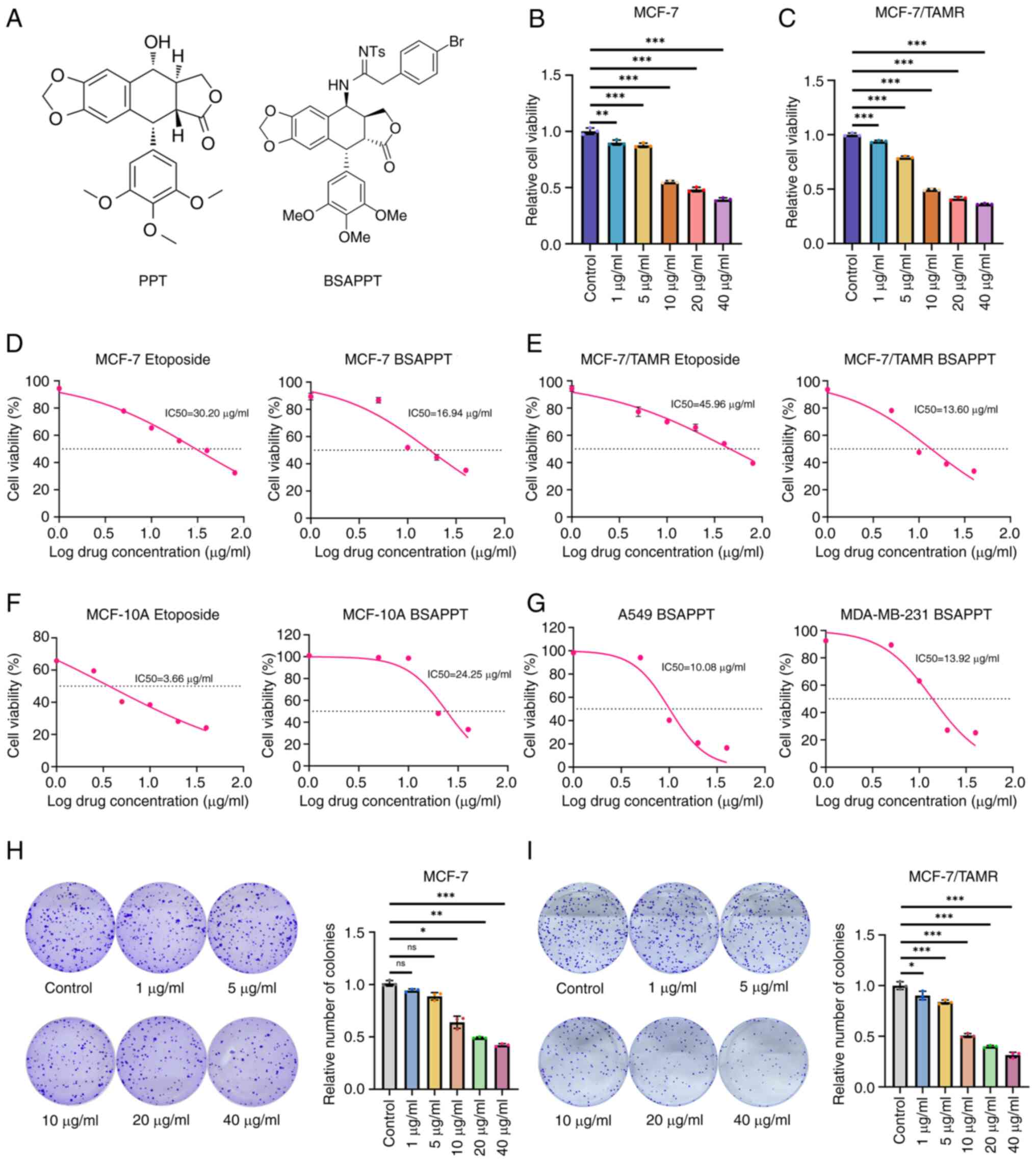
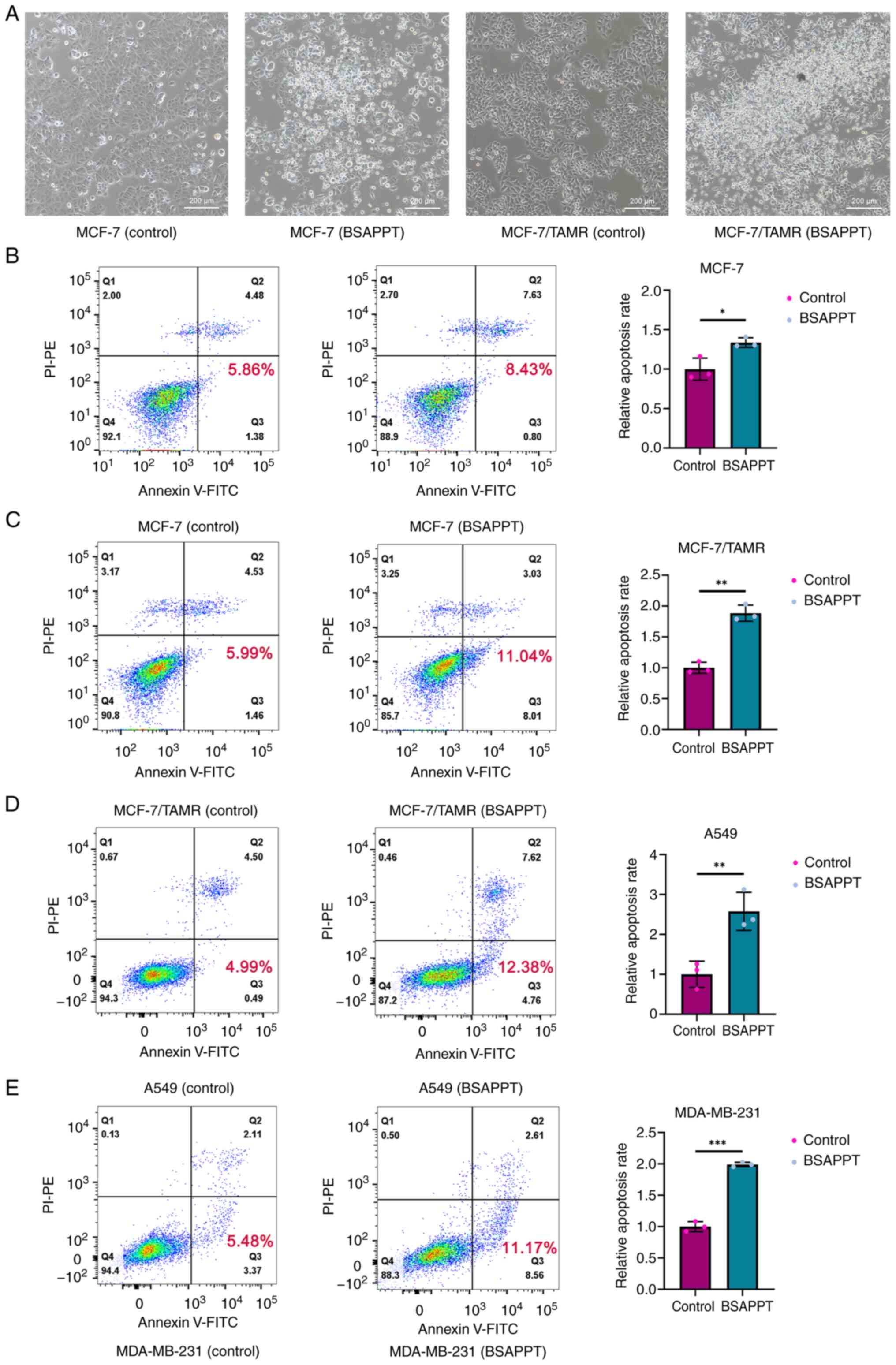
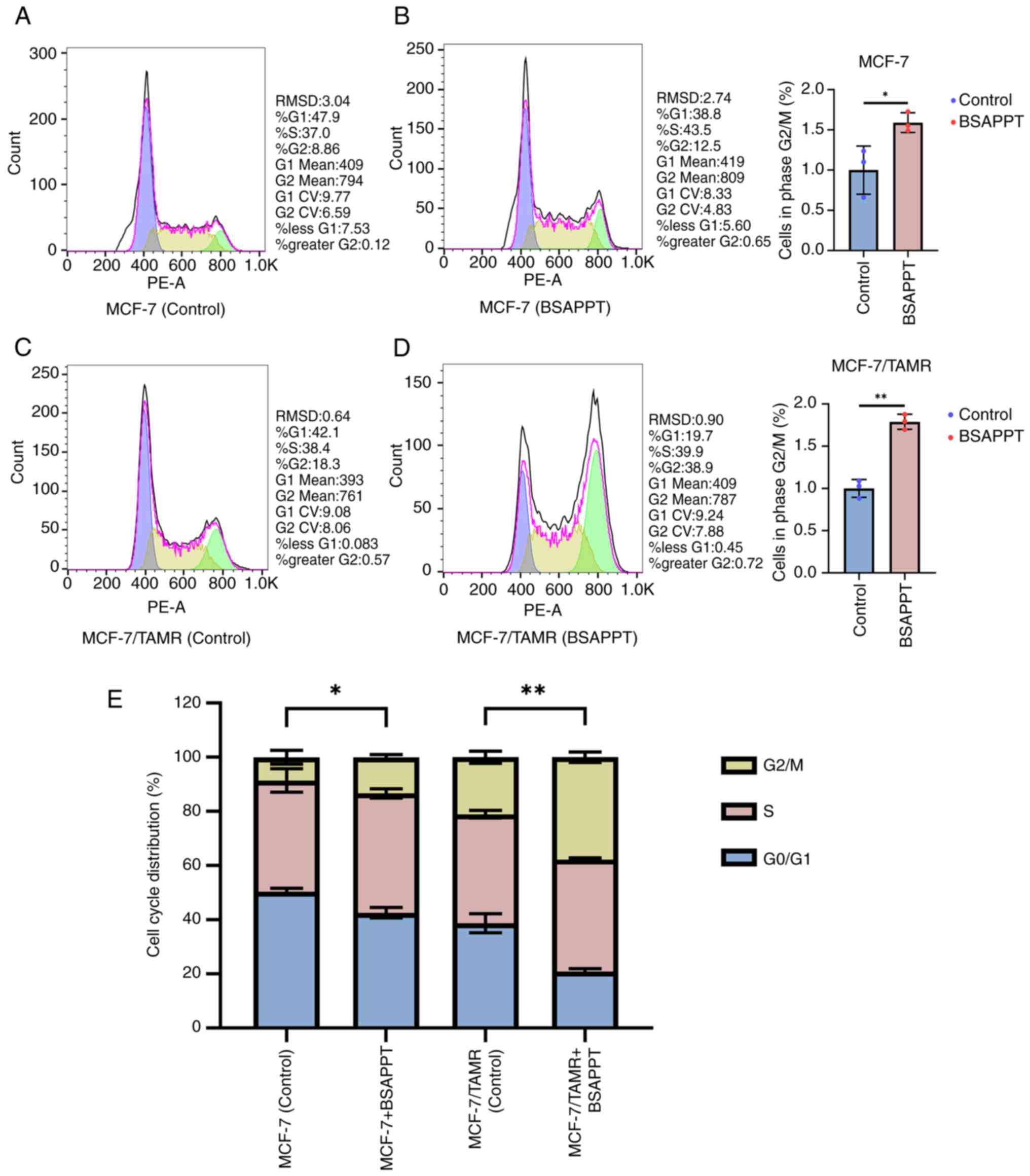
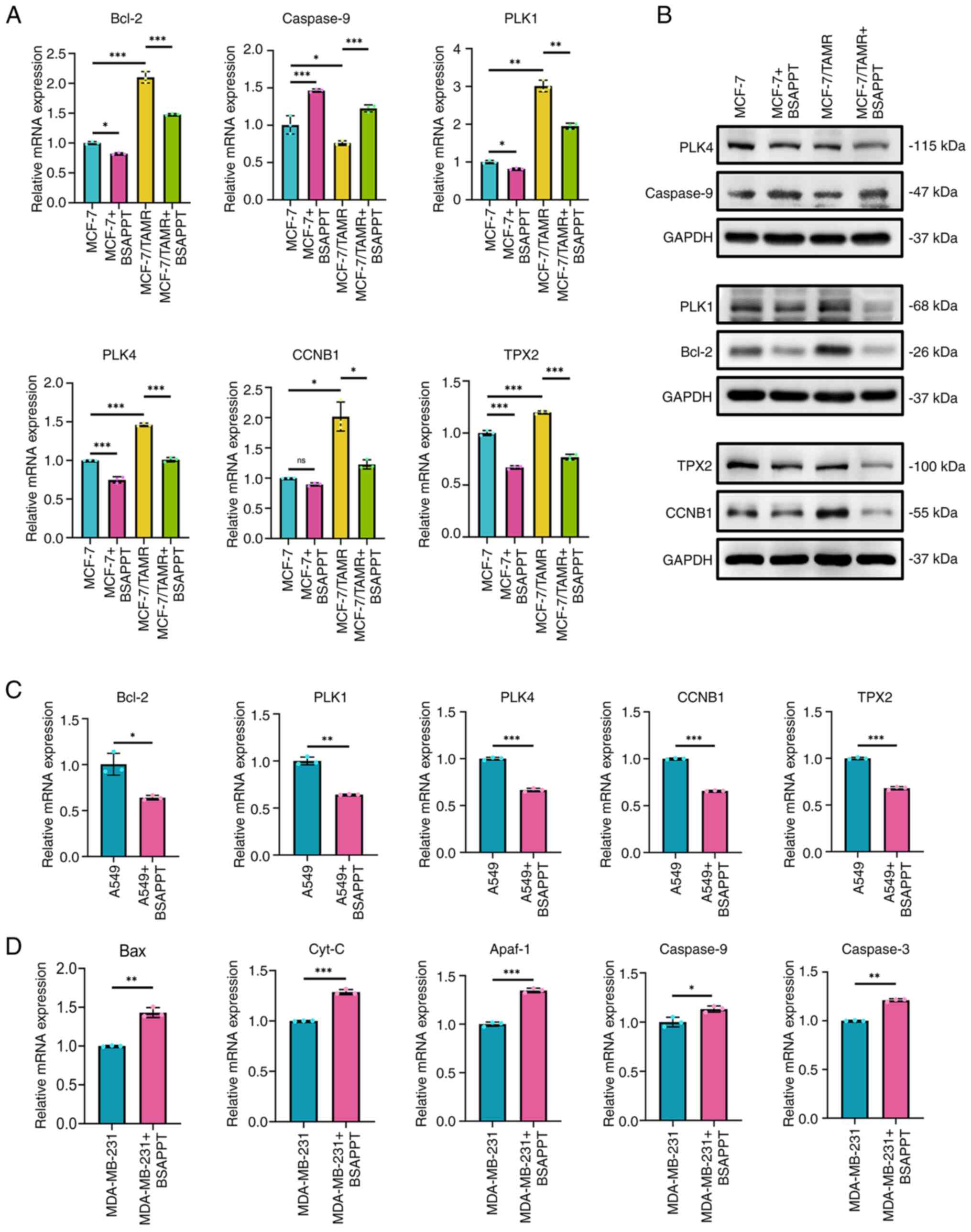
|
1
|
Shen Y, Zhong J, Liu J, Liu K, Zhao J, Xu
T, Zeng T, Li Z, Chen Y, Ding W, et al: Protein arginine
N-methyltransferase 2 reverses tamoxifen resistance in breast
cancer cells through suppression of ER-α36. Oncol Rep.
39:2604–2612. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mishra A, Srivastava A, Pateriya A, Tomar
MS, Mishra AK and Shrivastava A: Metabolic reprograming confers
tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Chem Biol Interact.
