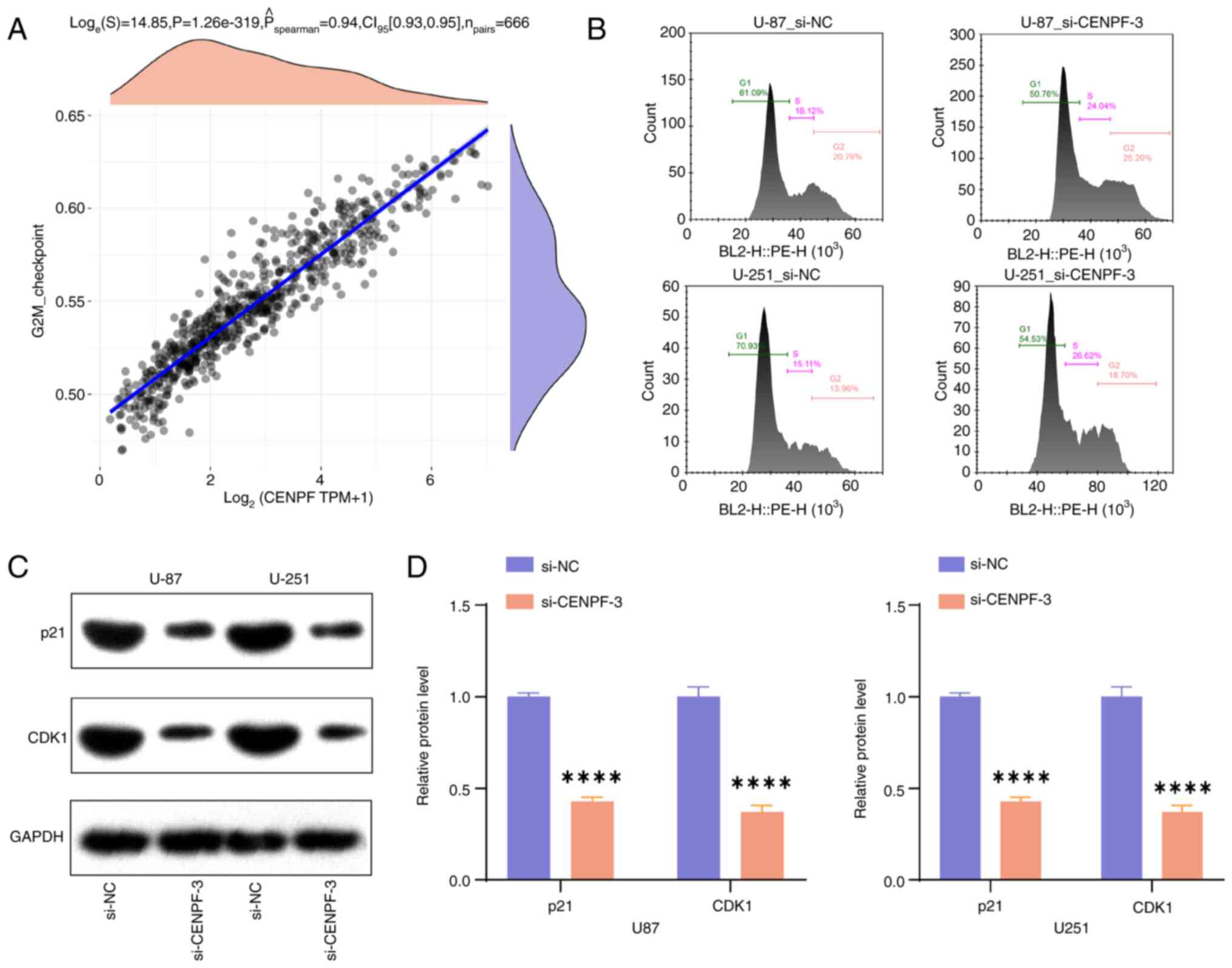
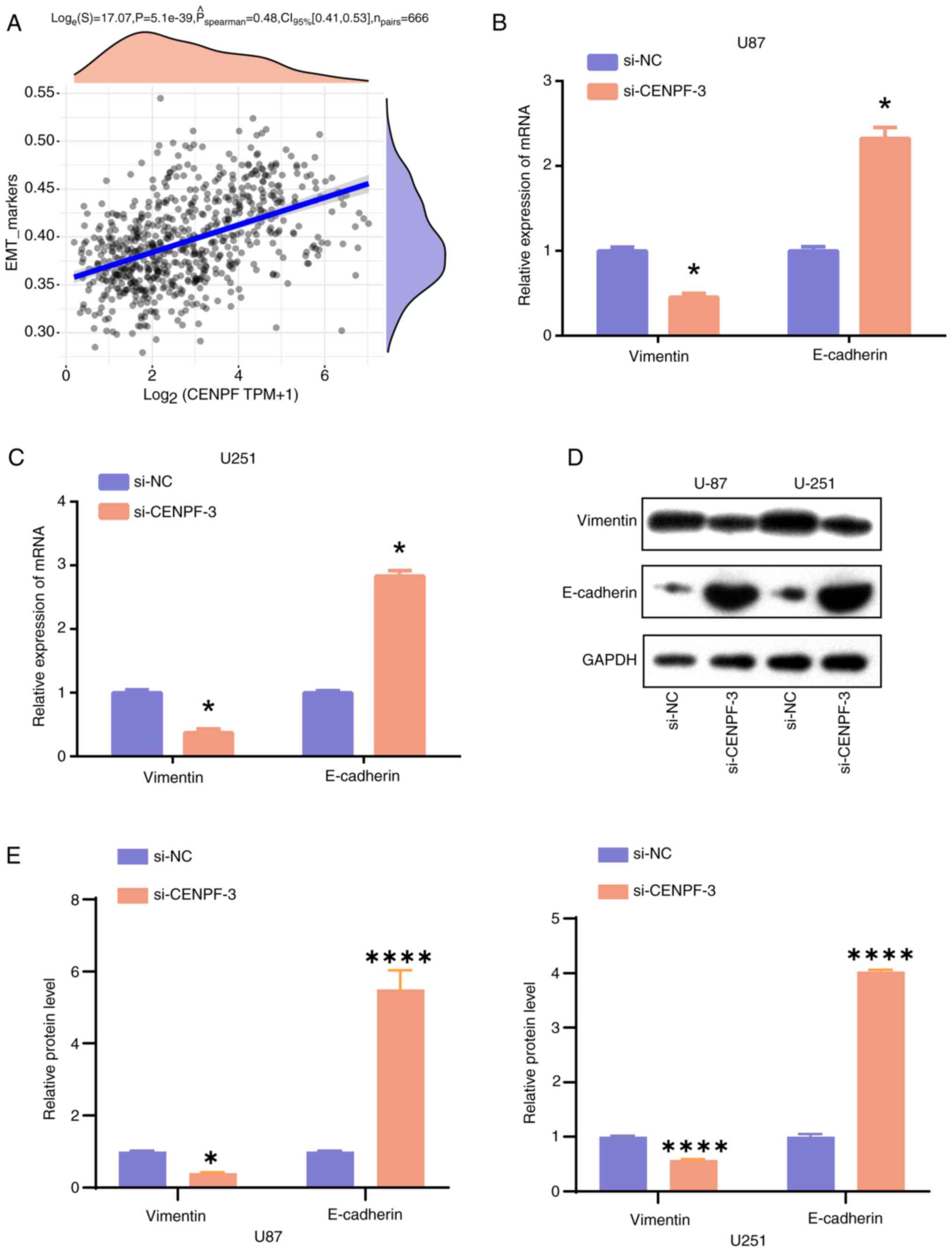
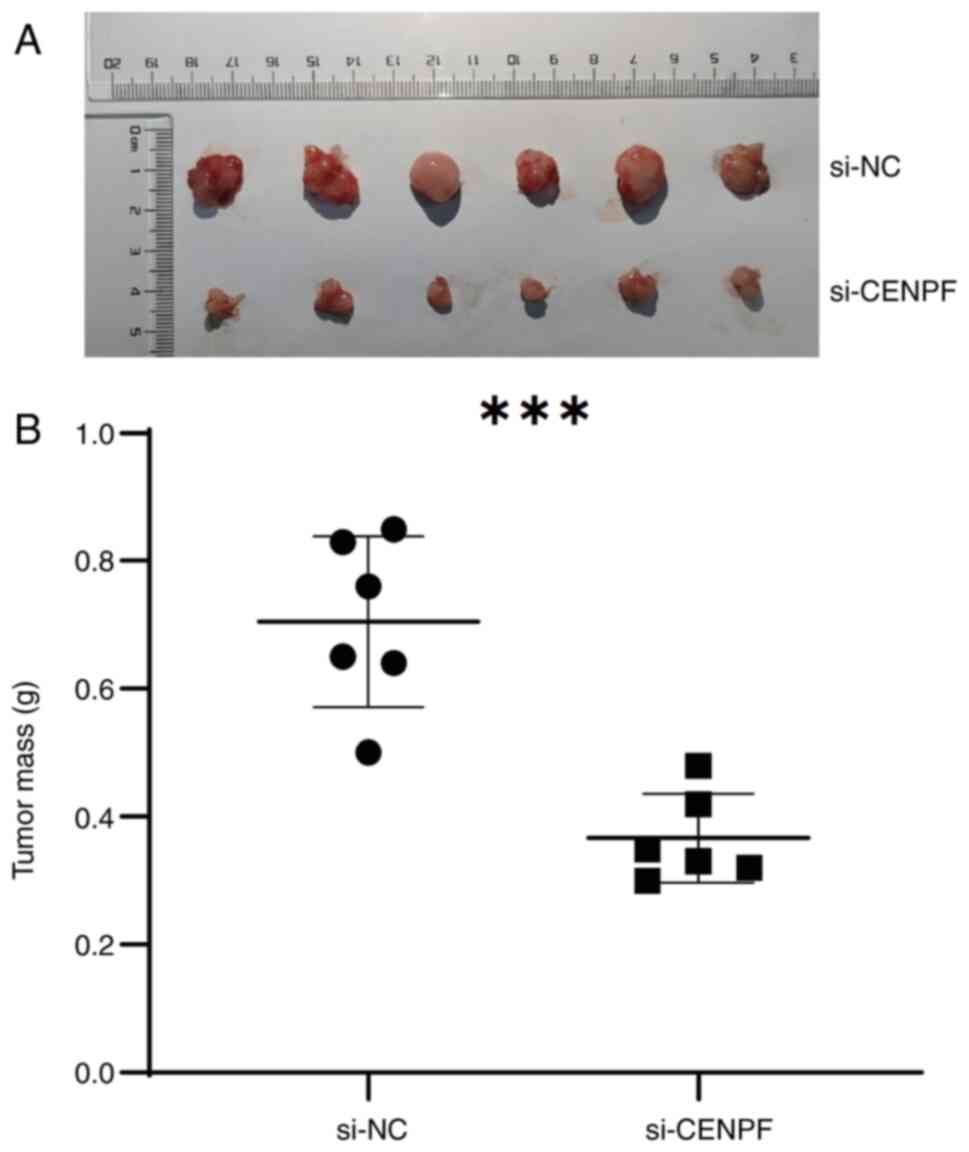
|
1
|
Weller M, Wick W, Aldape K, Brada M,
Berger M, Pfister SM, Nishikawa R, Rosenthal M, Wen PY, Stupp R and
Reifenberger G: Glioma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150172015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spanish DF: Types of brain tumors. Health.
2021.
|
|
3
|
Alifieris C and Trafalis DT: Glioblastoma
multiforme: Pathogenesis and treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 152:63–82.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Peeters MCM, Dirven L, Koekkoek JAF,
Gortmaker EG, Fritz L, Vos MJ and Taphoorn MJB: Prediagnostic
symptoms and signs of adult glioma: The patients' view. J
Neurooncol. 146:293–301. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roda E and Bottone MG: Editorial: Brain
cancers: New perspectives and therapies. Front Neurosci.
16:8574082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Y, Hong W and Wei X: The molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression
and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen H, Wu F, Xu H, Wei G, Ding M, Xu F,
Deivasigamani A, Zhou G, Hui KM and Xia H: Centromere protein F
promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through ERK and
cell cycle-associated pathways. Cancer Gene Ther. 29:1033–1042.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen H, Wang X, Wu F, Mo X, Hu C, Wang M,
Xu H, Yao C, Xia H and Lan L: Centromere protein F is identified as
a novel therapeutic target by genomics profile and contributing to
the progression of pancreatic cancer. Genomics. 113:1087–1095.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang YG, Li D, Wang L, Su XM and Tang XB:
CENPF/CDK1 signaling pathway enhances the progression of
adrenocortical carcinoma by regulating the G2/M-phase cell cycle. J
Transl Med. 20:782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Han Y, Xu S, Cheng K, Diao C, Liu S, Zou W
and Bi Y: CENPF promotes papillary thyroid cancer progression by
mediating cell proliferation and apoptosis. Exp Ther Med.
