|
1
|
Ciardiello F, Ciardiello D, Martini G,
Napolitano S, Tabernero J and Cervantes A: Clinical management of
metastatic colorectal cancer in the era of precision medicine. CA
Cancer J Clin. 72:372–401. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qu R, Ma Y, Zhang Z and Fu W: Increasing
burden of colorectal cancer in China. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol.
7:7002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Spaander MCW, Zauber AG, Syngal S, Blaser
MJ, Sung JJ, You YN and Kuipers EJ: Young-onset colorectal cancer.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 9:212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shaukat A and Levin TR: Current and future
colorectal cancer screening strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 19:521–531. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wong CC and Yu J: Gut microbiota in
colorectal cancer development and therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
20:429–452. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, Dan W, Zhang N, Fang J and Yang Y:
Colorectal cancer and gut microbiota studies in China. Gut
Microbes. 15:22363642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
van Ginkel J, Tomlinson I and Soriano I:
The evolutionary landscape of colorectal tumorigenesis: Recent
paradigms, models, and hypotheses. Gastroenterology. 164:841–846.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weiss JM, Gupta S, Burke CA, Axell L, Chen
LM, Chung DC, Clayback KM, Dallas S, Felder S, Gbolahan O, et al:
NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Genetic/Familial High-Risk
Assessment: Colorectal, Version 1.2021. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
19:1122–1132. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bodmer WF, Bailey CJ, Bodmer J, Bussey HJ,
Ellis A, Gorman P, Lucibello FC, Murday VA, Rider SH, Scambler P,
et al: Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis
on chromosome 5. Nature. 328:614–616. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karstensen JG, Burisch J, Pommergaard HC,
Aalling L, Hojen H, Jespersen N, Schmidt PN and Bülow S: Colorectal
cancer in individuals with familial adenomatous polyposis, based on
analysis of the danish polyposis registry. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 17:2294–2300.e1. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rowan AJ, Lamlum H, Ilyas M, Wheeler J,
Straub J, Papadopoulou A, Bicknell D, Bodmer WF and Tomlinson IP:
APC mutations in sporadic colorectal tumors: A mutational ‘hotspot’
and interdependence of the ‘two hits’. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:3352–3357. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
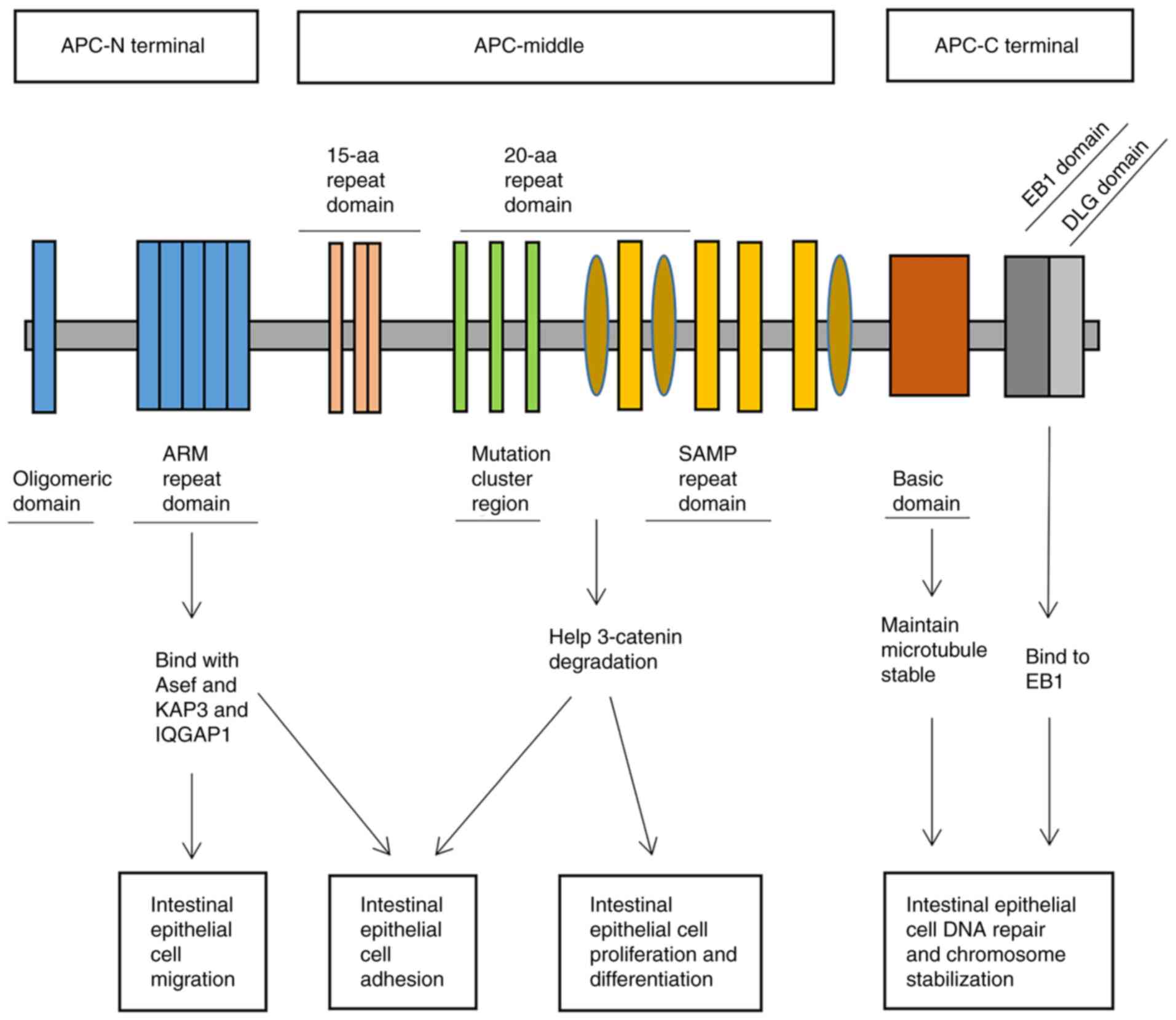
