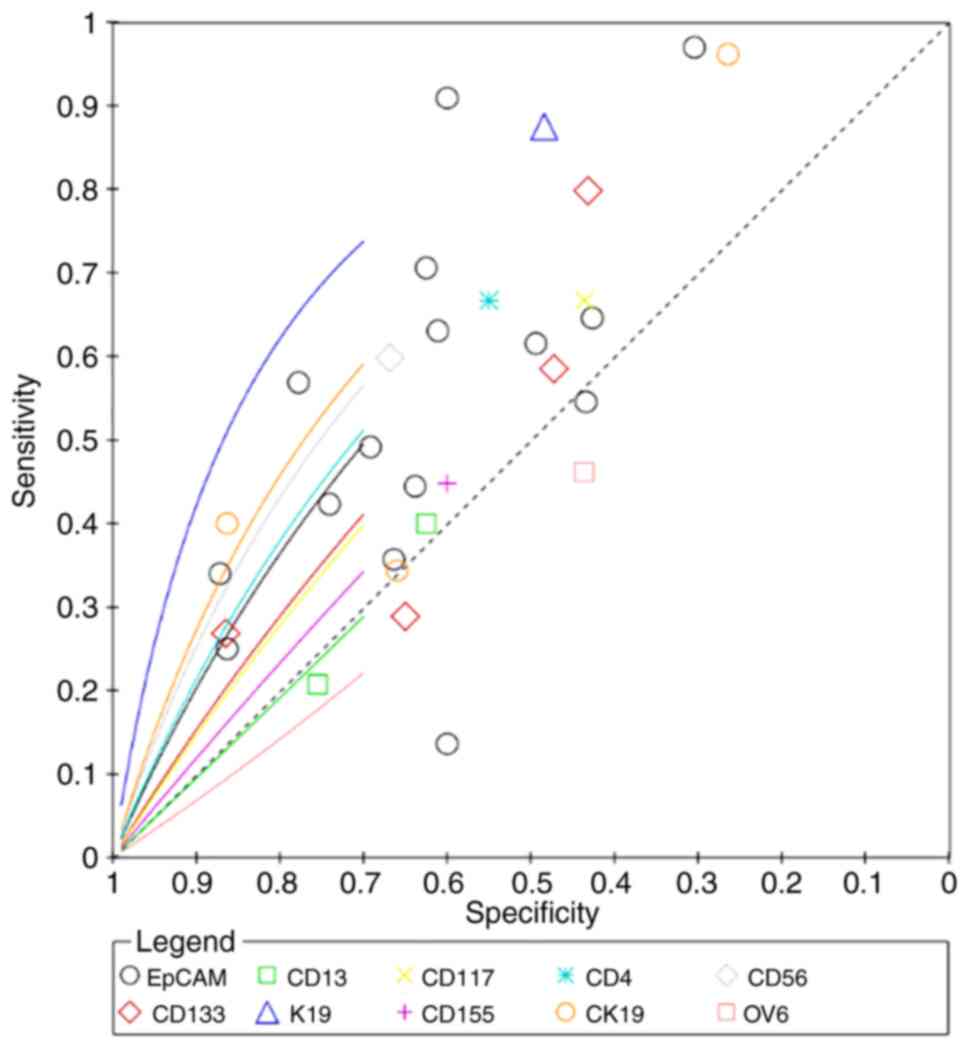
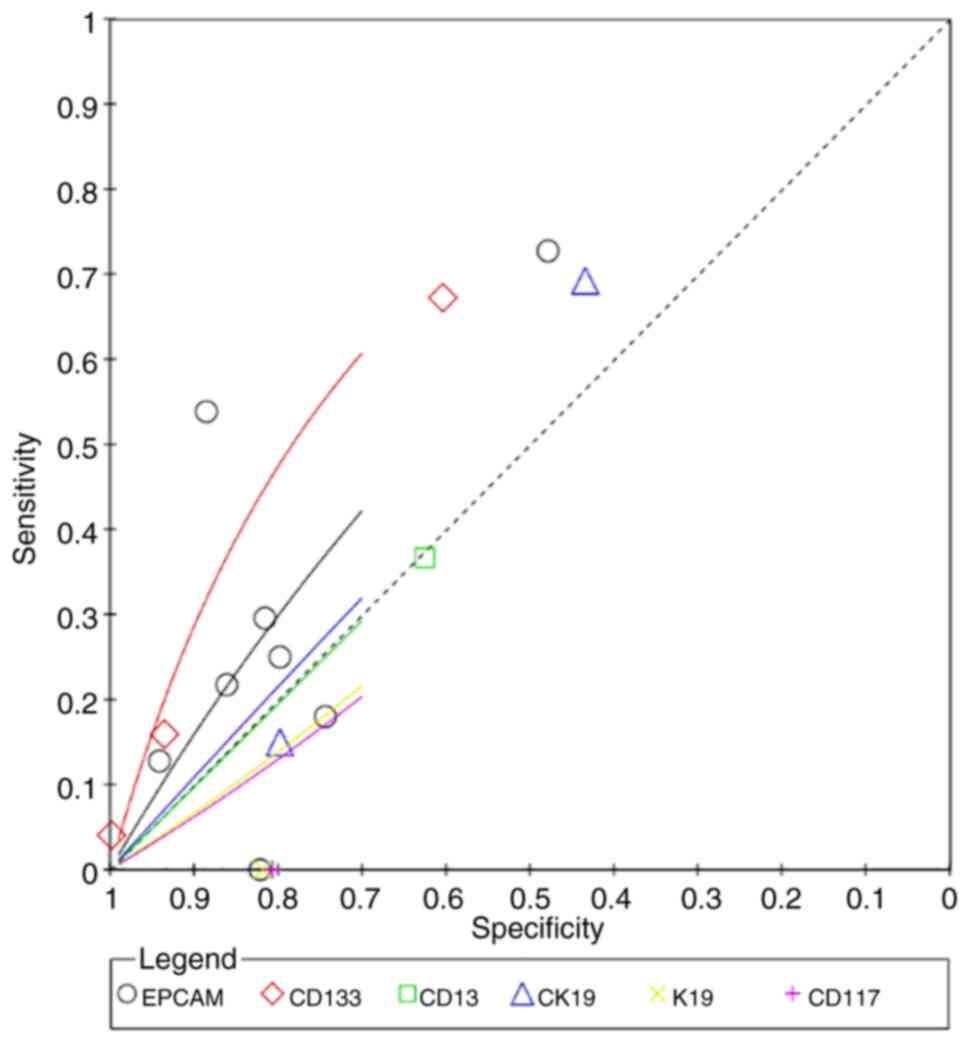
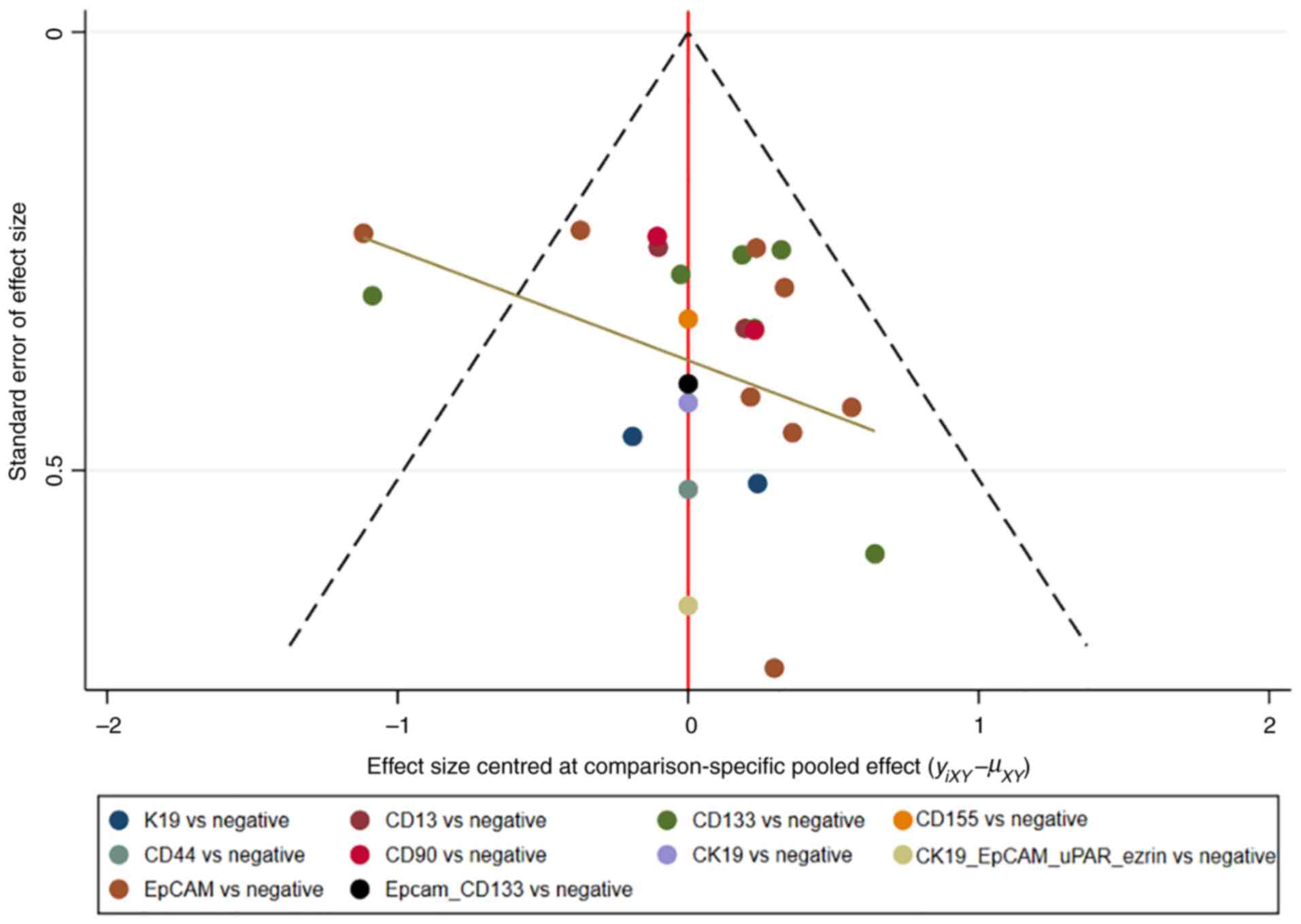
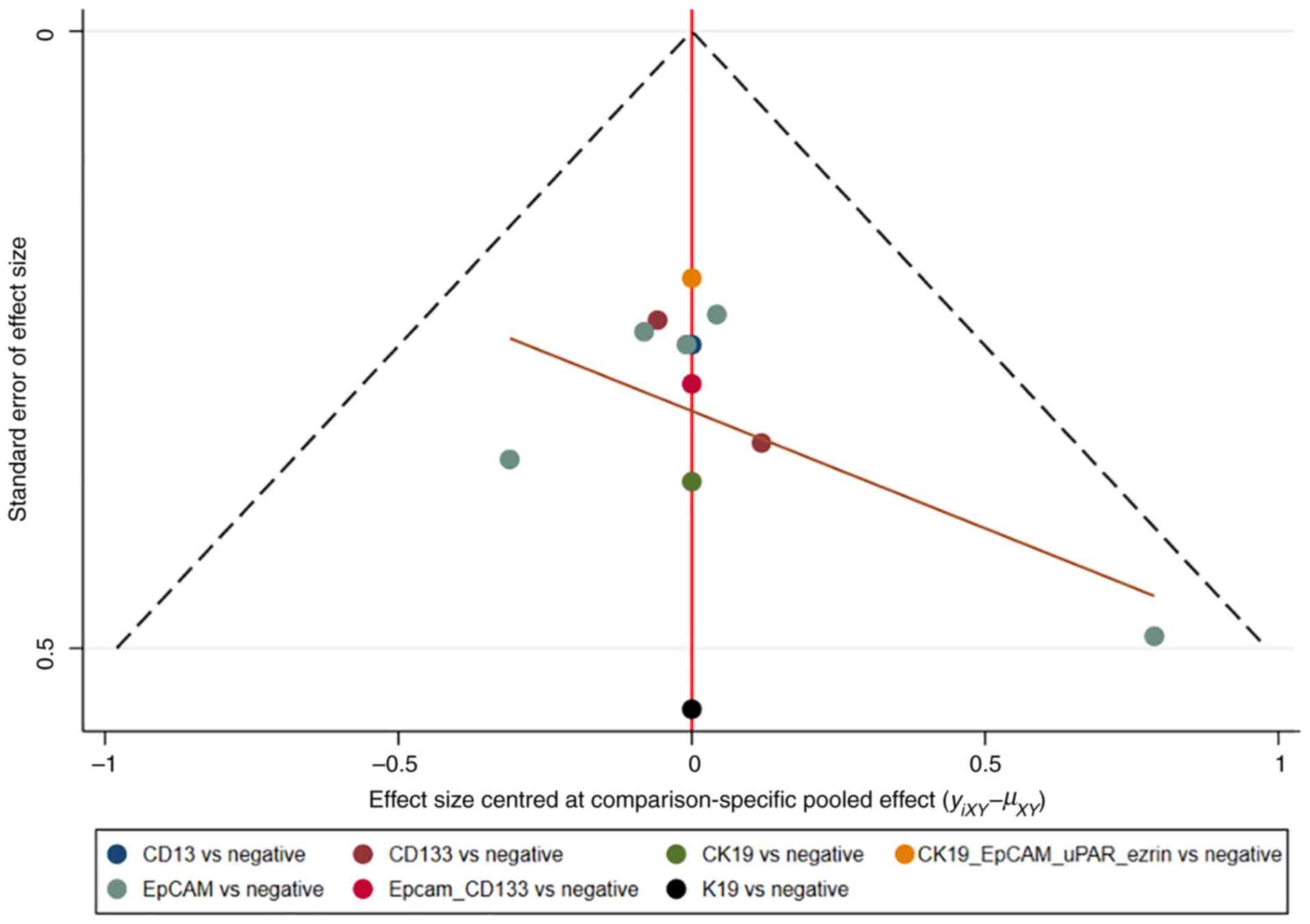
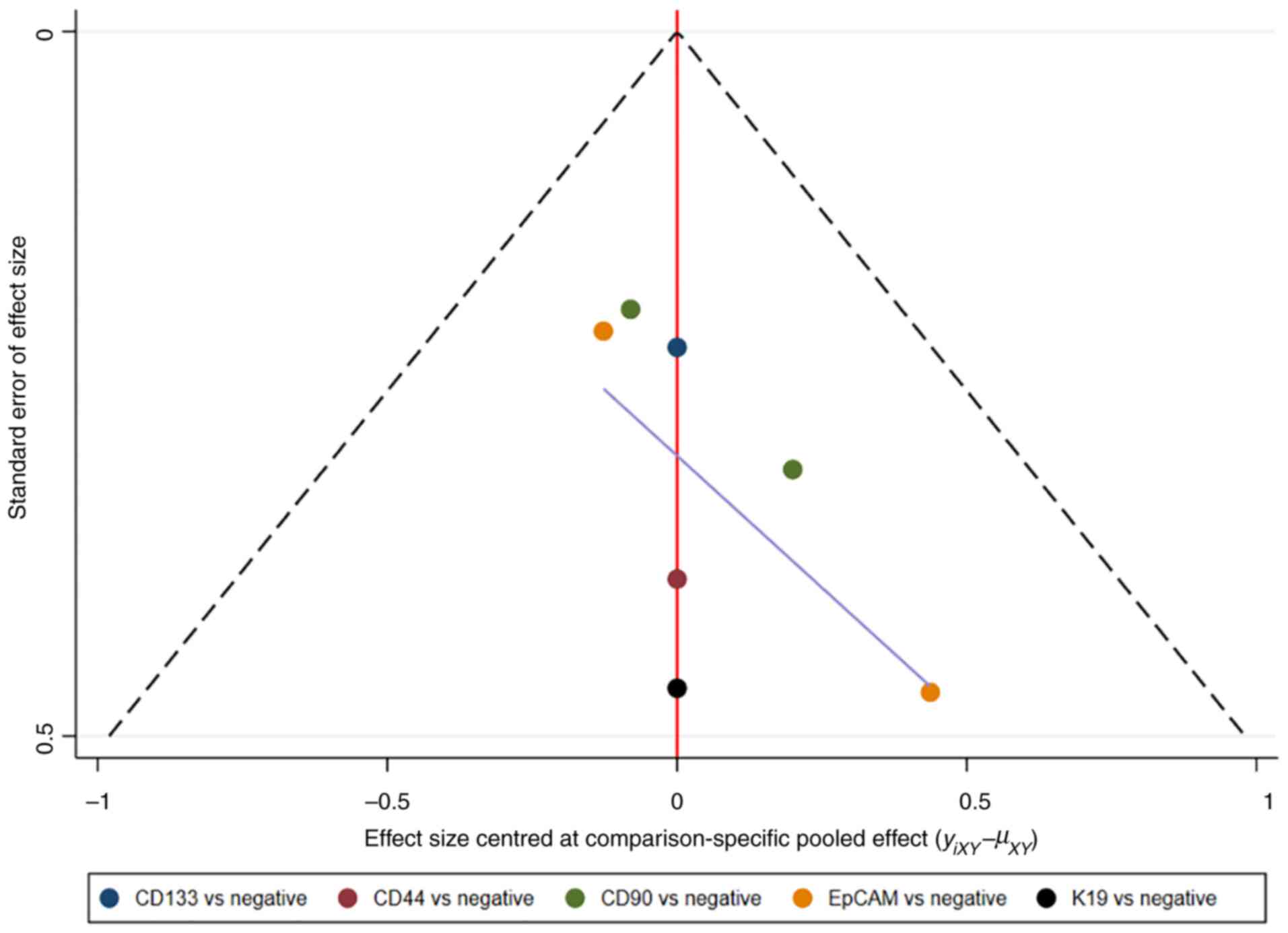
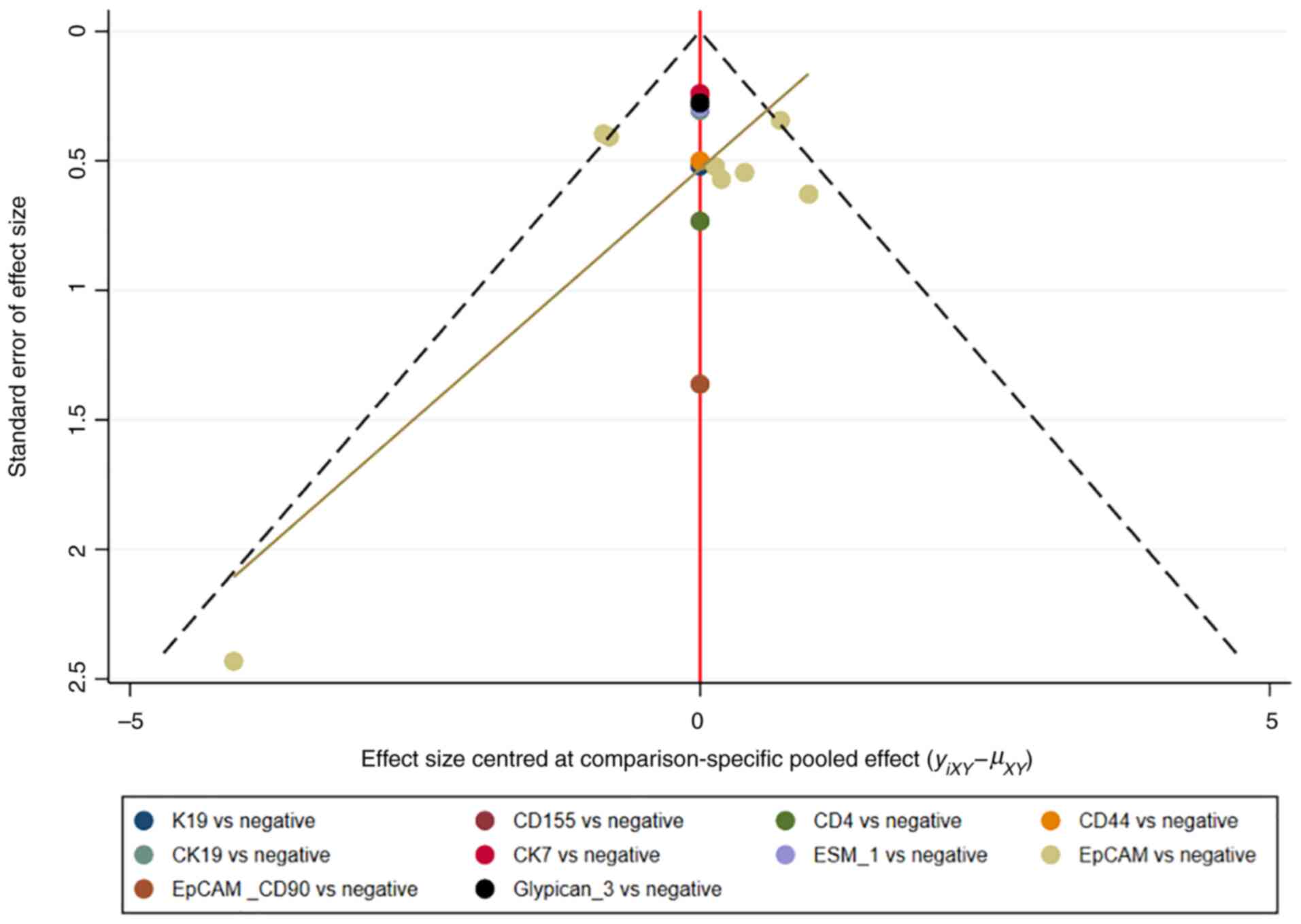
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
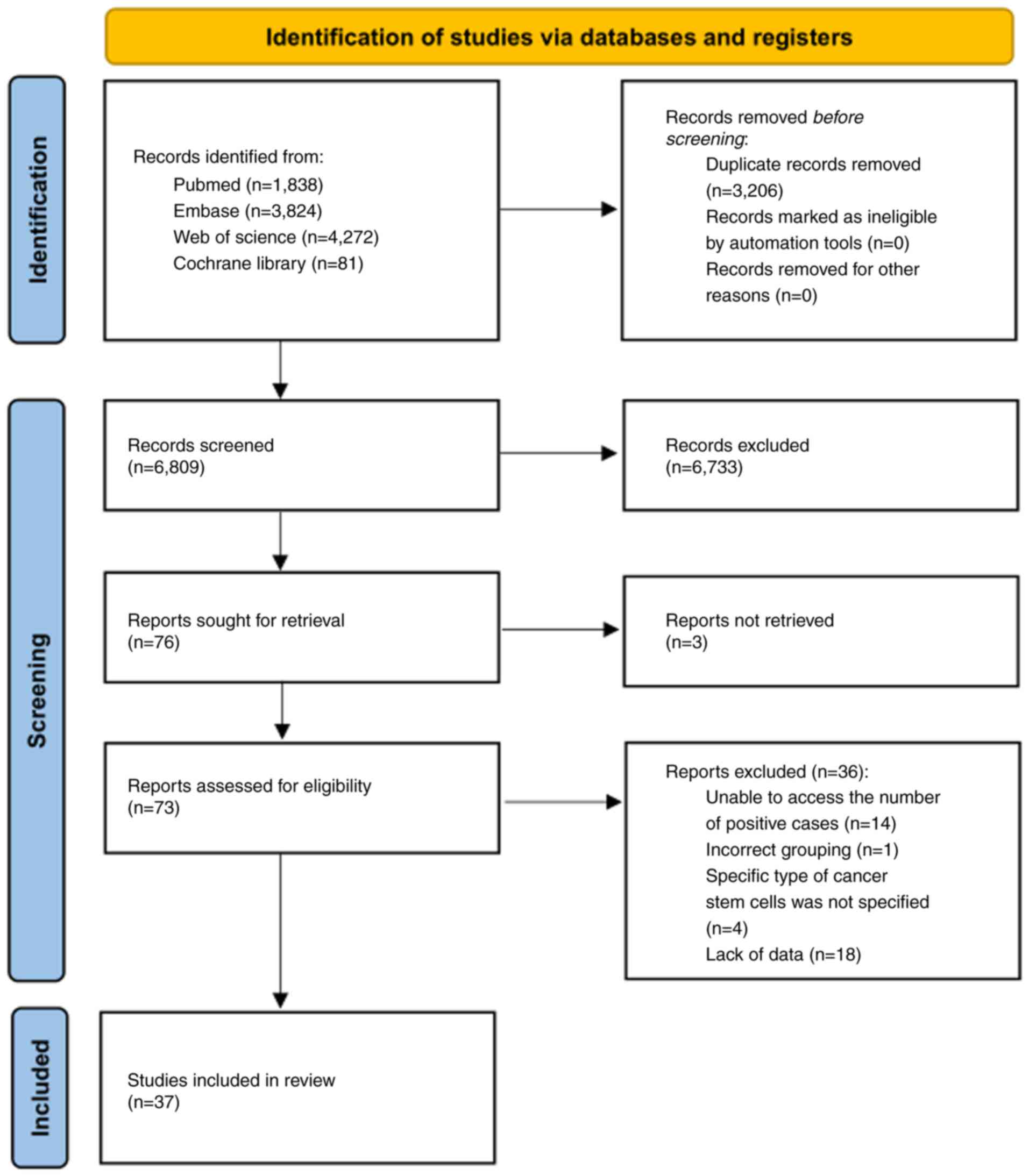
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
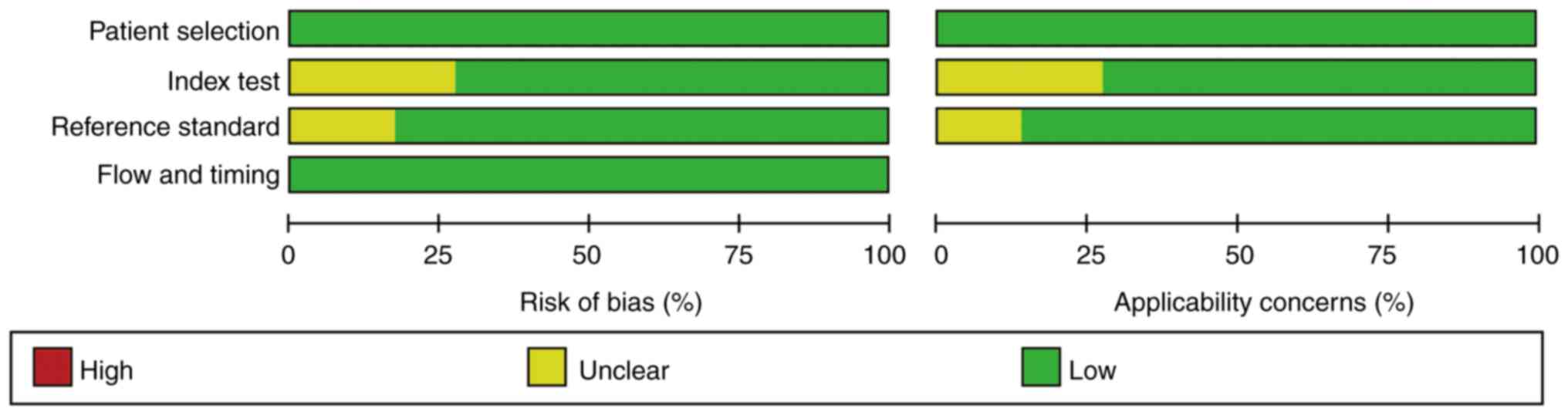
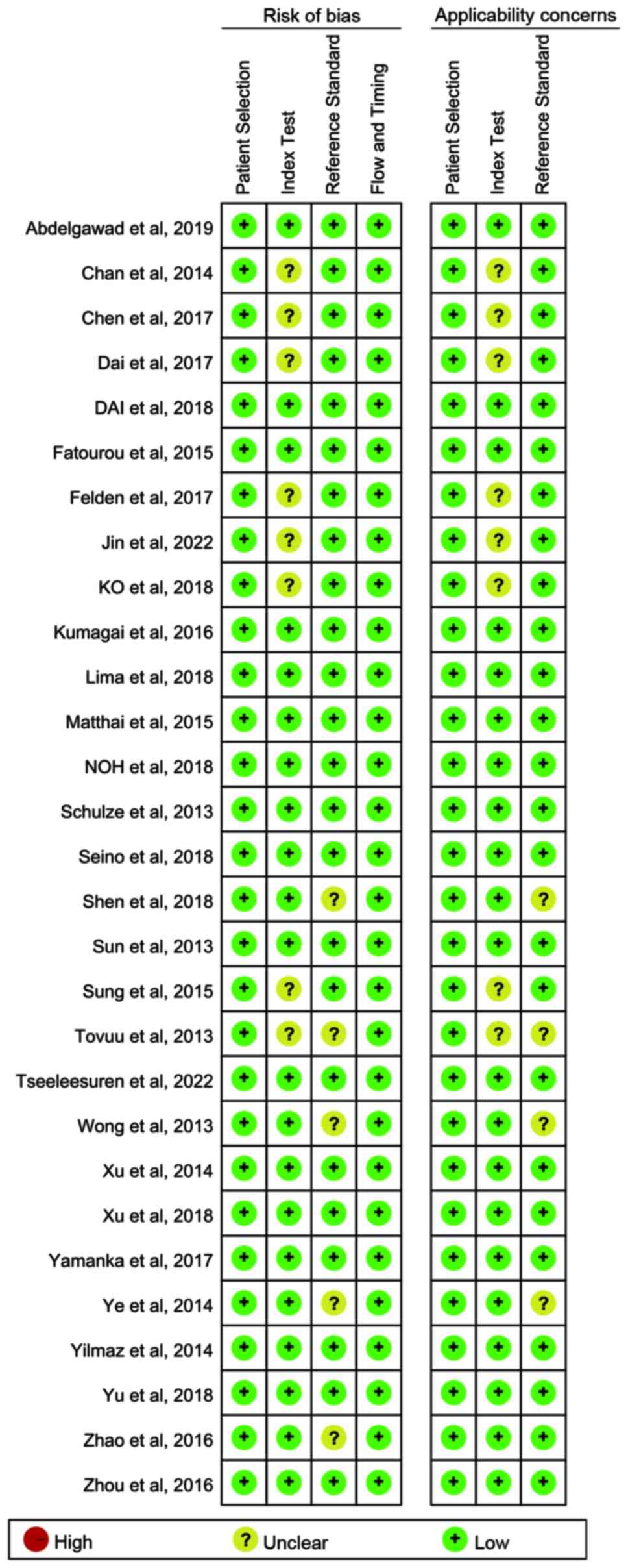
|
|
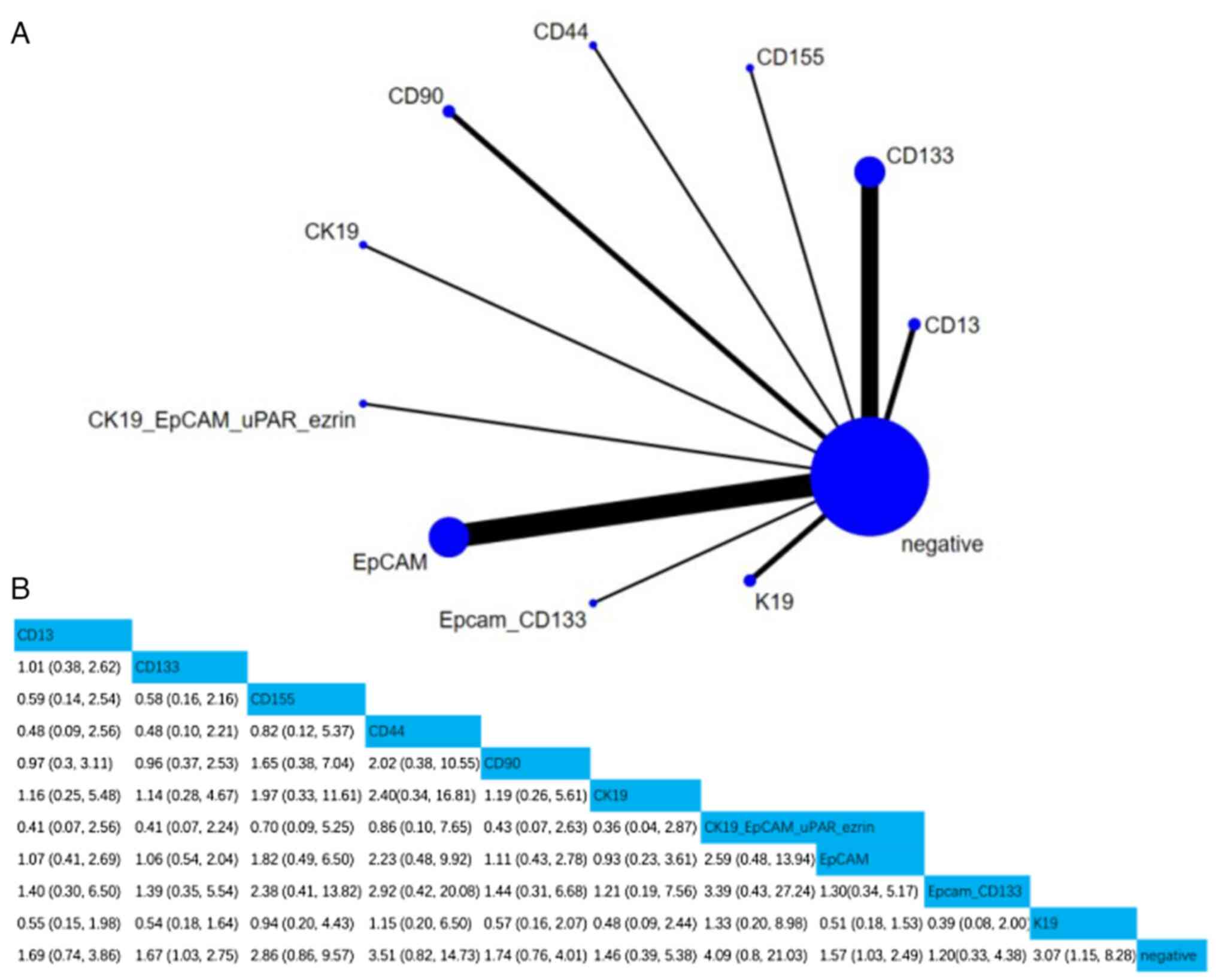
3
|
Yoh T, Seo S, Taura K, Iguchi K, Ogiso S,