21:4012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ren X, Chen X, Ji Y, Li L, Li Y, Qin C and
Fang K: Upregulation of KIF20A promotes tumor proliferation and
invasion in renal clear cell carcinoma and is associated with
adverse clinical outcome. Aging (Albany NY). 12:25878–25894. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang X, Li S, Gao W, Shi J, Cheng M, Mi
Y, Liu Y, Sang M, Li Z and Geng C: KIF20A is a prognostic marker
for female patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer
and receiving tamoxifen as adjuvant endocrine therapy. Int J Gen
Med. 16:3623–3635. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun X, Chen P, Chen X, Yang W, Chen X,
Zhou W, Huang D and Cheng Y: KIF4A enhanced cell proliferation and
migration via Hippo signaling and predicted a poor prognosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Thorac Cancer. 12:512–524.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin W and Ye L: KIF4A knockdown suppresses
ovarian cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by
downregulating BUB1 expression. Mol Med Rep. 24:5162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andrés-Sánchez N, Fisher D and Krasinska
L: Physiological functions and roles in cancer of the proliferation
marker Ki-67. J Cell Sci. 135:jcs258932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu X, Zhang H, Zheng X, Lin Z, Feng G,
Chen Y, Pan Q and Ni F: STMN1 and MKI67 are upregulated in uterine
leiomyosarcoma and are potential biomarkers for its diagnosis. Med
Sci Monit. 26:e9237492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meng X, Li W, Yuan H, Dong W, Xiao W and
Zhang X: KDELR2-KIF20A axis facilitates bladder cancer growth and
metastasis by enhancing Golgi-mediated secretion. Biol Proced
Online. 24:122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Comba A, Faisal SM, Varela ML, Hollon T,
Al-Holou WN, Umemura Y, Nunez FJ, Motsch S, Castro MG and
Lowenstein PR: Uncovering spatiotemporal heterogeneity of
high-grade gliomas: From disease biology to therapeutic
implications. Front Oncol. 11:7037642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pace A, Lombardi G, Villani V, Benincasa
D, Abbruzzese C, Cestonaro I, Corrà M, Cerretti G, Caccese M,
Silvani A, et al: Repurposing Chlorpromazine as add-on in the
adjuvant phase of first-line glioblastoma therapeutic protocol in
patients carrying hypo-/un-methylated MGMT gene promoter: RACTAC, a
phase II multicenter single arm clinical trial. medRxiv.
2023.2023.02. 21.23286088. 2023.
|
|
20
|
Jeanmougin M, Håvik AB, Cekaite L, Brandal
P, Sveen A, Meling TR, Ågesen TH, Scheie D, Heim S, Lothe RA and
Lind GE: Improved prognostication of glioblastoma beyond molecular
subtyping by transcriptional profiling of the tumor
microenvironment. Mol Oncol. 14:1016–1027. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gravendeel LA, Kouwenhoven MC, Gevaert O,
de Rooi JJ, Stubbs AP, Duijm JE, Daemen A, Bleeker FE, Bralten LB,
Kloosterhof NK, et al: Intrinsic Gene Expression Profiles of
Gliomas Are a Better Predictor of Survival than Histology. Cancer
Res. 69:9065–9072. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Berker Y, Muti IH and Cheng LL:
Visualizing metabolomics data with R. NMR Biomed. 36:e48652023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu CJ, Hu FF, Xie GY, Miao YR, Li XW,
Zeng Y and Guo AY: GSCA: An integrated platform for gene set cancer
analysis at genomic, pharmacogenomic and immunogenomic levels.
Brief Bioinform. 24:bbac5582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu
JS, Li B and Liu XS: TIMER: A web server for comprehensive analysis
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res. 77:e108–e110. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghouzlani A, Kandoussi S, Tall M, Reddy
KP, Rafii S and Badou A: Immune checkpoint inhibitors in human
glioma microenvironment. Front Immunol. 12:6794252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thul PJ and Lindskog C: The human protein
atlas: A spatial map of the human proteome. Protein Sci.
