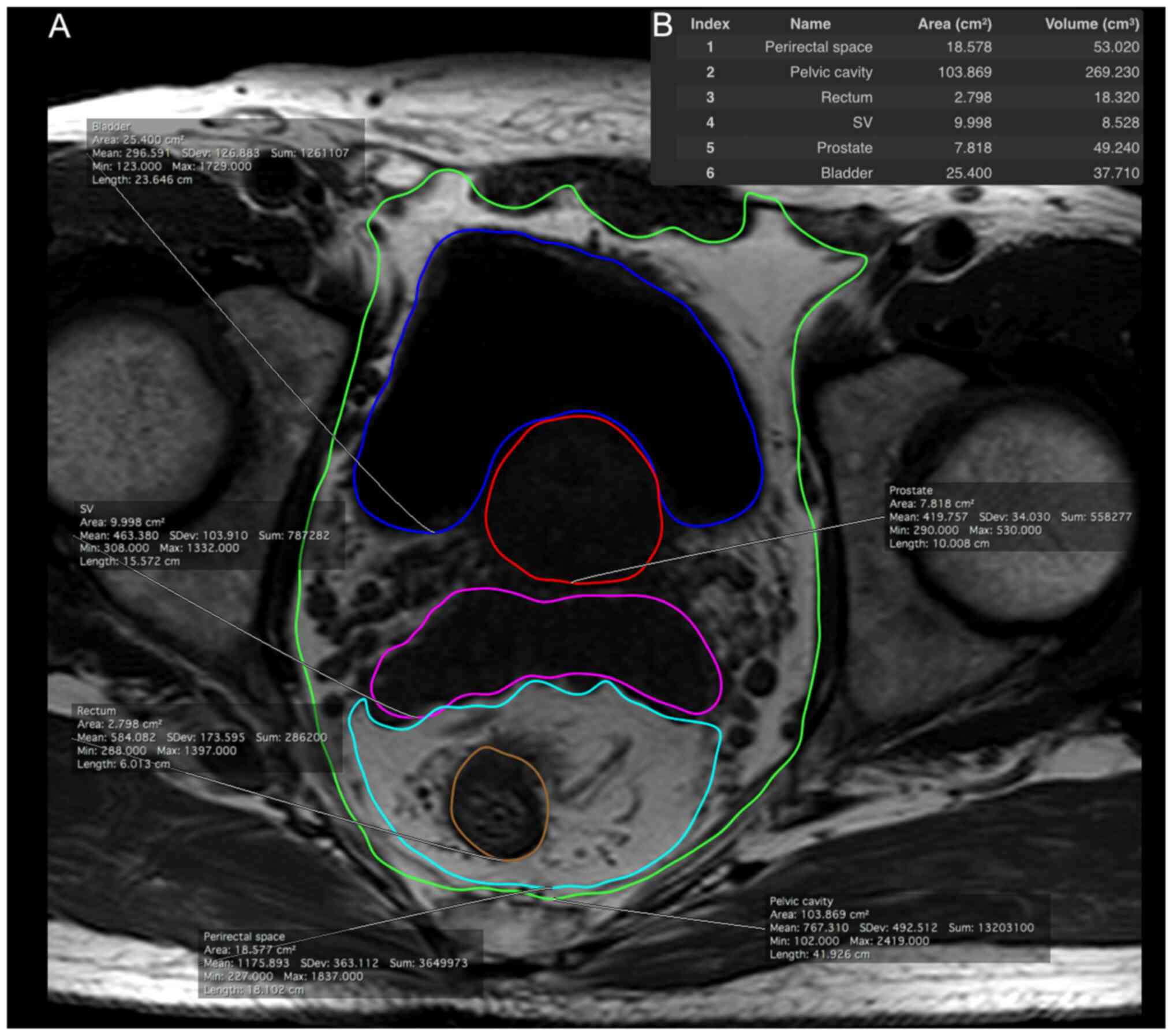
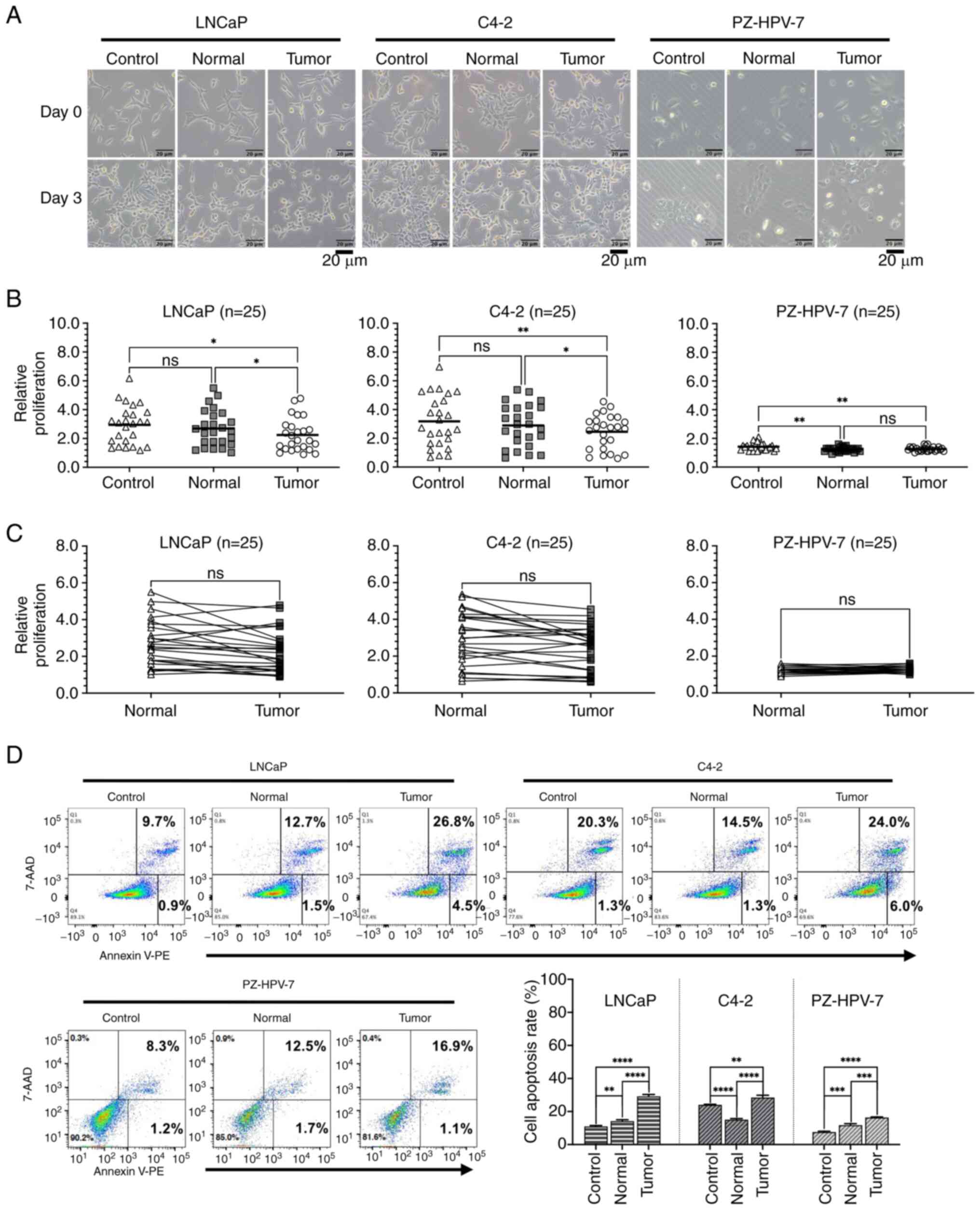
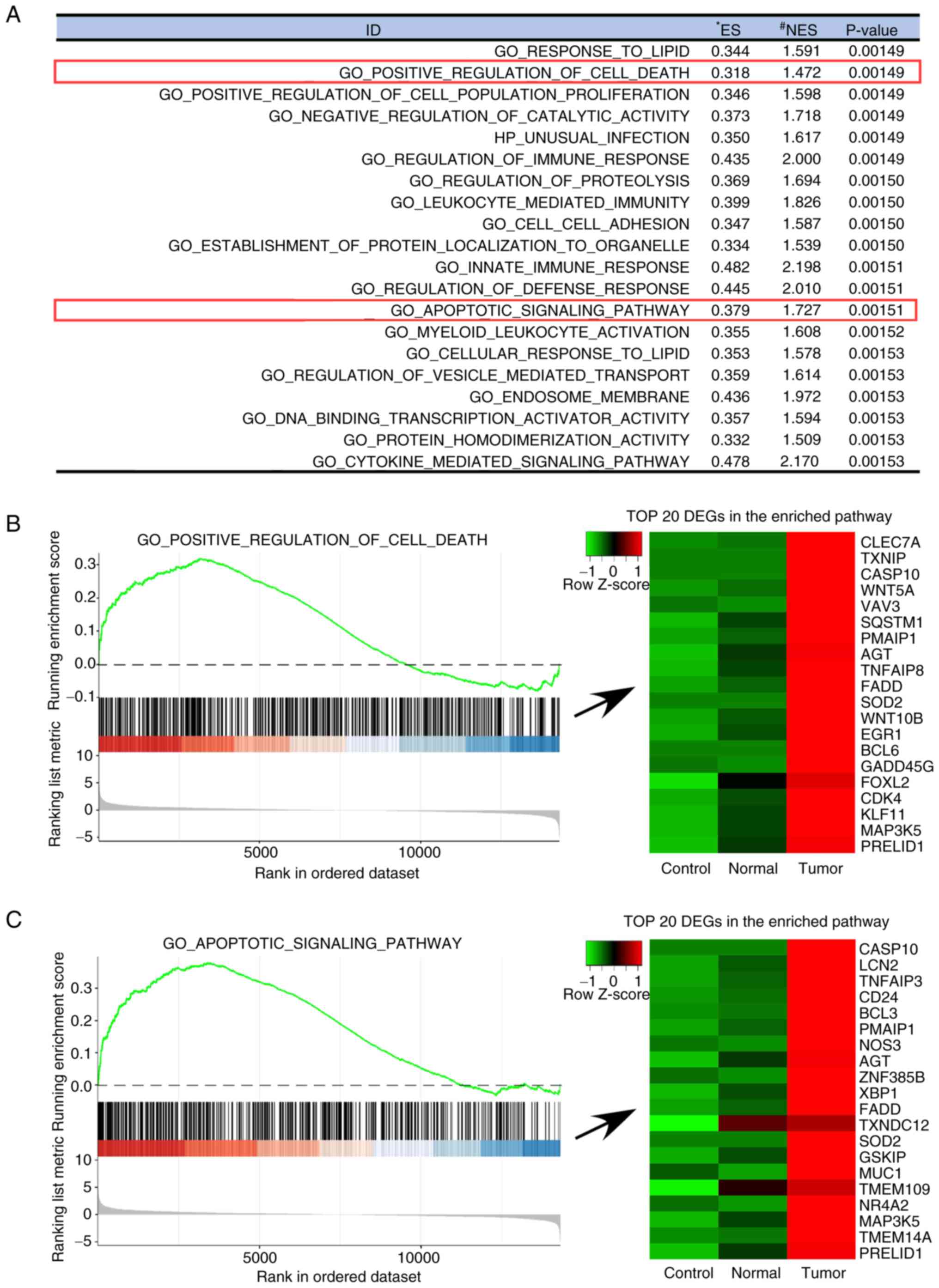
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
López Fontana C, Maselli ME, Pérez
Elizalde R, Di Milta N, Corica Alberto P and López Laur JD: Obesity
modifies prostatic specific antigen in men over 45 years. Arch Esp
Urol. 64:35–42. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parikesit D, Mochtar CA, Umbas R and Hamid
ARAH: The impact of obesity towards prostate diseases. Prostate
Int. 4:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cataño JG, Ramos-Hernández A, Bravo-Balado
A, Mariño-Álvarez AM, Caicedo JI, Trujillo CG and Plata M: Obesity
and radical prostatectomy: The enigma continues. Arch Esp Urol.