Aoki K and Taketo MM: Adenomatous
polyposis coli (APC): A Multi-functional tumor suppressor gene. J
Cell Sci. 120:3327–3335. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bressler SG, Mitrany A, Wenger A, Nathke I
and Friedler A: The oligomerization domains of the APC protein
mediate Liquid-liquid phase separation that is phosphorylation
controlled. Int J Mol Sci. 24:64782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Z, Lin K, Gao L, Chen L, Shi X and
Wu G: Crystal structure of the armadillo repeat domain of
adenomatous polyposis coli which reveals its inherent flexibility.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 412:732–736. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kawasaki Y, Senda T, Ishidate T, Koyama R,
Morishita T, Iwayama Y, Higuchi O and Akiyama T: Asef, a link
between the tumor suppressor APC and G-protein signaling. Science.
289:1194–1197. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rowling PJE, Murton BL, Du Z and Itzhaki
LS: Multivalent interaction of Beta-Catenin with its intrinsically
disordered binding partner adenomatous polyposis Coli. Front Mol
Biosci. 9:8964932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kunttas-Tatli E, Von Kleeck RA, Greaves
BD, Vinson D, Roberts DM and McCartney BM: The two SAMP repeats and
their phosphorylation state in Drosophila Adenomatous polyposis
coli-2 play mechanistically distinct roles in negatively regulating
Wnt signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 26:4503–4518. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Juanes MA, Fees CP, Hoeprich GJ, Jaiswal R
and Goode BL: EB1 directly regulates APC-Mediated actin nucleation.
Curr Biol. 30:4763–4772.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Honnappa S, John CM, Kostrewa D, Winkler
FK and Steinmetz MO: Structural insights into the EB1-APC
interaction. EMBO J. 24:261–269. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lui C, Ashton C, Sharma M, Brocardo MG and
Henderson BR: APC functions at the centrosome to stimulate
microtubule growth. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 70:39–47. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng H, Ying J, Zang J, Lu H, Zhao X, Yang
P, Wang X, Li J, Gong Z, Zhang D and Wang Z: Specific mutations in
APC, with prognostic implications in metastatic colorectal cancer.
Cancer Res Treat. 55:1270–1280. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lewis A, Davis H, Deheragoda M, Pollard P,
Nye E, Jeffery R, Segditsas S, East P, Poulsom R, Stamp G, et al:
The C-terminus of Apc does not influence intestinal adenoma
development or progression. J Pathol. 226:73–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nusse R and Clevers H: Wnt/β-Catenin
signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell.