Fukumitsu K, Ishii T, Kaido T and Uemoto S: Surgery for recurrent
hepatocellular carcinoma: Achieving Long-term survival. Ann Surg.
273:792–799. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lou J, Zhang L, Lv S, Zhang C and Jiang S:
Biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark Cancer. 9:1–9.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Debnath P, Dalal K, Dalal B, Athalye S,
Chandnani S, Jain S, Shukla A, Rathi P and Shankarkumar A:
Characterization of circulating tumor cells using imaging flow
cytometry in liver disease patients. J Clin Exp Hepatol.
13:608–617. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fang X, Yan Q, Liu S and Guan XY: Cancer
stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: Intrinsic and extrinsic
molecular mechanisms in stemness regulation. Int J Mol Sci.
23:123272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He G, Dhar D, Nakagawa H, Font-Burgada J,
Ogata H, Jiang Y, Shalapour S, Seki E, Yost SE, Jepsen K, et al:
Identification of liver cancer progenitors whose malignant
progression depends on autocrine IL-6 signaling. Cell. 155:384–396.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nio K, Yamashita T and Kaneko S: The
evolving concept of liver cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer. 16:42017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu K, Ding J, Chen C, Sun W, Ning BF, Wen
W, Huang L, Han T, Yang W, Wang C, et al: Hepatic transforming
growth factor beta gives rise to tumor-initiating cells and
promotes liver cancer development. Hepatology. 56:2255–2267. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jeng KS, Chang CF, Sheen IS, Jeng CJ and
Wang CH: Cellular and molecular biology of cancer stem cells of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 24:14172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tseeleesuren D, Hsiao HH, Kant R, Huang
YC, Tu HP, Lai CC, Huang SF and Yen CH: The Expression and
prognostic value of cancer stem cell markers, NRF2, and its target
genes in TAE/TACE-Treated hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicina
(Kaunas). 58:2122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sekar V, Veerabathiran R, Pandian A and
Sivamani G: Targeting liver cancer stem cell through EpCAM therapy
targeted with chemotherapy endorse enhanced progression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Egyptian Liver J. 13:292023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani
A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, Ioannidis JP, Straus S, Thorlund K, Jansen
JP, et al: The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of
systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health
care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med.
