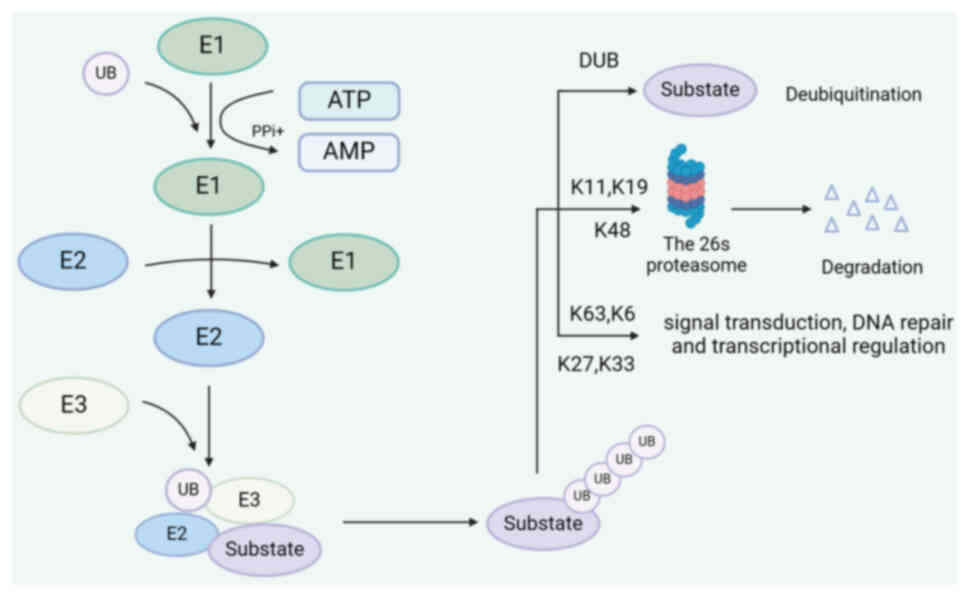
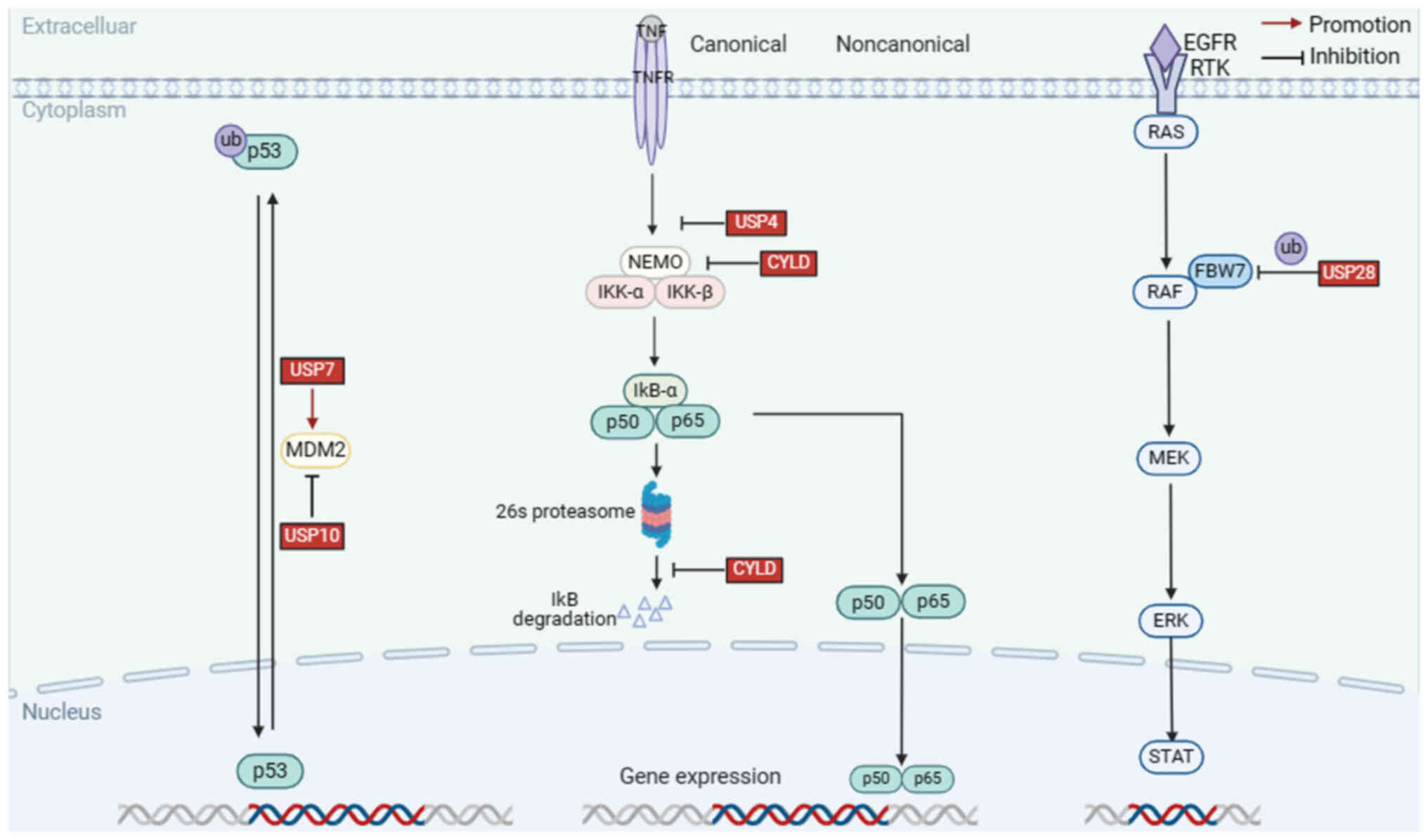
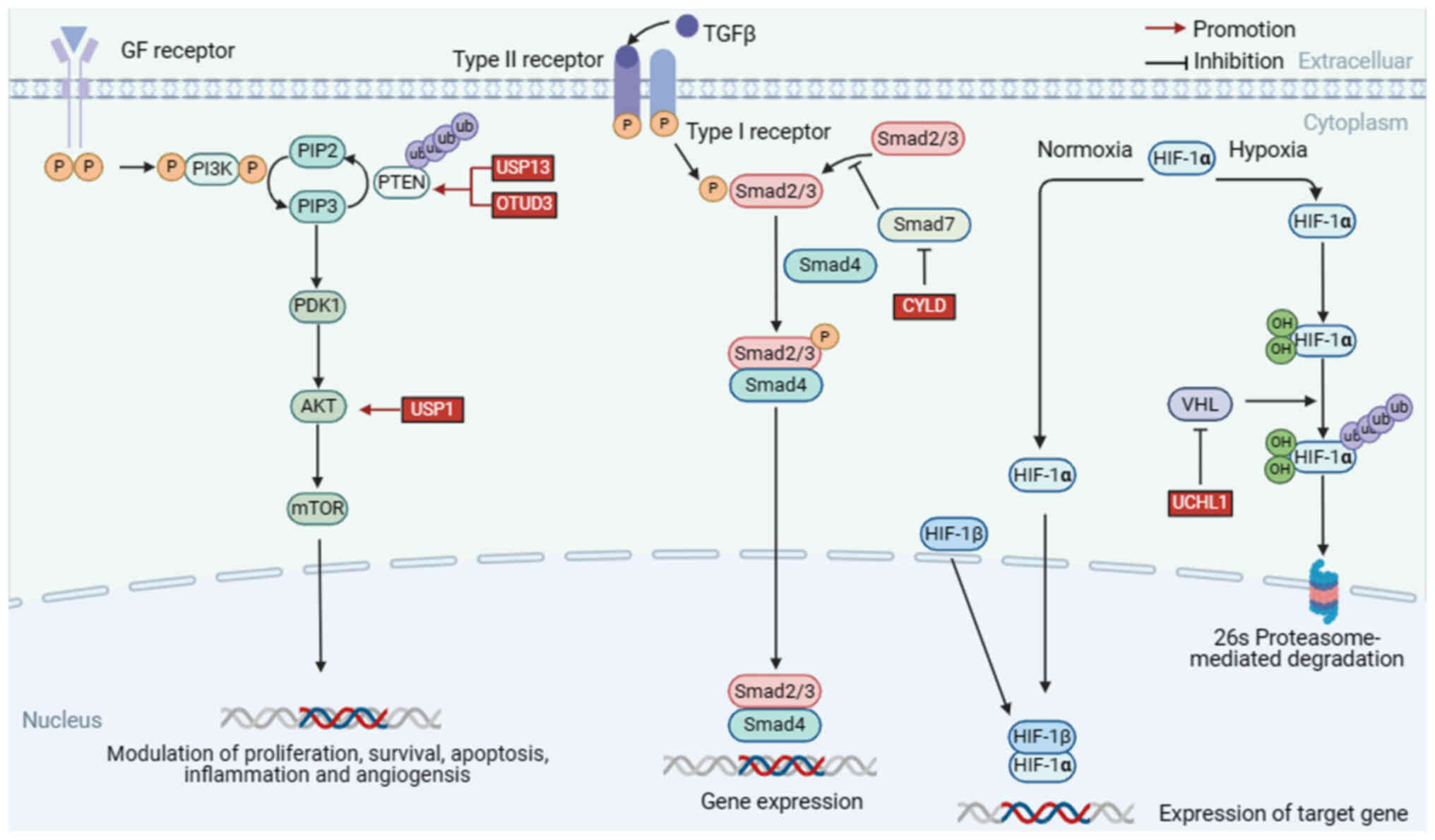
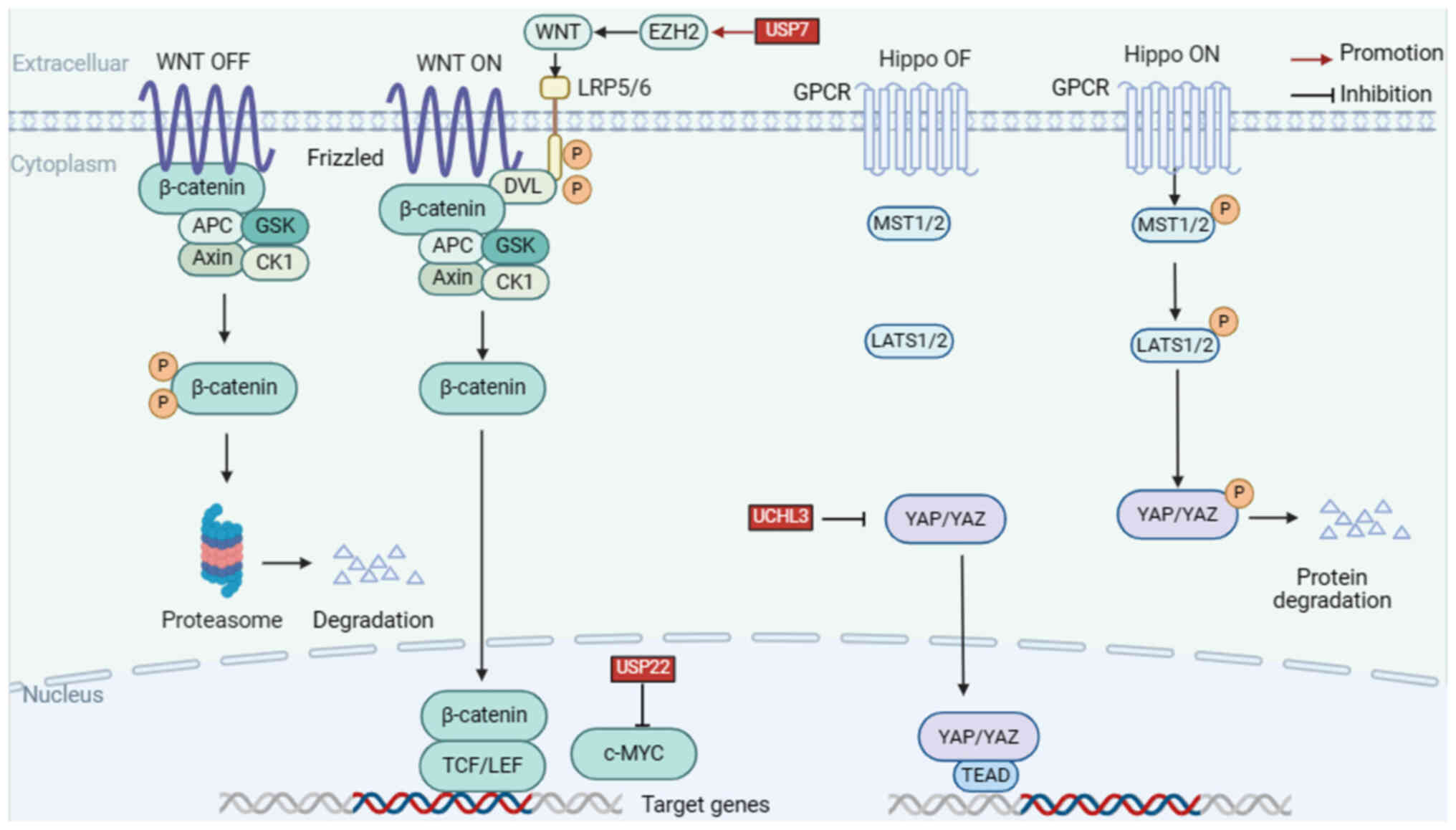
|
1
|
Parmar K, Mohamed A, Vaish E, Thawani R,
Cetnar J and Thein KZ: Immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: An updated review. Cancer Treat Res Commun.
