|
1
|
Hussain H: Effectiveness of exercise
interventions on body composition and functional outcomes in
sarcopenia: A systematic review. Clin Med (Lond). 23 (Suppl
6):S762023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gay-As MU, Lee SC and Lai FC: Sarcopenia
among older people in the philippines: A scoping review. Creat
Nurs. 30:133–144. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xiong Y, Jiang X, Zhong Q, Zhang Y, Zhang
H, Liu Z and Wang X: Possible sarcopenia and risk of chronic kidney
disease: A four-year follow-up study and Mendelian randomization
analysis. Endocr Res. 49:165–178. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bali T, Chrysavgis L and Cholongitas E:
Metabolic-Associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia. Endocrinol
Metab Clin North Am. 52:497–508. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blagec P, Sara S, Tripalo Batos A, Trivic
Mazuranic I, Mocic Pavic A, Misak Z and Hojsak I: Magnetic
resonance imaging can be used to assess sarcopenia in children with
newly diagnosed crohn's disease. Nutrients. 15:38382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Y and Tian L: Research progress on the
predictive role of sarcopenia in the course and prognosis of
inflammatory bowel disease. PeerJ. 11:e164212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu QW, Mao CJ, Lu ZH, Shi RF, Zhang YC,
Zhao P and Liu CF: Sarcopenia is associated with non-motor symptoms
in Han Chinese patients with Parkinson's Disease: A cross-sectional
study. BMC Geriatr. 23:4942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim M, Kim D, Kang H, Park S, Kim S and
Yoo JI: A machine learning model for prediction of sarcopenia in
patients with Parkinson's Disease. PLoS One. 19:e02962822024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nan Y, Zhou Y, Dai Z, Yan T, Zhong P,
Zhang F, Chen Q and Peng L: Role of nutrition in patients with
coexisting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sarcopenia.
Front Nutr. 10:12146842023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pedauye-Rueda B, Garcia-Fernandez P,
Maicas-Perez L, Mate-Munoz JL and Hernandez-Lougedo J: Different
diagnostic criteria for determining the prevalence of sarcopenia in
older adults: A systematic review. J Clin Med. 13:25202024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He Y, Cui W, Fang T, Zhang Z and Zeng M:
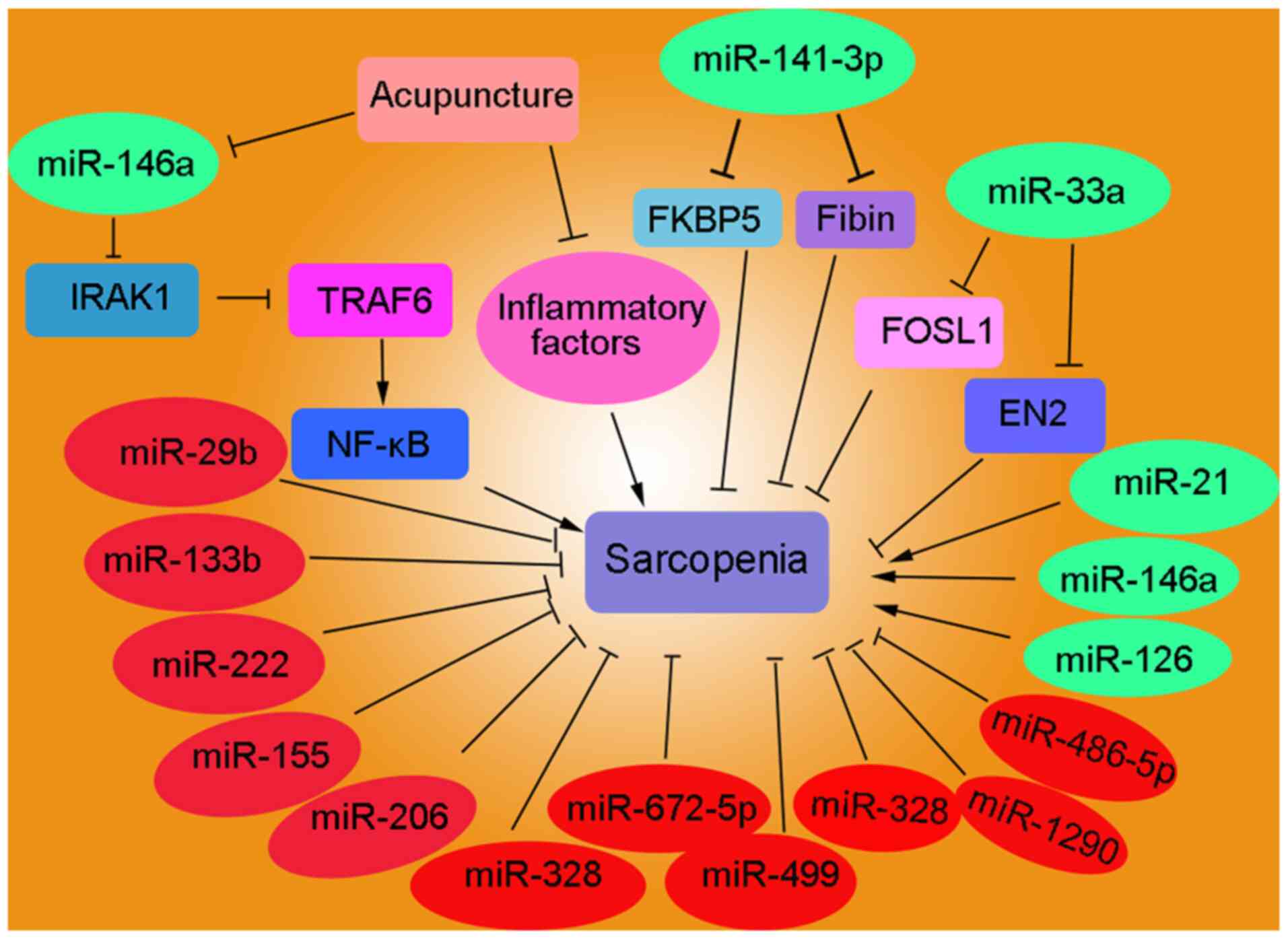
Metabolites of the gut microbiota may serve as precise diagnostic
markers for sarcopenia in the elderly. Front Microbiol.
14:13018052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lahiri S, Kim H, Garcia-Perez I, Reza MM,
Martin KA, Kundu P, Cox LM, Selkrig J, Posma JM, Zhang H, et al:
The gut microbiota influences skeletal muscle mass and function in
mice. Sci Transl Med. 11:eaan56622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan X, Li H, Xie R, Lin L, Ding L, Cheng
X, Xu J, Bai L and Qiao Y: Relationships between sarcopenia,
nutrient intake, and gut microbiota in Chinese community-dwelling
older women. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 113:1050632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Q, Li X, Huang T, Zhang S, Teng K,
Rousitemu N, Lan T and Wen Y: Alterations in the diversity,
composition and function of the gut microbiota in Uyghur
individuals with sarcopenia. Exp Gerontol. 187:1123762024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Picca A, Fanelli F, Calvani R, Mule G,
Pesce V, Sisto A, Pantanelli C, Bernabei R, Landi F and Marzetti E:
Gut dysbiosis and muscle aging: Searching for Novel Targets against
Sarcopenia. Mediators Inflamm. 2018:70261982018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Cheung WH, Li J, Chow SK, Yu J,
Wong SH, Ip M, Sung JJY and Wong RMY: Understanding the gut
microbiota and sarcopenia: A systematic review. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 12:1393–1407. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aboshady HM, Gavriilidou A, Ghanem N,
Radwan MA, Elnahas A, Agamy R, Fahim NH, Elsawy MH, Shaarawy ABM,
Abdel-Hafeez AM, et al: Gut microbiota diversity of local egyptian
cattle managed in different ecosystems. Animals (Basel).
14:27522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lim X, Ooi L, Ding U, Wu HHL and
Chinnadurai R: Gut microbiota in patients receiving dialysis: A
review. Pathogens. 13:8012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu S, Yin J, Wan D and Yin Y: The role of
iron in intestinal mucus: Perspectives from both the host and gut
microbiota. Adv Nutr. 15:1003072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao H, Nepovimova E, Adam V, Heger Z,
Valko M, Wu Q and Kuca K: Age-associated changes in innate and
adaptive immunity: Role of the gut microbiota. Front Immunol.