71:517–522. 2018.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Williams G: Aromatase up-regulation,
insulin and raised intracellular oestrogens in men, induce
adiposity, metabolic syndrome and prostate disease, via aberrant
ER-α and GPER signalling. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 351:269–278. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Caine M, Raz S and Zeigler M: Adrenergic
and cholinergic receptors in the human prostate, prostatic capsule
and bladder neck. Br J Urol. 47:193–202. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giovannucci E, Rimm EB, Chute CG, Kawachi
I, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ and Willett WC: Obesity and benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Am J Epidemiol. 140:989–1002. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamid ARAH, Umbas R and Mochtar CA: Recent
role of inflammation in prostate diseases: Chemoprevention
development opportunity. Acta Med Indones. 43:59–65.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Alukal JP and Lepor H: Testosterone
deficiency and the prostate. Urol Clin North Am. 43:203–208. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schnoeller T, Jentzmik F, Rinnab L,
Cronauer MV, Damjanoski I, Zengerling F, Ghazal AA, Schrader M and
Schrader AJ: Circulating free testosterone is an independent
predictor of advanced disease in patients with clinically localized
prostate cancer. World J Urol. 31:253–259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Theoret MR, Ning YM, Zhang JJ, Justice R,
Keegan P and Pazdur R: The risks and benefits of 5α-reductase
inhibitors for prostate-cancer prevention. N Engl J Med. 365:97–99.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gallagher EJ and LeRoith D: The
proliferating role of insulin and insulin-like growth factors in
cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:610–618. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ribeiro R, Lopes C and Medeiros R: Leptin
and prostate: Implications for cancer prevention-overview of
genetics and molecular interactions. Eur J Cancer Prev. 13:359–368.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Izadi V, Farabad E and Azadbakht L: Serum
adiponectin level and different kinds of cancer: A review of recent
evidence. ISRN Oncol. 2012:9827692012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Amling CL, Riffenburgh RH, Sun L, Moul JW,
Lance RS, Kusuda L, Sexton WJ, Soderdahl DW, Donahue TF, Foley JP,
et al: Pathologic variables and recurrence rates as related to
obesity and race in men with prostate cancer undergoing radical
prostatectomy. J Clin Oncol. 22:439–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rodriguez C, Freedland SJ, Deka A, Jacobs
EJ, McCullough ML, Patel AV, Thun MJ and Calle EE: Body mass index,
weight change, and risk of prostate cancer in the cancer prevention
study II nutrition cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
16:63–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF
and Zwahlen M: Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational
studies. Lancet. 371:569–578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
MacInnis RJ and English DR: Body size and
composition and prostate cancer risk: Systematic review and
meta-regression analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 17:989–1003. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bergström A, Pisani P, Tenet V, Wolk A and
Adami HO: Overweight as an avoidable cause of cancer in Europe. Int
J Cancer. 91:421–430. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao Y and Ma J: Body mass index, prostate
cancer-specific mortality, and biochemical recurrence: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:486–501. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Duong MN, Geneste A, Fallone F, Li X,
Dumontet C and Muller C: The fat and the bad: Mature adipocytes,
key actors in tumor progression and resistance. Oncotarget.