347:1096022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jin ML, Kim YW, Jin HL, Kang H, Lee EK,
Stallcup MR and Jeong KW: Aberrant expression of SETD1A promotes
survival and migration of estrogen receptor α-positive breast
cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 143:2871–2883. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ring A and Dowsett M: Mechanisms of
tamoxifen resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer. 11:643–658. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi Q, Li Y, Li S, Jin L, Lai H, Wu Y, Cai
Z, Zhu M, Li Q, Li Y, et al: LncRNA DILA1 inhibits Cyclin D1
degradation and contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast
cancer. Nat Commun. 11:55132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu Y, Liu Y, Zhang C, Chu J, Wu Y, Li Y,
Liu J, Li Q, Li S, Shi Q, et al: Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer
cells are resistant to DNA-damaging chemotherapy because of
upregulated BARD1 and BRCA1. Nat Commun. 9:15952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lüönd F, Sugiyama N, Bill R, Bornes L,
Hager C, Tang F, Santacroce N, Beisel C, Ivanek R, Bürglin T, et
al: Distinct contributions of partial and full EMT to breast cancer
malignancy. Dev Cell. 56:3203–3221.e11. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tufail M, Cui J and Wu C: Breast cancer:
Molecular mechanisms of underlying resistance and therapeutic
approaches. Am J Cancer Res. 12:2920–2949. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin L, Zhang XT, Bian XW, Guo YM and Wang
ZY: Disruption of the ER-α36-EGFR/HER2 positive regulatory loops
restores tamoxifen sensitivity in tamoxifen resistance breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e1073692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hosford SR and Miller TW: Clinical
potential of novel therapeutic targets in breast cancer: CDK4/6,
Src, JAK/STAT, PARP, HDAC, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways.
Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 7:203–215. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li D, Ji H, Niu X, Yin L, Wang Y, Gu Y,
Wang J, Zhou X, Zhang H and Zhang Q: Tumor-associated macrophages
secrete CC-chemokine ligand 2 and induce tamoxifen resistance by
activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 111:47–58.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mansouri S, Farahmand L, Teymourzadeh A
and Majidzadeh AK: Clinical evidence on the magnitude of change in
growth pathway activity in relation to tamoxifen resistance is
required. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 18:668–676. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Viedma-Rodriguez R, Baiza-Gutman L,
Salamanca-Gomez F, Diaz-Zaragoza M, Martinez-Hernandez G, Ruiz
Esparza-Garrido R, Velázquez-Flores MA and Arenas-Aranda D:
Mechanisms associated with resistance to tamoxifen in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 32:3–15. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao A, Sun T, Ma G, Cao J, Hu Q, Chen L,
Wang Y, Wang Q, Sun J, Wu R, et al: LEM4 confers tamoxifen
resistance to breast cancer cells by activating cyclin D-CDK4/6-Rb
and ERα pathway. Nat Commun. 9:41802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cai F, Xiao H, Sun Y, Wang D and Tang J:
Expression of Snail and E-cadherin in Drug-resistant MCF-7/ADM
breast cancer cell strains. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 29:240–244.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vesuna F, Bergman Y and Raman V: Genomic
pathways modulated by Twist in breast cancer. BMC Cancer.
17:522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Joseph C, Alsaleem M, Orah N, Narasimha
PL, Miligy IM, Kurozumi S, Ellis IO, Mongan NP, Green AR and Rakha
EA: Elevated MMP9 expression in breast cancer is a predictor of
shorter patient survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 182:267–282.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shah Z, Gohar UF, Jamshed I, Mushtaq A,
Mukhtar H, Zia-Ui-Haq M, Toma SI, Manea R, Moga M and Popovici B:
Podophyllotoxin: History, recent advances and future prospects.
Biomolecules. 11:6032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hong WG, Cho JH, Hwang SG, Lee E, Lee J,
Kim JI, Um HD and Park JK: Chemosensitizing effect of
podophyllotoxin acetate on topoisomerase inhibitors leads to
synergistic enhancement of lung cancer cell apoptosis. Int J Oncol.
48:2265–2276. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guerram M, Jiang ZZ and Zhang LY:
Podophyllotoxin, a medicinal agent of plant origin: Past, present
and future. Chin J Nat Med. 10:161–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xiao J, Gao M, Sun Z, Diao Q, Wang P and
Gao F: Recent advances of podophyllotoxin/epipodophyllotoxin
hybrids in anticancer activity, mode of action, and
structure-activity relationship: An update (2010–2020). Eur J Med
Chem. 208:1128302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma Y, Fang S, Li H, Han C, Lu Y, Zhao Y,
Liu Y and Zhao C: Biological evaluation and molecular modelling
study of podophyllotoxin derivatives as potent inhibitors of
tubulin polymerization. Chem Biol Drug Des. 82:12–21. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Rakesh KP, Shantharam CS,
Manukumar HM, Asiri AM, Marwani HM and Qin HL: Podophyllotoxin
derivatives as an excellent anticancer aspirant for future
chemotherapy: A key current imminent needs. Bioorg Med Chem.