33:1006492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui
VWY, Bauman JE and Grandis JR: Head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McDermott JD and Bowles DW: Epidemiology
of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: Impact on staging and
prevention strategies. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 20:432019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bhatia A and Burtness B: Treating head and
neck cancer in the age of immunotherapy: A 2023 update. Drugs.
83:217–248. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Daste A, Larroquette M, Gibson N, Lasserre
M and Domblides C: Immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: Current status and perspectives. Immunotherapy.
16:187–197. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim YJ, Lee Y, Shin H, Hwang S, Park J and
Song EJ: Ubiquitin-proteasome system as a target for anticancer
treatment-an update. Arch Pharm Res. 46:573–597. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Xiang Y, Fan M, Fang S and Hua Q:
The ubiquitin-proteasome system in tumor metabolism. Cancers
(Basel). 15:23852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schulman BA and Harper JW: Ubiquitin-like
protein activation by E1 enzymes: The apex for downstream
signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:319–331. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhai F, Wang J, Yang W, Ye M and Jin X:
The E3 ligases in cervical cancer and endometrial cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 14:53542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kong L and Jin X: Dysregulation of
deubiquitination in breast cancer. Gene. 902:1481752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park J, Cho J and Song EJ:
Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) as a target for anticancer
treatment. Arch Pharm Res. 43:1144–1161. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hochstrasser M: Ubiquitin, proteasomes,
and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 7:215–223. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Spano D and Catara G: Targeting the
ubiquitin-proteasome system and recent advances in cancer therapy.
Cells. 13:292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bennett EJ and Harper JW: DNA damage:
Ubiquitin marks the spot. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 15:20–22. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pickart CM and Eddins MJ: Ubiquitin:
Structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1695:55–72. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Komander D, Clague MJ and Urbé S: Breaking
the chains: Structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 10:550–563. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dewson G, Eichhorn PJA and Komander D:
Deubiquitinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 23:842–862. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
D'Arcy P, Wang X and Linder S:
Deubiquitinase inhibition as a cancer therapeutic strategy.
Pharmacol Ther. 147:32–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abdul Rehman SA, Kristariyanto YA, Choi
SY, Nkosi PJ, Weidlich S, Labib K, Hofmann K and Kulathu Y: MINDY-1
is a member of an evolutionarily conserved and structurally
distinct new family of deubiquitinating enzymes. Mol Cell.
63:146–155. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jin S, Kudo Y and Horiguchi T: The role of
deubiquitinating enzyme in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:5522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu M, Li P, Li M, Li W, Yao T, Wu JW, Gu
W, Cohen RE and Shi Y: Crystal structure of a UBP-family
deubiquitinating enzyme in isolation and in complex with ubiquitin
aldehyde. Cell. 111:1041–1054. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuhlbrodt K, Janiesch PC, Kevei É, Segref
A, Barikbin R and Hoppe T: The Machado-Joseph disease
deubiquitylase ATX-3 couples longevity and proteostasis. Nat Cell
Biol. 13:273–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nicastro G, Menon RP, Masino L, Knowles
PP, McDonald NQ and Pastore A: The solution structure of the
Josephin domain of ataxin-3: Structural determinants for molecular
recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:10493–10498. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hurley JH and Stenmark H: Molecular
mechanisms of ubiquitin-dependent membrane traffic. Annu Rev
Biophys. 40:119–142. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Davies CW, Paul LN, Kim MI and Das C:
Structural and thermodynamic comparison of the catalytic domain of
AMSH and AMSH-LP: Nearly identical fold but different stability. J
Mol Biol. 413:416–429. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liang J, Saad Y, Lei T, Wang J, Qi D, Yang
Q, Kolattukudy PE and Fu M: MCP-induced protein 1 deubiquitinates
TRAF proteins and negatively regulates JNK and NF-kappaB signaling.
J Exp Med. 207:2959–2973. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen SMY, Krinsky AL, Woolaver RA, Wang X,
Chen Z and Wang JH: Tumor immune microenvironment in head and neck
cancers. Mol Carcinog. 59:766–774. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gulve N, Su C, Deng Z, Soldan SS,
Vladimirova O, Wickramasinghe J, Zheng H, Kossenkov AV and
Lieberman PM: DAXX-ATRX regulation of p53 chromatin binding and DNA
damage response. Nat Commun. 13:50332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Shang L, Zhou F, Wang S, Liu N, Zhou
M, Lin Q, Zhang M, Cai Y, Chen G and Yang S: Herba patriniae and
its component isovitexin show anti-colorectal cancer effects by
inducing apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest via p53 activation. Biomed
Pharmacother. 168:1156902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang H, Guo M, Wei H and Chen Y: Targeting
p53 pathways: mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hassin O and Oren M: Drugging p53 in
cancer: One protein, many targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 22:127–144.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brummer T and Zeiser R: The role of the
MDM2/p53 axis in antitumor immune responses. Blood. 143:2701–2709.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bradford CR, Zhu S, Poore J, Fisher SG,
Beals TF, Thoraval D, Hanash SM, Carey TE and Wolf GT: p53 mutation
as a prognostic marker in advanced laryngeal carcinoma. Department
of veterans affairs laryngeal cancer cooperative study group. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 123:605–609. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nathan CA, Khandelwal AR, Wolf GT, Rodrigo
JP, Mäkitie AA, Saba NF, Forastiere AA, Bradford CR and Ferlito A:
TP53 mutations in head and neck cancer. Mol Carcinog. 61:385–391.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Koo N, Sharma AK and Narayan S:
Therapeutics targeting p53-MDM2 interaction to induce cancer cell
death. Int J Mol Sci. 23:50052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwon SK, Saindane M and Baek KH: p53
stability is regulated by diverse deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1868:404–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saha G, Roy S, Basu M and Ghosh MK: USP7-a
crucial regulator of cancer hallmarks. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev
Cancer. 1878:1889032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shin SC, Park J, Kim KH, Yoon JM, Cho J,
Ha BH, Oh Y, Choo H, Song EJ and Kim EE: Structural and functional
characterization of USP47 reveals a hot spot for inhibitor design.