8:57622–57641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van Roermund JG and Witjes JA: The impact
of obesity on prostate cancer. World J Urol. 25:491–497. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
von Hafe P, Pina F, Pérez A, Tavares M and
Barros H: Visceral fat accumulation as a risk factor for prostate
cancer. Obes Res. 12:1930–1935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zimmermann M, Delouya G, Barkati M,
Campeau S, Rompotinos D and Taussky D: Impact of visceral fat
volume and fat density on biochemical outcome after radical
prostatectomy and postoperative radiotherapy. Horm Mol Biol Clin
Investig. 26:173–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng L, Darson MF, Bergstralh EJ, Slezak
J, Myers RP and Bostwick DG: Correlation of margin status and
extraprostatic extension with progression of prostate carcinoma.
Cancer. 86:1775–1782. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miladinovic D, Cusick T, Mahon KL, Haynes
AM, Cortie CH, Meyer BJ, Stricker PD, Wittert GA, Butler LM,
Horvath LG and Hoy AJ: Assessment of periprostatic and subcutaneous
adipose tissue lipolysis and adipocyte size from men with localized
prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:13852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van Roermund JG, Hinnen KA, Tolman CJ, Bol
GH, Witjes JA, Bosch JL, Kiemeney LA and van Vulpen M:
Periprostatic fat correlates with tumour aggressiveness in prostate
cancer patients. BJU Int. 107:1775–1779. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Laurent V, Guérard A, Mazerolles C, Le
Gonidec S, Toulet A, Nieto L, Zaidi F, Majed B, Garandeau D,
Socrier Y, et al: Periprostatic adipocytes act as a driving force
for prostate cancer progression in obesity. Nat Commun.
7:102302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laurent V, Toulet A, Attané C, Milhas D,
Dauvillier S, Zaidi F, Clement E, Cinato M, Le Gonidec S, Guérard
A, et al: Periprostatic adipose tissue favors prostate cancer cell
invasion in an obesity-dependent manner: Role of oxidative stress.
Mol Cancer Res. 17:821–835. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ribeiro R, Monteiro C, Cunha V, Oliveira
MJ, Freitas M, Fraga A, Príncipe P, Lobato C, Lobo F, Morais A, et
al: Human periprostatic adipose tissue promotes prostate cancer
aggressiveness in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:322012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Finley DS, Calvert VS, Inokuchi J, Lau A,
Narula N, Petricoin EF, Zaldivar F, Santos R, Tyson DR and Ornstein
DK: Periprostatic adipose tissue as a modulator of prostate cancer
aggressiveness. J Urol. 182:1621–1627. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kaneko A, Satoh Y, Tokuda Y, Fujiyama C,
Udo K and Uozumi J: Effects of adipocytes on the proliferation and
differentiation of prostate cancer cells in a 3-D culture model.
Int J Urol. 17:369–376. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Estève D, Roumiguié M, Manceau C, Milhas D
and Muller C: Periprostatic adipose tissue: A heavy player in
prostate cancer progression. Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 10:29–35.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kulasegaran T and Oliveira N: Metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer: Advances in treatment and
symptom management. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 25:914–931. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Venkatachalam S, McFarland TR, Agarwal N
and Swami U: Immune checkpoint inhibitors in prostate cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 13:21872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gourdin T: Highlighting recent progress in
the treatment of men with advanced prostate cancer. Curr Opin
Oncol. 36:174–179. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gillette CM, Yette GA, Cramer SD and
Graham LS: Management of advanced prostate cancer in the precision
oncology era. Cancers (Basel). 15:25522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abida W, Armenia J, Gopalan A, Brennan R,
Walsh M, Barron D, Danila D, Rathkopf D, Morris M, Slovin S, et al:
Prospective Genomic profiling of prostate cancer across disease
states reveals germline and somatic alterations that may affect
clinical decision making. JCO Precis Oncol. 2017.PO.17.00029, 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Ming A, Wang J, Chen W and Fang
Z: PROTACs targeting androgen receptor signaling: Potential
therapeutic agents for castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Pharmacol Res. 205:1072342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sallam M, Nguyen NT, Sainsbury F, Kimizuka
N, Muyldermans S and Benešová-Schäfer M: PSMA-targeted
radiotheranostics in modern nuclear medicine: Then, now, and what