2:162:777–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eriksen MB and Frandsen TF: The impact of
patient and interventioncomparison and outcome (PICO) as a search
strategy tool on literature search quality: A systematic review. J
Med Libr Assoc. 106:420–431. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM: QUADAS-2: QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment
of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 155:529–536. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brennan B, Kirton L, Marec-Bérard P,
Gaspar N, Laurence V, Martín-Broto J, Sastre A, Gelderblom H, Owens
C, Fenwick N, et al: Comparison of two chemotherapy regimens in
patients with newly diagnosed Ewing sarcoma (EE2012): An
open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 400:1513–1521. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Veroniki AA, Straus SE, Fyraridis A and
Tricco AC: The rank-heat plot is a novel way to present the results
from a network meta-analysis including multiple outcomes. J Clin
Epidemiol. 76:193–199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye J, Hu Y, Chen X, Chang C and Li K:
Comparative effects of different nutritional supplements on
inflammation and nutritional status, and clinical outcomes in
colorectal cancer patients: A systematic review and network
meta-analysis. Nutrients. 15:27722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nyaga VN, Aerts M and Arbyn M: ANOVA model
for network meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy data. Stat
Methods Med Res. 27:1766–1784. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang S, Chen Y, Zhou F, Wang L and Luo Q:
Effect of care bundles for acute kidney injury: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 19:e03021792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bally S, Cottin J, Gagnieu MC, Lega JC,
Verstuyft C, Rheims S, Lesca G, Cucherat M and Grenet G:
Publication bias in pharmacogenetics of adverse reaction to
antiseizure drugs: An umbrella review and a meta-epidemiological
study. PLoS One. 17:e02788392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumagai A, Kondo F, Sano K, Inoue M, Fujii
T, Hashimoto M, Watanabe M, Soejima Y, Ishida T, Tokairin T, et al:
Immunohistochemical study of hepatocyte and cholangiocyte stem cell
markers of hepatocellular carcinoma: The second report:
Relationship with tumor size and cell differentiation. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 23:414–421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seino S, Tsuchiya A, Watanabe Y, Kawata Y,
Kojima Y, Ikarashi S, Yanai H, Nakamura K, Kumaki D, Hirano M, et
al: Clinical outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma can be predicted
by the expression of hepatic progenitor cell markers and serum
tumour markers. Oncotarget. 9:21844–21860. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
von Felden J, Schulze K, Krech T, Ewald F,
Nashan B, Pantel K, Lohse AW, Riethdorf S and Wege H: Circulating
tumor cells as liquid biomarker for high HCC recurrence risk after
curative liver resection. Oncotarget. 8:89978–89987. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ziol M, Sutton A, Calderaro J, Calderaro
J, Barget N, Aout M, Leroy V, Blanc JF, Sturm N, Bioulac-Sage P, et
al: ESM-1 expression in stromal cells is predictive of recurrence
after radiofrequency ablation in early hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Hepatol. 59:1264–1270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schulze K, Gasch C, Staufer K, Nashan B,
Lohse AW, Pantel K, Riethdorf S and Wege H: Presence of
EpCAM-positive circulating tumor cells as biomarker for systemic
disease strongly correlates to survival in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 133:2165–2171. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matthai SM and Ramakrishna B: Cancer stem
cells in hepatocellular carcinoma-An immuno-histochemical study
with histopathological association. Indian J Med Res. 142:391–398.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu M, Qian G, Xie F, Shi C, Yan L, Yu L,
Zheng T, Wei L and Yang J: Expression of epithelial cell adhesion
molecule associated with elevated ductular reactions in
hepatocellar carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 38:699–705.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hwang HS, Yoo JE, Han DH, Choi JS, Lee JG,
Joo DJ, Kim MS, Kim SI, Choi GH and Park YN: Circulating cancer
stem cells expressing EpCAM/CD90 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A
pilot study for predicting tumor recurrence after living donor
liver transplantation. Gut Liver. 16:443–455. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Qi YP, Ma N, Lu F, Gong WF, Chen
B, Ma L, Zhong JH, Xiang BD and Li LQ: Overexpression of epcam and
CD133 correlates with poor prognosis in Dual-phenotype
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 11:3400–3406. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Krause J, von Felden J, Casar C, Fründt
TW, Galaski J, Schmidt C, Jung C, Ittrich H, Weidemann SA, Krech T,
et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Intratumoral EpCAM-positive cancer
stem cell heterogeneity identifies high-risk tumor subtype. BMC
Cancer. 20:11302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abdelgawad IA: Epithelial cell adhesion
molecule mRNA can be a potential marker to predict metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
21:861–866. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamanaka C, Wada H, Eguchi H, Hatano H,
Gotoh K, Noda T, Yamada D, Asaoka T, Kawamoto K, Nagano H, et al:
Clinical significance of CD13 and epithelial mesenchymal transition
(EMT) markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
48:52–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shen J, Wang WS, Zhu XL and Ni CF: High
epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive circulating tumor cell
count predicts poor survival of patients with unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 29:1678–1684. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Noh CK, Wang HJ, Kim CM, Kim J, Yoon SY,
Lee GH, Cho HJ, Yang MJ, Kim SS, Hwang JC, et al: EpCAM as a
predictive marker of tumor recurrence and survival in patients who
underwent surgical resection for hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 38:4101–4109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lima LDP, Machado CJ, Rodrigues JBSR,
Vasconcellos LS, Junior EP, Vidigal PVT and Resende V:
Immunohistochemical coexpression of epithelial cell adhesion
molecule and alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. Can J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018:59708522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ko CJ, Li CJ, Wu MY and Chu PY:
Overexpression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule as a predictor
of poor outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Ther
Med. 16:4810–4816. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dai XM, Yang SL, Zheng XM, Chen GG, Chen J
and Zhang T: CD133 expression and α-fetoprotein levels define novel
prognostic subtypes of HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: A
long-term follow-up analysis. Oncol Lett. 15:2985–2991.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dai XM, Huang T, Yang SL, Zheng XM, Chen
GG and Zhang T: Peritumoral EpCAM is an independent prognostic
marker after curative resection of HBV-Related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2017:84953262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen YL, Lin PY, Ming YZ, Huang WC, Chen
RF, Chen PM and Chu PY: The effects of the location of cancer stem
cell marker CD133 on the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. BMC Cancer. 17:4742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao Q, Zhou H, Liu Q, Cao Y, Wang G, Hu
A, Ruan L, Wang S, Bo Q, Chen W, et al: Prognostic value of the
expression of cancer stem cell-related markers CD133 and CD44 in
hepatocellular carcinoma: From patients to patient-derived tumor
xenograft models. Oncotarget. 7:47431–47443. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nam SJ, Yeo HY, Chang HJ, Kim BH, Hong EK
and Park JW: A new cell block method for multiple
immunohistochemical analysis of circulating tumor cells in patients
with liver cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 48:1229–1242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ye F, Jing YY, Guo SW, Yu GF, Fan QM, Qu
FF, Gao L, Yang Y, Wu D, Meng Y, et al: Proliferative ductular
reactions correlate with hepatic progenitor cell and predict
recurrence in HCC patients after curative resection. Cell Biosci.
4:502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chan AWH, Tong JHM, Chan SL, Lai PBS and
To KF: Expression of stemness markers (CD133 and EpCAM) in
prognostication of hepatocellular carcinoma. Histopathology.