27:233–244. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clark JA and Sun D: Guidelines for the
ethical review of laboratory animal welfare People's Republic of
China National Standard GB/T 35892-2018 [Issued 6 February 2018
Effective from 1 September 2018]. Animal Model Exp Med. 3:103–113.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kan LK, Drummond K, Hunn M, Williams D,
O'Brien TJ and Monif M: Potential biomarkers and challenges in
glioma diagnosis, therapy and prognosis. BMJ Neurol Open.
2:e0000692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang K, Wu Z, Zhang H, Zhang N, Wu W, Wang
Z, Dai Z, Zhang X, Zhang L, Peng Y, et al: Glioma targeted therapy:
Insight into future of molecular approaches. Mol Cancer. 21:1–32.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bush NAO, Chang SM and Berger MS: Current
and future strategies for treatment of glioma. Neurosurg Rev.
40:1–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhuang Q, Yang H and Mao Y: The
oncogenesis of glial cells in diffuse gliomas and clinical
opportunities. Neurosci Bull. 39:393–408. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Escamilla-Ramírez A, Castillo-Rodríguez
RA, Zavala-Vega S, Jimenez-Farfan D, Anaya-Rubio I, Briseño E,
Palencia G, Guevara P, Cruz-Salgado A, Sotelo J and Trejo-Solís C:
Autophagy as a potential therapy for malignant glioma.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 13:1562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vicente JJ and Wordeman L: The
quantification and regulation of microtubule dynamics in the
mitotic spindle. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 60:36–43. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang J, An L, Zhao R, Shi R, Zhou X, Wei
S, Zhang Q, Zhang T, Feng D, Yu Z and Wang H: KIF4A promotes
genomic stability and progression of endometrial cancer through
regulation of TPX2 protein degradation. Mol Carcinog. 62:303–318.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hou PF, Jiang T, Chen F, Shi PC, Li HQ,
Bai J and Song J: KIF4A facilitates cell proliferation via
induction of p21-mediated cell cycle progression and promotes
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9:4772018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hou G, Dong C, Dong Z, Liu G, Xu H, Chen
L, Liu L, Wang H and Zhou W: Upregulate kif4a enhances
proliferation, invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma and indicates
poor prognosis across human cancer types. Sci Rep. 7:41482017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Meng S, Chu K, Chu S, Fan YC, Bai
J and Yu ZQ: KIF4A drives gliomas growth by transcriptional
repression of Rac1/Cdc42 to induce cytoskeletal remodeling in
glioma cells. J Cancer. 13:3640–3651. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu WD, Yu KW, Zhong N, Xiao Y and She ZY:
Roles and mechanisms of Kinesin-6 KIF20A in spindle organization
during cell division. Eur J Cell Biol. 98:74–80. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qiu R, Wu J, Gudenas B, Northcott PA,
Wechsler-Reya RJ and Lu Q: Depletion of kinesin motor KIF20A to
target cell fate control suppresses medulloblastoma tumour growth.
Commun Biol. 4:5522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Taniuchi K, Nakagawa H, Nakamura T, Eguchi
H, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O, Katagiri T and Nakamura Y:
Down-regulation of RAB6KIFL/KIF20A, a kinesin involved with
membrane trafficking of discs large homologue 5, can attenuate
growth of pancreatic cancer cell. Cancer Res. 65:105–112. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gasnereau I, Boissan M, Margall-Ducos G,
Couchy G, Wendum D, Bourgain-Guglielmetti F, Desdouets C, Lacombe
ML, Zucman-Rossi J and Sobczak-Thépot J: KIF20A mRNA and its
product MKlp2 are increased during hepatocyte proliferation and
hepatocarcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 180:131–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yan GR, Zou FY, Dang BL, Zhang Y, Yu G,
Liu X and He QY: Genistein-induced mitotic arrest of gastric cancer
cells by downregulating KIF20A, a proteomics study. Proteomics.
12:2391–2399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marin-Acevedo JA, Dholaria B, Soyano AE,
Knutson KL, Chumsri S and Lou Y: Next generation of immune
checkpoint therapy in cancer: New developments and challenges. J
Hematol Oncol. 11:392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fujiwara Y, Okada K, Omori T, Sugimura K,
Miyata H, Ohue M, Kobayashi S, Takahashi H, Nakano H, Mochizuki C,
et al: Multiple therapeutic peptide vaccines for patients with
advanced gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 50:1655–1662. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Copello VA and Burnstein KL: The kinesin
KIF20A promotes progression to castration-resistant prostate cancer
through autocrine activation of the androgen receptor. Oncogene.