26:340–355. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Renouard S, Lopez T, Hendrawati O, Dupre
P, Doussot J, Falguieres A, Ferroud C, Hagege D, Lamblin F, Laine E
and Hano C: Podophyllotoxin and deoxypodophyllotoxin in Juniperus
bermudiana and 12 other Juniperus species: Optimization of
extraction, method validation, and quantification. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:8101–8107. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu X, Xu T, Su B, Zhou J, Xu B, Zhang Y,
Zhu Y, Jiang N and He Z: The novel role of etoposide in inhibiting
the migration and proliferation of small cell lung cancer and
breast cancer via targeting Daam1. Biochem Pharmacol.
210:1154682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Orr MS, Fornari FA, Randolph JK and
Gewirtz DA: Transcriptional down-regulation of c-myc expression in
the MCF-7 breast tumor cell line by the topoisomerase II inhibitor,
VM-26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1262:139–145. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sledge GW Jr: Etoposide in the management
of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer. 67 (Suppl 1):S266–S270. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cabel L, Carton M, Cheaib B, Pierga JY,
Dalenc F, Mailliez A, Levy C, Jacot W, Debled M, Leheurteur M, et
al: Oral etoposide in heavily pre-treated metastatic breast cancer:
Results from the ESME cohort and comparison with other chemotherapy
regimens. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 173:397–406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alpsoy A, Yasa S and Gündüz U: Etoposide
resistance in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line is marked by multiple
mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:351–355. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hartmann JT and Lipp HP: Camptothecin and
podophyllotoxin derivatives: Inhibitors of topoisomerase I and
II-mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics and toxicity profile.
Drug Saf. 29:209–230. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Allen TM and Cullis PR: Drug delivery
systems: Entering the mainstream. Science. 303:1818–1822. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carstensen H, Nolte H and Hertz H:
Teniposide-induced hypersensitivity reactions in children. Lancet.
2:551989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chu B, Shi S, Li X, Hu L, Shi L, Zhang H,
Xu Q, Ye L, Lin G, Zhang N and Zhang X: Preparation and evaluation
of teniposide-loaded polymeric micelles for breast cancer therapy.
Int J Pharm. 513:118–129. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nielsen D, Boas J, Engelholm SA, Hansen OP
and Dombernowsky P: Teniposide in advanced breast cancer. A phase
II trial in patients with no prior chemotherapy. Ann Oncol.
3:377–378. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zi CT, Yang L, Xu FQ, Dong FW, Yang D, Li
Y, Ding ZT, Zhou J, Jiang ZH and Hu JM: Synthesis and anticancer
activity of dimeric podophyllotoxin derivatives. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 12:3393–3406. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pujol MD, Romero M and Sánchez I:
Synthesis and biological activity of new class of dioxygenated
anticancer agents. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 5:215–237.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang TM, Qi SN, Zhao N, Yang YJ, Yuan HQ,
Zhang B and Jin S: Induction of apoptosis through
caspase-independent or caspase-9-dependent pathway in mouse and
human osteosarcoma cells by a new nitroxyl spin-labeled derivative
of podophyllotoxin. Apoptosis. 18:727–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han HW, Lin HY, He DL, Ren Y, Sun WX,
Liang L, Du MH, Li DC, Chu YC, Yang MK, et al: Novel
podophyllotoxin derivatives as potential tubulin inhibitors:
Design, synthesis, and antiproliferative activity evaluation. Chem
Biodivers. 15:e18002892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Qin X, Zhang Y, Yu H and Ma L: Progress in
the Study of spindle assembly checkpoint in lung cancer. Zhongguo
Fei Ai Za Zhi. 26:310–318. 2023.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim B, Srivastava SK and Kim SH: Caspase-9
as a therapeutic target for treating cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 19:113–127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu Z, Sun Q and Wang X: PLK1, A potential
target for cancer therapy. Transl Oncol. 10:22–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao Y and Wang X: PLK4: A promising
target for cancer therapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 145:2413–2422.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen G, Yu M, Cao J, Zhao H, Dai Y, Cong Y
and Qiao G: Identification of candidate biomarkers correlated with
poor prognosis of breast cancer based on bioinformatics analysis.