15:14210622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Guo Q, Wang W and Zhang L:
High-throughput sequencing analysis of the characteristics of the
gut microbiota in aged patients with sarcopenia. Exp Gerontol.
182:1122872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Casati M, Ferri E, Azzolino D, Cesari M
and Arosio B: Gut microbiota and physical frailty through the
mediation of sarcopenia. Exp Gerontol. 124:1106392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang J and Zhang H, Yin L, Zhou Q and
Zhang H: The gut microbiota from maintenance hemodialysis patients
with sarcopenia influences muscle function in mice. Front Cell
Infect Microbiol. 13:12259912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O'Toole PW and Jeffery IB:
Microbiome-health interactions in older people. Cell Mol Life Sci.
75:119–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S, Power
SE, O'Connor EM, Cusack S, Harris HM, Coakley M, Lakshminarayanan
B, O'Sullivan O, et al: Gut microbiota composition correlates with
diet and health in the elderly. Nature. 488:178–184. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Biagi E, Candela M, Turroni S, Garagnani
P, Franceschi C and Brigidi P: Ageing and gut microbes:
Perspectives for health maintenance and longevity. Pharmacol Res.
69:11–20. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ning M, An L, Dong L, Zhu R, Hao J, Liu X
and Zhang Y: Causal associations between gut microbiota, gut
microbiota-derived metabolites, and Alzheimer's Disease: A
Multivariable Mendelian Randomization Study. J Alzheimers Dis.
100:229–237. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu J, Gong X, Zhang C, Yang T and Pei D: A
multi-omics approach to investigate characteristics of gut
microbiota and metabolites in hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
SPF rat models. Front Microbiol. 15:13561762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee SY, Kim JH, Lee DY and Hur SJ:
Characterization of gut microbiota in mouse models of aging and
sarcopenia. Microbiol Res. 275:1274622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan ZX, Gao XJ, Li T, Wei B, Wang PP, Yang
Y and Yan R: Fecal microbiota transplantation in experimental
ulcerative colitis reveals associated gut microbial and host
metabolic reprogramming. Appl Environ Microbiol. 84:e00434–18.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qaisar R, Burki A, Karim A, Iqbal MS and
Ahmad F: Probiotics supplements improve the sarcopenia-related
quality of life in older adults with age-related muscle decline.
Calcif Tissue Int. 114:583–591. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nistor-Cseppento CD, Moga TD, Bungau AF,
Tit DM, Negrut N, Pasca B, Bochis CF, Ghitea TC, Jurcau A, Purza AL
and Uivarosan D: The contribution of diet therapy and probiotics in
the treatment of sarcopenia induced by prolonged immobilization
caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients. 14:47012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu X, Li P, Li B, Yu F, Zhao W, Wang X,
Wang X, Wang Y, Gao H, Cheng M and Li X: d-pinitol improves
diabetic sarcopenia by regulation of the gut microbiome,
metabolome, and proteome in STZ-Induced SAMP8 Mice. J Agric Food
Chem. 72:14466–14478. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mo X, Shen L, Cheng R, Wang P, Wen L, Sun
Y, Wang Q, Chen J, Lin S, Liao Y, et al: Faecal microbiota
transplantation from young rats attenuates age-related sarcopenia
revealed by multiomics analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.