Commun Biol. 6:9702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nininahazwe L, Liu B, He C, Zhang H and
Chen ZS: The emerging nature of Ubiquitin-specific protease 7
(USP7): A new target in cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today.
26:490–502. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pozhidaeva A and Bezsonova I: USP7:
Structure, substrate specificity, and inhibition. DNA Repair
(Amst). 76:30–39. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brooks CL, Li M, Hu M, Shi Y and Gu W: The
p53-Mdm2-HAUSP complex is involved in p53 stabilization by HAUSP.
Oncogene. 26:7262–7266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sacco JJ, Coulson JM, Clague MJ and Urbé
S: Emerging roles of deubiquitinases in cancer-associated pathways.
IUBMB Life. 62:140–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Niu H, Zhu Y, Wang J, Wang T, Wang X and
Yan L: Effects of USP7 on radiation sensitivity through p53 pathway
in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Transl Oncol. 22:1014662022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guo Q, Jin Y, Chen X, Ye X, Shen X, Lin M,
Zeng C, Zhou T and Zhang J: NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy:
New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 9:532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H and Hu H:
Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and
clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:2092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tan Y, Sun R, Liu L, Yang D, Xiang Q, Li
L, Tang J, Qiu Z, Peng W, Wang Y, et al: Tumor suppressor DRD2
facilitates M1 macrophages and restricts NF-κB signaling to trigger
pyroptosis in breast cancer. Theranostics. 11:5214–5231. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schrank TP, Prince AC, Sathe T, Wang X,
Liu X, Alzhanov DT, Burtness B, Baldwin AS, Yarbrough WG and
Issaeva N: NF-κB over-activation portends improved outcomes in
HPV-associated head and neck cancer. Oncotarget. 13:707–722. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jackson-Bernitsas DG, Ichikawa H, Takada
Y, Myers JN, Lin XL, Darnay BG, Chaturvedi MM and Aggarwal BB:
Evidence that TNF-TNFR1-TRADD-TRAF2-RIP-TAK1-IKK pathway mediates
constitutive NF-kappaB activation and proliferation in human head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 26:1385–1397. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Napetschnig J and Wu H: Molecular basis of
NF-κB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys. 42:443–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Courtois G: Tumor suppressor CYLD:
Negative regulation of NF-kappaB signaling and more. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 65:1123–1132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang Y and Zhou J: CYLD-a deubiquitylase
that acts to fine-tune microtubule properties and functions. J Cell
Sci. 129:2289–2295. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cui Z, Kang H, Grandis JR and Johnson DE:
CYLD alterations in the tumorigenesis and progression of human
papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancers. Mol Cancer Res.
19:14–24. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Massoumi R: CYLD: A deubiquitination
enzyme with multiple roles in cancer. Future Oncol. 7:285–297.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Verhoeft KR, Ngan HL and Lui VWY: The
cylindromatosis (CYLD) gene and head and neck tumorigenesis.
Cancers Head Neck. 1:102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Deng M, Dai W, Yu VZ, Tao L and Lung ML:
Cylindromatosis lysine 63 deubiquitinase (CYLD) regulates NF-kB
signaling pathway and modulates fibroblast and endothelial cells
recruitment in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
12:19242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hu B, Zhang D, Zhao K, Wang Y, Pei L, Fu Q
and Ma X: Spotlight on USP4: Structure, function, and regulation.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:5951592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tao Y and You W: The deubiquitinating
enzyme USP4 functions as an oncoprotein in gastric cancer and
mediates NF-κB signaling by regulating PRL-3 expression. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 27:2862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hou X, Wang L, Zhang L, Pan X and Zhao W:
Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 promotes TNF-α-induced apoptosis by
deubiquitination of RIP1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
FEBS Lett. 587:311–316. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shi A, Liu L, Li S and Qi B: Natural
products targeting the MAPK-signaling pathway in cancer: Overview.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 150:62024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cheng Y, Chen J, Shi Y, Fang X and Tang Z:
MAPK signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Biological
function and targeted therapy. Cancers (Basel). 14:46252022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Roskoski R Jr: ERK1/2 MAP kinases:
Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 66:105–143.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ngan HL, Law CH, Choi YCY, Chan JY and Lui
VWY: Precision drugging of the MAPK pathway in head and neck
cancer. NPJ Genom Med. 7:202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y and
Hu LL: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med.
19:1997–2007. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wu PK, Becker A and Park JI: Growth
inhibitory signaling of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Int J Mol Sci.
21:54362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shen J, Xie M, Xu Y, Qian Q, Qiu T, Shi W,
Ren D, Ji J and Huang J: Identification of the deubiquitinase USP28
as a novel molecular therapeutic target of ovarian cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 638:184–191. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li J, Peng J, Wu L, Shen X, Zhen X, Zhang
Y, Ma H, Xu Y, Xiong Q, Zhu Q and Zhang P: The deubiquitinase USP28
maintains the expression of the transcription factor MYCN and is
essential in neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 299:1048562023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Prieto-Garcia C, Tomašković I, Shah VJ,
Dikic I and Diefenbacher M: USP28: oncogene or tumor suppressor? A
unifying paradigm for squamous cell carcinoma. Cells. 10:26522021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Park HB and Baek KH: E3 ligases and
deubiquitinating enzymes regulating the MAPK signaling pathway in
cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1877:1887362022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Arita H, Nagata M, Yoshida R, Matsuoka Y,
Hirosue A, Kawahara K, Sakata J, Nakashima H, Kojima T, Toya R, et
al: FBXW7 expression affects the response to chemoradiotherapy and
overall survival among patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma:
A single-center retrospective study. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177317712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yu H, Ling T, Shi R, Shu Q, Li Y and Tan
Z: Expression of FBXW7 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and
its clinical significance. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 37:347–351.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Saei A, Palafox M, Benoukraf T, Kumari N,
Jaynes PW, Iyengar PV, Muñoz-Couselo E, Nuciforo P, Cortés J,
Nötzel C, et al: Loss of USP28-mediated BRAF degradation drives
resistance to RAF cancer therapies. J Exp Med. 215:1913–1928. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Cheng Y and Tian H: Current development
status of MEK inhibitors. Molecules. 22:15512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, Yap KCH,
Jacot W, Jones RH, Eng H, Nair MG, Makvandi P, Geoerger B, et al:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies
in cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Jin J, He J, Li X, Ni X and Jin X: The
role of ubiquitination and deubiquitination in PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway: A potential target for cancer therapy. Gene.
