 and PD-L2 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. 49:246–254. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
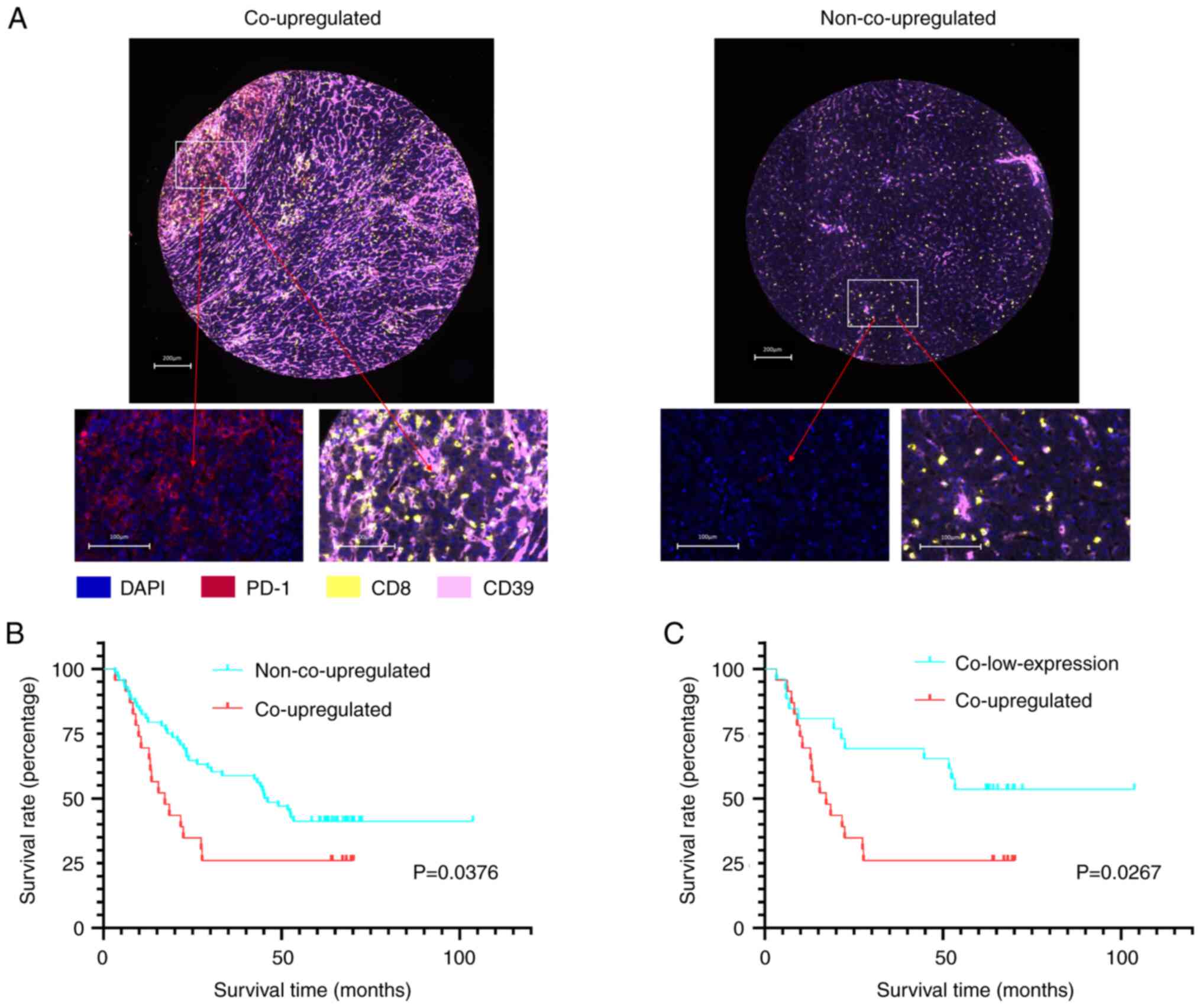
Guo M, Yuan F, Qi F, Sun J, Rao Q, Zhao Z,
Huang P, Fang T, Yang B and Xia J: Expression and clinical
significance of LAG-3, FGL1, PD-L1 and CD8+T cells in
hepatocellular carcinoma using multiplex quantitative analysis. J
Transl Med. 18:3062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang CY, Wang Y, Luo GY, Han F, Li YQ,
Zhou ZG and Xu GL: Relationship between PD-L1 expression and CD8+
T-cell immune responses in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother.
40:323–333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yugawa K, Itoh S, Yoshizumi T, Iseda N,
Tomiyama T, Morinaga A, Toshima T, Harada N, Kohashi K, Oda Y and
Mori M: CMTM6 stabilizes PD-L1 expression and is a new prognostic
impact factor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Commun.
5:334–348. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu K, Wang ZM, Li JN, Zhang S, Xiao ZF and
Tao YM: CLEC1B expression and PD-L1 expression predict clinical
outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor hemorrhage. Transl
Oncol. 11:552–558. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Q, Liu F and Liu L: Prognostic
significance of PD-L1 in solid tumor: An updated meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e63692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega
J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Kelley RK, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V,
Salem R, et al: BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and
treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 76:681–693.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou J, Sun H, Wang Z, Cong W, Zeng M,
Zhou W, Bie P, Liu L, Wen T, Kuang M, et al: Guidelines for the
diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition).
Liver Cancer. 12:405–444. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang A, Yang XR, Chung WY, Dennison AR
and Zhou J: Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 5:1462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xing R, Gao J, Cui Q and Wang Q:
Strategies to improve the antitumor effect of immunotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. 12:7832362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ribas A and Wolchok JD: Cancer
immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. 359:1350–1355.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han Y, Liu D and Li L: PD-1/PD-L1 pathway:
current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 10:727–742.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang S, Yuan B, Wang Y, Li M, Liu X, Cao
J, Li C and Hu J: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance
of PD-L1 expression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 36:117–130. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brody R, Zhang Y, Ballas M, Siddiqui MK,
Gupta P, Barker C, Midha A and Walker J: PD-L1 expression in
advanced NSCLC: Insights into risk stratification and treatment
selection from a systematic literature review. Lung Cancer.
112:200–215. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang M, Sun H, Zhao S, Wang Y, Pu H, Wang
Y and Zhang Q: Expression of PD-L1 and prognosis in breast cancer:
A meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 8:31347–31354. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wherry EJ and Kurachi M: Molecular and
cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol.
15:486–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|