14:2168–2183. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Baek JS, Shin YJ, Ma X, Park HS, Hwang YH
and Kim DH: Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus paracasei
alleviate sarcopenia and cognitive impairment in aged mice by
regulating gut microbiota-mediated AKT, NF-ĸB, and FOXO3a signaling
pathways. Immun Ageing. 20:562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lou J, Wang Q, Wan X and Cheng J: Changes
and correlation analysis of intestinal microflora composition,
inflammatory index, and skeletal muscle mass in elderly patients
with sarcopenia. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 24:140–146. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee J, Kang M, Yoo J, Lee S, Kang M, Yun
B, Kim JN, Moon H, Chung Y and Oh S: Lactobacillus rhamnosus JY02
ameliorates sarcopenia by anti-atrophic effects in a
dexamethasone-induced cellular and murine model. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 33:915–925. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Karimian S, Farahmandzad N and
Mohammadipanah F: Manipulation and epigenetic control of silent
biosynthetic pathways in actinobacteria. World J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 40:652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zahr R, Zahr S, El Hajj R and Khalil M:
Characterization of Actinobacteria strains in Lebanese soil with an
emphasis on investigating their antibacterial activity. Braz J
Microbiol. 55:255–267. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Z, Xu X, Deji Y, Gao S, Wu C, Song Q,
Shi Z, Xiang X, Zang J and Su J: Bifidobacterium as a potential
biomarker of Sarcopenia in elderly women. Nutrients. 15:12662023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lv WQ, Lin X, Shen H, Liu HM, Qiu X, Li
BY, Shen WD, Ge CL, Lv FY, Shen J, et al: Human gut microbiome
impacts skeletal muscle mass via gut microbial synthesis of the
short-chain fatty acid butyrate among healthy menopausal women. J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 12:1860–1870. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sugimura Y, Yang Y, Kanda A, Mawatari A,
Tamada Y, Mikami T, Nakaji S and Ihara K: Association between Gut
Microbiota and Muscle Strength in Japanese General Population of
the Iwaki Health Promotion Project. Microorganisms. 12:6222024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang M, Ren F, Zhou Y, He Y, Du T and Tan
Y: Age-related sarcopenia and altered gut microbiota: A systematic
review. Microb Pathog. 195:1068502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ticinesi A, Nouvenne A, Cerundolo N,
Catania P, Prati B, Tana C and Meschi T: Gut microbiota, muscle
mass and function in aging: A focus on physical frailty and
sarcopenia. Nutrients. 11:16332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Aliwa B, Horvath A, Traub J, Feldbacher N,
Habisch H, Fauler G, Madl T and Stadlbauer V: Altered gut
microbiome, bile acid composition and metabolome in sarcopenia in
liver cirrhosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 14:2676–2691. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Lane NE, Wu J, Yang T, Li
J, He H, Wei J, Zeng C and Lei G: Population-based metagenomics
analysis reveals altered gut microbiome in sarcopenia: Data from
the Xiangya Sarcopenia Study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.
13:2340–2351. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee YA, Song SW, Jung SY, Bae J, Hwang N
and Kim HN: Sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults is
associated with the diversity and composition of the gut
microbiota. Exp Gerontol. 167:1119272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shan Z, Cheng N, Zhu J, Chen F and Ji J:
Meilibana: Analysis of intestinal flora in elderly Uygur patients
with sarcopenia. Immun Inflamm Dis. 12:e10972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu X, Wu J, Tang J, Xu Z, Zhou B, Liu Y,
Hu F, Zhang G, Cheng R, Xia X, et al: Prevotella copri alleviates
sarcopenia via attenuating muscle mass loss and function decline. J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 14:2275–2288. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tseng CW, Kyme P, Low J, Rocha MA, Alsabeh
R, Miller LG, Otto M, Arditi M, Diep BA, Nizet V, et al:
Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin contributes to
inflammation and muscle tissue injury. PLoS One. 4:e63872009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Avila-Novoa MG, Solis-Velazquez OA,
Guerrero-Medina PJ, Gonzalez-Gomez JP, Gonzalez-Torres B,
Velazquez-Suarez NY, Martínez-Chávez L, Martínez-Gonzáles NE, De la
Cruz-Color L, Ibarra-Velázquez LM, et al: Genetic and compositional
analysis of biofilm formed by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from
food contact surfaces. Front Microbiol. 13:10017002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu S, Yi J, Zhang YG, Zhou J and Sun J:
Leaky intestine and impaired microbiome in an amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis mouse model. Physiol Rep. 3:e123562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang Y, Ogbu D, Garrett S, Xia Y and Sun
J: Aberrant enteric neuromuscular system and dysbiosis in
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Gut Microbes. 13:19968482021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bin-Jumah MN, Gilani SJ, Hosawi S,
Al-Abbasi FA, Zeyadi M, Imam SS, Alshehri S, Ghoneim MM, Nadeem MS
and Kazmi I: Pathobiological relationship of excessive dietary
intake of Choline/L-Carnitine: A TMAO precursor-associated
aggravation in heart failure in sarcopenic patients. Nutrients.