41:2824–2832. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Han L and Wang J: Bioinformatics Analysis
of KIF20A, a Potential Therapeutic Target for Glioblastoma.
Accepted at. January 5–2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Verheijen R, Kuijpers HJ, Schlingemann RO,
Boehmer AL, van Driel R, Brakenhoff GJ and Ramaekers FC: Ki-67
detects a nuclear matrix-associated proliferation-related antigen.
I. Intracellular localization during interphase. J Cell Sci.
92:123–130. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schlüter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C,
Becker MH, Key G, Flad HD and Gerdes J: The cell
proliferation-associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: A very large,
ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements,
representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. J Cell
Biol. 123:513–522. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Duchrow M, Schlüter C, Wohlenberg C, Flad
HD and Gerdes J: Molecular characterization of the gene locus of
the human cell proliferation-associated nuclear protein defined by
monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Cell Prolif. 29:1–12. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH,
Schwab U and Stein H: Cell cycle analysis of a cell
proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the
monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 133:1710–1715. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xiong DD, Zeng CM, Jiang L, Luo DZ and
Chen G: Ki-67/MKI67 as a predictive biomarker for clinical outcome
in gastric cancer patients: An updated meta-analysis and systematic
review involving 53 studies and 7078 Patients. J Cancer.
10:5339–5354. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zeng S, Li W, Ouyang H, Xie Y, Feng X and
Huang L: A novel prognostic pyroptosis-related gene signature
correlates to oxidative stress and immune-related features in
gliomas. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 31:42561162023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Visapää H, Bui M, Huang Y, Seligson D,
Tsai H, Pantuck A, Figlin R, Rao JY, Belldegrun A, Horvath S and
Palotie A: Correlation of Ki-67 and gelsolin expression to clinical
outcome in renal clear cell carcinoma. Urology. 61:845–850. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zini L, Porpiglia F and Fassnacht M:
Contemporary management of adrenocortical carcinoma. Eur Urol.
60:1055–1065. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nakanishi K, Sakamoto M, Yamasaki S, Todo
S and Hirohashi S: Akt phosphorylation is a risk factor for early
disease recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer. 103:307–312. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Guzman G, Alagiozian-Angelova V,
Layden-Almer JE, Layden TJ, Testa G, Benedetti E, Kajdacsy-Balla A
and Cotler SJ: p53, Ki-67, and serum alpha feto-protein as
predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence in liver
transplant patients. Mod Pathol. 18:1498–1503. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li R, Wang X, Zhao X, Zhang X, Chen H, Ma
Y and Liu Y: Centromere protein F and Forkhead box M1 correlation
with prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett.
19:1368–1374. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Lefebvre C,
Alvarez MJ, Castillo-Martin M, Zheng T, Eastham JA, Gopalan A,
Pienta KJ, Shen MM, et al: Cross-species regulatory network
analysis identifies a synergistic interaction between FOXM1 and
CENPF that drives prostate cancer malignancy. Cancer Cell.
25:638–651. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sun J, Huang J, Lan J, Zhou K, Gao Y, Song
Z, Deng Y, Liu L, Dong Y and Liu X: Overexpression of CENPF
correlates with poor prognosis and tumor bone metastasis in breast
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 19:2642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Dai Y, Liu L, Zeng T, Zhu YH, Li J, Chen
L, Li Y, Yuan YF, Ma S and Guan XY: Characterization of the
oncogenic function of centromere protein F in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 436:711–718. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang M, Zhang Q, Bai J, Zhao Z and Zhang
J: Transcriptome analysis revealed CENPF associated with glioma
prognosis. Math Biosci Eng. 18:2077–2096. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Brabletz S, Schuhwerk H, Brabletz T and
Stemmler MP: Dynamic EMT: A multi-tool for tumor progression. EMBO
J. 40:e1086472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang G, Feng W and Wu J: Down-regulation
of SEPT9 inhibits glioma progression through suppressing
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Biomed
Pharmacother. 125:1097682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|