169:985–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Klaus A and Birchmeier W: Wnt signalling
and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:387–398. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
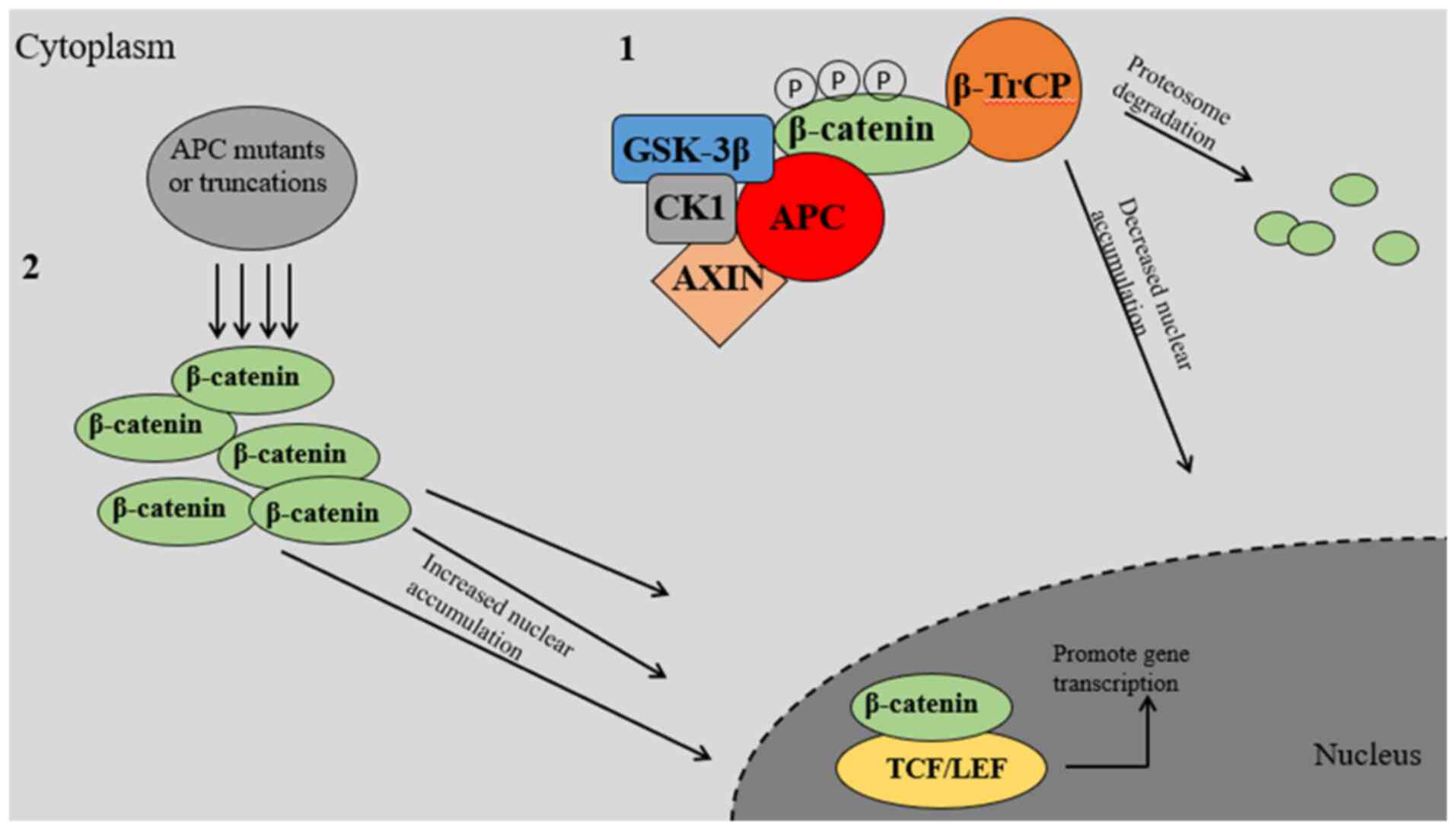
Kennell J and Cadigan KM: APC and
beta-catenin degradation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 656:1–12. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mishra L: STRAP: A bridge between mutant
APC and Wnt/ß-Catenin signaling in intestinal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 162:44–46. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li W, Hou Y, Ming M, Yu L, Seba A and Qian
Z: Apc regulates the function of hematopoietic stem cells largely
through beta-catenin-dependent mechanisms. Blood. 121:4063–4072.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Odenwald MA, Prosperi JR and Goss KH:
APC/β-catenin-rich complexes at membrane protrusions regulate
mammary tumor cell migration and mesenchymal morphology. BMC
Cancer. 13:122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bakker ER, Hoekstra E, Franken PF,
Helvensteijn W, van Deurzen CH, van Veelen W, Kuipers EJ and Smits
R: β-Catenin signaling dosage dictates tissue-specific tumor
predisposition in Apc-driven cancer. Oncogene. 32:4579–4585. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cole JM, Simmons K and Prosperi JR: Effect
of adenomatous polyposis coli loss on tumorigenic potential in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cells. 8:10842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ranes M, Zaleska M, Sakalas S, Knight R
and Guettler S: Reconstitution of the destruction complex defines
roles of AXIN polymers and APC in β-catenin capture,
phosphorylation, and ubiquitylation. Mol Cell. 81:3246–3261.e11.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roberts DM, Pronobis MI, Poulton JS,
Waldmann JD, Stephenson EM, Hanna S and Peifer M: Deconstructing
the sscatenin destruction complex: Mechanistic roles for the tumor
suppressor APC in regulating Wnt signaling. Mol Biol Cell.