13:34532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hata S, Okamura T, Kobayashi A, Bamba R,
Miyoshi T, Nakajima H, Hashimoto Y, Majima S, Senmaru T, Okada H,
et al: Gut Microbiota Changes by an SGLT2 inhibitor,
luseogliflozin, alters metabolites compared with those in a low
carbohydrate diet in db/db Mice. Nutrients. 14:35312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Potgens SA, Brossel H, Sboarina M, Catry
E, Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM and Bindels LB: Klebsiella
oxytoca expands in cancer cachexia and acts as a gut pathobiont
contributing to intestinal dysfunction. Sci Rep. 8:123212018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ma WW, Huang ZQ, Liu K, Li DZ, Mo TL and
Liu Q: The role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites in
intestinal inflammation. Microbiol Res. 288:1278382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bourqqia-Ramzi M, Mansilla-Guardiola J,
Munoz-Rodriguez D, Quarta E, Lombardo-Hernandez J,
Murciano-Cespedosa A, Conejero-Meca FJ, Mateos González Á, Geuna S,
Garcia-Esteban MT and Herrera-Rincon C: From the Microbiome to the
Electrome: Implications for the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Int J
Mol Sci. 25:62332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang J, Yu Y and Wang J: Protein
nutritional support: The classical and potential new mechanisms in
the prevention and therapy of sarcopenia. J Agric Food Chem.
68:4098–4108. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mendes J, Simoes CD, Martins JO and Sousa
AS: Inflammatory bowel disease and sarcopenia: A focus on muscle
strength - narrative review. Arq Gastroenterol. 60:373–382. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Agostini D, Gervasi M, Ferrini F,
Bartolacci A, Stranieri A, Piccoli G, Barbieri E, Sestili P, Patti
A, Stocchi V and Donati Zeppa S: An integrated approach to skeletal
muscle health in aging. Nutrients. 15:18022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wu S, Chen X, Cai R, Chen X, Zhang J, Xie
J and Shen M: Sulfated Chinese yam polysaccharides alleviate
LPS-induced acute inflammation in mice through modulating
intestinal microbiota. Foods. 12:17722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li C, Wang Y, Zhao X, Li J, Wang H, Ren Y,
Sun H, Zhu X, Song Q and Wang J: Comparative analysis of intestinal
inflammation and microbiota dysbiosis of LPS-Challenged Piglets
between Different Breeds. Animals (Basel). 14:6652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bian AL, Hu HY, Rong YD, Wang J, Wang JX
and Zhou XZ: A study on relationship between elderly sarcopenia and
inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α. Eur J Med Res. 22:252017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xuekelati S, Maimaitiwusiman Z, Bai X,
Xiang H, Li Y and Wang H: Sarcopenia is associated with
hypomethylation of TWEAK and increased plasma levels of TWEAK and
its downstream inflammatory factor TNF-α in older adults: A
case-control study. Exp Gerontol. 188:1123902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK,
Venema K, Reijngoud DJ and Bakker BM: The role of short-chain fatty
acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host
energy metabolism. J Lipid Res. 54:2325–2340. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kang M, Kang M, Yoo J, Lee J, Lee S, Yun
B, Song M, Kim JM, Kim HW, Yang J, et al: Dietary supplementation
with Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus IDCC3201 alleviates sarcopenia by
modulating the gut microbiota and metabolites in
dexamethasone-induced models. Food Funct. 15:4936–4953. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xu Y, Mao T, Wang Y, Qi X, Zhao W, Chen H,
Zhang C and Li X: Effect of gut microbiota-mediated tryptophan
metabolism on inflammaging in frailty and sarcopenia. J Gerontol A
Biol Sci Med Sci. 79:glae0442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ciernikova S, Sevcikova A, Mladosievicova
B and Mego M: Microbiome in cancer development and treatment.
Microorganisms. 12:242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gellhaus B, Boker KO, Schilling AF and
Saul D: Therapeutic consequences of targeting the
IGF-1/PI3K/AKT/FOXO3 axis in sarcopenia: A narrative review. Cells.