889:1478072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen M, Choi S, Wen T, Chen C, Thapa N,
Lee JH, Cryns VL and Anderson RA: A p53-phosphoinositide
signalosome regulates nuclear AKT activation. Nat Cell Biol.
24:1099–1113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Marquard FE and Jücker M: PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling as a molecular target in head and neck cancer. Biochem
Pharmacol. 172:1137292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
De Felice F and Guerrero Urbano T: New
drug development in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: The
PI3-K inhibitors. Oral Oncol. 67:119–123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Borgato GB, Borges GA, Souza AP, Squarize
CH and Castilho RM: Loss of PTEN sensitizes head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma to 5-AZA-2′-deoxycytidine. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral
Pathol Oral Radiol. 130:181–190. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Psyrri A, Seiwert TY and Jimeno A:
Molecular pathways in head and neck cancer: EGFR, PI3K, and more.
Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013:246–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tewari D, Patni P and Bishayee A, Sah AN
and Bishayee A: Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR
signaling pathway in cancer: A novel therapeutic strategy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 80:1–17. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Vander Broek R, Mohan S, Eytan DF, Chen Z
and Van Waes C: The PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in head and neck cancer:
Functions, aberrations, cross-talk, and therapies. Oral Dis.
21:815–825. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Li X, Yang G, Zhang W, Qin B, Ye Z, Shi H,
Zhao X, Chen Y, Song B, Mei Z, et al: USP13: Multiple functions and
target inhibition. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8751242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang J, Zhang P, Wei Y, Piao HL, Wang W,
Maddika S, Wang M, Chen D, Sun Y, Hung MC, et al: Deubiquitylation
and stabilization of PTEN by USP13. Nat Cell Biol. 15:1486–1494.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Qu Z, Zhang R, Su M and Liu W: USP13
serves as a tumor suppressor via the PTEN/AKT pathway in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 11:9175–9183. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Huang J, Ye Z, Wang J, Chen Q, Huang D and
Liu H: USP13 mediates PTEN to ameliorate osteoarthritis by
restraining oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation via
AKT-dependent manner. Biomed Pharmacother. 133:1110892021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang K, Liu J, Li YL, Li JP and Zhang R:
Ubiquitination/de-ubiquitination: A promising therapeutic target
for PTEN reactivation in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1877:1887232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang M, Li Y, Xiao Y, Yang M, Chen J, Jian
Y, Chen X, Shi D, Chen X, Ouyang Y, et al: Nicotine-mediated OTUD3
downregulation inhibits VEGF-C mRNA decay to promote lymphatic
metastasis of human esophageal cancer. Nat Commun. 12:70062021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Geng W, Song H, Zhao Q, Dong K, Pu Q, Gao
H and Lv Y: miR-520h stimulates drug resistance to paclitaxel by
targeting the OTUD3-PTEN axis in breast cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2020:95127932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yuan L, Lv Y, Li H, Gao H, Song S, Zhang
Y, Xing G, Kong X, Wang L, Li Y, et al: Deubiquitylase OTUD3
regulates PTEN stability and suppresses tumorigenesis. Nat Cell
Biol. 17:1169–1181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhao M, Yang F, Sang C, Yan C and Wang Z:
BGL3 inhibits papillary thyroid carcinoma progression via
regulating PTEN stability. J Endocrinol Invest. 44:2165–2174. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Antonenko S, Zavelevich M and Telegeev G:
The role of USP1 deubiquitinase in the pathogenesis and therapy of
cancer. Acta Biochim Pol. 70:219–231. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Xu J, Li B, Song W, Cao L, Zhu C and Lin
S: Tumor suppressor functions of miRNA-375 in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma through inhibition of ubiquitin-specific protease 1
expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 141:1060922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Vucic D, Dixit VM and Wertz IE:
Ubiquitylation in apoptosis: A post-translational modification at
the edge of life and death. Nat Rev Mol Cell. 12:439–452. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Schaefer A, Nethe M and Hordijk PL:
Ubiquitin links to cytoskeletal dynamics, cell adhesion and
migration. Biochem J. 442:13–25. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ulrich HD and Walden H: Ubiquitin
signalling in DNA replication and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
11:479–489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ma A, Tang M, Zhang L, Wang B, Yang Z, Liu
Y, Xu G, Wu L, Jing T, Xu X, et al: Correction to: USP1 inhibition
destabilizes KPNA2 and suppresses breast cancer metastasis.
Oncogene. 41:16732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Liu D, Li Q, Zang Y, Li X, Li Z, Zhang P,
Feng C, Yang P, Cui J, Sun Y, et al: USP1 modulates hepatocellular
carcinoma progression via the Hippo/TAZ axis. Cell Death Dis.
14:2642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Huang Z, Chen Y, Chen R, Zhou B, Wang Y,
Hong L, Wang Y, Wang J, Xu X, Huang Z and Chen W: HPV Enhances
HNSCC chemosensitization by inhibiting SERPINB3 expression to
disrupt the fanconi anemia pathway. Adv Sci (Weinh).
10:e22024372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Goldbraikh D, Neufeld D, Eid-Mutlak Y,
Lasry I, Gilda JE, Parnis A and Cohen S: USP1 deubiquitinates Akt
to inhibit PI3K-Akt-FoxO signaling in muscle during prolonged
starvation. EMBO Rep. 21:e487912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Heldin CH, Miyazono K and ten Dijke P:
TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD
proteins. Nature. 390:465–471. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Derynck R and Budi EH: Specificity,
versatility, and control of TGF-β family signaling. Sci Signal.
12:eaav51832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Meulmeester E and Ten Dijke P: The dynamic
roles of TGF-β in cancer. J Pathol. 223:205–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Britton WR, Cioffi I, Stonebraker C,
Spence M, Okolo O, Martin C, Henick B, Nakagawa H and Parikh AS:
Advancements in TGF-β Targeting Therapies for Head and Neck
Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 16:30472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ibi H, Takahashi K, Harada H, Watabe T and
Podyma-Inoue KA: Transforming growth factor-β signals promote
progression of squamous cell carcinoma by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 714:1499652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Itoh S and ten Dijke P: Negative
regulation of TGF-beta receptor/Smad signal transduction. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 19:176–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Shinriki S, Jono H, Maeshiro M, Nakamura
T, Guo J, Li JD, Ueda M, Yoshida R, Shinohara M, Nakayama H, et al:
Loss of CYLD promotes cell invasion via ALK5 stabilization in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol. 244:367–379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhao Y, Thornton AM, Kinney MC, Ma CA,
Spinner JJ, Fuss IJ, Shevach EM and Jain A: The deubiquitinase CYLD
targets Smad7 protein to regulate transforming growth factor β
(TGF-β) signaling and the development of regulatory T cells. J Biol
Chem. 286:40520–40530. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhao Y, Xing C, Deng Y, Ye C and Peng H:
HIF-1α signaling: Essential roles in tumorigenesis and implications
in targeted therapies. Genes Dis. 11:234–251. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yu Z, Li H, Zhu J, Wang H and Jin X: The
roles of E3 ligases in Hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res.