22:1845–1863. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Montagne J, Preza M, Castillo E, Brehm K
and Koziol U: Divergent Axin and GSK-3 paralogs in the beta-catenin
destruction complexes of tapeworms. Dev Genes Evol. 229:89–102.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Faux MC, Coates JL, Catimel B, Cody S,
Clayton AH, Layton MJ and Burgess AW: Recruitment of adenomatous
polyposis coli and beta-catenin to axin-puncta. Oncogene.
27:5808–5820. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nong J, Kang K, Shi Q, Zhu X, Tao Q and
Chen YG: Phase separation of Axin organizes the beta-catenin
destruction complex. J Cell Biol. 220:e2020121122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY,
Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Maurice MM, Mahmoudi
T and Clevers H: Wnt signaling through inhibition of beta-catenin
degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell. 149:1245–1256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ain QU, Seemab U, Rashid S, Nawaz MS and
Kamal MA: Prediction of structure of human WNT-CRD (FZD) complex
for computational drug repurposing. PLoS One. 8:e546302013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aghabozorgi AS, Bahreyni A, Soleimani A,
Bahrami A, Khazaei M, Ferns GA, Avan A and Hassanian SM: Role of
adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene mutations in the pathogenesis
of colorectal cancer; current status and perspectives. Biochimie;
157. pp. 64–71. 2019, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Albuquerque C, Breukel C, van der Luijt R,
Fidalgo P, Lage P, Slors FJ, Leitao CN, Fodde R and Smits R: The
‘just-right’ signaling model: APC somatic mutations are selected
based on a specific level of activation of the beta-catenin
signaling cascade. Hum Mol Genet. 11:1549–1560. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Segditsas S, Rowan AJ, Howarth K, Jones A,
Leedham S, Wright NA, Gorman P, Chambers W, Domingo E, Roylance RR,
et al: APC and the Three-hit hypothesis. Oncogene. 28:146–155.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Henderson BR and Fagotto F: The ins and
outs of APC and beta-catenin nuclear transport. EMBO Rep.
3:834–839. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rosin-Arbesfeld R, Cliffe A, Brabletz T
and Bienz M: Nuclear export of the APC tumour suppressor controls
beta-catenin function in transcription. EMBO J. 22:1101–1113. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Elliott KL, Catimel B, Church NL, Coates
JL, Burgess AW, Layton MJ and Faux MC: Immunopurification of
adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) proteins. BMC Res Notes.
6:4292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hamada F and Bienz M: The APC tumor
suppressor binds to C-terminal binding protein to divert nuclear
beta-catenin from TCF. Dev Cell. 7:677–685. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sumner ET, Chawla AT, Cororaton AD,
Koblinski JE, Kovi RC, Love IM, Szomju BB, Korwar S, Ellis KC and
Grossman SR: Transforming activity and therapeutic targeting of
C-terminal-binding protein 2 in Apc-mutated neoplasia. Oncogene.
36:4810–4816. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nadauld LD, Phelps R, Moore BC, Eisinger
A, Sandoval IT, Chidester S, Peterson PW, Manos EJ, Sklow B, Burt
RW and Jones DA: Adenomatous polyposis coli control of C-terminal
binding protein-1 stability regulates expression of intestinal
retinol dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 281:37828–37835. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Serre L, Stoppin-Mellet V and Arnal I:
Adenomatous polyposis coli as a scaffold for microtubule
End-binding proteins. J Mol Biol. 431:1993–2005. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chinnadurai G: The transcriptional
corepressor CtBP: A foe of multiple tumor suppressors. Cancer Res.