of the future? Theranostics. 14:3043–3079. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Current K, Meyer C, Magyar CE, Mona CE,
Almajano J, Slavik R, Stuparu AD, Cheng C, Dawson DW, Radu CG, et
al: Investigating PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy efficacy as a
function of cellular PSMA levels and intratumoral PSMA
heterogeneity. Clin Cancer Res. 26:2946–2955. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Isaacsson Velho P, Qazi F, Hassan S,
Carducci MA, Denmeade SR, Markowski MC, Thorek DL, DeWeese TL, Song
DY, Tran PT, et al: Efficacy of radium-223 in bone-metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer with and without homologous
repair gene defects. Eur Urol. 76:170–176. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Buyyounouski MK, Choyke PL, McKenney JK,
Sartor O, Sandler HM, Amin MB, Kattan MW and Lin DW: Prostate
cancer-major changes in the American joint committee on cancer
eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:245–253.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chien YH, Hsieh ML, Sheng TW, Chang YH,
Wang LJ, Chuang CK, Pang ST, Wu CT and Shao IH: Body composition
and pelvic fat distribution are associated with prostate cancer
aggressiveness and can predict biochemical recurrence. Medicine
(Baltimore). 101:e310762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: a
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 102:15545–15550. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF,
Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, Puigserver P, Carlsson E,
Ridderstråle M, Laurila E, et al: PGC-1alpha-responsive genes
involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately
downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet. 34:267–273. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdóttir H,
Ghandi M, Mesirov JP and Tamayo P: The molecular signatures
database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst.
1:417–425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Woo S, Cho JY, Kim SY and Kim SH:
Periprostatic fat thickness on MRI: Correlation with Gleason score
in prostate cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 204:W43–W47. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang Q, Sun LJ, Qi J, Yang ZG, Huang T
and Huo RC: Periprostatic adiposity measured on magnetic resonance
imaging correlates with prostate cancer aggressiveness. Urol J.
11:1793–1799. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bhindi B, Trottier G, Elharram M,
Fernandes KA, Lockwood G, Toi A, Hersey KM, Finelli A, Evans A, van
der Kwast TH and Fleshner NE: Measurement of peri-prostatic fat
thickness using transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS): A new risk
factor for prostate cancer. BJU Int. 110:980–986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Taussky D, Barkati M, Campeau S, Zerouali
K, Nadiri A, Saad F and Delouya G: Changes in periprostatic adipose
tissue induced by 5α-reductase inhibitors. Andrology. 5:511–515.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tiberi D, Gruszczynski N, Meissner A,
Delouya G and Taussky D: Influence of body mass index and
periprostatic fat on rectal dosimetry in permanent seed prostate
brachytherapy. Radiat Oncol. 9:932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
van Roermund JG, Bol GH, Witjes JA, Ruud
Bosch JL, Kiemeney LA and van Vulpen M: Periprostatic fat measured
on computed tomography as a marker for prostate cancer
aggressiveness. World J Urol. 28:699–704. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nassar ZD, Aref AT, Miladinovic D, Mah CY,
Raj GV, Hoy AJ and Butler LM: Peri-prostatic adipose tissue: The
metabolic microenvironment of prostate cancer. BJU Int. 121 (Suppl
3):S9–S21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sacca PA, Creydt VP, Choi H, Mazza ON,
Fletcher SJ, Vallone VB, Scorticati C, Chasseing NA and Calvo JC:
Human periprostatic adipose tissue: Its influence on prostate
cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 30:113–122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tokuda Y, Satoh Y, Fujiyama C, Toda S,
Sugihara H and Masaki Z: Prostate cancer cell growth is modulated
by adipocyte-cancer cell interaction. BJU Int. 91:716–720. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
König JJ, Kamst E, Hagemeijer A, Romijn
JC, Horoszewicz J and Schröder FH: Cytogenetic characterization of
several androgen responsive and unresponsive sublines of the human
prostatic carcinoma cell line LNCaP. Urol Res. 17:79–86. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wu HC, Hsieh JT, Gleave ME, Brown NM,
Pathak S and Chung LW: Derivation of androgen-independent human
LNCaP prostatic cancer cell sublines: Role of bone stromal cells.