12:1179–1214. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Semenza GL: Oxygen sensing,
hypoxia-inducible factors, and disease pathophysiology. Annu Rev
Pathol. 9:47–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Wenger RH, Stiehl DP and Camenisch G:
Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci STKE.
2005:re122005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI,
Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, von Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji
M, Schofield CJ, et al: Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von
Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl
hydroxylation. Science. 292:468–472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Gong L, Zhang W, Zhou J, Lu J, Xiong H,
Shi X and Chen J: Prognostic value of HIFs expression in head and
neck cancer: A systematic review. PLoS One. 8:e750942013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Grethe C, Schmidt M, Kipka GM, O'Dea R,
Gallant K, Janning P and Gersch M: Structural basis for specific
inhibition of the deubiquitinase UCHL1. Nat Commun. 13:59502022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Bishop P, Rocca D and Henley JM: Ubiquitin
C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1): Structure, distribution and roles
in brain function and dysfunction. Biochem J. 473:2453–2462. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Lee KC, Chen HH, Cheng KC, Liu TT, Lee KF,
Teng CC, Huang CY, Hsieh MC and Kuo HC: Use of iTRAQ-based
quantitative proteomic identification of CHGA and UCHL1 correlated
with lymph node metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med.
27:2004–2020. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Li J, Liang Y, Zhou S, Chen J and Wu C:
UCHL1 contributes to insensitivity to endocrine therapy in
triple-negative breast cancer by deubiquitinating and stabilizing
KLF5. Breast Cancer Res. 26:442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zhang D, Fu Y, Tian G, Li J, Shang D and
Zhou S: UCHL1 promotes proliferation and metastasis in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma and could be a potential therapeutic
target. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 133:684–697.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Li X, Hattori A, Takahashi S, Goto Y,
Harada H and Kakeya H: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1
promotes hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent tumor cell malignancy
in spheroid models. Cancer Sci. 111:239–252. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zanoni M, Piccinini F, Arienti C, Zamagni
A, Santi S, Polico R, Bevilacqua A and Tesei A: 3D tumor spheroid
models for in vitro therapeutic screening: A systematic approach to
enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci Rep.
6:191032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Günter J, Ruiz-Serrano A, Pickel C, Wenger
RH and Scholz CC: The functional interplay between the HIF pathway
and the ubiquitin system-more than a one-way road. Exp Cell Res.
356:152–159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tejeda-Muñoz N and Robles-Flores M:
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 in Wnt signaling pathway and cancer.
IUBMB Life. 67:914–922. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Gordon MD and Nusse R: Wnt signaling:
Multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription
factors. J Biol Chem. 281:22429–22433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Xie J, Huang L, Lu YG and Zheng DL: Roles
of the Wnt signaling pathway in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 7:5909122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Yang F, Zeng Q, Yu G, Li S and Wang CY:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling inhibits death receptor-mediated
apoptosis and promotes invasive growth of HNSCC. Cell Signal.
18:679–687. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Moon JH, Lee SH and Lim YC:
Wnt/β-catenin/Slug pathway contributes to tumor invasion and lymph
node metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 38:163–174. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zheng N, Chu M, Lin M, He Y and Wang Z:
USP7 stabilizes EZH2 and enhances cancer malignant progression. Am
J Cancer Res. 10:299–313. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Yamagishi M and Uchimaru K: Targeting EZH2
in cancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 29:375–381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Wang L, Jin Q, Lee JE, Su IH and Ge K:
Histone H3K27 methyltransferase Ezh2 represses Wnt genes to
facilitate adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:7317–7322.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhang MJ, Chen DS, Li H, Liu WW, Han GY
and Han YF: Clinical significance of USP7 and EZH2 in predicting
prognosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and their possible
functional mechanism. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 12:2184–2194.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Liu S, Qin Z, Mao Y, Zhang W, Wang Y, Jia
L and Peng X: Therapeutic targeting of MYC in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 11:21305832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Llombart V and Mansour MR: Therapeutic
targeting of ‘undruggable’ MYC. EBioMedicine. 75:1037562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Dejure FR and Eilers M: MYC and tumor
metabolism: Chicken and egg. EMBO J. 36:3409–3420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Wang L, Chen C, Song Z, Wang H, Ye M, Wang
D, Kang W, Liu H and Qing G: EZH2 depletion potentiates MYC
degradation inhibiting neuroblastoma and small cell carcinoma tumor
formation. Nat Commun. 13:122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Dou Y, Lin J, Shu H and Jiang N: Role of
ubiquitin-specific peptidase 22 in carcinogenesis of human
pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 10:2973–2978.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Kim D, Hong A, Park HI, Shin WH, Yoo L,
Jeon SJ and Chung KC: Deubiquitinating enzyme USP22 positively
regulates c-Myc stability and tumorigenic activity in mammalian and
breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 232:3664–3676. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Li L, Wen S, Wang B, Gao W, Zhang W, Meng
X, Yang L and Kong L: Expression of cancer stem cell marker USP22
in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou
Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 49:479–482. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Shin E and Kim J: The potential role of
YAP in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Med.
52:1264–1274. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Faraji F, Ramirez SI, Anguiano Quiroz PY,
Mendez-Molina AN and Gutkind JS: Genomic hippo pathway alterations
and persistent YAP/TAZ activation: New hallmarks in head and neck
cancer. Cells. 11:13702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Segrelles C, Paramio JM and Lorz C: The
transcriptional co-activator YAP: A new player in head and neck
cancer. Oral Oncol. 86:25–32. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Chan EH, Nousiainen M, Chalamalasetty RB,
Schäfer A, Nigg EA and Silljé HH: The Ste20-like kinase Mst2
activates the human large tumor suppressor kinase Lats1. Oncogene.
24:2076–2086. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D, Yagi
R, Hall RA, Donowitz M, Hisaminato A, Fujiwara T, Ito Y, Cantley LC
and Yaffe MB: TAZ: A novel transcriptional co-activator regulated
by interactions with 14-3-3 and PDZ domain proteins. EMBO J.