69:731–734. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schneikert J, Brauburger K and Behrens J:
APC mutations in colorectal tumours from FAP patients are selected
for CtBP-mediated oligomerization of truncated APC. Hum Mol Genet.
20:3554–3564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chandra SH, Wacker I, Appelt UK, Behrens J
and Schneikert J: A common role for various human truncated
adenomatous polyposis coli isoforms in the control of beta-catenin
activity and cell proliferation. PLoS One. 7:e344792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang L, Theodoropoulos PC, Eskiocak U,
Wang W, Moon YA, Posner B, Williams NS, Wright WE, Kim SB, Nijhawan
D, et al: Selective targeting of mutant adenomatous polyposis coli
(APC) in colorectal cancer. Sci Transl Med. 8:361ra1402016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mizutani A, Yashiroda Y, Muramatsu Y,
Yoshida H, Chikada T, Tsumura T, Okue M, Shirai F, Fukami T,
Yoshida M and Seimiya H: RK-287107, a potent and specific tankyrase
inhibitor, blocks colorectal cancer cell growth in a preclinical
model. Cancer Sci. 109:4003–4014. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Novellasdemunt L, Foglizzo V, Cuadrado L,
Antas P, Kucharska A, Encheva V, Snijders AP and Li VSW: USP7 is a
Tumor-specific WNT activator for APC-mutated colorectal cancer by
mediating β-Catenin deubiquitination. Cell Rep. 21:612–627. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang L, Kim SB, Luitel K and Shay JW:
Cholesterol depletion by TASIN-1 induces apoptotic cell death
through the ER Stress/ROS/JNK signaling in colon cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 17:943–951. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qian J, Steigerwald K, Combs KA, Barton MC
and Groden J: Caspase cleavage of the APC tumor suppressor and
release of an Amino-terminal domain is required for the
Transcription-independent function of APC in apoptosis. Oncogene.
26:4872–4876. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Brocardo M, Lei Y, Tighe A, Taylor SS, Mok
MT and Henderson BR: Mitochondrial targeting of adenomatous
polyposis coli protein is stimulated by truncating cancer
mutations: Regulation of Bcl-2 and implications for cell survival.
J Biol Chem. 283:5950–5959. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Baro L, Islam A, Brown HM, Bell ZA and
Juanes MA: APC-driven actin nucleation powers collective cell
dynamics in colorectal cancer cells. iScience. 26:1065832023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Juzans M, Cuche C, Rose T, Mastrogiovanni
M, Bochet P, Di Bartolo V and Alcover A: Adenomatous polyposis coli
modulates actin and microtubule cytoskeleton at the immunological
synapse to tune CTL functions. Immunohorizons. 4:363–381. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang X, Zhong J, Zhang Q, Feng L, Zheng Z,
Zhang J and Lu S: Advances and insights of APC-Asef inhibitors for
metastatic colorectal cancer therapy. Front Mol Biosci.
8:6625792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kawasaki Y, Furukawa S, Sato R and Akiyama
T: Differences in the localization of the adenomatous polyposis
coli-Asef/Asef2 complex between adenomatous polyposis coli
wild-type and mutant cells. Cancer Sci. 104:1135–1138. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nelson SA, Li Z, Newton IP, Fraser D,
Milne RE, Martin DM, Schiffmann D, Yang X, Dormann D, Weijer CJ, et
al: Tumorigenic fragments of APC cause dominant defects in
directional cell migration in multiple model systems. Dis Model
Mech. 5:940–947. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mimori-Kiyosue Y, Shiina N and Tsukita S:
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) protein moves along microtubules
and concentrates at their growing ends in epithelial cells. J Cell
Biol. 148:505–518. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jaulin F and Kreitzer G: KIF17 stabilizes
microtubules and contributes to epithelial morphogenesis by acting
at MT plus ends with EB1 and APC. J Cell Biol. 190:443–460. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jimbo T, Kawasaki Y, Koyama R, Sato R,
Takada S, Haraguchi K and Akiyama T: Identification of a link
between the tumour suppressor APC and the kinesin superfamily. Nat
Cell Biol. 4:323–327. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ruane PT, Gumy LF, Bola B, Anderson B,
Wozniak MJ, Hoogenraad CC and Allan VJ: Tumour suppressor
adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) localisation is regulated by both
Kinesin-1 and Kinesin-2. Sci Rep. 6:274562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Marshall TW, Lloyd IE, Delalande JM,
Nathke I and Rosenblatt J: The tumor suppressor adenomatous
polyposis coli controls the direction in which a cell extrudes from