Int J Cancer. 57:406–412. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu AY, Brubaker KD, Goo YA, Quinn JE,
Kral S, Sorensen CM, Vessella RL, Belldegrun AS and Hood LE:
Lineage relationship between LNCaP and LNCaP-derived prostate
cancer cell lines. Prostate. 60:98–108. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kaighn ME, Narayan KS, Ohnuki Y, Lechner
JF and Jones LW: Establishment and characterization of a human
prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC-3). Invest Urol. 17:16–23.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Stone KR, Mickey DD, Wunderli H, Mickey GH
and Paulson DF: Isolation of a human prostate carcinoma cell line
(DU 145). Int J Cancer. 21:274–281. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Alimirah F, Chen J, Basrawala Z, Xin H and
Choubey D: DU-145 and PC-3 human prostate cancer cell lines express
androgen receptor: Implications for the androgen receptor functions
and regulation. FEBS Lett. 580:2294–2300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sramkoski RM, Pretlow TG II, Giaconia JM,
Pretlow TP, Schwartz S, Sy MS, Marengo SR, Rhim JS, Zhang D and
Jacobberger JW: A new human prostate carcinoma cell line, 22Rv1. In
Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 35:403–409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wu Y, Kim JY, Zhou S and Smas CM:
Differential screening identifies transcripts with depot-dependent
expression in white adipose tissues. BMC Genomics. 9:3972008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mistry T, Digby JE, Desai KM and Randeva
HS: Obesity and prostate cancer: A role for adipokines. Eur Urol.
52:46–53. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fletcher SJ, Sacca PA, Pistone-Creydt M,
Coló FA, Serra MF, Santino FE, Sasso CV, Lopez-Fontana CM, Carón
RW, Calvo JC and Pistone-Creydt V: Human breast adipose tissue:
Characterization of factors that change during tumor progression in
human breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Karagiannis GS, Pavlou MP and Diamandis
EP: Cancer secretomics reveal pathophysiological pathways in cancer
molecular oncology. Mol Oncol. 4:496–510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kim KY, Baek A, Park YS, Park MY, Kim JH,
Lim JS, Lee MS, Yoon SR, Lee HG, Yoon Y, et al: Adipocyte culture
medium stimulates invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 cell via CCL20
production. Oncol Rep. 22:1497–1504. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Schnäbele K, Roser S, Rechkemmer G, Hauner
H and Skurk T: Effects of adipocyte-secreted factors on cell cycle
progression in HT29 cells. Eur J Nutr. 48:154–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Culig Z and Puhr M: Interleukin-6 and
prostate cancer: Current developments and unsolved questions. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 462:25–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lopez Fontana CM, Maselli Artola ME, Di
Milta Monaco N, Recalde Rincon GM, Vanrell Rodriguez MC, Uvilla
Recupero A, Messina Lombino D, Perez Elizalde RF and Lopez Laur JD:
Influence of leptin and adiponectin on prostate cancer. Arch Esp
Urol. 62:103–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hu X, Hu C, Zhang C, Zhang M, Long S and
Cao Z: Role of adiponectin in prostate cancer. Int Braz J Urol.
45:220–228. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Balkwill F: Tumour necrosis factor and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:361–371. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sacca PA, Mazza ON, Scorticati C,
Vitagliano G, Casas G and Calvo JC: Human periprostatic adipose
tissue: secretome from patients with prostate cancer or benign
prostate hyperplasia. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 16:29–58. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|