19:6778–6791. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Zhao B, Ye X, Yu J, Li L, Li W, Li S, Yu
J, Lin JD, Wang CY, Chinnaiyan AM, et al: TEAD mediates
YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes Dev.
22:1962–1971. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Pocaterra A, Romani P and Dupont S:
YAP/TAZ functions and their regulation at a glance. J Cell Sci.
133:jcs2304252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Fang Y, Fu D and Shen XZ: The potential
role of ubiquitin c-terminal hydrolases in oncogenesis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1806:1–6. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Mtango NR, Sutovsky M, Susor A, Zhong Z,
Latham KE and Sutovsky P: Essential role of maternal UCHL1 and
UCHL3 in fertilization and preimplantation embryo development. J
Cell Physiol. 227:1592–1603. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Suzuki M, Setsuie R and Wada K: Ubiquitin
carboxyl-terminal hydrolase l3 promotes insulin signaling and
adipogenesis. Endocrinology. 150:5230–5239. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Mtango NR, Sutovsky M, Vandevoort CA,
Latham KE and Sutovsky P: Essential role of ubiquitin C-terminal
hydrolases UCHL1 and UCHL3 in mammalian oocyte maturation. J Cell
Physiol. 227:2022–2029. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Nishi R, Wijnhoven PWG, Kimura Y, Matsui
M, Konietzny R, Wu Q, Nakamura K, Blundell TL and Kessler BM: The
deubiquitylating enzyme UCHL3 regulates Ku80 retention at sites of
DNA damage. Sci Rep. 8:178912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Zhang X, Smits AH, van Tilburg GB, Jansen
PW, Makowski MM, Ovaa H and Vermeulen M: An interaction landscape
of ubiquitin signaling. Mol Cell. 65:941–955.e8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Tang J, Yang Q, Mao C, Xiao D, Liu S, Xiao
L, Zhou L, Wu G and Tao Y: The deubiquitinating enzyme UCHL3
promotes anaplastic thyroid cancer progression and metastasis
through Hippo signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 30:1247–1259.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Wang J, Xiang Y, Xie Z, Fan M, Fang S, Wan
H, Zhao R, Zeng F and Hua Q: USP14 positively modulates head and
neck squamous carcinoma tumorigenesis and potentiates heat shock
pathway through HSF1 Stabilization. Cancers (Basel). 15:43852023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Wang F, Ning S, Yu B and Wang Y: USP14:
Structure, function, and target inhibition. Front Pharmacol.
12:8013282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Shi D, Wu X, Jian Y, Wang J, Huang C, Mo
S, Li Y, Li F, Zhang C, Zhang D, et al: USP14 promotes tryptophan
metabolism and immune suppression by stabilizing IDO1 in colorectal
cancer. Nat Commun. 13:56442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Ji J, Lv J, Lv M, Jing A, Xu M, Yuan Q, Ma
X, Qian Q, Wang W, Geng T, et al: USP14 regulates heme metabolism
and ovarian cancer invasion through BACH1 deubiquitination and
stabilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 667:186–193. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Tao L, Liu X, Jiang X, Zhang K, Wang Y, Li
X, Jiang S and Han T: USP10 as a potential therapeutic target in
human cancers. Genes (Basel). 13:8312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Xu Y, Pan J, Lin Y, Wu Y, Chen Y and Li H:
Ceramide synthase 1 inhibits brain metastasis of non-small cell
lung cancer by interacting with USP14 and downregulating the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancers (Basel). 15:19942023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Zhao C, Gong J, Bai Y, Yin T, Zhou M, Pan
S, Liu Y, Gao Y, Zhang Z, Shi Y, et al: A self-amplifying USP14-TAZ
loop drives the progression and liver metastasis of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 30:1–15. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Scherz-Shouval R, Santagata S, Mendillo
ML, Sholl LM, Ben-Aharon I, Beck AH, Dias-Santagata D, Koeva M,
Stemmer SM, Whitesell L and Lindquist S: The reprogramming of tumor
stroma by HSF1 is a potent enabler of malignancy. Cell.
158:564–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Carpenter RL and Gökmen-Polar Y: HSF1 as a
cancer biomarker and therapeutic target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
19:515–524. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Tang Q, Chen Y, Li X, Long S, Shi Y, Yu Y,
Wu W, Han L and Wang S: The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of
immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front Immunol.
13:9644422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Yi M, Zheng X, Niu M, Zhu S, Ge H and Wu
K: Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current
advances and future directions. Mol Cancer. 21:282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Fasano M, Corte CMD, Liello RD, Viscardi
G, Sparano F, Iacovino ML, Paragliola F, Piccolo A, Napolitano S,
Martini G, et al: Immunotherapy for head and neck cancer: Present
and future. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 174:1036792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Jiang S, Li X, Huang L, Xu Z and Lin J:
Prognostic value of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 deserves attention in
head and neck cancer. Front Immunol. 13:9884162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Kapuria V, Peterson LF, Fang D, Bornmann
WG, Talpaz M and Donato NJ: Deubiquitinase inhibition by
small-molecule WP1130 triggers aggresome formation and tumor cell
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 70:9265–9276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Huang G, Liao J, Wang M, Huang Y, Tang M
and Hao Y: USP9X increased tumor angiogenesis in mantle cell
lymphoma by upregulation of CCND1-mediated SOX11. Mediterr J
Hematol Infect Dis. 14:e20220482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Zhang FK, Ni QZ, Wang K, Cao HJ, Guan DX,
Zhang EB, Ma N, Wang YK, Zheng QW, Xu S, et al: Targeting
USP9X-AMPK axis in ARID1A-deficient hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:101–127. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Li X, Song N, Liu L, Liu X, Ding X, Song
X, Yang S, Shan L, Zhou X, Su D, et al: USP9X regulates centrosome
duplication and promotes breast carcinogenesis. Nat Commun.
8:148662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Yang B, Cao H, Yang CX,
Ouyang W, Zhang SM, Yang GF, Zhou FX, Zhou YF and Xie CH: Elevated
expression of USP9X correlates with poor prognosis in human
non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 7:672–679.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Nanayakkara DM, Nguyen MN and Wood SA:
Deubiquitylating enzyme, USP9X, regulates proliferation of cells of
head and neck cancer lines. Cell Prolif. 49:494–502. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Potu H, Peterson LF, Kandarpa M, Pal A,
Sun H, Durham A, Harms PW, Hollenhorst PC, Eskiocak U, Talpaz M and
Donato NJ: Usp9× regulates Ets-1 ubiquitination and stability to
control NRAS expression and tumorigenicity in melanoma. Nat Commun.