64:935–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wong E, Srivastava S, Yeoh KG, Teh M and
Salto-Tellez M: Clinical and biological relevance of thy-1/CD90
protein overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Onco
Pathol. 1:1–9. 2013.
|
|
46
|
Sun YF, Xu Y, Yang XR, Guo W, Zhang X, Qiu
SJ, Shi RY, Hu B, Zhou J and Fan J: Circulating stem cell-like
epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive tumor cells indicate
poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
resection. Hepatology. 57:1458–1468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao RC, Zhou J, Chen KF, Gong J, Liu J,
He JY, Guan P, Li B and Qin Y: The prognostic value of combination
of CD90 and OCT4 for hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
resection. Neoplasma. 63:288–298. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sung JJ, Noh SJ, Bae JS, Park HS, Jang KY,
Chung MJ and Moon WS: Immunohistochemical expression and clinical
significance of suggested stem cell markers in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Pathol Transl Med. 50:52–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rhee H, Nahm JH, Kim H, Choi GH, Yoo JE,
Lee HS, Koh MJ and Park YN: Poor outcome of hepatocellular
carcinoma with stemness marker under hypoxia: Resistance to
transarterial chemoembolization. Mod Pathol. 29:1038–1049. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fatourou E, Koskinas J, Karandrea D,
Palaiologou M, Syminelaki T, Karanikolas M, Felekouras E, Antoniou
E, Manesis EK, Delladetsima J and Tiniakos D: Keratin 19 protein
expression is an independent predictor of survival in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
27:1094–1102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yilmaz G, Akyol G, Cakir A and Ilhan M:
Investigation of diagnostic utility and expression profiles of stem
cell markers (CD133 and CD90) in hepatocellular carcinoma, small
cell dysplasia, and cirrhosis. Pathol Res Pract. 210:419–425. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tovuu LO, Imura S, Utsunomiya T, Morine Y,
Ikemoto T, Arakawa Y, Mori H, Hanaoka J, Kanamoto M, Sugimoto K, et
al: Role of CD44 expression in non-tumor tissue on intrahepatic
recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol.
18:651–656. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee Y, Park H, Lee H, Cho JY, Yoon YS,
Choi YR, Han HS, Jang ES, Kim JW, Jeong SH, et al: The
clinicopathological and prognostic significance of the gross
classification of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pathol Transl Med.
52:85–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu J, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Tao X, Cheng L, Wu
S and Tao Y: Correlation of KAI1, CD133 and vasculogenic mimicry
with the prediction of metastasis and prognosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 11:3638–3646. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jin AL, Zhang CY, Zheng WJ, Xian JR, Yang
WJ, Liu T, Chen W, Li T, Wang BL, Pan BS, et al: CD155/SRC complex
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inhibiting the
p38 MAPK signalling pathway and correlates with poor prognosis.
Clin Transl Med. 12:e7942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yu GF, Lin X, Luo RC and Fang WY: Nuclear
CD133 expression predicts poor prognosis for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 11:2092–2099. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou Y, Wang B, Wu J, Zhang C, Zhou Y,
Yang X, Zhou J, Guo W and Fan J: Association of preoperative EpCAM
circulating tumor cells and peripheral treg cell levels with early
recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma following radical hepatic
resection. BMC Cancer. 16:5062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sun DW, Zhang YY, Sun XD, Chen YG, Qiu W,
Ji M and Lv GY: Prognostic value of cytokeratin 19 in
hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta.
448:161–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhuo JY, Lu D, Tan WY, Zheng SS, Shen YQ
and Xu X: CK19-positive hepatocellular carcinoma is a
characteristic subtype. J Cancer. 11:5069–5077. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhan T, Rindtorff N and Boutros M: Wnt
signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1461–1473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ma YC, Yang JY and Yan LN: Relevant
markers of cancer stem cells indicate a poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A meta-analysis. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:1007–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kawai T, Yasuchika K, Ishii T, Katayama H,
Yoshitoshi EY, Ogiso S, Kita S, Yasuda K, Fukumitsu K, Mizumoto M,
et al: Keratin 19, a cancer stem cell marker in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3081–3091. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yokomichi N, Nishida N, Umeda Y, Taniguchi
F, Yasui K, Toshima T, Mori Y, Nyuya A, Tanaka T, Yamada T, et al:
Heterogeneity of epigenetic and epithelial mesenchymal transition
marks in hepatocellular carcinoma with keratin 19 proficiency.
Liver Cancer. 8:239–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bae JS, Choi HN, Noh SJ, Park BH, Jang KY,
Park CK and Moon WS: Expression of K19 and K7 in dysplastic nodules
and hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 4:213–220. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kim H, Choi GH, Na DC, Ahn EY, Kim GI, Lee
JE, Cho JY, Yoo JE, Choi JS and Park YN: Human hepatocellular
carcinomas with ‘Stemness’-Related marker expression: Keratin 19
expression and a poor prognosis. Hepatology. 54:1707–1717. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Park DJ, Sung PS, Kim JH, Lee GW, Jang JW,
Jung ES, Bae SH, Choi JY and Yoon SK: EpCAM-high liver cancer stem
cells resist natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity by
upregulating CEACAM1. J Immunother Cancer. 8:e0003012020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shousha HI, Fouad R, Elbaz TM, Sabry D,
Mahmoud Nabeel M, Hosni Abdelmaksoud A, Mahmoud Elsharkawy A,
Soliman ZA, Habib G, Abdelaziz AO, et al: Predictors of recurrence
and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study
including transient elastography and cancer stem cell markers. Arab
J Gastroenterol. 21:95–101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Luo J, Wang P, Wang R, Wang J, Liu M,
Xiong S, Li Y and Cheng B: The Notch pathway promotes the cancer
stem cell characteristics of CD90+ cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:9526–9538. 2016.
|
|
69
|
Liu R, Shen Y, Nan K, Mi B, Wu T, Guo J,
Li M, Lv Y and Guo H: Association between expression of cancer stem
cell markers and poor differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma:
A Meta-Analysis (PRISMA). Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e13062015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Takano M, Shimada K, Fujii T, Morita K,
Takeda M, Nakajima Y, Nonomura A, Konishi N and Obayashi C: Keratin
19 as a key molecule in progression of human hepatocellular
carcinomas through invasion and angiogenesis. BMC Cancer.
16:9032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
You H, Ding W and Rountree CB: Epigenetic
regulation of cancer stem cell marker CD133 by transforming growth
factor-beta. Hepatology. 51:1635–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yan M, Li H, Zhu M, Zhao F, Zhang L, Chen
T, Jiang G, Xie H, Cui Y, Yao M, et al: G protein-coupled receptor
87 (GPR87) promotes the growth and metastasis of CD133+ cancer
stem-like cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e610562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhong C, Wu JD, Fang MM and Pu LY:
Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of the
expression of the cancer stem cell marker CD133 in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 36:7623–7630. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|