12:27872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Abuduwaili H, Kamoshita K, Ishii KA,
Takahashi K, Abuduyimiti T, Qifang L, Isobe Y, Goto H, Nakano Y,
Takeshita Y, et al: Selenoprotein P deficiency protects against
immobilization-induced muscle atrophy by suppressing
atrophy-related E3 ubiquitin ligases. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 324:E542–E552. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
He P, Du G, Qin X and Li Z: Reduced energy
metabolism contributing to aging of skeletal muscle by serum
metabolomics and gut microbiota analysis. Life Sci. 323:1216192023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang X, Yang G, Jiang S, Ji B, Xie W, Li
H, Sun J and Li Y: Causal relationship between gut microbiota,
metabolites, and sarcopenia: A mendelian randomization study. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 79:glae1732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cailleaux PE, Dechelotte P and Coeffier M:
Novel dietary strategies to manage sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr
Metab Care. 27:234–243. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lapauw L, Rutten A, Dupont J, Amini N,
Vercauteren L, Derrien M, Raes J and Gielen E: Associations between
gut microbiota and sarcopenia or its defining parameters in older
adults: A systematic review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. Aug
27–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Han DS, Wu WK, Liu PY, Yang YT, Hsu HC,
Kuo CH, Wu MS and Wang TG: Differences in the gut microbiome and
reduced fecal butyrate in elders with low skeletal muscle mass.
Clin Nutr. 41:1491–1500. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
de Conti A, Tryndyak V, Koturbash I,
Heidor R, Kuroiwa-Trzmielina J, Ong TP, Beland FA, Moreno FS and
Pogribny IP: The chemopreventive activity of the butyric acid
prodrug tributyrin in experimental rat hepatocarcinogenesis is
associated with p53 acetylation and activation of the p53 apoptotic
signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis. 34:1900–1906. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ticinesi A, Nouvenne A, Cerundolo N,
Parise A, Mena P and Meschi T: The interaction between
Mediterranean diet and intestinal microbiome: Relevance for
preventive strategies against frailty in older individuals. Aging
Clin Exp Res. 36:582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Dong J, Gu W, Yang X, Zeng L, Wang X, Mu
J, Wang Y, Li F, Yang M and Yu J: Crosstalk between polygonatum
kingianum, the miRNA, and gut microbiota in the regulation of lipid
metabolism. Front Pharmacol. 12:7405282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Prukpitikul P, Sirivarasai J and Sutjarit
N: The molecular mechanisms underlying gut microbiota-miRNA
interaction in metabolic disorders. Benef Microbes. 15:83–96. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Huang LY, Lim AY, Hsu CC, Tsai YF, Fu TC,
Shyu YC, Peng SC and Wang JS: Sustainability of exercise-induced
benefits on circulating MicroRNAs and physical fitness in
community-dwelling older adults: A randomized controlled trial with
follow up. BMC Geriatr. 24:4732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lee H, Kim YI, Nirmala FS, Kim JS, Seo HD,
Ha TY, Jang YJ, Jung CH and Ahn J: MiR-141-3p promotes
mitochondrial dysfunction in ovariectomy-induced sarcopenia via
targeting Fkbp5 and Fibin. Aging (Albany NY). 13:4881–4894. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Iannone F, Montesanto A, Cione E, Crocco
P, Caroleo MC, Dato S, Rose G and Passarino G: Expression patterns
of muscle-specific miR-133b and miR-206 correlate with nutritional
status and sarcopenia. Nutrients. 12:2972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chen FX, Shen Y, Liu Y, Wang HF, Liang CY
and Luo M: Inflammation-dependent downregulation of miR-532-3p
mediates apoptotic signaling in human sarcopenia through targeting
BAK1. Int J Biol Sci. 16:1481–1494. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Jin J, Yang Z, Liu H, Guo M, Chen B, Zhu
H, Wang Y, Lin J, Wang S and Chen S: Effects of acupuncture on the
miR-146a-mediated IRAK1/TRAF6/NF-ĸB signaling pathway in rats with
sarcopenia induced by D-galactose. Ann Transl Med. 11:472023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Okugawa Y, Yao L, Toiyama Y, Yamamoto A,
Shigemori T, Yin C, Omura Y, Ide S, Kitajima T, Shimura T, et al:
Prognostic impact of sarcopenia and its correlation with
circulating miR-21 in colorectal cancer patients. Oncol Rep.