an epithelium. Mol Biol Cell. 22:3962–3970. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bienz M and Hamada F: Adenomatous
polyposis coli proteins and cell adhesion. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:528–535. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang C, Zhao R, Huang P, Yang F, Quan Z,
Xu N and Xi R: APC Loss-induced intestinal tumorigenesis in
Drosophila: Roles of Ras in Wnt signaling activation and tumor
progression. Dev Biol. 378:122–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
De Graeve FM, Van de Bor V, Ghiglione C,
Cerezo D, Jouandin P, Ueda R, Shashidhara LS and Noselli S:
Drosophila apc regulates delamination of invasive epithelial
clusters. Dev Biol. 368:76–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Faux MC, Coates JL, Kershaw NJ, Layton MJ
and Burgess AW: Independent interactions of phosphorylated
β-catenin with E-cadherin at Cell-cell contacts and APC at cell
protrusions. PLoS One. 5:e141272010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Restucci B, Martano M, G DEV, Lo Muzio L
and Maiolino P: Expression of E-cadherin, beta-catenin and APC
protein in canine colorectal tumours. Anticancer Res. 29:2919–2925.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lim JW, Mathias RA, Kapp EA, Layton MJ,
Faux MC, Burgess AW, Ji H and Simpson RJ: Restoration of
full-length APC protein in SW480 colon cancer cells induces
exosome-mediated secretion of DKK-4. Electrophoresis. 33:1873–1880.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Faux MC, Ross JL, Meeker C, Johns T, Ji H,
Simpson RJ, Layton MJ and Burgess AW: Restoration of Full-length
adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) protein in a colon cancer cell
line enhances cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 117:427–439. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Neufeld KL: Nuclear APC. Adv Exp Med Biol.
656:13–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
de Boer HR, Guerrero Llobet S and van Vugt
MA: Controlling the response to DNA damage by the APC/C-Cdh1. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 73:949–960. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yamada M, Watanabe K, Mistrik M, Vesela E,
Protivankova I, Mailand N, Lee M, Masai H, Lukas J and Bartek J:
ATR-Chk1-APC/CCdh1-dependent stabilization of Cdc7-ASK (Dbf4)
kinase is required for DNA lesion bypass under replication stress.
Genes Dev. 27:2459–2472. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Das D, Preet R, Mohapatra P, Satapathy SR,
Siddharth S, Tamir T, Jain V, Bharatam PV, Wyatt MD and Kundu CN:
5-Fluorouracil mediated Anti-cancer activity in colon cancer cells
is through the induction of adenomatous polyposis coli: Implication
of the Long-patch base excision repair pathway. DNA Repair (Amst).
24:15–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Tudek B and Speina E: Oxidatively damaged
DNA and its repair in colon carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 736:82–92.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Brocardo MG, Borowiec JA and Henderson BR:
Adenomatous polyposis coli protein regulates the cellular response
to DNA replication stress. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:1354–1364.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Stefanski CD, Keffler K, McClintock S,
Milac L and Prosperi JR: APC loss affects DNA damage repair causing
doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Neoplasia.
21:1143–1150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Baumann SJ, Grawenhoff J, Rodrigues EC,
Speroni S, Gili M, Komissarov A and Maurer SP: APC couples neuronal
mRNAs to multiple kinesins, EB1, and shrinking microtubule ends for
bidirectional mRNA motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
119:e22115361192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Overlack K, Bange T, Weissmann F, Faesen
AC, Maffini S, Primorac I, Muller F, Peters JM and Musacchio A:
BubR1 promotes Bub3-Dependent APC/C inhibition during spindle
assembly checkpoint signaling. Curr Biol. 27:2915–2927.e7. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Dikovskaya D, Schiffmann D, Newton IP,
Oakley A, Kroboth K, Sansom O, Jamieson TJ, Meniel V, Clarke A and
Näthke IS: Loss of APC induces polyploidy as a result of a
combination of defects in mitosis and apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
176:183–195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Cheng L and Mao Y: mDia3-EB1-APC: A
connection between kinetochores and microtubule plus ends. Commun
Integr Biol. 4:480–482. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Meniel V, Megges M, Young MA, Cole A,
Sansom OJ and Clarke AR: Apc and p53 interaction in DNA damage and
genomic instability in hepatocytes. Oncogene. 34:4118–4129. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|