8:144492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Wu J, Guo W, Wen D, Hou G, Zhou A and Wu
W: Deubiquitination and stabilization of programmed cell death
ligand 1 by ubiquitin-specific peptidase 9, X-linked in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 7:4004–4011. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Pandruvada S, Kessler R and Thai A: Head
and neck cancer treatment in the era of molecular medicine. Adv
Cancer Res. 160:205–252. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Runnels J, Bloom JR, Hsieh K, Dickstein
DR, Shi Y, Jones BM, Lehrer EJ and Bakst RL: Combining radiotherapy
and immunotherapy in head and neck cancer. Biomedicines.
11:20972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Chung CH, Li J, Steuer CE, Bhateja P,
Johnson M, Masannat J, Poole MI, Song F, Hernandez-Prera JC, Molina
H, et al: Phase II multi-institutional clinical trial result of
concurrent cetuximab and nivolumab in recurrent and/or metastatic
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
28:2329–2338. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Kitamura N, Sento S, Yoshizawa Y, Sasabe
E, Kudo Y and Yamamoto T: Current trends and future prospects of
molecular targeted therapy in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 22:2402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Harrington KJ, Burtness B, Greil R,
Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr, Psyrri A, Brana I, Basté N,
Neupane P, et al: Pembrolizumab with or without chemotherapy in
recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
Updated results of the phase III KEYNOTE-048 study. J Clin Oncol.
41:790–802. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Cai Y, Dodhia S and Su GH: Dysregulations
in the PI3K pathway and targeted therapies for head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:22203–22217. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Bozec A, Ebran N, Radosevic-Robin N,
Chamorey E, Yahia HB, Marcie S, Gautier M, Penault-Llorca F and
Milano G: Combination of phosphotidylinositol-3-kinase targeting
with cetuximab and irradiation: A preclinical study on an
orthotopic xenograft model of head and neck cancer. Head Neck.
39:151–159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Liao YM, Kim C and Yen Y: Mammalian target
of rapamycin and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck
Oncol. 3:222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Marret G, Isambert N, Rezai K, Gal J,
Saada-Bouzid E, Rolland F, Chausson M, Borcoman E, Alt M,
Klijanienko J, et al: Phase I trial of copanlisib, a selective PI3K
inhibitor, in combination with cetuximab in patients with recurrent
and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Invest New
Drugs. 39:1641–1648. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Nathan CO, Hayes DN, Karrison T,
Harismendy O, Flores JM, Moore-Medlin T, Vokes EE, Gutkind JS,
Neupane P, Mills G, et al: A Randomized multi-institutional phase
II trial of everolimus as adjuvant therapy in patients with locally
advanced squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Clin Cancer
Res. 28:5040–5048. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Poondla N, Chandrasekaran AP, Kim KS and
Ramakrishna S: Deubiquitinating enzymes as cancer biomarkers: New
therapeutic opportunities? BMB Rep. 52:181–189. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Lee HR, Choi WC, Lee S, Hwang J, Hwang E,
Guchhait K, Haas J, Toth Z, Jeon YH, Oh TK, et al: Bilateral
inhibition of HAUSP deubiquitinase by a viral interferon regulatory
factor protein. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:1336–1344. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Hu T, Zhang J, Sha B, Li M, Wang L, Zhang
Y, Liu X, Dong Z, Liu Z, Li P and Chen P: Targeting the
overexpressed USP7 inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell
growth by inducing NOXA-mediated apoptosis. Mol Carcinog. 58:42–54.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Yoshizaki T, Kondo S, Endo K, Nakanishi Y,
Aga M, Kobayashi E, Hirai N, Sugimoto H, Hatano M, Ueno T, et al:
Modulation of the tumor microenvironment by Epstein-Barr virus
latent membrane protein 1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
109:272–278. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Kondo S, Seo SY, Yoshizaki T, Wakisaka N,
Furukawa M, Joab I, Jang KL and Pagano JS: EBV latent membrane
protein 1 up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha through
Siah1-mediated down-regulation of prolyl hydroxylases 1 and 3 in
nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 66:9870–9877. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Kobayashi E, Hwang D, Bheda-Malge A,
Whitehurst CB, Kabanov AV, Kondo S, Aga M, Yoshizaki T, Pagano JS,
Sokolsky M and Shakelford J: Inhibition of UCH-L1 deubiquitinating
activity with two forms of LDN-57444 has anti-invasive effects in
metastatic carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20:37332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Ding W, Wang JX, Wu JZ, Liu AC, Jiang LL,
Zhang HC, Meng Y, Liu BY, Peng GJ, Lou EZ, et al: Targeting
proteasomal deubiquitinases USP14 and UCHL5 with b-AP15 reduces
5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer cells. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 44:2537–2548. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Kropp KN, Maurer S, Rothfelder K, Schmied
BJ, Clar KL, Schmidt M, Strunz B, Kopp HG, Steinle A, Grünebach F,
et al: The novel deubiquitinase inhibitor b-AP15 induces direct and
NK cell-mediated antitumor effects in human mantle cell lymphoma.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 67:935–947. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Wang S, Wang T, Yang Q, Cheng S, Liu F,
Yang G, Wang F, Wang R, Yang D, Zhou M, et al: Proteasomal
deubiquitylase activity enhances cell surface recycling of the
epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cell Oncol (Dordr). 45:951–965. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Tian Z, D'Arcy P, Wang X, Ray A, Tai YT,
Hu Y, Carrasco RD, Richardson P, Linder S, Chauhan D and Anderson
KC: A novel small molecule inhibitor of deubiquitylating enzyme
USP14 and UCHL5 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma and overcomes
bortezomib resistance. Blood. 123:706–716. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Nalawansha DA and Crews CM: PROTACs: An
emerging therapeutic modality in precision medicine. Cell Chem
Biol. 27:998–1014. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Noblejas-López MDM, Tébar-García D,
López-Rosa R, Alcaraz-Sanabria A, Cristóbal-Cueto P, Pinedo-Serrano
A, Rivas-García L and Galán-Moya EM: TACkling cancer by targeting
selective protein degradation. Pharmaceutics. 15:24422023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Henning NJ, Boike L, Spradlin JN, Ward CC,
Liu G, Zhang E, Belcher BP, Brittain SM, Hesse MJ, Dovala D, et al:
Deubiquitinase-targeting chimeras for targeted protein
stabilization. Nat Chem Biol. 18:412–421. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Chen Y, Xue H and Jin J: Applications of
protein ubiquitylation and deubiquitylation in drug discovery. J
Biol Chem. 300:1072642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|