39:1555–1564. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang W, Liu W, Xu J and Jin H: MiR-33a
targets FOSL1 and EN2 as a clinical prognostic marker for
sarcopenia by glioma. Front Genet. 13:9535802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
He N, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Feng B, Zheng Z
and Ye H: Circulating miR-29b decrease in response to sarcopenia in
patients with cardiovascular risk factors in older Chinese. Front
Cardiovasc Med. 9:10943882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Qaisar R, Karim A, Muhammad T, Shah I and
Khan J: Circulating MicroRNAs as biomarkers of accelerated
sarcopenia in chronic heart failure. Glob Heart. 16:562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Faraldi M, Sansoni V, Vitale J, Perego S,
Gomarasca M, Verdelli C, Messina C, Sconfienza LM, Banfi G,
Corbetta S and Lombardi G: Plasma microRNA signature associated
with skeletal muscle wasting in post-menopausal osteoporotic women.
J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 15:690–701. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
He N, Zhang YL, Zhang Y, Feng B, Zheng Z,
Wang D, Zhang S, Guo Q and Ye H: Circulating MicroRNAs in plasma
decrease in response to sarcopenia in the elderly. Front Genet.
11:1672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Salamanna F, Contartese D, Ruffilli A,
Barile F, Bellavia D, Marchese L, Manzetti M, Viroli G, Faldini C
and Giavaresi G: Sharing circulating Micro-RNAs between
osteoporosis and sarcopenia: A systematic review. Life (Basel).
13:6022023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li Z, Liu C, Li S, Li T, Li Y, Wang N, Bao
X, Xue P and Liu S: BMSC-derived exosomes inhibit
dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy via the miR-486-5p/FoxO1 Axis.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:6812672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Che J, Xu C, Wu Y, Jia P, Han Q, Ma Y,
Wang X and Zheng Y: MiR-1290 promotes myoblast differentiation and
protects against myotube atrophy via Akt/p70/FoxO3 pathway
regulation. Skelet Muscle. 11:62021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ahmad N, Kushwaha P, Karvande A, Tripathi
AK, Kothari P, Adhikary S, Khedgikar V, Mishra VK and Trivedi R:
MicroRNA-672-5p identified during weaning reverses osteopenia and
sarcopenia in ovariectomized mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
14:536–549. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Stewart-Hunt L, Pratt-Phillips S,
McCutcheon LJ and Geor RJ: Dietary energy source and physical
conditioning affect insulin sensitivity and skeletal muscle glucose
metabolism in horses. Equine Vet J. Suppl (38):355–360. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Barres R and Zierath JR: The role of diet
and exercise in the transgenerational epigenetic landscape of T2DM.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 12:441–451. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Critchlow AJ, Williams RM and Alexander
SE: The PoWeR of exercise: Exploring the anti-ageing effects of
exercise through epigenetic modifications to skeletal muscle. J
Physiol. 601:1175–1177. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Sohi G and Dilworth FJ: Noncoding RNAs as
epigenetic mediators of skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS J.
282:1630–1646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Pinheiro A and Naya FJ: The Key Lnc (RNA)s
in cardiac and skeletal muscle development, regeneration, and
disease. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 8:842021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Human Microbiome Project Consortium, .
Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome.