Bioengineered. 12:5149–5161. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yamaguchi H, Paranawithana S, Lee M, Huang
Z, Bhalla K, Wang HG. Yamaguchi H, Paranawithana SR, Lee MW, Huang
Z, et al: Epothilone B analogue (BMS-247550)-mediated cytotoxicity
through induction of Bax conformational change in human breast
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:466–471. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li Z, Guo D, Yin X, Ding S, Shen M, Zhang
R, Wang Y and Xu R: Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce human multiple
myeloma cell death via reactive oxygen species and
Cyt-C/Apaf-1/Caspase-9/Caspase-3 signaling pathway in vitro. Biomed
Pharmacother. 122:1097122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yadav N, Gogada R, O'Malley J, Gundampati
RK, Jayanthi S, Hashmi S, Lella R, Zhang D, Wang J, Kumar R, et al:
Molecular insights on cytochrome c and nucleotide regulation of
apoptosome function and its implication in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Cell Res. 1867:1185732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li M, Zhao Y, Sun J, Chen H, Liu Z, Lin K,
Ma P, Zhang W, Zhen Y and Zhang S and Zhang S: pH/reduction
dual-responsive hyaluronic acid-podophyllotoxin prodrug micelles
for tumor targeted delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 288:1194022022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Paidakula S, Nerella S, Vadde R, Kamal A
and Kankala S: Design and synthesis of
4β-Acetamidobenzofuranone-podophyllotoxin hybrids and their
anti-cancer evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 29:2153–2156. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao W, Cong Y, Li HM, Li S, Shen Y, Qi Q,
Zhang Y, Li YZ and Tang YJ: Challenges and potential for improving
the druggability of podophyllotoxin-derived drugs in cancer
chemotherapy. Nat Prod Rep. 38:470–488. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ji CF and Ji YB: Apoptosis of human
gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells induced by podophyllotoxin. Exp Ther
Med. 7:1317–1322. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jeong D, Ham J, Kim HW, Kim H, Ji HW, Yun
SH, Park JE, Lee KS, Jo H, Han JH, et al: ELOVL2: A novel tumor
suppressor attenuating tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Am J
Cancer Res. 11:2568–2589. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dawson SJ, Makretsov N, Blows FM, Driver
KE, Provenzano E, Le Quesne J, Baglietto L, Severi G, Giles GG,
McLean CA, et al: BCL2 in breast cancer: A favourable prognostic
marker across molecular subtypes and independent of adjuvant
therapy received. Br J Cancer. 103:668–675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang L, Zhang X, Wang X, He M and Qiao S:
MicroRNA-224 promotes tumorigenesis through downregulation of
caspase-9 in triple-negative breast cancer. Dis Markers.
2019:73789672019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Frenzel A, Labi V, Chmelewskij W, Ploner
C, Geley S, Fiegl H, Tzankov A and Villunger A: Suppression of
B-cell lymphomagenesis by the BH3-only proteins Bmf and Bad. Blood.
115:995–1005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Goodger NM, Gannon J, Hunt T and Morgan
PR: Cell cycle regulatory proteins-an overview with relevance to
oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 33:61–73. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fang L, Liu Q, Cui H, Zheng Y and Wu C:
Bioinformatics analysis highlight differentially expressed CCNB1
and PLK1 genes as potential anti-breast cancer drug targets and
prognostic markers. Genes (Basel). 13:6542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jiawei W, Xiajun B, Tian S, Xuzheng G and
Zhenwang Z: Comprehensive analysis of PLKs expression and prognosis
in breast cancer. Cancer Genet. 268–269. 83–92. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ma S, Rong X, Gao F, Yang Y and Wei L:
TPX2 promotes cell proliferation and migration via PLK1 in OC.
Cancer Biomark. 22:443–451. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|