Nature. 486:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Quigley EM: Gut bacteria in health and
disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 9:560–569. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Knight R, Vrbanac A, Taylor BC, Aksenov A,
Callewaert C, Debelius J, Gonzalez A, Kosciolek T, McCall LI,
McDonald D, et al: Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat
Rev Microbiol. 16:410–422. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Collins SL, Stine JG, Bisanz JE, Okafor CD
and Patterson AD: Bile acids and the gut microbiota: Metabolic
interactions and impacts on disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 21:236–247.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Lapiere A and Richard ML: Bacterial-fungal
metabolic interactions within the microbiota and their potential
relevance in human health and disease: A short review. Gut
Microbes. 14:21056102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wagner J, Kancherla J, Braccia D,
Matsumara J, Felix V, Crabtree J, Mahurkar A and Corrada Bravo H:
Interactive exploratory data analysis of integrative human
microbiome project data using metaviz. F1000Res. 9:6012020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Rahman S, Ikram AR, Azeem F, Tahir Ul
Qamar M, Shaheen T and Mehboob-Ur-Rahman: Precision genome editing
with CRISPR-Cas9. Methods Mol Biol. 2788:355–372. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Li Y, Li C, Yan J, Liao Y, Qin C, Wang L,
Huang Y, Yang C, Wang J, Ding X, et al: Polymeric micellar
nanoparticles for effective CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in cancer.
Biomaterials. 309:1225732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Adlard B, Donaldson SG, Odland JO, Weihe
P, Berner J, Carlsen A, Bonefeld-Jorgensen EC, Dudarev AA, Gibson
JC, Krümmel EM, et al: Future directions for monitoring and human
health research for the arctic monitoring and assessment programme.
Glob Health Action. 11:14800842018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Jackson R, Yao T, Bulut N, Cantu-Jungles
TM and Hamaker BR: Protein combined with certain dietary fibers
increases butyrate production in gut microbiota fermentation. Food
Funct. 15:3186–3198. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Modoux M, Rolhion N, Lefevre JH, Oeuvray
C, Nadvornik P, Illes P, Emond P, Parc Y, Mani S, Dvorak Z and
Sokol H: Butyrate acts through HDAC inhibition to enhance aryl
hydrocarbon receptor activation by gut microbiota-derived ligands.
Gut Microbes. 14:21056372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Wan F, Deng FL, Chen L, Zhong RQ, Wang MY,
Yi B, Liu L, Zhao HB and Zhang HF: Long-term chemically protected
sodium butyrate supplementation in broilers as an antibiotic
alternative to dynamically modulate gut microbiota. Poult Sci.
101:1022212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Drut A, Mkaouar H, Kriaa A, Mariaule V,
Akermi N, Meric T, Sénécat O, Maguin E, Hernandez J and Rhimi M:
Gut microbiota in cats with inflammatory bowel disease and
low-grade intestinal T-cell lymphoma. Front Microbiol.
15:13466392024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Yang Y, Huang S, Liao Y, Wu X, Zhang C,
Wang X and Yang Z: Hippuric acid alleviates dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis via suppressing inflammatory activity and
modulating gut microbiota. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
710:1498792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Liu M, Ma J, Xu J, Huangfu W, Zhang Y, Ali
Q, Liu B, Li D, Cui Y, Wang Z, et al: Fecal microbiota
transplantation alleviates intestinal inflammatory diarrhea caused
by oxidative stress and pyroptosis via reducing gut
microbiota-derived lipopolysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol.
261((Pt 1)): 1296962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wu R, Xiong R, Li Y, Chen J and Yan R: Gut
microbiome, metabolome, host immunity associated with inflammatory
bowel disease and intervention of fecal microbiota transplantation.
J Autoimmun. 141:1030622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Monda V, Villano I, Messina A, Valenzano
A, Esposito T, Moscatelli F, Viggiano A, Cibelli G, Chieffi S,
Monda M and Messina G: Exercise modifies the gut microbiota with
positive health effects. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:38319722017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Mimee M, Tucker AC, Voigt CA and Lu TK:
Programming a human commensal bacterium, bacteroides
thetaiotaomicron, to sense and respond to stimuli in the murine gut
microbiota. Cell Syst. 2:2142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Das S, Preethi B, Kushwaha S and
Shrivastava R: Therapeutic strategies to modulate gut microbial
health: Approaches for sarcopenia management. Histol Histopathol.
39:1395–1425. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Li T, Yin D and Shi R: Gut-muscle axis
mechanism of exercise prevention of sarcopenia. Front Nutr.
11:14187782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zhang T, Cheng JK and Hu YM: Gut
microbiota as a promising therapeutic target for age-related
sarcopenia. Ageing Res Rev. 81:1017392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|